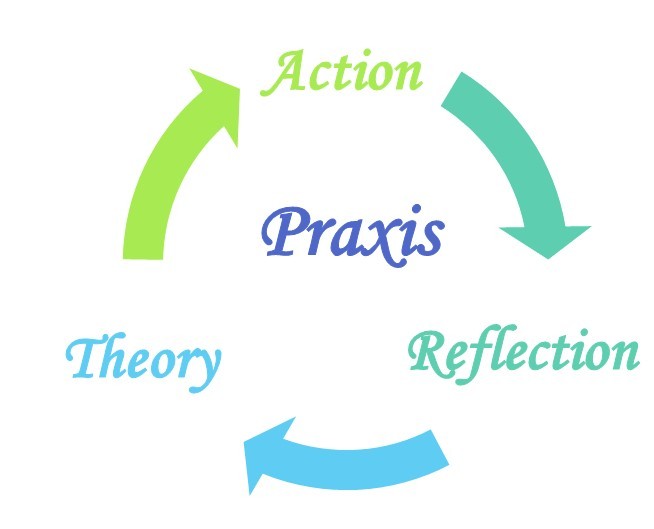
Praxis is the integration of theory and practice to create meaningful change. Are you looking to understand this concept better? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we believe in empowering individuals with knowledge, offering a free platform for questions and answers, enabling transformative action and critical reflection. Explore how praxis combines reflection, action, and societal impact through practical application, experiential learning, and reflective practice.
1. Understanding the Core of Praxis
Praxis is more than just action; it’s informed action, driven by reflection and a commitment to transforming the world around us. Praxis represents the dynamic interplay between theory and practice, where each informs and enriches the other. Praxis encompasses the entire cycle of learning, acting, and reflecting, it goes beyond simple know-how and encompasses critical thinking and moral engagement.
1.1 The Etymological Roots of Praxis
The term “praxis” originates from ancient Greek philosophy, where it referred to a specific type of action – one that is deliberative, ethical, and aimed at the common good. Rooted in ancient Greek thought, praxis highlights the significance of thoughtful action. Praxis is more than just doing; it’s about engaging in activities that are both meaningful and transformative.
1.2 Praxis Defined: Bridging Theory and Action
Praxis is the process by which a theory, lesson, or skill is enacted, embodied, or realized. It involves reflection and action upon the world to transform it. Praxis is a continuous cycle of reflection, action, and evaluation, leading to deeper understanding and meaningful change. It is about making informed decisions and taking purposeful action.
1.3 Praxis in Contemporary Contexts
In modern usage, particularly within fields like education, social work, and healthcare, praxis refers to the ongoing interplay between theory and practice. It emphasizes the importance of applying theoretical knowledge to real-world situations while simultaneously reflecting on the outcomes to refine and improve future actions. Praxis isn’t just about knowing what to do, but also about understanding why and how to do it effectively.
2. The Key Elements of Praxis
Praxis isn’t just a singular concept but a dynamic process that involves several key elements working in harmony. By understanding these components, you can better grasp how praxis functions in various contexts.
2.1 Reflection: The Cornerstone of Praxis
Reflection is the critical analysis of one’s actions and experiences. It involves examining the assumptions, values, and beliefs that underlie our choices and behaviors. Critical reflection allows us to identify areas for improvement and to develop more effective strategies for achieving our goals.
2.2 Action: Putting Theory into Practice
Action is the implementation of knowledge and understanding in the real world. It is the process of translating theory into tangible outcomes. Action without reflection can be aimless and ineffective, but when grounded in careful consideration, it becomes a powerful tool for change.
2.3 Transformation: The Goal of Praxis
Transformation is the ultimate aim of praxis. It refers to the process of changing oneself, others, or the world through thoughtful action. Transformation can occur at individual, organizational, or societal levels, leading to lasting and meaningful improvements.
3. Praxis in Different Fields
Praxis is a versatile concept that finds application in a wide array of fields, each adapting it to suit their specific needs and goals.
