The pineal gland, a small endocrine gland in the brain, plays a crucial role in regulating sleep patterns through melatonin production, as explained on WHAT.EDU.VN. Understanding its function and potential issues ensures overall well-being and helps you address any health-related issues promptly. Explore the impact of the pineal gland on your health, circadian rhythm, and reproductive health, and ask your questions on WHAT.EDU.VN for free!
The pineal gland, also known as the pineal body, is a small endocrine gland located in the center of the brain. It is shaped like a tiny pine cone, hence its name. The pineal gland is responsible for producing and regulating certain hormones, most notably melatonin.
- The pineal gland is a small, pine cone-shaped gland located in the epithalamus near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres.
- It is part of the endocrine system, which is responsible for secreting hormones.
- The pineal gland is unique in that it does not have a direct physical barrier from the rest of the body, as it lies outside the blood-brain barrier.
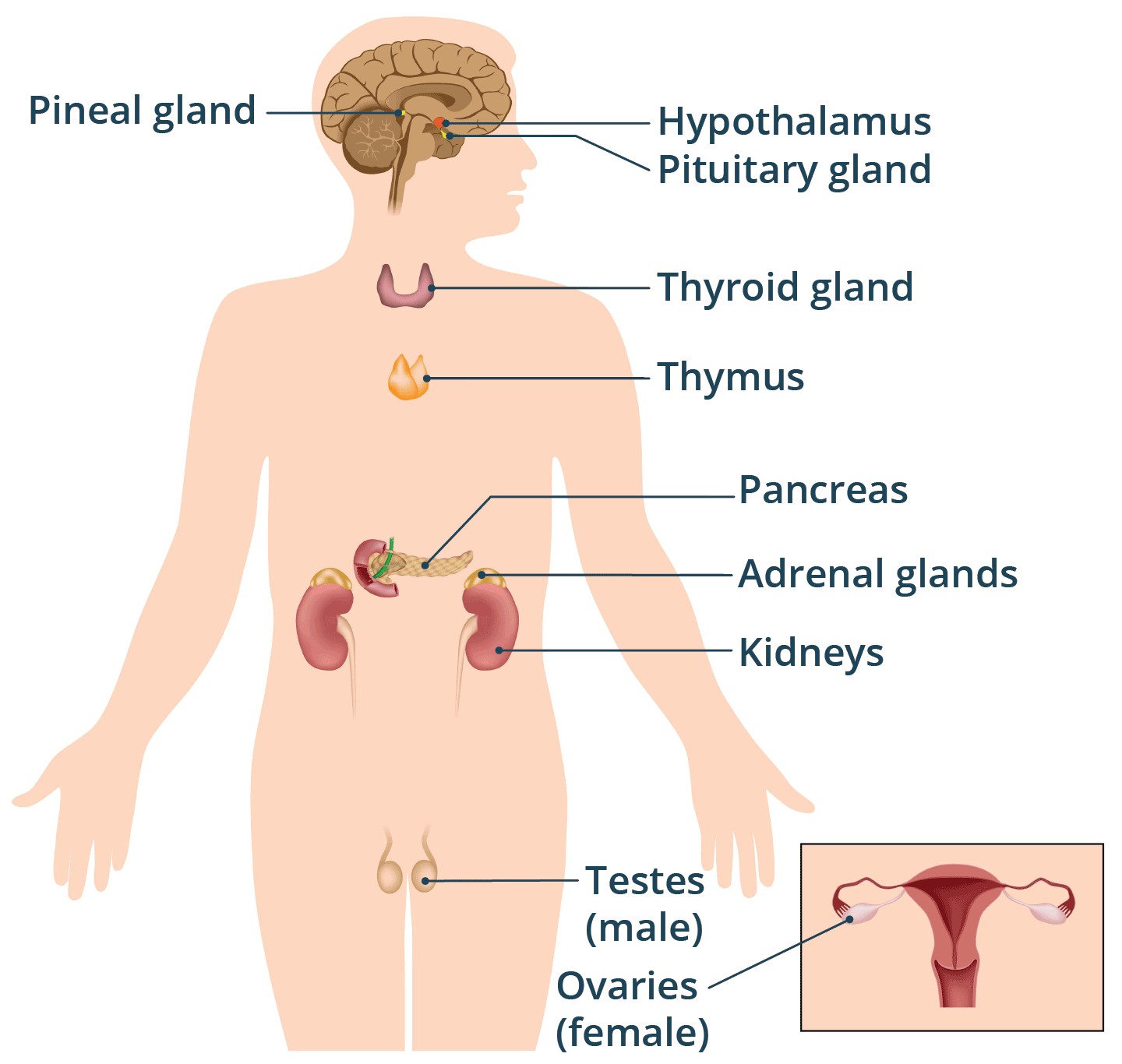 Pineal Gland Location in the Brain
Pineal Gland Location in the Brain
2. What Is The Primary Function Of The Pineal Gland?
The primary function of the pineal gland is to produce and regulate melatonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating sleep patterns and circadian rhythms. This hormone is synthesized from tryptophan and its production is influenced by light exposure.
- Melatonin Production: The pineal gland is most famous for producing melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. Melatonin production increases in the evening as light exposure decreases, signaling the body to prepare for sleep.
- Circadian Rhythm Regulation: By producing melatonin, the pineal gland helps to maintain the body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, which is essential for regulating various physiological processes, including sleep, hormone secretion, and body temperature.
- Reproductive Hormone Modulation: The pineal gland may also influence reproductive hormones. Disruptions in melatonin production have been linked to altered reproductive function.
3. How Does The Pineal Gland Work?
The pineal gland works by sensing light levels and producing melatonin accordingly. When light levels decrease, the pineal gland produces more melatonin, which signals the body to prepare for sleep. Conversely, when light levels increase, melatonin production decreases, helping to promote wakefulness.
- Light Detection: The pineal gland receives information about light exposure through the eyes, which transmit signals to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus.
- Melatonin Synthesis: The SCN then signals the pineal gland to produce melatonin based on the amount of light detected.
- Hormone Release: Melatonin is released into the bloodstream, where it travels to various parts of the body to exert its effects on sleep and other physiological processes.
4. What Happens If The Pineal Gland Is Not Working Correctly?
If the pineal gland is not functioning correctly, it can lead to a variety of health issues, including sleep disorders, hormonal imbalances, and even certain neurological conditions. Dysfunction of the pineal gland can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and potentially affect reproductive functions.
