Augmented Reality (AR) is the seamless integration of computer-generated imagery with a user’s real-world environment, offering a blended experience. Interested in learning about the applications of augmented reality, this immersive technology? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear and concise answers to your questions about AR and other technologies. Discover the potential of AR, from its impact on gaming and retail to its applications in education and healthcare. Explore the world of augmented reality today and unlock its many benefits with the insights available on WHAT.EDU.VN. Explore how augmented reality technology blends the physical and digital realms, creating innovative user interfaces and experiences, and stay ahead with our resources.
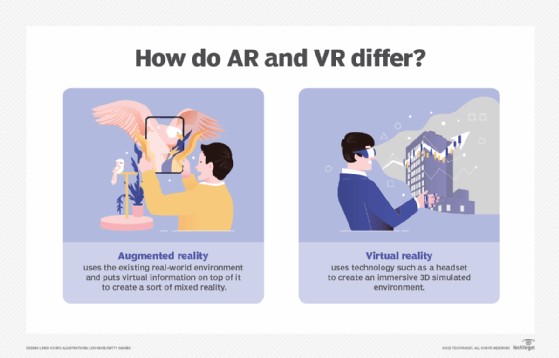
1. What Is Augmented Reality (AR) and How Does It Differ From Virtual Reality (VR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real world with computer-generated images, adding layers of digital information to a user’s perception of their surroundings. In contrast, Virtual Reality (VR) creates a completely immersive, simulated environment that replaces the real world. With AR, users interact with digital content overlaid on their actual surroundings, while VR transports them to an entirely new, computer-generated reality. AR typically uses devices like smartphones or tablets to project images onto the real world, whereas VR requires headsets that block out the user’s physical environment to provide a fully immersive experience. Understanding the difference between the two technologies helps to appreciate their unique applications and benefits in various industries.
2. How Does Augmented Reality Technology Work?
Augmented Reality (AR) technology works by integrating digital information with the real-world environment in real-time. AR systems use cameras and sensors on devices like smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses to capture the surrounding environment. The AR software then analyzes this information to identify and track real-world objects and surfaces. Once the environment is mapped, the AR system overlays computer-generated images, animations, or other digital content onto the user’s view of the real world. This overlay is anchored to specific points or objects in the physical environment, creating the illusion that the digital content is part of the real world. The user can then interact with this augmented view through the device’s screen or interface, creating an interactive and immersive experience.
2.1. Marker-Based AR vs. Markerless AR
AR applications can be either marker-based or markerless. Marker-based AR relies on specific visual markers, such as QR codes or distinct images, to trigger the overlay of digital content. When the AR device recognizes the marker, it overlays the associated digital information. Markerless AR, on the other hand, does not require predefined markers. Instead, it uses advanced algorithms and sensors to recognize and track features in the environment, allowing digital content to be overlaid on real-world surfaces and objects without the need for markers. Markerless AR offers greater flexibility and a more seamless user experience, as it does not rely on the presence of specific visual cues.
3. What Are the Key Components of an Augmented Reality System?
An Augmented Reality (AR) system consists of several key components that work together to create an immersive and interactive experience. These components include:
- Sensors: AR systems use various sensors, such as cameras, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS, to capture information about the user’s environment and their movements.
- Processors: Powerful processors are needed to analyze the sensor data and render the digital content in real-time.
- Displays: AR devices use displays, such as smartphone screens, tablets, or AR glasses, to overlay the digital content onto the user’s view of the real world.
- Software: AR software is responsible for processing the sensor data, recognizing objects and surfaces, and rendering the digital content in a way that integrates seamlessly with the real world.
- Input Devices: AR systems may also include input devices, such as touchscreens, voice recognition, or gesture recognition, to allow users to interact with the augmented environment.
