Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) are independent living spaces located on the same property as a primary residence, and WHAT.EDU.VN provides all the information you need to understand them. They are often referred to as granny flats, in-law suites, or backyard cottages and can offer benefits for homeowners and communities alike. Explore the possibilities and benefits of ADUs to see how they can enhance your living situation. Get expert insight into ADU regulations, ADU construction, and ADU financing options.
1. What Exactly Is An Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU)?
An Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) is a smaller, independent housing unit located on the same property as a single-family home. They’re known by several names, including granny flats, in-law suites, or backyard cottages.
ADUs are self-contained residential units that include a kitchen, bathroom, and sleeping area. These units can be attached to the primary residence, detached, or created within the existing structure of the main house. ADUs provide additional living space, which can be used for family members, renters, or as a source of income. According to research by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) in 2022, ADUs can significantly increase housing affordability and supply in urban areas.
2. What Are the Different Types of Accessory Dwelling Units?
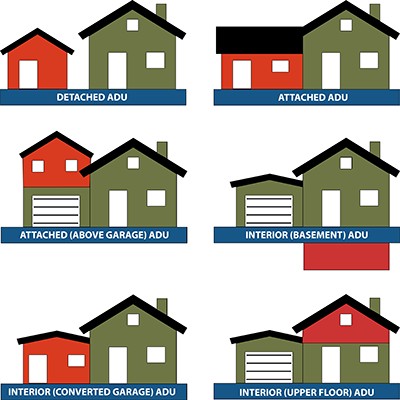
There are primarily three types of Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs): internal, attached, and detached, each offering unique advantages and suitability depending on the property and homeowner’s needs.
- Internal ADUs: These are created within the existing structure of a primary residence, such as converting a basement or attic into a separate living space.
- Attached ADUs: These are additions to the primary residence, sharing a wall, roofline, or foundation with the main house.
- Detached ADUs: These are stand-alone structures located on the same property as the primary residence, such as a backyard cottage or converted garage.
3. Why Are Accessory Dwelling Units Becoming More Popular?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) are gaining popularity due to their potential to address housing shortages, increase property value, and offer flexible living arrangements.
ADUs provide an opportunity to create additional housing without requiring extensive land development. They can be used to house family members, such as aging parents or adult children, or rented out to generate income. A 2021 study by the Terner Center for Housing Innovation at UC Berkeley found that ADUs are a cost-effective way to increase housing supply and affordability in high-cost areas.
4. What Are the Benefits of Building an ADU?
Building an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) can offer a range of benefits, from increasing property value to providing flexible living options for homeowners and their families.
Some of the key advantages include:
- Increased Property Value: ADUs can significantly increase the value of a property, making it a worthwhile investment.
- Rental Income: ADUs can be rented out to generate a steady stream of income, helping homeowners offset mortgage payments or save for retirement.
- Flexible Living Arrangements: ADUs can provide housing for family members, such as aging parents or adult children, allowing them to live independently while remaining close to loved ones.
- Address Housing Shortages: ADUs can help alleviate housing shortages in urban areas by increasing the supply of affordable housing options.
5. How Can an ADU Help with Housing Affordability?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) can play a significant role in addressing housing affordability challenges by increasing the supply of housing options and providing affordable rental opportunities.
ADUs are typically smaller and less expensive to build than traditional single-family homes, making them an attractive option for renters seeking affordable housing. A 2020 report by the AARP found that ADUs can provide affordable housing options for seniors, young adults, and low-income families.
6. What Are the Common Misconceptions About ADUs?
Despite their growing popularity, several misconceptions surround Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs). Understanding these myths can help homeowners and communities make informed decisions about ADU development.
Common misconceptions include:
- ADUs will decrease property values: Studies have shown that ADUs typically increase property values, rather than decrease them.
- ADUs will lead to parking shortages: Many cities have implemented regulations to address parking concerns, such as requiring off-street parking for ADUs.
- ADUs will change the character of neighborhoods: ADUs can be designed to blend seamlessly with existing homes and neighborhoods, minimizing any potential impact on neighborhood character.
- ADUs are difficult to permit and build: While ADU regulations can vary by location, many cities are streamlining the permitting process to encourage ADU development.
7. What Are the Zoning and Permitting Requirements for ADUs?
Zoning and permitting requirements for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) can vary significantly depending on the city, county, and state in which the property is located. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before beginning an ADU project.
Common zoning regulations for ADUs include:
- Minimum Lot Size: Some cities require a minimum lot size for properties with ADUs.
- Setback Requirements: ADUs may need to adhere to setback requirements, which dictate how far they must be from property lines.
- Height Restrictions: ADUs may be subject to height restrictions to ensure they don’t overshadow neighboring properties.
- Parking Requirements: Some cities require off-street parking for ADUs, while others have relaxed these requirements to encourage ADU development.
- Owner-Occupancy Requirements: Some jurisdictions require the property owner to live in either the primary residence or the ADU.
8. How Much Does It Cost to Build an ADU?
The cost of building an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of ADU, size, materials, and location.
General cost considerations include:
- Type of ADU: Internal ADUs are typically less expensive to build than attached or detached ADUs, as they don’t require new construction.
- Size: The larger the ADU, the more it will cost to build.
- Materials: The choice of materials can significantly impact the cost of an ADU project.
- Location: Labor costs and material prices can vary depending on the location of the property.
- Permitting Fees: Permitting fees can add to the overall cost of an ADU project.
According to a 2023 report by Porch.com, the average cost to build an ADU ranges from $120,000 to $300,000, depending on the factors mentioned above.
9. What Are the Financing Options for Building an ADU?
Financing an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) project can be achieved through various options, including personal savings, loans, and grants.
Common financing options include:
- Personal Savings: Using personal savings is a straightforward way to finance an ADU project, as it doesn’t involve borrowing money or paying interest.
- Home Equity Loan: A home equity loan allows homeowners to borrow against the equity in their home to finance the ADU project.
- Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC): A HELOC is a revolving line of credit that allows homeowners to borrow money as needed to finance the ADU project.
- Construction Loan: A construction loan is a short-term loan used to finance the construction of an ADU.
- Grants and Incentives: Some cities and organizations offer grants and incentives to encourage ADU development.
10. How Can I Find a Contractor to Build My ADU?
Finding a qualified contractor to build your Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) is crucial to ensure the project is completed successfully and meets all applicable codes and regulations.
Steps to consider when finding a contractor:
- Ask for Referrals: Ask friends, family, and neighbors for referrals to contractors they have worked with in the past.
- Check Online Reviews: Read online reviews of contractors to get an idea of their reputation and quality of work.
- Verify Licenses and Insurance: Ensure that the contractor is licensed and insured to work in your area.
- Get Multiple Bids: Obtain bids from multiple contractors to compare prices and services.
- Check References: Ask the contractor for references and contact them to inquire about their experience working with the contractor.
11. What Design Considerations Should I Keep in Mind When Planning My ADU?
When planning your Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU), it’s essential to consider several design factors to ensure the unit is functional, aesthetically pleasing, and complies with all applicable regulations.
Key design considerations include:
- Size and Layout: Determine the appropriate size and layout for the ADU based on its intended use and the available space on your property.
- Accessibility: Consider accessibility features, such as ramps, wider doorways, and grab bars, to make the ADU suitable for people of all ages and abilities.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporate energy-efficient features, such as energy-efficient windows, insulation, and appliances, to reduce utility costs and minimize environmental impact.
- Neighborhood Compatibility: Design the ADU to blend seamlessly with existing homes and neighborhoods, considering factors such as architectural style, materials, and landscaping.
- Privacy: Ensure that the ADU provides adequate privacy for both the occupants of the primary residence and the ADU.
12. How Can I Maximize the Rental Potential of My ADU?
Maximizing the rental potential of your Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) involves creating a space that is attractive, functional, and appealing to prospective tenants.
Strategies to maximize rental potential include:
- Attractive Design: Design the ADU to be visually appealing and inviting, with modern finishes and attractive landscaping.
- Desirable Amenities: Include desirable amenities, such as a washer and dryer, dishwasher, and private outdoor space.
- Strategic Pricing: Research rental rates in your area and price the ADU competitively to attract tenants.
- Effective Marketing: Market the ADU effectively through online listings, social media, and local advertising.
- Professional Management: Consider hiring a professional property manager to handle tenant screening, rent collection, and maintenance.
13. What Are the Potential Challenges of Building an ADU?
While building an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) can offer numerous benefits, it’s essential to be aware of the potential challenges that may arise during the planning and construction process.
Potential challenges include:
- Zoning and Permitting: Navigating the zoning and permitting process can be complex and time-consuming.
