Mupirocin ointment is a topical antibiotic primarily used to treat a variety of bacterial skin infections. Have questions about mupirocin ointment and its uses? WHAT.EDU.VN provides accessible answers and free guidance for all your queries about this common medication, offering a helpful solution when you need reliable information quickly. Learn about its effectiveness against specific bacteria, common conditions it treats, and important usage guidelines. This includes topics such as impetigo treatment, Staphylococcus aureus infections, and antibacterial properties.
1. Understanding Mupirocin Ointment: An Overview
Mupirocin ointment is a topical antibacterial medication used to treat various skin infections caused by bacteria. It’s available by prescription and is applied directly to the affected area. This medication is a valuable tool in combating bacterial growth and promoting healing.
1.1. What is Mupirocin?
Mupirocin, also known under the brand names Bactroban, Centany, and others, is a naturally occurring antibiotic. It’s produced by the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens. Mupirocin works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, which stops the growth and spread of bacteria. This targeted action makes it effective against a range of bacterial skin infections.
1.2. How Does Mupirocin Ointment Work?
Mupirocin ointment works by preventing bacteria from producing essential proteins. These proteins are necessary for bacteria to grow and multiply. By blocking protein synthesis, mupirocin effectively stops the bacteria from spreading, allowing the body’s immune system to clear the infection. This mechanism is particularly effective against common skin bacteria.
1.3. Forms of Mupirocin
Mupirocin is available in two main forms:
- Ointment: This is the most common form, typically containing 2% mupirocin. It’s used for treating various skin infections, such as impetigo, folliculitis, and infected wounds.
- Cream: Mupirocin cream is also available, although it’s less commonly prescribed. It is often used for skin conditions that require a lighter application.
The ointment is generally preferred for its occlusive properties, which help to keep the medication in contact with the infected area and promote healing. Both forms require a prescription and should be used as directed by a healthcare professional. Have any questions about which form is right for you? Ask our experts for free at WHAT.EDU.VN.
2. Common Uses of Mupirocin Ointment
Mupirocin ointment is used to treat a variety of bacterial skin infections. Its effectiveness stems from its ability to target and inhibit bacterial growth.
2.1. Impetigo Treatment
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that commonly affects children, but can also occur in adults. It’s characterized by red sores that quickly rupture, ooze, and form a yellowish crust. Mupirocin ointment is a first-line treatment for impetigo, effectively eradicating the bacteria responsible for the infection.
How Mupirocin Helps with Impetigo:
- Targets the Cause: Mupirocin targets Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria most commonly responsible for impetigo.
- Reduces Contagion: By eliminating the bacteria, mupirocin helps to reduce the spread of impetigo to others.
- Promotes Healing: The ointment helps to clear the infection, allowing the skin to heal properly.
2.2. Staphylococcus Aureus Infections
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a common bacterium that can cause a variety of skin infections, from minor issues like boils to more serious conditions. Mupirocin is effective against many strains of S. aureus, making it a valuable treatment option.
Types of S. Aureus Infections Treated with Mupirocin:
- Boils (Furuncles): Localized skin infections that start in a hair follicle or oil gland.
- Carbuncles: Clusters of boils that are connected under the skin.
- Folliculitis: Inflammation of hair follicles, often appearing as small, red bumps.
- Cellulitis: A deeper skin infection that can spread rapidly and cause significant discomfort.
 Mupirocin Ointment for Folliculitis Treatment
Mupirocin Ointment for Folliculitis Treatment
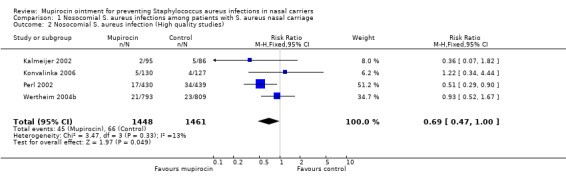
2.3. Eradicating Nasal Carriage of S. Aureus
Mupirocin is also used to eradicate nasal carriage of S. aureus, particularly methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Nasal carriage refers to the presence of bacteria in the nasal passages without causing symptoms. Eliminating nasal carriage can help prevent the spread of bacteria to other parts of the body or to other people.
How Mupirocin Works for Nasal Carriage:
- Reduces Bacterial Load: Mupirocin ointment is applied inside the nostrils to reduce the amount of S. aureus present.
- Prevents Transmission: By reducing nasal carriage, mupirocin helps to prevent the spread of bacteria to others, especially in healthcare settings.
