The Big Bang Theory is the leading explanation about how the universe began, suggesting it originated from an extremely hot, dense state that expanded rapidly. For a comprehensive understanding and answers to all your questions, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. This expansion, the Big Bang Nucleosynthesis, continues today, shaping the cosmos as we know it with cosmic microwave background radiation and the Hubble constant.
1. What Is The Big Bang Theory In Simple Terms?
The Big Bang Theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe, stating that it emerged from an extremely hot and dense state about 13.8 billion years ago and has been expanding and cooling ever since. It’s essentially the story of how the universe went from a tiny, hot speck to the vast cosmos we observe today.
Expanding on this, imagine the universe as a balloon being inflated. The balloon’s surface represents space, and as you blow air into it, the surface expands. Similarly, after the Big Bang, space itself began to expand rapidly, carrying matter and energy along with it. This expansion caused the universe to cool down, leading to the formation of atoms, stars, and eventually galaxies. Key evidence for the Big Bang includes the cosmic microwave background (CMB), a faint afterglow of the early universe, and the abundance of light elements like hydrogen and helium, which were created in the first few minutes after the Big Bang Nucleosynthesis. Learn more at WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can ask any question and receive expert answers.
2. What Is The Big Bang Theory And Its Evidence?
The Big Bang Theory describes the universe’s origin as an event where space itself expanded from an extremely high-density and high-temperature state. Key pieces of evidence support this theory:
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): This is the afterglow of the Big Bang, a uniform radiation field that permeates the universe.
- Redshift: Galaxies are moving away from us, indicating that the universe is expanding, as described by Hubble’s Law.
- Abundance of Light Elements: The observed amounts of hydrogen, helium, and lithium match predictions made by the Big Bang model.
- Large-Scale Structure: The distribution of galaxies and galaxy clusters aligns with simulations based on the Big Bang.
Understanding these points allows us to understand how the universe evolved from its nascent state to its current form. The redshift phenomenon, for example, demonstrates that galaxies are receding from us at speeds proportional to their distance, a key prediction of an expanding universe originating from a central point. Further exploration into the intricacies of cosmology and the Big Bang model can be found at WHAT.EDU.VN, your trusted source for academic insights.
3. What Is The Big Bang Theory Timeline?
The Big Bang timeline outlines the major epochs in the universe’s evolution:
- Planck Epoch (0 to 10^-43 seconds): The earliest known period, where the laws of physics as we know them break down.
- Inflationary Epoch (10^-36 to 10^-32 seconds): An incredibly rapid expansion of the universe.
- Quark Epoch (10^-12 to 10^-6 seconds): The universe is a hot, dense plasma of quarks, leptons, and bosons.
- Hadron Epoch (10^-6 to 1 second): Quarks combine to form hadrons like protons and neutrons.
- Lepton Epoch (1 second to 10 seconds): Leptons (like electrons and neutrinos) dominate the universe.
- Nucleosynthesis (3 minutes to 20 minutes): Protons and neutrons combine to form light atomic nuclei like hydrogen and helium.
- Photon Epoch (10 seconds to 380,000 years): Photons dominate the energy of the universe.
- Recombination (380,000 years): Electrons combine with nuclei to form neutral atoms, making the universe transparent to light.
- Dark Ages (380,000 years to 150 million years): The universe is dark, with no stars or galaxies formed yet.
- Reionization (150 million years to 1 billion years): The first stars and galaxies form, and their radiation reionizes the neutral hydrogen.
- Galaxy Formation (1 billion years to present): Galaxies form and evolve, leading to the universe we see today.
Each epoch represents a significant shift in the conditions and constituents of the universe. The nucleosynthesis phase, for example, is critical as it set the stage for the elemental composition of the universe, with hydrogen and helium being the most abundant elements. Delve deeper into cosmological timelines and ask your burning questions at WHAT.EDU.VN for instant, free answers.
