The Big Island in Hawaii, also known as the Island of Hawai’i, is celebrated for its diverse landscapes and unique geological features; WHAT.EDU.VN is the place to ask if you want to know more. From active volcanoes to snow-capped mountains, it offers a wide range of experiences, all on one island. Discover the geological marvels, tropical adventures, and serene beaches that define this extraordinary destination with geographical diversity, volcanic activity, and climate zones.
1. What Is The Big Island In Hawaii?
The Big Island, officially named the Island of Hawai’i, is the largest of the Hawaiian Islands, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes, climates, and geological features. According to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the island covers an area of over 4,000 square miles, making it larger than all the other Hawaiian Islands combined.
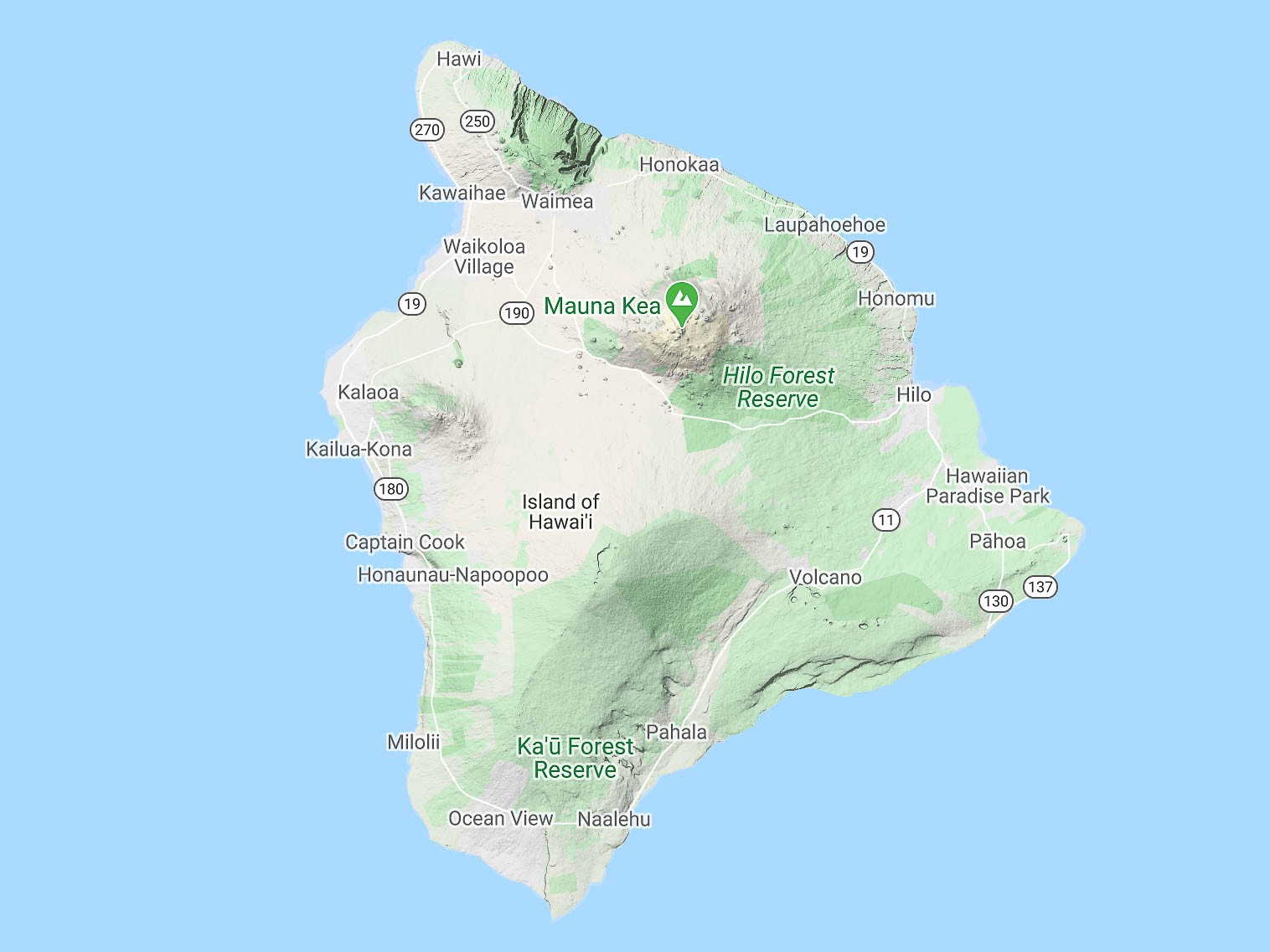 Map of the Big Island of Hawaii showing different regions and landmarks
Map of the Big Island of Hawaii showing different regions and landmarks
1.1 How Did The Big Island Form?
The Big Island was formed by volcanic activity over millions of years. Five volcanoes make up the island: Kohala, Mauna Kea, Hualalai, Mauna Loa, and Kilauea. Mauna Loa and Kilauea are still active, contributing to the island’s ongoing growth. According to a study by the University of Hawai’i at Mānoa, the Hawaiian Islands were created by the movement of the Pacific Plate over a hotspot in the Earth’s mantle.
1.2 What Are Some Key Geographical Features Of The Big Island?
The Big Island boasts a variety of geographical features:
- Active Volcanoes: Kilauea is one of the world’s most active volcanoes, attracting scientists and tourists alike.
- Snow-Capped Mountains: Mauna Kea, the highest point in Hawai’i, is often covered in snow during winter.