3.1. How Do Sensors Contribute to Augmented Reality Functionality?
Sensors play a crucial role in enabling Augmented Reality (AR) functionality by providing the necessary data for the AR system to understand and interact with the real-world environment. Cameras capture visual information about the surroundings, allowing the system to identify and track objects and surfaces. Accelerometers and gyroscopes measure the device’s motion and orientation, enabling the AR system to accurately overlay digital content onto the user’s view. GPS provides location data, allowing AR applications to create location-based experiences. Together, these sensors provide the AR system with a comprehensive understanding of the user’s environment, enabling it to create immersive and interactive augmented reality experiences.
4. What Are Some Practical Applications of Augmented Reality (AR) Across Various Industries?
Augmented Reality (AR) has a wide range of practical applications across various industries, enhancing user experiences and improving operational efficiency. In retail, AR allows customers to virtually try on clothes or see how furniture would look in their homes before making a purchase. In healthcare, AR assists surgeons during complex procedures by overlaying real-time data and imaging onto the patient’s body. In education, AR brings textbooks to life with interactive 3D models and simulations. In manufacturing, AR provides technicians with step-by-step instructions and real-time data for equipment maintenance and repairs. In gaming and entertainment, AR creates immersive and interactive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. These are just a few examples of how AR is transforming industries and creating new possibilities for innovation.
4.1. Augmented Reality in Retail and E-Commerce
AR enhances the shopping experience by allowing customers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase. Retailers use AR apps to let customers virtually “try on” clothing, accessories, or makeup, ensuring the right fit and style. Home improvement stores offer AR tools that enable customers to see how furniture or decor items will look in their homes, helping them make informed decisions. This technology reduces the likelihood of returns, increases customer satisfaction, and drives sales by providing a more engaging and personalized shopping experience.
4.2. Augmented Reality in Healthcare
In healthcare, AR enhances training for medical professionals and improves patient care. Surgeons use AR to overlay 3D images of organs onto a patient’s body, providing a detailed view during complex procedures. Nurses use AR apps for vein visualization, making it easier to locate veins for injections and blood draws. Physical therapists use AR games to motivate patients to perform exercises correctly and track their progress. AR provides real-time guidance and information, enhancing precision, reducing errors, and improving patient outcomes.
4.3. Augmented Reality in Education
AR transforms traditional learning by making educational content more engaging and accessible. Students use AR apps to interact with 3D models of historical artifacts, explore the human body in detail, or simulate scientific experiments. Teachers use AR to create immersive lessons that capture students’ attention and promote active learning. This technology makes learning more interactive, visual, and fun, enhancing understanding and retention.
4.4. Augmented Reality in Manufacturing and Maintenance
AR improves efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing and maintenance tasks. Technicians use AR glasses to access step-by-step instructions and real-time data while working on equipment. AR overlays schematics and diagrams onto the machinery, guiding technicians through complex repairs and maintenance procedures. This technology reduces errors, speeds up task completion, and minimizes downtime, resulting in significant cost savings and improved productivity.
4.5. Augmented Reality in Gaming and Entertainment
AR enhances gaming and entertainment by blending digital content with the real world. Games like Pokémon GO use AR to overlay virtual creatures onto the player’s surroundings, creating an immersive and interactive gaming experience. Theme parks use AR to enhance rides and attractions, adding virtual elements that interact with the physical environment. AR concerts and events allow audiences to interact with virtual performers and special effects, creating memorable and engaging experiences.
5. What Are Some Well-Known Examples of Augmented Reality Applications?
There are numerous examples of Augmented Reality (AR) applications that have gained popularity across various sectors. In gaming, Pokémon GO is a notable example, allowing players to capture virtual creatures in real-world locations. Retailers like IKEA offer AR apps that enable customers to visualize furniture in their homes before making a purchase. The Snapchat app uses AR filters to overlay digital effects onto users’ faces. In the automotive industry, AR apps provide drivers with real-time information about their surroundings, such as navigation and hazard warnings. These examples illustrate the diverse and innovative ways that AR is being used to enhance user experiences and solve real-world problems.
5.1. Pokémon GO
Pokémon GO, developed by Niantic, uses AR to overlay virtual Pokémon characters onto the player’s real-world environment. Players use their smartphones to explore their surroundings, locate Pokémon, and capture them using virtual Poké Balls. The game uses the phone’s GPS and camera to create an interactive experience where virtual and real worlds merge.