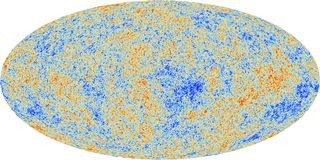
4. What Is The Big Bang Theory Evidence Cosmic Microwave Background?
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) is a critical piece of evidence supporting the Big Bang Theory. It is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in the early universe.
The CMB has several key properties that support the Big Bang:
- Uniformity: The CMB is incredibly uniform in temperature across the sky, indicating that the early universe was in thermal equilibrium.
- Blackbody Spectrum: The CMB has a blackbody spectrum, which is characteristic of thermal radiation.
- Anisotropies: Tiny temperature fluctuations in the CMB reveal the seeds of structure that would eventually grow into galaxies and galaxy clusters.
Observations from missions like COBE, WMAP, and Planck have mapped the CMB with increasing precision, providing strong evidence for the Big Bang and helping to refine our understanding of the universe’s age, composition, and evolution. The discovery of the CMB’s uniformity suggests that the early universe underwent a period of rapid inflation, smoothing out any initial irregularities. For more detailed explanations and to ask any question, visit WHAT.EDU.VN for expert insights.
5. What Is The Big Bang Theory Inflation?
Inflation is a period of extremely rapid expansion in the very early universe, thought to have occurred between 10^-36 and 10^-32 seconds after the Big Bang. During this period, the universe expanded exponentially, increasing in size by a factor of at least 10^78.
Inflation solves several problems with the standard Big Bang model:
- Horizon Problem: Inflation explains why the CMB is so uniform across the sky, as regions that are now far apart were once in causal contact before inflation.
- Flatness Problem: Inflation predicts that the universe should be very close to flat, which is consistent with observations.
- Monopole Problem: Inflation dilutes the density of exotic particles like magnetic monopoles, which are predicted by some theories but have not been observed.
Inflation is thought to have been driven by a hypothetical field called the inflaton, and it provides a natural mechanism for generating the initial density fluctuations that seeded the formation of galaxies and large-scale structures in the universe. The concept of inflation addresses fundamental questions about the universe’s large-scale properties and homogeneity. If you have more questions or need further clarification, visit WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can get free answers to all your queries.
6. What Is The Big Bang Theory Nucleosynthesis?
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN) is the process by which light atomic nuclei were formed in the first few minutes after the Big Bang. During this time, the universe was hot and dense enough for nuclear reactions to occur.
BBN produced primarily hydrogen and helium, along with trace amounts of lithium and deuterium. The predicted abundances of these elements depend on the conditions in the early universe, such as the baryon-to-photon ratio.
The observed abundances of these light elements are in excellent agreement with the predictions of BBN, providing strong support for the Big Bang theory. BBN is a crucial link between particle physics and cosmology, as it depends on the fundamental laws of nuclear physics and provides constraints on the properties of dark matter and other exotic particles. The precise calculations of element abundances during BBN match the observed values, solidifying confidence in the Big Bang model. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask any question and get immediate answers.
7. What Is The Big Bang Theory Dark Matter And Dark Energy?
Dark matter and dark energy are mysterious components of the universe that make up about 95% of its total energy density.
- Dark Matter: This is a form of matter that does not interact with light, making it invisible to telescopes. We know it exists because of its gravitational effects on visible matter, such as the rotation curves of galaxies and the gravitational lensing of light.
- Dark Energy: This is a form of energy that is causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate. Its nature is even more mysterious than dark matter, and it may be related to the cosmological constant or some other unknown physics.
Both dark matter and dark energy play crucial roles in the evolution of the universe. Dark matter provides the gravitational scaffolding for the formation of galaxies and large-scale structures, while dark energy drives the accelerated expansion that will determine the universe’s ultimate fate. The ongoing research into dark matter and dark energy is one of the most exciting frontiers in modern cosmology. These enigmatic components challenge our understanding of the fundamental laws of physics and the nature of the cosmos. For more insights into these topics, ask questions and receive free answers at WHAT.EDU.VN.