- Decreases Infection Risk: Eradicating nasal carriage can lower the risk of developing infections, particularly in individuals undergoing surgery or other medical procedures.
2.4. Treating Secondary Skin Infections
Mupirocin ointment is often used to treat secondary skin infections that occur as a result of other skin conditions, such as eczema or minor burns. These secondary infections can develop when the skin’s protective barrier is compromised, allowing bacteria to enter and cause infection.
Common Scenarios for Secondary Infections:
- Eczema: Scratching can break the skin and allow bacteria to enter, leading to secondary infections.
- Minor Burns: Damaged skin is more susceptible to bacterial invasion.
- Cuts and Abrasions: Open wounds can become infected if not properly cared for.
- Insect Bites: Scratching at insect bites can lead to secondary infections.
2.5. Other Bacterial Skin Infections
Mupirocin ointment can also be used to treat other types of bacterial skin infections, including:
- Ecthyma: A deeper form of impetigo that causes ulcers on the skin.
- Infected Wounds: Minor cuts, scrapes, and surgical incisions that become infected.
- Paronychia: Infection around the fingernails or toenails.
- Ulcers: Open sores on the skin that can become infected.
Have more questions about specific conditions? Get your answers for free at WHAT.EDU.VN.
3. How to Use Mupirocin Ointment Correctly
Using mupirocin ointment correctly is essential to ensure its effectiveness and minimize the risk of side effects. Always follow the directions provided by your healthcare provider or the instructions on the product label.
3.1. Application Instructions
- Wash Your Hands: Before applying mupirocin ointment, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. This helps prevent the introduction of additional bacteria to the infected area.
- Clean the Affected Area: Gently clean the affected skin with mild soap and water. Pat the area dry with a clean towel.
- Apply a Thin Layer: Apply a thin layer of mupirocin ointment to the infected area. Use enough ointment to cover the entire affected area.
- Cover with a Bandage (If Necessary): If your healthcare provider recommends it, cover the treated area with a clean bandage. This can help protect the area and prevent the spread of infection.
- Wash Your Hands Again: After applying the ointment, wash your hands again to remove any remaining medication.
3.2. Dosage and Frequency
The typical dosage of mupirocin ointment is to apply it to the affected area two to three times daily for a period of 5 to 14 days, or as directed by your healthcare provider. It’s important to complete the full course of treatment, even if your symptoms improve before the end of the treatment period. Stopping treatment too early can allow the infection to return.
3.3. Duration of Treatment
The duration of treatment with mupirocin ointment depends on the type and severity of the infection. In most cases, treatment lasts for 5 to 14 days. However, your healthcare provider may recommend a longer or shorter course of treatment depending on your specific situation.
3.4. What to Avoid During Treatment
During treatment with mupirocin ointment, it’s important to avoid certain things to prevent further irritation or infection:
- Avoid Getting the Ointment in Your Eyes, Nose, or Mouth: If the ointment accidentally gets into these areas, rinse them thoroughly with water.
- Avoid Using Other Topical Medications: Unless directed by your healthcare provider, avoid using other topical medications on the same area as mupirocin ointment.
- Avoid Covering the Treated Area with Airtight Dressings: Unless specifically instructed by your healthcare provider, avoid covering the treated area with airtight dressings, such as plastic wrap.
- Avoid Prolonged Use: Prolonged use of mupirocin ointment can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
3.5. Missed Dose Instructions
If you miss a dose of mupirocin ointment, apply it as soon as you remember. However, if it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule. Do not apply a double dose to make up for a missed one.
4. Potential Side Effects of Mupirocin Ointment
Like all medications, mupirocin ointment can cause side effects. However, most people tolerate it well, and side effects are usually mild and temporary.
4.1. Common Side Effects
The most common side effects of mupirocin ointment include:
- Burning or Stinging: Some people may experience a mild burning or stinging sensation at the application site.
- Itching: Itching is another common side effect, which may be accompanied by redness or rash.
- Redness: The skin around the application site may become red or inflamed.
- Dryness: The skin may become dry or flaky after applying mupirocin ointment.
4.2. Rare Side Effects
Rare side effects of mupirocin ointment include:
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may experience an allergic reaction to mupirocin, which can include rash, hives, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Severe Burning or Stinging: In rare cases, the burning or stinging sensation may be severe.
- Increased Skin Irritation: The skin may become more irritated or inflamed.
4.3. Allergic Reactions: What to Watch For
Allergic reactions to mupirocin are rare but can be serious. Watch for the following symptoms:
- Rash: A skin rash, which may be red, itchy, or bumpy.