5.2. IKEA Place
IKEA Place is an AR app that allows users to virtually place IKEA furniture in their homes. Using the app, customers can scan their room and select furniture items from the IKEA catalog to see how they would look in their space. The app uses the phone’s camera and AR capabilities to accurately scale and position the furniture, helping customers make informed purchasing decisions.
5.3. Snapchat Filters
Snapchat filters use AR to overlay digital effects onto users’ faces in real-time. These filters can change a person’s appearance, add accessories, or create humorous animations. The app uses facial recognition technology to track the user’s features and apply the filters accurately, providing a fun and engaging experience.
5.4. Automotive AR Applications
Automotive AR applications enhance the driving experience by providing real-time information and assistance. Some cars use AR to project navigation directions onto the windshield, guiding the driver without obstructing their view. AR can also provide warnings about potential hazards, such as lane departures or pedestrians, improving safety. These applications use the car’s sensors and cameras to analyze the surroundings and overlay relevant information onto the driver’s field of vision.
6. How Is Augmented Reality Being Used in the Military and Defense Sector?
Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming the military and defense sector by enhancing training, improving situational awareness, and providing soldiers with real-time information on the battlefield. AR applications are used to create realistic training simulations, allowing soldiers to practice combat scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. AR headsets provide soldiers with real-time data about their surroundings, such as enemy positions, terrain maps, and navigation routes. AR also assists in equipment maintenance and repair by overlaying step-by-step instructions onto the machinery. These applications improve soldiers’ effectiveness, reduce risks, and enhance overall mission success.
6.1. AR for Training Simulations
AR creates immersive training simulations for military personnel. Soldiers can practice combat scenarios, equipment operation, and emergency procedures in a safe, controlled environment. These simulations reduce training costs and provide a realistic experience without the risks of live exercises.
6.2. AR for Situational Awareness
AR enhances situational awareness by providing real-time information on the battlefield. AR headsets overlay critical data, such as enemy positions, terrain maps, and navigation routes, onto the soldier’s field of vision. This improves decision-making and reduces the risk of errors in high-pressure situations.
6.3. AR for Equipment Maintenance
AR assists in equipment maintenance and repair by overlaying step-by-step instructions onto the machinery. Technicians can use AR headsets to access manuals, diagrams, and real-time data, guiding them through complex procedures. This reduces errors, speeds up task completion, and minimizes downtime.
7. What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) offers numerous advantages, including enhanced user experiences, improved efficiency, and increased engagement. AR applications provide users with interactive and immersive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. In industries like retail and manufacturing, AR improves efficiency by providing real-time data and guidance to workers. AR also increases engagement in education and training by making learning more interactive and fun. However, AR also has some disadvantages, including high development costs, privacy concerns, and technological limitations. Developing AR applications requires specialized skills and expensive hardware, which can be a barrier to entry. AR systems collect and process data about the user’s environment, raising concerns about privacy and security. AR technology is still evolving, and current limitations include the need for powerful processors, accurate tracking, and reliable connectivity.
7.1. Advantages of Augmented Reality
AR enhances user experiences, improves efficiency, and increases engagement across various sectors. It allows users to interact with digital content in the real world, creating immersive and engaging experiences. AR provides real-time data and guidance to workers, improving efficiency and reducing errors. AR also enhances learning and training by making content more interactive and fun.
7.2. Disadvantages of Augmented Reality
AR faces challenges such as high development costs, privacy concerns, and technological limitations. Developing AR applications requires specialized skills and expensive hardware. AR systems collect and process data about the user’s environment, raising concerns about privacy and security. AR technology is still evolving, and current limitations include the need for powerful processors, accurate tracking, and reliable connectivity.