8. What Is The Big Bang Theory Alternatives?
While the Big Bang Theory is widely accepted, some alternative theories have been proposed:
- Steady-State Theory: This theory proposes that the universe has always existed in its current state, with new matter continuously being created to maintain a constant density as the universe expands. However, it does not explain the CMB or the abundance of light elements.
- Cyclic Models: These models propose that the universe undergoes cycles of expansion and contraction, with the Big Bang being just one phase in an infinite series of cycles.
- Ekpyrotic Universe: A variation of cyclic models where the universe originates from the collision of branes in a higher-dimensional space.
- Conformal Cyclic Cosmology (CCC): Proposed by Roger Penrose, this theory suggests that the universe goes through infinite cycles, with each cycle starting with a Big Bang and ending with a state where all mass has decayed away.
These alternatives aim to address some of the conceptual challenges of the Big Bang Theory, such as the nature of the singularity at the beginning of time. However, they generally lack the broad observational support that the Big Bang Theory enjoys. Though these alternatives offer different perspectives, they often struggle to provide explanations for observed phenomena as comprehensively as the Big Bang Theory does. If you are curious to learn more or have any questions, visit WHAT.EDU.VN for free answers and expert advice.
9. What Is The Big Bang Theory Future Research?
Future research on the Big Bang Theory will focus on several key areas:
- Dark Matter and Dark Energy: Identifying the nature of these mysterious components of the universe is a top priority. Experiments like the Large Hadron Collider and direct detection experiments aim to detect dark matter particles, while observations of distant supernovae and galaxy surveys will help to constrain the properties of dark energy.
- Cosmic Microwave Background: Future CMB experiments, such as the CMB-S4 project, will measure the polarization of the CMB with unprecedented precision, searching for evidence of primordial gravitational waves from inflation.
- James Webb Space Telescope (JWST): JWST will observe the first galaxies and stars that formed after the Big Bang, providing insights into the early stages of galaxy formation and the reionization of the universe.
- Gravitational Waves: Detecting and studying gravitational waves from the early universe could provide new information about inflation and other high-energy phenomena.
These research efforts will push the boundaries of our knowledge about the Big Bang and the origins of the universe. By probing the universe at ever-earlier times and with ever-greater precision, scientists hope to unravel some of the deepest mysteries of cosmology. Future research will provide critical tests of the Big Bang Theory and potentially reveal new physics beyond our current understanding. For reliable and insightful answers to all your questions, visit WHAT.EDU.VN, your go-to platform for academic exploration.
10. What Is The Big Bang Theory Misconceptions?
Several common misconceptions surround the Big Bang Theory:
- The Big Bang was not an explosion in space, but rather an expansion of space itself. There was no pre-existing space into which the universe expanded.
- The Big Bang did not originate from a single point in space. The expansion happened everywhere in the universe simultaneously.
- The Big Bang Theory does not explain the origin of the universe. It describes the evolution of the universe from an extremely hot and dense state, but it does not address what came before the Big Bang or what caused it.
- The Big Bang Theory is not just a guess. It is based on a wealth of observational evidence and is supported by rigorous mathematical models.
Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for a proper understanding of the Big Bang Theory. It’s important to recognize that the Big Bang model is a framework for understanding the universe’s evolution, not necessarily its ultimate origin. For clear explanations and to ask any question, visit WHAT.EDU.VN for instant and accurate answers.
Are you struggling to find quick, free answers to your burning questions? Do you feel lost in a sea of information, unsure of where to turn for reliable guidance? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand your challenges. We provide a free platform where you can ask any question and receive prompt, accurate answers from knowledgeable individuals.
Don’t let unanswered questions hold you back. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today, and experience the ease and convenience of accessing expert knowledge at your fingertips. We are located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890, or visit our website what.edu.vn. Ask away, and let us illuminate your path to understanding.