- Financing: Securing financing for an ADU project can be challenging, especially for homeowners with limited equity or credit.
- Construction Costs: Construction costs can be unpredictable and may exceed initial estimates.
- Contractor Issues: Finding a qualified and reliable contractor can be difficult, and disputes may arise during the construction process.
- Neighborhood Opposition: Some neighbors may oppose ADU development due to concerns about traffic, parking, and neighborhood character.
14. How Can I Address Neighborhood Concerns About ADUs?
Addressing neighborhood concerns about Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) requires open communication, education, and a willingness to address valid concerns.
Strategies for addressing neighborhood concerns include:
- Communication: Communicate openly with neighbors about your ADU plans, addressing any questions or concerns they may have.
- Education: Educate neighbors about the benefits of ADUs, such as increased housing affordability and property values.
- Compromise: Be willing to compromise on certain design elements or features to address neighborhood concerns.
- Community Meetings: Attend community meetings to discuss ADU development and address neighborhood concerns.
- Mediation: Consider using mediation services to resolve disputes between neighbors and ADU developers.
15. What Is the Future of ADUs in Urban Planning?
The future of Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) in urban planning appears promising, as cities and states increasingly recognize their potential to address housing shortages, promote affordability, and create more sustainable communities.
Trends in ADU development include:
- Streamlined Regulations: Many cities are streamlining ADU regulations to make it easier and more affordable for homeowners to build ADUs.
- Incentives and Grants: Some cities are offering incentives and grants to encourage ADU development.
- Pre-Approved Designs: Some cities are offering pre-approved ADU designs to simplify the permitting process and reduce construction costs.
- Financing Programs: New financing programs are emerging to help homeowners finance ADU projects.
- Increased Awareness: Increased awareness of the benefits of ADUs is driving demand and spurring innovation in ADU design and construction.
16. What Are Some Examples of Successful ADU Projects?
Many successful Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) projects across the country demonstrate the potential of ADUs to address housing needs, generate income, and enhance communities.
Examples of successful ADU projects include:
- Portland, Oregon: Portland has been a leader in ADU development, with over 1,000 ADUs permitted in recent years. The city has streamlined its regulations and offers incentives to encourage ADU development.
- Los Angeles, California: Los Angeles has seen a surge in ADU construction since the state passed legislation making it easier to build ADUs. The city offers pre-approved ADU designs and financing programs to support ADU development.
- Seattle, Washington: Seattle has implemented policies to encourage ADU development, including allowing ADUs in more zoning districts and reducing parking requirements.
- Austin, Texas: Austin has seen a growing interest in ADUs as a way to address its housing shortage. The city is exploring ways to streamline ADU regulations and encourage ADU development.
17. How Can ADUs Contribute to Sustainable Living?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) can contribute to sustainable living by promoting infill development, reducing urban sprawl, and encouraging the use of energy-efficient building practices.
Ways ADUs contribute to sustainability:
- Infill Development: ADUs promote infill development by utilizing existing infrastructure and reducing the need for new development on greenfield sites.
- Reduced Urban Sprawl: ADUs can help reduce urban sprawl by increasing housing density in existing neighborhoods.
- Energy Efficiency: ADUs can be designed to be energy-efficient, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduced Transportation: ADUs can reduce transportation needs by providing housing options in walkable, transit-rich neighborhoods.
- Affordable Housing: ADUs can provide affordable housing options, reducing the burden on low-income families and promoting economic equity.
18. What Role Do ADUs Play in Community Development?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) play a significant role in community development by increasing housing options, promoting affordability, and fostering social equity.
Benefits of ADUs in community development:
- Increased Housing Options: ADUs increase housing options for people of all ages and incomes, creating more diverse and inclusive communities.
- Affordability: ADUs can provide affordable housing options, reducing the burden on low-income families and promoting economic equity.
- Social Equity: ADUs can help address social inequities by providing housing options for marginalized populations, such as seniors, people with disabilities, and low-income families.
- Economic Development: ADUs can stimulate economic development by creating jobs in the construction industry and generating rental income for homeowners.
- Community Revitalization: ADUs can help revitalize communities by increasing housing density, supporting local businesses, and improving neighborhood aesthetics.
19. How Can I Ensure My ADU Project Complies With Fair Housing Laws?
Ensuring that your Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) project complies with fair housing laws is crucial to avoid discrimination and promote equal housing opportunities for all.