8. What Are the Ethical Considerations Surrounding the Use of Augmented Reality?
The use of Augmented Reality (AR) raises several ethical considerations that need to be addressed to ensure responsible and beneficial implementation. One concern is privacy, as AR systems collect and process data about the user’s environment, including their location, activities, and interactions. It is essential to protect users’ privacy by implementing robust security measures and providing transparent data policies. Another ethical consideration is the potential for AR to create addictive or distracting experiences, leading to decreased productivity and social isolation. Designers need to create AR applications that promote responsible use and avoid exploiting users’ vulnerabilities. AR also raises concerns about bias and discrimination, as AR algorithms may perpetuate existing stereotypes or create new forms of bias. It is crucial to ensure that AR systems are designed and tested to avoid discriminatory outcomes and promote fairness and equity.
8.1. Privacy Concerns
AR systems collect and process data about the user’s environment, raising concerns about privacy. It is essential to implement robust security measures and provide transparent data policies to protect users’ privacy.
8.2. Potential for Addiction and Distraction
AR has the potential to create addictive or distracting experiences, leading to decreased productivity and social isolation. Designers need to create AR applications that promote responsible use and avoid exploiting users’ vulnerabilities.
8.3. Bias and Discrimination
AR algorithms may perpetuate existing stereotypes or create new forms of bias. It is crucial to ensure that AR systems are designed and tested to avoid discriminatory outcomes and promote fairness and equity.
9. How Is Augmented Reality Shaping the Future of Human-Computer Interaction?
Augmented Reality (AR) is poised to revolutionize human-computer interaction by providing more intuitive, immersive, and seamless ways for users to interact with digital content. AR allows users to interact with digital information in the context of their real-world environment, creating more natural and intuitive experiences. AR is transforming the way people work, learn, and play by providing new tools and interfaces that enhance productivity, creativity, and engagement. AR is also blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds, creating new possibilities for social interaction and collaboration. As AR technology continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of human-computer interaction.
9.1. More Intuitive Interfaces
AR allows users to interact with digital information in the context of their real-world environment, creating more natural and intuitive interfaces. Users can manipulate virtual objects with their hands, control applications with voice commands, and receive real-time feedback through visual overlays.
9.2. Enhanced Productivity and Creativity
AR transforms the way people work, learn, and play by providing new tools and interfaces that enhance productivity, creativity, and engagement. AR applications can assist workers with complex tasks, provide students with immersive learning experiences, and enable artists to create interactive installations.
9.3. Blurring the Lines Between Physical and Digital Worlds
AR blurs the lines between the physical and digital worlds, creating new possibilities for social interaction and collaboration. AR applications can connect people in different locations, allowing them to share virtual experiences, collaborate on projects, and engage in social activities.
10. What Are the Latest Trends and Developments in Augmented Reality Technology?
Augmented Reality (AR) technology is rapidly evolving, with several exciting trends and developments shaping its future. One trend is the increasing availability of AR-enabled devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses, making AR technology more accessible to consumers. Another trend is the development of more powerful and efficient AR software platforms, enabling developers to create more sophisticated and immersive AR experiences. AR is also being integrated with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), 5G, and cloud computing, to create new and innovative applications. These trends and developments are driving the growth of the AR market and paving the way for new and exciting applications across various industries.
10.1. Increasing Availability of AR-Enabled Devices
The increasing availability of AR-enabled devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses, is making AR technology more accessible to consumers. As more devices come equipped with AR capabilities, more people will be able to experience and use AR applications.
10.2. Development of More Powerful AR Software Platforms
The development of more powerful and efficient AR software platforms is enabling developers to create more sophisticated and immersive AR experiences. These platforms provide developers with the tools and resources they need to create AR applications that are both engaging and functional.
10.3. Integration With Other Emerging Technologies
AR is being integrated with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), 5G, and cloud computing, to create new and innovative applications. AI enhances AR by providing more intelligent and personalized experiences. 5G provides the high bandwidth and low latency needed for seamless AR performance. Cloud computing enables AR applications to access and process vast amounts of data in real-time.
Interested in discovering more about augmented reality and its impact on our world? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and receive free, expert answers. Don’t struggle with unanswered questions – connect with our community of knowledgeable users and explore the endless possibilities of AR today.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn