Information is the lifeblood of understanding, but what exactly is it? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we believe information is more than just data; it’s the processed, contextualized knowledge that empowers us to learn, communicate, and make informed decisions. This guide breaks down the concept of information, exploring its various facets and helping you understand its true value. Discover the power of knowledge and elevate your understanding of the world around you with reliable information, and get those answers answered at WHAT.EDU.VN for free. This covers information science, information theory, and information management.
1. Defining Information: Beyond Raw Data
Information is often defined as the result of analyzing, contextualizing, and structuring raw data. But what does that really mean?
Information transforms meaningless content into something usable and understandable. It is facts provided or learned about something or someone. Information is the meaning assigned to data within a specific context, making it valuable for understanding, communication, and decision-making. This definition is supported by research from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which defines information as any communication or representation of knowledge.
1.1. Key Aspects of Information
- Context: Information provides context to data, making it relevant.
- Meaning: It assigns meaning to otherwise meaningless facts.
- Usefulness: Information is valuable for understanding and decision-making.
- Communication: It facilitates communication and knowledge sharing.
2. Data vs. Information: Understanding the Difference
While often used interchangeably, data and information are distinct. Data consists of raw, unorganized facts, figures, or symbols. Information emerges when data is processed, organized, and given meaning.
Data is raw, unorganized, and lacks context. Information is processed, organized, and provides meaning. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, effective data management is crucial for transforming raw data into actionable information.
2.1. Examples to Illustrate the Difference
| Feature | Data | Information |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw, unorganized facts and figures | Processed, organized data with meaning |
| Characteristics | Unprocessed, lacking context | Meaningful, contextualized, useful |
| Example | List of temperatures: 25°C, 28°C, 30°C | Daily temperature trends showing a rise in temperature over time |
| Purpose | Recording observations | Understanding trends and making informed decisions |

2.2. Turning Data into Information
Transforming data into information involves:
- Organizing: Structuring data in a coherent manner.
- Contextualizing: Adding relevant details and background.
- Analyzing: Identifying patterns, trends, and relationships.
- Interpreting: Drawing conclusions and insights.
3. The Six Types of Information: A Comprehensive Categorization
J.H. Shera, a renowned librarian and information scientist, proposed six categories of information, each serving a unique purpose.
Shera’s categorization offers a comprehensive framework for understanding the diverse nature of information. Information is divided into Conceptual, Empirical, Procedural, Policy, Directive, and Stimulatory types. This framework is recognized in the field of information science, as noted in the Journal of Information Science.
3.1. Exploring the Six Categories
- Conceptual Information: Based on abstract ideas, theories, and concepts.
- Example: Philosophical theories, scientific hypotheses
- Empirical Information: Derived from observation, experimentation, and verifiable methodologies.
- Example: Scientific research findings, statistical data
- Procedural Information: Describes how to perform a task or carry out a procedure.
- Example: Instruction manuals, step-by-step guides
- Policy Information: Related to laws, regulations, and guidelines.
- Example: Government regulations, company policies
- Directive Information: Provides directions or descriptions to aid understanding.
- Example: Road signs, instructional videos
- Stimulatory Information: Intended to provoke a response or motivate action.
- Example: Advertisements, motivational speeches
3.2. Other Ways to Categorize Information
- Factual vs. Analytical: Factual information is based on known facts, while analytical information is the interpretation of those facts.
- Subjective vs. Objective: Subjective information is based on personal opinions, while objective information aims to be free from bias.
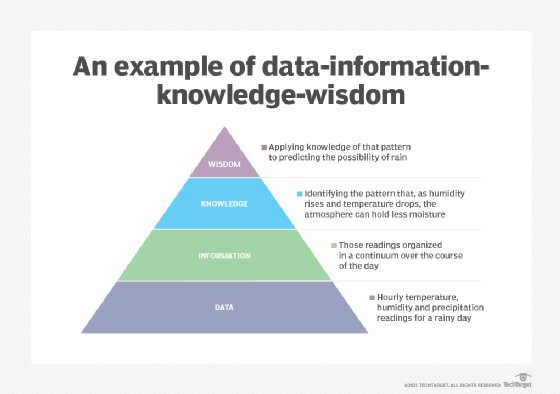
4. The Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom (DIKW) Pyramid
The DIKW pyramid illustrates the hierarchical progression from raw data to wisdom, emphasizing how each level builds upon the previous one.
The DIKW model provides a structured view of how data evolves into actionable wisdom. This model is widely used in information management and knowledge management, as discussed in Information and Knowledge Management by Debowski (2006).
4.1. Understanding the Levels of the Pyramid
- Data: Raw, unorganized facts and figures.
- Example: Individual sales transactions
- Information: Data that has been organized and given meaning.
- Example: Total monthly sales
- Knowledge: Information that has been analyzed and interpreted to provide understanding.
- Example: Identifying the best-selling products based on sales data
- Wisdom: The application of knowledge to make informed decisions and take effective action.
- Example: Deciding to increase production of best-selling products
4.2. The Role of AI in the DIKW Pyramid
Artificial intelligence can automate the process of turning data into information and knowledge, but it has not yet reached the level of human wisdom. AI can analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions, but it lacks the judgment and experience needed to apply knowledge to real-life situations effectively.
5. The Importance of Information in Decision-Making
Information is crucial for making informed decisions in various aspects of life, from personal choices to business strategies.
Access to reliable and relevant information is essential for effective decision-making. According to a study by Harvard Business Review, companies that leverage data-driven insights make better decisions and achieve superior performance.
5.1. How Information Enhances Decision-Making
- Reduces Uncertainty: Provides clarity and reduces ambiguity.
- Identifies Opportunities: Reveals potential areas for growth and innovation.
- Evaluates Options: Allows for a thorough assessment of different choices.
- Mitigates Risks: Helps identify potential challenges and develop strategies to overcome them.
5.2. Examples of Information-Driven Decisions
| Scenario | Information Needed | Decision Made |
|---|---|---|
| Investing in Stocks | Company financials, market trends, economic indicators | Deciding which stocks to buy or sell |
| Choosing a Career Path | Job market outlook, skills requirements, personal interests | Selecting a career that aligns with interests and opportunities |
| Developing a Marketing Strategy | Customer demographics, competitor analysis, market trends | Targeting specific customer segments with tailored marketing campaigns |
6. Information Sources: Where to Find Reliable Information
Information comes from various sources, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Selecting reliable information sources is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and credibility of the information. A study by Stanford University found that many people struggle to distinguish between reliable and unreliable information sources online.
6.1. Types of Information Sources
- Books: Provide in-depth coverage of specific topics.
- Academic Journals: Offer peer-reviewed research and scholarly analysis.
- Reputable Websites: Provide current and reliable information on a wide range of subjects.
- Government Publications: Offer official data, reports, and policy information.
- News Media: Provide up-to-date coverage of current events.
6.2. Evaluating Information Sources
- Authority: Is the source reputable and knowledgeable?
- Accuracy: Is the information accurate and supported by evidence?
- Objectivity: Is the information free from bias and personal opinions?
- Currency: Is the information up-to-date and relevant?
- Coverage: Does the source provide comprehensive coverage of the topic?
7. Information Overload: Managing the Flood of Data
In the digital age, we are constantly bombarded with information, leading to information overload.
Effectively managing information overload is crucial for maintaining productivity and making informed decisions. A study by the University of California, Irvine, found that information overload can lead to stress, anxiety, and decreased cognitive performance.
7.1. Strategies for Managing Information Overload
- Filtering: Focus on relevant and reliable sources.
- Prioritizing: Identify the most important information.
- Summarizing: Condense information into key points.
- Delegating: Assign information gathering and analysis to others.
- Time Management: Allocate specific times for information processing.
7.2. Tools for Managing Information
- RSS Feed Readers: Aggregate content from multiple sources in one place.
- Note-Taking Apps: Organize and summarize information.
- Task Management Software: Prioritize and manage information-related tasks.
- Email Filters: Sort and prioritize incoming emails.
8. Information Ethics: Ensuring Responsible Use of Data
Information ethics deals with the moral principles governing the collection, use, and dissemination of information.
Adhering to information ethics is crucial for protecting privacy, ensuring accuracy, and promoting responsible use of data. According to the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), ethical considerations are paramount in the design and implementation of information systems.
8.1. Key Principles of Information Ethics
- Privacy: Respecting individuals’ rights to control their personal information.
- Accuracy: Ensuring the information is truthful and reliable.
- Property: Protecting intellectual property rights.
- Accessibility: Providing equal access to information for all.
8.2. Ethical Considerations in the Digital Age
- Data Breaches: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Misinformation: Combating the spread of false or misleading information.
- Algorithmic Bias: Ensuring algorithms are fair and do not discriminate.
- Surveillance: Balancing security needs with individual privacy rights.
9. The Future of Information: Trends and Technologies
The field of information is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing societal needs.
Staying abreast of emerging trends and technologies is crucial for effectively managing and utilizing information in the future. According to Gartner, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things will significantly impact how information is collected, processed, and used.
9.1. Emerging Trends in Information
- Artificial Intelligence: Automating information processing and analysis.
- Big Data: Analyzing large datasets to extract valuable insights.
- Cloud Computing: Storing and accessing information remotely.
- Internet of Things: Connecting devices to collect and share information.
- Blockchain: Securing and verifying information using decentralized ledgers.
9.2. How Technology is Shaping Information
- Improved Access: Mobile devices and high-speed internet provide instant access to information.
- Enhanced Analysis: AI and machine learning enable more sophisticated data analysis.
- Increased Collaboration: Cloud-based tools facilitate information sharing and collaboration.
- Personalized Experiences: Data-driven insights allow for tailored information experiences.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Information
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the main difference between data and information? | Data is raw and unorganized, while information is processed and organized data that provides meaning and context. |
| How can I ensure the information I find is reliable? | Evaluate the source’s authority, accuracy, objectivity, currency, and coverage. Look for reputable sources and cross-reference information. |
| What are the ethical considerations when using information? | Key principles include respecting privacy, ensuring accuracy, protecting intellectual property, and providing equal access to information. |
| How can artificial intelligence help in information management? | AI can automate information processing, analyze large datasets, improve information retrieval, and personalize information experiences. |
| What Is Information overload, and how can I manage it? | Information overload is the state of being overwhelmed by the amount of information available. Manage it by filtering, prioritizing, summarizing, delegating, and using time management techniques. |
| What is the DIKW pyramid? | The DIKW pyramid illustrates the progression from raw data to wisdom, with each level building upon the previous one: Data, Information, Knowledge, and Wisdom. |
| What are the six types of information? | Conceptual, Empirical, Procedural, Policy, Directive, and Stimulatory. |
| How does information influence decision-making? | Information reduces uncertainty, identifies opportunities, evaluates options, and mitigates risks, leading to more informed and effective decisions. |
| What are some emerging trends in information? | Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, and Blockchain. |
| Why is it important to evaluate information sources? | Evaluating information sources ensures that the information you are using is accurate, reliable, and trustworthy, which is crucial for making informed decisions and avoiding misinformation. |
11. Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN for Your Information Needs?
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of having access to reliable and accurate information. We’re here to provide you with a free platform where you can ask any question and receive answers from a community of knowledgeable individuals.
12. Get Your Questions Answered Today!
Don’t let your curiosity go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and start asking your questions. Our community is ready to provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions and expand your knowledge. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply a curious individual, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for free, reliable information.
We are located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890 or visit our website at WHAT.EDU.VN.
13. Conclusion: Empowering You Through Information
Information is more than just data; it’s the key to understanding, learning, and making informed decisions. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with a platform where you can access the information you need to thrive. Start exploring, start asking, and start learning today!
Visit what.edu.vn now for reliable, free answers to all your questions! Unlock the power of knowledge with our expert community.