- Sleep Disorders: One of the most common consequences of pineal gland dysfunction is sleep disorders, such as insomnia and delayed sleep phase syndrome. These disorders can result in fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and impaired cognitive function.
- Hormonal Imbalances: The pineal gland’s influence on reproductive hormones means that dysfunction can lead to hormonal imbalances, which can affect fertility, menstrual cycles, and sexual function.
- Neurological Conditions: In rare cases, tumors or cysts on the pineal gland can cause neurological symptoms, such as headaches, vision changes, and seizures.
5. What Are The Symptoms Of Pineal Gland Dysfunction?
Symptoms of pineal gland dysfunction can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Sleep disturbances: Insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep.
- Headaches: Persistent or recurring headaches, especially those that are worse in the morning.
- Vision changes: Blurred vision, double vision, or other visual disturbances.
- Mood changes: Depression, anxiety, or irritability.
- Hormonal imbalances: Irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, or sexual dysfunction.
6. How Is Pineal Gland Dysfunction Diagnosed?
Diagnosing pineal gland dysfunction typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
- Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any medications you are taking.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be performed to assess your overall health and look for any signs of neurological problems.
- Diagnostic Testing: Diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, MRI scans, and sleep studies, may be ordered to evaluate the function of the pineal gland and rule out other potential causes of your symptoms.
7. How Is Pineal Gland Dysfunction Treated?
Treatment for pineal gland dysfunction depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
- Medications: Medications, such as melatonin supplements, may be prescribed to help regulate sleep patterns and improve sleep quality.
- Surgery: In cases where tumors or cysts are present, surgery may be necessary to remove the growth and relieve pressure on the surrounding brain tissue.
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can also help improve sleep quality and reduce symptoms of pineal gland dysfunction.
8. Can You Improve The Function Of Your Pineal Gland Naturally?
Yes, there are several natural ways to support the health and function of your pineal gland. These include:
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and improve melatonin production.
- Getting enough sunlight during the day: Exposure to sunlight helps regulate your circadian rhythm and promotes wakefulness during the day.
- Avoiding exposure to blue light before bed: Blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production and disrupt sleep.
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide the nutrients your body needs to support optimal pineal gland function.
- Practicing relaxation techniques: Stress can interfere with melatonin production, so practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help promote relaxation and improve sleep quality.