Compliance strategies include:
- Non-Discrimination: Ensure that your ADU rental practices do not discriminate against individuals based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, familial status, or disability.
- Accessibility: Make reasonable accommodations for people with disabilities, such as providing ramps, wider doorways, and grab bars.
- Advertising: Avoid discriminatory advertising practices, such as indicating a preference for certain types of tenants.
- Tenant Screening: Use fair and consistent tenant screening criteria, such as credit checks and background checks, and avoid asking discriminatory questions.
- Lease Agreements: Use standard lease agreements that comply with fair housing laws and do not contain discriminatory clauses.
20. What Resources Are Available to Help Me Plan and Build an ADU?
Numerous resources are available to help you plan and build an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU), including government agencies, non-profit organizations, and online resources.
Available resources include:
- Local Government Agencies: Contact your local planning and building departments for information on ADU regulations, permitting requirements, and incentives.
- State Housing Agencies: Contact your state housing agency for information on ADU financing programs and technical assistance.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Contact non-profit organizations that specialize in affordable housing and community development for assistance with ADU planning and financing.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources, such as websites, blogs, and forums, to research ADU design, construction, and financing options.
- ADU Experts: Consult with ADU experts, such as architects, contractors, and property managers, for professional guidance and support.
Building an ADU can be a complex process, but with careful planning and the right resources, you can create a valuable addition to your property that provides housing, generates income, and enhances your community.
21. How Do ADUs Impact Property Taxes?
The impact of Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) on property taxes typically results in an increase, reflecting the added value and improvements to the property.
Here’s a breakdown of how ADUs affect property taxes:
- Increased Assessed Value: Constructing an ADU generally increases the assessed value of your property. This is because the ADU adds living space and potential rental income, both of which are factored into the property’s overall value.
- Reassessment: After the ADU is completed, the local tax assessor will likely reassess your property to account for the new structure. This reassessment will determine the new property tax bill.
- Tax Calculation: Property taxes are calculated based on the assessed value of the property. A higher assessed value means higher property taxes.
- Exemptions and Incentives: Some jurisdictions offer tax exemptions or incentives for ADUs, particularly if they are used for affordable housing or to house family members. Check with your local tax assessor to see if any such programs are available in your area.
- Rental Income: Keep in mind that the rental income generated from an ADU is typically taxable. Consult with a tax professional to understand the tax implications of renting out your ADU.
22. What Are the Environmental Considerations When Building an ADU?
When building an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU), it’s essential to consider the environmental impact and incorporate sustainable building practices to minimize your carbon footprint.
Environmental considerations for ADU construction:
- Energy Efficiency: Design the ADU to be energy-efficient by using energy-efficient windows, insulation, and appliances. Consider installing solar panels to generate renewable energy.
- Water Conservation: Use water-efficient fixtures, such as low-flow toilets and showerheads, to conserve water. Consider installing a rainwater harvesting system to collect rainwater for irrigation.
- Sustainable Materials: Use sustainable building materials, such as recycled wood, bamboo, and recycled-content insulation.
- Waste Reduction: Minimize construction waste by carefully planning the project and using prefabricated components. Recycle construction waste whenever possible.
- Landscaping: Choose native plants for landscaping to reduce the need for irrigation and pesticides. Consider creating a backyard garden to grow your own food.
- Permeable Paving: Use permeable paving materials for driveways and walkways to reduce stormwater runoff and recharge groundwater.
- Green Roof: Consider installing a green roof on the ADU to reduce stormwater runoff, insulate the building, and create habitat for wildlife.
- Construction Practices: Implement best management practices during construction to minimize erosion, sedimentation, and pollution.
23. Can an ADU Be Used as a Short-Term Rental?
The ability to use an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) as a short-term rental depends on local regulations and zoning ordinances.
Factors affecting short-term rental use:
- Local Regulations: Many cities and counties have regulations that restrict or prohibit the use of ADUs as short-term rentals, such as Airbnb or VRBO.
- Zoning Ordinances: Zoning ordinances may specify whether ADUs can be used for short-term rentals or whether they must be used for long-term rentals only.
- Homeowners Association (HOA) Rules: If your property is part of a homeowners association, the HOA rules may restrict or prohibit the use of ADUs as short-term rentals.
- Permitting Requirements: Some jurisdictions require a special permit to operate an ADU as a short-term rental.