- Hives: Raised, itchy welts on the skin.
- Itching: Severe itching, which may be accompanied by redness or rash.
- Swelling: Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Difficulty Breathing: Trouble breathing or wheezing.
4.4. Managing Side Effects
Most side effects of mupirocin ointment are mild and can be managed with simple measures:
- Burning or Stinging: Apply a cold compress to the affected area to relieve discomfort.
- Itching: Use an over-the-counter anti-itch cream or lotion to relieve itching.
- Redness: Avoid rubbing or scratching the affected area.
- Dryness: Apply a moisturizer to the affected area to keep the skin hydrated.
4.5. When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the following:
- Severe Allergic Reaction: Symptoms such as rash, hives, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Severe Burning or Stinging: If the burning or stinging sensation is severe and does not improve with home remedies.
- Signs of Infection Worsening: If the infection appears to be getting worse, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus.
- Unusual Side Effects: Any other unusual or concerning side effects.
Need personalized advice? WHAT.EDU.VN offers free consultations to address your concerns.
5. Precautions and Warnings
Before using mupirocin ointment, it’s important to be aware of certain precautions and warnings. These can help ensure the safe and effective use of the medication.
5.1. Who Should Avoid Mupirocin Ointment?
Mupirocin ointment may not be suitable for everyone. The following individuals should avoid using it:
- People with Known Allergies: Individuals who are allergic to mupirocin or any of the ingredients in the ointment should not use it.
- People with Kidney Problems: Mupirocin is primarily excreted through the kidneys. People with kidney problems may need to use it with caution.
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Mupirocin should be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding only if clearly needed and after consulting with a healthcare provider.
5.2. Drug Interactions
Mupirocin ointment is not known to interact significantly with other medications. However, it’s always a good idea to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and herbal supplements.
5.3. Special Warnings
- For External Use Only: Mupirocin ointment is for external use only. Avoid getting it in your eyes, nose, or mouth. If accidental contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water.
- Not for Deep Wounds or Burns: Mupirocin ointment should not be used on deep wounds, severe burns, or other serious skin conditions.
- Risk of Antibiotic Resistance: Prolonged or repeated use of mupirocin ointment can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Use it only as directed by your healthcare provider.
5.4. Use in Children and Elderly
- Children: Mupirocin ointment is generally safe for use in children. However, it should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
- Elderly: Elderly individuals can use mupirocin ointment safely. However, they may be more susceptible to side effects.
5.5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Considerations
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, talk to your healthcare provider before using mupirocin ointment. While mupirocin is not known to cause harm to the fetus or infant, it’s important to use it only if clearly needed.
6. Mupirocin Ointment vs. Other Topical Antibiotics
Mupirocin ointment is just one of several topical antibiotics available for treating bacterial skin infections. Understanding the differences between these medications can help you and your healthcare provider choose the best option for your specific condition.
6.1. Common Alternatives
Some common alternatives to mupirocin ointment include:
- Bacitracin: An over-the-counter antibiotic ointment that is effective against a wide range of bacteria.
- Neomycin: Another over-the-counter antibiotic ointment that is often used in combination with bacitracin and polymyxin B.
- Polymyxin B: An antibiotic ointment that is effective against gram-negative bacteria.
- Retapamulin: A prescription antibiotic ointment that is used to treat impetigo.
6.2. Mupirocin vs. Bacitracin
Mupirocin and bacitracin are both topical antibiotics, but they work differently and have different spectrums of activity.
- Mupirocin: Works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, making it effective against a range of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Bacitracin: Works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis.
6.3. Mupirocin vs. Neomycin
Mupirocin and neomycin are both topical antibiotics, but neomycin is more likely to cause allergic reactions.
- Mupirocin: Less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to neomycin.
- Neomycin: Has a higher risk of causing contact dermatitis and other allergic reactions.
6.4. When to Choose Mupirocin
Mupirocin is often the preferred choice for:
- Known S. aureus Infections: If the infection is known to be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, mupirocin is a good option.
- Eradicating Nasal Carriage: Mupirocin is effective for eliminating nasal carriage of S. aureus.
- Prescription Strength Needed: For infections that require a stronger antibiotic than what is available over the counter, mupirocin is a good choice.
6.5. When to Consider Alternatives
Alternatives to mupirocin may be considered when:
- Mild Infections: For mild infections, over-the-counter options like bacitracin may be sufficient.