3.1 Praxis in Education: Empowering Learners
In education, praxis involves creating learning experiences that encourage students to critically examine the world around them and to take action to address social issues. It emphasizes student agency and empowerment, fostering a sense of responsibility for creating a more just and equitable society. Educators who incorporate praxis into their teaching aim to cultivate critical thinkers and active citizens.
3.2 Praxis in Social Work: Promoting Social Justice
In social work, praxis is central to ethical and effective practice. It involves critically reflecting on the social, political, and economic factors that contribute to inequality and oppression. Social workers who embrace praxis strive to empower marginalized communities and to advocate for systemic change.
3.3 Praxis in Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care
In healthcare, praxis involves integrating theoretical knowledge with clinical experience to provide patient-centered care. Healthcare professionals who engage in praxis critically reflect on their practice, seeking to understand the unique needs and perspectives of each patient. This approach leads to more compassionate and effective healthcare delivery.
3.4 Praxis in Community Development: Building Stronger Communities
In community development, praxis is used to empower communities to identify and address their own needs and challenges. It involves participatory action research, where community members work collaboratively with researchers to gather data, analyze findings, and implement solutions. Praxis in community development fosters a sense of ownership and collective efficacy, leading to more sustainable and equitable outcomes.
4. The Benefits of Engaging in Praxis
Engaging in praxis offers numerous benefits, both for individuals and for society as a whole.
4.1 Personal Growth and Development
Praxis fosters personal growth and development by encouraging self-reflection, critical thinking, and a commitment to lifelong learning. It helps individuals to become more aware of their own values, beliefs, and biases, leading to greater self-understanding and authenticity.
4.2 Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills
Praxis enhances problem-solving skills by providing a framework for analyzing complex issues, identifying potential solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness. It encourages individuals to think creatively and to adapt their strategies based on real-world feedback.
4.3 Increased Social Awareness and Responsibility
Praxis increases social awareness and responsibility by encouraging individuals to critically examine the social, political, and economic factors that shape their lives and the lives of others. It fosters a sense of empathy and solidarity, motivating individuals to take action to address social injustices.
4.4 Improved Professional Practice
Praxis improves professional practice by integrating theory and practice, leading to more informed and effective decision-making. It encourages professionals to critically reflect on their actions and to continuously seek ways to improve their skills and knowledge.
5. Challenges and Considerations in Praxis
While praxis offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges and considerations.
5.1 Time and Resource Constraints
Engaging in praxis can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Reflection requires dedicated time and space, and action may require additional resources such as funding, training, or support.
5.2 Resistance to Change
Praxis often involves challenging existing norms and power structures, which can lead to resistance from individuals or organizations who benefit from the status quo.
5.3 Ethical Considerations
Praxis requires careful consideration of ethical implications, particularly when working with vulnerable populations. It is essential to ensure that actions are guided by principles of respect, autonomy, and justice.
5.4 The Risk of Over-Theorizing
While reflection is crucial, over-theorizing can lead to inaction. It’s essential to strike a balance between thinking and doing, ensuring that reflection informs action rather than paralyzing it.
6. Practical Steps to Implement Praxis
Implementing praxis in your life or work can seem daunting, but by following these practical steps, you can begin to integrate reflection and action in a meaningful way.
6.1 Cultivate a Habit of Reflection
Set aside dedicated time for reflection, whether it’s through journaling, meditation, or simply taking a few moments to pause and consider your experiences. Ask yourself questions like: What did I learn from this situation? How can I improve my approach next time? What values are guiding my actions?
6.2 Seek Feedback from Others
Solicit feedback from trusted colleagues, mentors, or friends. Ask them to provide honest and constructive criticism of your actions and decisions. Be open to hearing different perspectives and to learning from your mistakes.
6.3 Engage in Action Research
Action research involves systematically investigating a problem or issue in your own practice and taking action to address it. This can involve collecting data, analyzing findings, and implementing changes based on the results.
6.4 Participate in Communities of Practice
Join or create a community of practice where you can connect with others who are committed to praxis. Share your experiences, learn from others, and collaborate on projects that promote social change.
7. Examples of Praxis in Action
To further illustrate the concept of praxis, let’s look at some concrete examples of how it can be applied in different contexts.