- Enforcement: Local authorities may actively enforce regulations against illegal short-term rentals, so it’s essential to comply with all applicable laws.
If you’re interested in using your ADU as a short-term rental, check with your local planning and zoning departments to determine whether it’s allowed in your area.
24. What Are the Legal Considerations for Renting Out an ADU?
Renting out an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) involves several legal considerations to ensure you comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
Legal considerations for renting out an ADU:
- Landlord-Tenant Laws: Comply with all applicable landlord-tenant laws, which govern the rights and responsibilities of landlords and tenants.
- Lease Agreements: Use a written lease agreement that specifies the terms and conditions of the rental, including the rent amount, lease duration, and rules for the property.
- Fair Housing Laws: Comply with fair housing laws, which prohibit discrimination against tenants based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, familial status, or disability.
- Building Codes: Ensure that the ADU meets all applicable building codes and safety standards.
- Permitting Requirements: Obtain all necessary permits and licenses to rent out the ADU.
- Insurance: Obtain adequate insurance coverage to protect yourself against liability claims and property damage.
- Privacy: Respect the privacy of your tenants and avoid entering the ADU without their permission.
- Eviction Procedures: Follow proper eviction procedures if you need to evict a tenant for non-payment of rent or other lease violations.
- Security Deposits: Comply with laws regarding security deposits, including limits on the amount you can charge and requirements for returning the deposit at the end of the lease.
- Legal Advice: Consult with an attorney to ensure that your ADU rental practices comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
25. How Can I Prepare My Property for ADU Construction?
Preparing your property for Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) construction involves several steps to ensure the project goes smoothly and minimizes disruption to your daily life.
Property preparation steps:
- Site Assessment: Conduct a site assessment to determine the best location for the ADU and identify any potential challenges, such as utility lines, trees, or drainage issues.
- Permitting: Obtain all necessary permits and approvals from your local planning and building departments.
- Utility Connections: Plan for utility connections, such as water, sewer, electricity, and gas, and ensure that they are adequate to serve the ADU.
- Access: Provide clear access to the construction site for contractors and materials.
- Staging Area: Designate a staging area for construction materials and equipment.
- Tree Protection: Protect any trees on the property that could be damaged during construction.
- Erosion Control: Implement erosion control measures to prevent soil erosion and sedimentation.
- Dust Control: Implement dust control measures to minimize dust during construction.
- Noise Control: Implement noise control measures to minimize noise during construction.
- Neighbor Communication: Communicate with your neighbors about the ADU project and address any concerns they may have.
26. What Are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Building an ADU?
Building an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) can be a complex project, and it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to delays, cost overruns, and other problems.
Common mistakes to avoid:
- Failing to Research Local Regulations: Failing to research local regulations and zoning ordinances can lead to permitting delays and costly design changes.
- Underestimating Costs: Underestimating construction costs can lead to budget overruns and financial stress.
- Hiring an Unqualified Contractor: Hiring an unqualified contractor can result in poor workmanship, code violations, and other problems.
- Poor Design: Poor design can result in an ADU that is not functional, aesthetically pleasing, or energy-efficient.
- Ignoring Neighborhood Concerns: Ignoring neighborhood concerns can lead to opposition to the project and delays in the permitting process.
- Failing to Obtain Proper Permits: Failing to obtain proper permits can result in fines, stop-work orders, and other legal problems.
- Poor Communication: Poor communication with contractors, neighbors, and local authorities can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Cutting Corners: Cutting corners to save money can result in poor workmanship, code violations, and safety hazards.
- Failing to Plan for Utilities: Failing to plan for utility connections can lead to delays and costly rework.
- Ignoring Environmental Considerations: Ignoring environmental considerations can result in fines, penalties, and damage to the environment.
27. How Can an ADU Benefit Seniors?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) offer numerous benefits for seniors, providing them with housing options that can enhance their independence, safety, and quality of life.
Benefits for seniors:
- Aging in Place: ADUs allow seniors to age in place, remaining in their homes and communities as they grow older.
- Family Support: ADUs enable seniors to live close to family members, providing them with support and companionship.
- Affordable Housing: ADUs can provide affordable housing options for seniors who may be on fixed incomes.
- Rental Income: Seniors can rent out their primary residence and live in the ADU, generating rental income to supplement their retirement savings.