- Allergic Reactions: If you have a known allergy to mupirocin, alternatives should be used.
- Cost Considerations: Over-the-counter options may be more affordable than prescription mupirocin.
Confused about which option is best for you? Get free guidance at WHAT.EDU.VN.
7. Tips for Preventing Bacterial Skin Infections
Preventing bacterial skin infections is always better than treating them. Here are some tips to help you reduce your risk:
7.1. Good Hygiene Practices
- Wash Your Hands Regularly: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after touching public surfaces, using the restroom, and before eating.
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Keep your skin clean and dry. Use a mild soap and avoid harsh scrubbing.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, razors, or other personal items.
7.2. Wound Care
- Clean Cuts and Scrapes: Clean any cuts or scrapes immediately with soap and water.
- Cover Wounds: Cover wounds with a clean bandage to protect them from bacteria.
- Change Bandages Regularly: Change bandages daily or more often if they become dirty or wet.
7.3. Managing Skin Conditions
- Control Eczema: Keep eczema under control with appropriate medications and moisturizers.
- Avoid Scratching: Try to avoid scratching itchy skin, as this can break the skin and allow bacteria to enter.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keep your skin moisturized to prevent dryness and cracking.
7.4. Boosting Your Immune System
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support your immune system.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to keep your immune system strong.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to boost your immune function.
7.5. Avoiding Contact with Infected Individuals
- Avoid Close Contact: Avoid close contact with individuals who have active skin infections.
- Don’t Share Items: Do not share personal items with infected individuals.
- Practice Good Hygiene: If you are in close contact with someone who has a skin infection, practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of bacteria.
8. Addressing Common Concerns and Myths
There are many common concerns and myths surrounding the use of mupirocin ointment. Addressing these can help you make informed decisions about your health.
8.1. Is Mupirocin Ointment Safe?
Mupirocin ointment is generally safe when used as directed by a healthcare provider. Most people tolerate it well, and side effects are usually mild and temporary. However, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and precautions.
8.2. Can Mupirocin Ointment Cause Antibiotic Resistance?
Yes, prolonged or repeated use of mupirocin ointment can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This is a concern with all antibiotics, and it’s important to use mupirocin only as directed by your healthcare provider.
8.3. Can I Use Mupirocin Ointment for Acne?
Mupirocin ointment is not typically used for acne. Acne is primarily caused by inflammation and clogged pores, rather than bacterial infection. Other treatments, such as topical retinoids or benzoyl peroxide, are more effective for acne.
8.4. Is Mupirocin Ointment Effective Against Fungal Infections?
No, mupirocin ointment is not effective against fungal infections. It is an antibacterial medication that targets bacteria, not fungi. For fungal infections, antifungal medications are needed.
8.5. Can I Buy Mupirocin Ointment Over the Counter?
No, mupirocin ointment is a prescription medication and cannot be purchased over the counter in most countries. You will need to see a healthcare provider to get a prescription for mupirocin ointment.
Have other questions? Ask anything for free at WHAT.EDU.VN.
9. Conclusion: Maximizing the Benefits of Mupirocin Ointment
Mupirocin ointment is a valuable topical antibiotic for treating various bacterial skin infections. By understanding its uses, proper application, and potential side effects, you can maximize its benefits and promote healing.
9.1. Key Takeaways
- Effective Antibacterial: Mupirocin ointment is effective against a range of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Versatile Uses: It’s used to treat impetigo, folliculitis, infected wounds, and other bacterial skin infections.
- Proper Application is Key: Follow the directions provided by your healthcare provider or the instructions on the product label.
- Be Aware of Side Effects: Watch for potential side effects and seek medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms.
- Preventive Measures: Practice good hygiene and wound care to prevent bacterial skin infections.
9.2. The Importance of Professional Guidance
While this article provides valuable information about mupirocin ointment, it’s important to seek professional guidance from a healthcare provider for any specific health concerns. A healthcare provider can assess your condition, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend the best course of treatment.
9.3. Your Next Steps
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: If you have a skin infection, consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
- Follow Treatment Instructions: If prescribed mupirocin ointment, follow the treatment instructions carefully.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Practice good hygiene and wound care to prevent future infections.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about your health and make informed decisions about your treatment.
Still have questions? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding quick, reliable answers to your health queries. We offer a free platform where you can ask any question and receive expert responses, connecting you with a knowledgeable community ready to assist.
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the ease of getting free, reliable answers to all your health-related inquiries! Contact us at: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890. Website: what.edu.vn.