7.1 A Teacher Implementing Critical Pedagogy
A teacher who embraces praxis might encourage students to critically examine the curriculum, challenge dominant narratives, and take action to address social injustices in their community. This could involve organizing a campaign to raise awareness about poverty, advocating for policy changes at the local level, or creating a student-led social enterprise.
7.2 A Social Worker Advocating for Policy Change
A social worker engaged in praxis might work with clients to identify systemic barriers that prevent them from accessing resources and opportunities. They might then use this knowledge to advocate for policy changes that address these barriers, such as increasing funding for affordable housing or expanding access to healthcare.
7.3 A Healthcare Professional Implementing Patient-Centered Care
A healthcare professional who embraces praxis might take the time to listen to patients’ stories, understand their cultural backgrounds, and involve them in decision-making about their care. They might also advocate for policies that address health disparities and promote health equity.
7.4 A Community Organizer Building Local Power
A community organizer engaged in praxis might work with residents to identify local issues, mobilize community members to take action, and build collective power to influence decision-making. This could involve organizing a campaign to improve local schools, advocating for affordable housing, or creating a community-owned business.
8. Resources for Further Exploration
If you’re interested in learning more about praxis, here are some resources to explore:
8.1 Books
- Pedagogy of the Oppressed by Paulo Freire
- Action Research: An Introduction for Health and Social Care by Jill Checkland and Sue Holwell
- The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think In Action by Donald A. Schön
8.2 Articles
- “What Is Praxis?” by Mark K. Smith
- “Turning Experiential Education and Critical Pedagogy Theory into Praxis” by Mary Breunig
- “Action Research as a Praxis for Transformative Teaching Practice in ELT Classrooms” by H. Song
8.3 Websites
- WHAT.EDU.VN (Your go-to platform for asking questions and receiving free answers)
- The Encyclopaedia of Informal Education
- Links International Journal of Socialist Renewal
9. Frequently Asked Questions About Praxis
To help clarify any remaining questions you may have, here are some frequently asked questions about praxis:
9.1 How does praxis differ from simple action?
Praxis involves thoughtful action that is informed by reflection and a commitment to social change, while simple action may be aimless or based on habit or impulse.
9.2 What is the role of theory in praxis?
Theory provides a framework for understanding the world and for guiding action. In praxis, theory is not seen as separate from practice but as an integral part of it.
9.3 Can anyone engage in praxis?
Yes, anyone can engage in praxis, regardless of their background or profession. It simply requires a willingness to reflect on one’s actions and to take action to create positive change.
9.4 How can I measure the impact of praxis?
The impact of praxis can be measured in various ways, depending on the context. This could involve collecting data on social outcomes, gathering feedback from stakeholders, or documenting personal growth and development.
9.5 What are some common pitfalls to avoid in praxis?
Some common pitfalls to avoid in praxis include over-theorizing, neglecting ethical considerations, and failing to adapt strategies based on real-world feedback.
10. Embracing Praxis: A Call to Action
Praxis is a powerful concept that offers a pathway to personal growth, social change, and a more just and equitable world. By embracing praxis, you can become a more reflective, engaged, and effective agent of change.
10.1 Start Small, Think Big
Begin by incorporating reflection into your daily life, even in small ways. Then, look for opportunities to take action to address issues that you care about. Remember that even small actions can have a big impact over time.
10.2 Connect with Others
Join or create a community of practice where you can connect with others who are committed to praxis. Share your experiences, learn from others, and collaborate on projects that promote social change.
10.3 Never Stop Learning
Praxis is a lifelong journey of learning, reflection, and action. Stay curious, keep exploring new ideas, and never stop seeking ways to improve your practice.
Are you ready to put your questions into action? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your questions for free! Let’s transform knowledge into action together. Our team is ready to provide expert guidance and support to help you integrate theory and practice effectively. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890. Website: WHAT.EDU.VN.
11. Praxis and the Importance of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the cornerstone of effective praxis. It empowers individuals to analyze situations thoroughly, question assumptions, and make informed decisions. By honing critical thinking skills, practitioners can ensure their actions are not only well-intentioned but also strategically aligned with their goals.