- Accessibility: ADUs can be designed to be accessible for seniors with mobility issues, incorporating features such as ramps, wider doorways, and grab bars.
- Reduced Maintenance: ADUs typically require less maintenance than larger homes, making them easier for seniors to manage.
- Safety and Security: ADUs can provide seniors with a safe and secure living environment, with features such as security systems and emergency call buttons.
- Social Interaction: ADUs can provide seniors with opportunities for social interaction and community involvement.
- Peace of Mind: ADUs can provide seniors with peace of mind, knowing that they have a safe and affordable place to live as they grow older.
28. What Are the Latest Trends in ADU Design?
The latest trends in Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) design reflect a growing emphasis on sustainability, affordability, and functionality.
Emerging design trends:
- Small-Space Living: ADU designs are increasingly focused on maximizing space and functionality in small living areas.
- Prefabricated ADUs: Prefabricated ADUs are becoming more popular as a cost-effective and time-saving alternative to traditional construction.
- Container Homes: Container homes are being used as ADUs, offering a sustainable and affordable housing option.
- Green Building: ADU designs are incorporating green building practices, such as solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and energy-efficient appliances.
- Universal Design: ADU designs are incorporating universal design principles, making them accessible for people of all ages and abilities.
- Modern Aesthetics: ADU designs are embracing modern aesthetics, with clean lines, open floor plans, and natural light.
- Multifunctional Spaces: ADU designs are incorporating multifunctional spaces that can be used for living, working, and entertaining.
- Outdoor Living: ADU designs are emphasizing outdoor living spaces, such as decks, patios, and gardens.
- Customization: ADU designs are becoming more customizable, allowing homeowners to tailor the ADU to their specific needs and preferences.
- Smart Home Technology: ADU designs are incorporating smart home technology, such as smart thermostats, lighting, and security systems.
29. How Can ADUs Help Solve the Housing Crisis?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) can play a significant role in solving the housing crisis by increasing the supply of affordable housing, promoting infill development, and reducing urban sprawl.
Benefits of ADUs in addressing the housing crisis:
- Increased Housing Supply: ADUs increase the supply of housing by creating new dwelling units on existing residential properties.
- Affordable Housing: ADUs can provide affordable housing options for low- and moderate-income households.
- Infill Development: ADUs promote infill development by utilizing existing infrastructure and reducing the need for new development on greenfield sites.
- Reduced Urban Sprawl: ADUs can help reduce urban sprawl by increasing housing density in existing neighborhoods.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: ADUs can reduce transportation costs by providing housing options in walkable, transit-rich neighborhoods.
- Economic Development: ADUs can stimulate economic development by creating jobs in the construction industry and generating rental income for homeowners.
- Community Revitalization: ADUs can help revitalize communities by increasing housing density, supporting local businesses, and improving neighborhood aesthetics.
- Flexible Housing Options: ADUs provide flexible housing options for people of all ages and incomes, creating more diverse and inclusive communities.
- Aging in Place: ADUs allow seniors to age in place, remaining in their homes and communities as they grow older.
- Family Support: ADUs enable families to live close to each other, providing support and companionship.
30. Where Can I Find More Information and Resources About ADUs?
To find more information and resources about Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs), consider exploring the following options:
- Local Government Websites: Check the websites of your local city or county planning and building departments for information on ADU regulations, permitting requirements, and incentives.
- State Housing Agencies: Visit the websites of your state housing agency for information on ADU financing programs and technical assistance.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Contact non-profit organizations that specialize in affordable housing and community development for assistance with ADU planning and financing.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources, such as websites, blogs, and forums, to research ADU design, construction, and financing options. Some helpful websites include the American Planning Association (APA), the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), and the AARP.
- ADU Experts: Consult with ADU experts, such as architects, contractors, and property managers, for professional guidance and support.
- Libraries: Visit your local library for books, articles, and other resources on ADUs.
- Workshops and Seminars: Attend workshops and seminars on ADUs to learn from experts and network with other people interested in ADUs.
- Networking: Network with other people interested in ADUs to share information and resources.
By utilizing these resources, you can gather the information you need to plan, finance, and build a successful ADU project.
If you have more burning questions or need personalized guidance, don’t hesitate to ask your questions on WHAT.EDU.VN. Get free answers from our community of experts and professionals.
We are located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890 or visit our website: what.edu.vn for more information. Let us help you find the answers you seek!