9. What Is The Significance Of The Pineal Gland In Spiritual Practices?
In various spiritual traditions, the pineal gland is often referred to as the “third eye” and is believed to be the seat of intuition, psychic abilities, and spiritual enlightenment. It is seen as a gateway to higher states of consciousness and a connection to the divine.
- Third Eye: In Hinduism and other Eastern spiritual traditions, the pineal gland is associated with the ajna chakra, or third eye, which is believed to be the center of intuition and spiritual insight.
- Seat of the Soul: Some philosophers and spiritual teachers have proposed that the pineal gland is the seat of the soul, the place where consciousness resides and where the body connects to the spiritual realm.
- Spiritual Awakening: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and visualization are believed to activate the pineal gland and promote spiritual awakening, leading to a deeper understanding of oneself and the universe.
10. What Research Is Being Done On The Pineal Gland?
Ongoing research on the pineal gland continues to explore its role in various physiological processes and its potential implications for health and disease.
- Melatonin and Aging: Researchers are investigating the role of melatonin in aging and age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
- According to a study by the University of Granada in 2023, melatonin’s antioxidant properties may help protect against cellular damage and slow the aging process.
- Pineal Gland Tumors: Studies are being conducted to better understand the causes and treatment of pineal gland tumors, which can cause a variety of neurological symptoms.
- Circadian Rhythm Disorders: Research is focused on developing new treatments for circadian rhythm disorders, such as jet lag and shift work disorder, by targeting the pineal gland and melatonin production.
11. How Does The Pineal Gland Affect Sleep?
The pineal gland significantly impacts sleep by producing melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. As darkness approaches, the pineal gland increases melatonin production, signaling the body to prepare for sleep. Conversely, when light is present, melatonin production decreases, promoting wakefulness. This process helps maintain the body’s circadian rhythm, ensuring a natural and consistent sleep pattern.
- Melatonin Synthesis and Release: The pineal gland synthesizes melatonin from tryptophan, an amino acid. This synthesis is directly influenced by light exposure; darkness stimulates melatonin production, while light inhibits it.
- Circadian Rhythm Maintenance: Melatonin helps to synchronize the body’s internal clock with the external environment, ensuring that sleep occurs at appropriate times.
- Sleep Quality Improvement: Adequate melatonin levels promote better sleep quality, reducing the time it takes to fall asleep and increasing the duration of deep, restful sleep.
12. What Factors Can Disrupt Pineal Gland Function?
Several factors can disrupt the normal function of the pineal gland, leading to sleep disturbances and other health issues. These include:
- Exposure to Blue Light: The blue light emitted from electronic devices (smartphones, tablets, computers) can suppress melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
- Irregular Sleep Schedules: Inconsistent sleep patterns can disrupt the pineal gland’s ability to regulate melatonin production, leading to sleep disorders.
- Stress: Chronic stress can interfere with melatonin synthesis and release, causing sleep disturbances and affecting overall health.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: Consuming caffeine and alcohol, especially close to bedtime, can disrupt sleep patterns and impair pineal gland function.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can interfere with melatonin production or disrupt sleep cycles, affecting the pineal gland’s performance.
13. How Can You Protect Your Pineal Gland From Calcification?
Calcification of the pineal gland is a natural process that occurs as we age, but certain lifestyle factors can accelerate it. While complete prevention may not be possible, you can take steps to minimize calcification:
- Reduce Fluoride Intake: Fluoride can accumulate in the pineal gland and contribute to calcification. Minimize fluoride intake by using fluoride-free toothpaste and drinking purified water.
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain additives and chemicals that can contribute to calcification. Opt for a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods.
- Increase Antioxidant Intake: Antioxidants can help protect against cellular damage and reduce calcification. Consume plenty of fruits, vegetables, and herbs rich in antioxidants.
- Avoid Excessive Calcium Supplementation: While calcium is essential for health, excessive supplementation can lead to calcium deposits in the pineal gland.
- Detoxify Regularly: Regular detoxification practices, such as drinking plenty of water and consuming detoxifying foods, can help remove toxins and prevent calcification.
14. What Are The Potential Benefits Of A Healthy Pineal Gland?
Maintaining a healthy pineal gland can lead to numerous benefits for overall health and well-being:
- Improved Sleep Quality: Proper melatonin production ensures a natural and consistent sleep-wake cycle, leading to better sleep quality and reduced sleep disturbances.
- Enhanced Mood: Melatonin has mood-regulating properties, and a healthy pineal gland can contribute to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Stronger Immune System: Adequate melatonin levels support a healthy immune system, helping the body fight off infections and diseases.
- Better Cognitive Function: Good sleep and balanced hormone levels contribute to improved cognitive function, including memory, focus, and concentration.
- Anti-Aging Effects: Melatonin’s antioxidant properties can help protect against cellular damage and slow the aging process.
15. Can The Pineal Gland Shrink Or Grow?
The pineal gland can undergo changes in size, although significant growth or shrinkage is usually associated with specific conditions:
- Calcification: As mentioned earlier, calcification is a natural process that can cause the pineal gland to shrink over time.
- Tumors: Tumors or cysts in the pineal gland can cause it to grow in size, leading to various neurological symptoms.
- Age: The pineal gland typically reaches its maximum size during childhood and gradually shrinks as we age.
16. What Is The Connection Between The Pineal Gland And Mental Health?
The pineal gland plays a significant role in mental health through its production of melatonin, which influences mood, sleep, and overall well-being. Disruptions in melatonin production have been linked to various mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Mood Regulation: Melatonin helps regulate mood by influencing neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and dopamine.
- Sleep and Mental Health: Poor sleep quality is closely linked to mental health issues. A healthy pineal gland ensures proper sleep patterns, contributing to better mental well-being.
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): SAD is a type of depression that occurs during the winter months when there is less sunlight. The pineal gland’s response to light exposure plays a key role in SAD, as reduced sunlight can lead to decreased melatonin production and symptoms of depression.
17. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About The Pineal Gland?
There are several common misconceptions about the pineal gland, often fueled by misinformation and pseudoscience:
- “The Pineal Gland Is A Vestigial Organ”: This is incorrect. The pineal gland is an active endocrine gland with crucial functions, particularly in regulating sleep-wake cycles.
- “The Pineal Gland Can Be ‘Decalcified’ With Special Diets”: While reducing fluoride intake and consuming a healthy diet can support pineal gland health, the idea of completely “decalcifying” it through diet alone is not scientifically supported.
- “Activating The Pineal Gland Unlocks Psychic Powers”: The pineal gland’s association with spiritual practices has led to claims that activating it can unlock psychic abilities. However, there is no scientific evidence to support this.
18. How Does Light Exposure Affect The Pineal Gland?
Light exposure is a primary regulator of pineal gland function. The pineal gland receives information about light levels through the eyes, which transmit signals to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus, and then to the pineal gland.
- Darkness Stimulates Melatonin Production: When it’s dark, the SCN signals the pineal gland to produce more melatonin, preparing the body for sleep.
- Light Inhibits Melatonin Production: When light is present, the SCN signals the pineal gland to reduce melatonin production, promoting wakefulness.
- Importance of Natural Light: Exposure to natural sunlight during the day helps regulate the circadian rhythm and ensures proper melatonin production at night.
19. What Are The Potential Risks Of Pineal Gland Surgery?
Surgery on the pineal gland is a complex procedure that carries potential risks, including:
- Neurological Damage: Damage to surrounding brain tissue can lead to neurological deficits, such as vision changes, motor weakness, and cognitive impairment.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Disruption of the pineal gland or nearby structures can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting sleep, mood, and reproductive function.
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection.
- Bleeding: Bleeding during or after surgery can cause complications and may require additional intervention.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak: Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can occur, leading to headaches and increasing the risk of infection.
20. How Can You Support Your Overall Health To Benefit The Pineal Gland?
Supporting overall health through various lifestyle choices can positively impact the pineal gland’s function and well-being:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides the nutrients needed for optimal pineal gland function.
- Get Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity improves sleep quality, reduces stress, and supports overall hormonal balance, benefiting the pineal gland.
- Practice Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help reduce stress levels and support pineal gland function.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out toxins and supports overall health, including the health of the pineal gland.
- Limit Exposure to Toxins: Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins, such as pollutants and chemicals, can help protect the pineal gland from damage.
Do you have more questions about the pineal gland and its function? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a platform where you can ask any question and receive answers from knowledgeable experts. Don’t hesitate to seek answers to your health concerns!
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
We understand that finding reliable answers can be challenging. That’s why WHAT.EDU.VN is dedicated to offering a free and easy-to-use platform where you can ask questions and connect with a community of experts. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone with a curious mind, we’re here to provide the information you need. Visit what.edu.vn today and start exploring!