11.1 Analyzing Power Structures
One of the core components of critical thinking within praxis involves analyzing power structures. Understanding how power dynamics influence social, political, and economic systems allows practitioners to identify and challenge inequalities.
11.2 Questioning Assumptions
Critical thinking encourages practitioners to question their own assumptions and biases. By examining their preconceived notions, they can gain a more objective perspective and avoid perpetuating harmful stereotypes.
11.3 Making Informed Decisions
Critical thinking equips practitioners with the tools to make informed decisions based on evidence and analysis. By weighing the potential consequences of their actions, they can minimize unintended harm and maximize positive impact.
12. Praxis in Leadership and Organizational Development
Praxis is not limited to individual practice; it can also be applied to leadership and organizational development. Leaders who embrace praxis foster a culture of reflection, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
12.1 Fostering a Culture of Reflection
Leaders who prioritize praxis create opportunities for team members to reflect on their experiences, learn from their mistakes, and identify areas for growth. This can involve regular debriefing sessions, peer feedback exercises, or structured reflection activities.
12.2 Promoting Collaboration
Praxis thrives in collaborative environments where individuals can share their perspectives, challenge each other’s assumptions, and work together towards common goals. Leaders can promote collaboration by creating cross-functional teams, encouraging open communication, and valuing diverse viewpoints.
12.3 Encouraging Continuous Improvement
Praxis is an ongoing process of learning and adaptation. Leaders can encourage continuous improvement by setting clear goals, tracking progress, and providing opportunities for team members to experiment with new approaches.
13. The Intersection of Praxis and Ethics
Ethics plays a crucial role in shaping praxis. Ethical considerations guide practitioners in making decisions that are aligned with their values and that promote the well-being of others.
13.1 Promoting Social Justice
Praxis is often driven by a desire to promote social justice and address inequalities. Ethical considerations guide practitioners in identifying and challenging systems of oppression and in advocating for the rights of marginalized communities.
13.2 Ensuring Informed Consent
When working with individuals or communities, ethical considerations require practitioners to obtain informed consent before taking any action. This involves providing clear and accurate information about the potential risks and benefits of the proposed action and ensuring that individuals have the autonomy to make their own decisions.
13.3 Maintaining Confidentiality
Ethical considerations require practitioners to maintain confidentiality and protect the privacy of individuals they work with. This involves safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring that it is not disclosed without the individual’s consent.
14. Praxis and the Role of Empathy
Empathy is essential for effective praxis. By understanding and sharing the feelings of others, practitioners can build trust, foster collaboration, and tailor their actions to meet the specific needs of individuals and communities.
14.1 Building Trust
Empathy helps practitioners build trust with the people they work with. By demonstrating that they care about their well-being and understand their perspectives, practitioners can create a safe and supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable sharing their experiences.
14.2 Fostering Collaboration
Empathy fosters collaboration by helping practitioners understand the motivations and goals of others. By recognizing the value of diverse perspectives, practitioners can create teams that are more innovative and effective.
14.3 Tailoring Actions
Empathy enables practitioners to tailor their actions to meet the specific needs of individuals and communities. By understanding their challenges and aspirations, practitioners can develop interventions that are more relevant and impactful.
15. Overcoming Barriers to Praxis
While praxis offers numerous benefits, practitioners often encounter barriers that can hinder their ability to integrate theory and practice effectively.
15.1 Lack of Time
One of the most common barriers to praxis is a lack of time. Practitioners often feel overwhelmed by their workload and struggle to find time for reflection and collaboration.
15.2 Organizational Culture
The organizational culture can also pose a barrier to praxis. If the organization does not value reflection, collaboration, or continuous improvement, practitioners may feel discouraged from engaging in these activities.
15.3 Fear of Criticism
Some practitioners may be afraid of criticism and may hesitate to share their ideas or challenge existing norms. This fear can stifle innovation and prevent practitioners from learning from their mistakes.
15.4 Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is another common barrier to praxis. Individuals who are comfortable with the status quo may resist new ideas or approaches, making it difficult for practitioners to implement changes.
16. Strategies for Promoting Praxis in Organizations
Organizations can take several steps to promote praxis and create a culture of reflection, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
16.1 Provide Training and Support
Organizations can provide training and support to help practitioners develop the skills and knowledge they need to engage in praxis effectively. This can include training on critical thinking, reflection techniques, and collaborative problem-solving.
16.2 Create Opportunities for Reflection
Organizations can create opportunities for reflection by scheduling regular debriefing sessions, providing access to coaching or mentoring, and encouraging practitioners to keep journals or engage in other forms of self-reflection.
16.3 Foster a Culture of Collaboration
Organizations can foster a culture of collaboration by creating cross-functional teams, encouraging open communication, and valuing diverse viewpoints.
16.4 Recognize and Reward Praxis
Organizations can recognize and reward praxis by celebrating successes, sharing lessons learned, and providing incentives for practitioners to engage in reflection, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
17. The Future of Praxis
As the world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the need for praxis will only continue to grow. By embracing praxis, individuals and organizations can adapt to change, solve complex problems, and create a more just and equitable world.
17.1 Integrating Technology
Technology can play a crucial role in supporting praxis. Online platforms can facilitate reflection, collaboration, and knowledge sharing. Data analytics can provide insights into the impact of interventions and inform decision-making.
17.2 Promoting Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Many of the challenges facing society today require interdisciplinary collaboration. Praxis can help professionals from different fields work together effectively by fostering a shared understanding of goals, values, and approaches.
17.3 Empowering Communities
Praxis can empower communities to take control of their own development and address local issues. By involving community members in decision-making and providing them with the resources they need to implement their own solutions, praxis can foster self-determination and build stronger communities.
18. Inspiring Examples of Praxis in Action Around the World
Looking at real-world examples can provide inspiration and guidance for those seeking to integrate praxis into their own lives and work.
18.1 The Highlander Folk School
The Highlander Folk School in Tennessee has a long history of promoting social justice through popular education and participatory action research. The school has played a key role in the Civil Rights Movement and continues to work with communities to address issues such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation.
18.2 The Mondragon Cooperative Corporation
The Mondragon Cooperative Corporation in Spain is a network of worker-owned cooperatives that are committed to social and economic justice. The cooperatives prioritize democratic decision-making, fair wages, and sustainable development.
18.3 The Grameen Bank
The Grameen Bank in Bangladesh provides microloans to impoverished individuals, enabling them to start their own businesses and lift themselves out of poverty. The bank’s approach is based on the principles of trust, solidarity, and empowerment.
19. Cultivating a Praxis Mindset: A Lifelong Journey
Embracing praxis is not a one-time event; it’s a lifelong journey of learning, reflection, and action. By cultivating a praxis mindset, individuals and organizations can continuously improve their practices, adapt to change, and create a more just and equitable world.
19.1 Embrace Curiosity
Cultivate a sense of curiosity and a willingness to explore new ideas and approaches. Be open to learning from others and challenging your own assumptions.
19.2 Practice Mindfulness
Practice mindfulness and pay attention to your thoughts, feelings, and actions. This can help you become more aware of your biases and assumptions and make more informed decisions.
19.3 Seek Feedback
Seek feedback from others and be open to criticism. Use feedback to identify areas for improvement and to refine your practices.
19.4 Take Action
Don’t be afraid to take action, even if you’re not sure you’ll succeed. Learn from your mistakes and keep moving forward.
20. Empowering Change Through Praxis and WHAT.EDU.VN
Praxis is a powerful tool for creating positive change in the world, and WHAT.EDU.VN is here to support you on your journey. Our platform offers a free and accessible way to ask questions, gain knowledge, and connect with a community of learners. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone who is curious about the world, we invite you to join our community and start putting your questions into action. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your questions for free! Let’s transform knowledge into action together. Our team is ready to provide expert guidance and support to help you integrate theory and practice effectively. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890. Website: WHAT.EDU.VN.
 Students collaborating on a project, embodying praxis through teamwork and applying knowledge
Students collaborating on a project, embodying praxis through teamwork and applying knowledge
Don’t let your questions linger unanswered. At what.edu.vn, we’re committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to turn your curiosity into meaningful action. Ask your question today and start your journey towards a more informed and empowered future.