- Black Sand Beaches: Punalu’u Beach is famous for its black sand, formed from volcanic rock.
- Lush Rainforests: The Hilo side of the island is known for its dense, tropical rainforests.
- Lava Deserts: The Ka’u Desert features vast, barren landscapes of hardened lava.
1.3 How Does The Size Of The Big Island Compare To Other Hawaiian Islands?
The Big Island is more than twice the size of all the other Hawaiian Islands combined. According to the Hawai’i Department of Business, Economic Development & Tourism (DBEDT), its area accounts for approximately 63% of the state’s total landmass.
2. What Makes The Big Island’s Volcanoes So Special?
The Big Island’s volcanoes are unique due to their shield volcano structure and continuous activity, particularly at Kilauea. Shield volcanoes are characterized by their broad, gently sloping shape, formed by the effusive eruption of fluid lava.
2.1 What Is A Shield Volcano?
A shield volcano is a type of volcano built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. The lava spreads out in all directions from a central vent, creating a broad, shield-like shape. The USGS explains that shield volcanoes are common in Hawai’i because the lava is low in silica, making it very fluid.
2.2 Which Volcanoes On The Big Island Are Active?
Mauna Loa and Kilauea are the two active volcanoes on the Big Island. Kilauea has been continuously erupting since 1983, while Mauna Loa last erupted in 1984. Both volcanoes are closely monitored by the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) to provide warnings and conduct research.
2.3 What Is The Significance Of Kilauea Volcano?
Kilauea is one of the most active volcanoes in the world. Its ongoing eruption has provided scientists with valuable insights into volcanic processes. The constant flow of lava has also reshaped the landscape, creating new land and altering coastlines.
2.4 How Do Volcanic Eruptions Affect The Big Island’s Landscape?
Volcanic eruptions have a profound impact on the Big Island’s landscape. Lava flows can create new land, destroy forests, and alter the course of rivers. Volcanic ash can enrich the soil, promoting plant growth in certain areas.
3. What Are The Different Climate Zones On The Big Island?
The Big Island is known for having multiple climate zones, ranging from tropical rainforests to polar tundra. This diversity is due to the island’s varied topography, which creates different microclimates at different elevations and locations.
3.1 How Many Climate Zones Exist On The Big Island?
The Big Island has 10 of the world’s 15 climate zones, as classified by the Köppen Climate Classification System. These include:
- Tropical Rainforest
- Tropical Monsoon
- Savanna
- Steppe
- Desert
- Mediterranean
- Humid Subtropical
- Oceanic
- Subarctic
- Tundra
3.2 What Causes The Climate Zones To Vary So Greatly?
The varying climate zones are caused by several factors:
- Elevation: Higher elevations are cooler and receive more precipitation.
- Rain Shadow Effect: The windward (eastern) side of the island receives more rainfall, while the leeward (western) side is drier.
- Volcanic Activity: Volcanic activity can create unique microclimates.
3.3 Where Can You Experience Each Climate Zone?
- Tropical Rainforest: Hilo and the Hamakua Coast
- Desert: Ka’u Desert
- Tundra: Summit of Mauna Kea
3.4 How Does The Climate Affect The Flora And Fauna?
The climate has a significant impact on the flora and fauna:
- Rainforests: Support lush vegetation and diverse wildlife.
- Deserts: Host drought-resistant plants and specialized animals.
- Mountains: Provide habitat for alpine species.
4. What Are The Best Beaches On The Big Island?
The Big Island boasts a variety of beaches, each offering unique experiences. From black sand beaches to pristine white sand, there’s something for every beach lover.
4.1 What Are The Most Popular White Sand Beaches?
- Hapuna Beach: Known for its clear water and soft sand.
- Mauna Kea Beach (Kauna’oa): Offers excellent swimming and snorkeling.
- Waialea Beach (Beach 69): A popular spot for families.
4.2 Where Can You Find Black Sand Beaches?
- Punalu’u Black Sand Beach: Famous for its black sand and sea turtles.
- Kehena Black Sand Beach: A secluded beach known for its dramatic cliffs.
4.3 Are There Any Green Sand Beaches On The Big Island?
Yes, Papakolea Green Sand Beach is one of the few green sand beaches in the world. The green color comes from olivine crystals eroded from a nearby volcanic cinder cone.
4.4 What Activities Are Popular At Big Island Beaches?
Popular activities include:
- Swimming: Many beaches offer calm, clear waters perfect for swimming.
- Snorkeling: Coral reefs near the shore provide excellent snorkeling opportunities.
- Surfing: Some beaches, like Honolii, are known for their surfing waves.
- Sunbathing: Relax and soak up the sun on the sandy shores.
- Wildlife Viewing: Keep an eye out for sea turtles, dolphins, and other marine life.
5. What Cultural And Historical Sites Can You Visit On The Big Island?
The Big Island is rich in cultural and historical sites, offering a glimpse into Hawai’i’s past and traditions.
5.1 What Are Some Significant Historical Landmarks?
- Pu’uhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park: A well-preserved ancient Hawaiian refuge.
- Lapakahi State Historical Park: A partially restored ancient Hawaiian fishing village.
- Pu’ukoholā Heiau National Historic Site: The largest heiau (temple) in Hawai’i, built by King Kamehameha I.
5.2 Where Can You Learn About Hawaiian Culture?
- Imiloa Astronomy Center: Offers exhibits on Hawaiian culture and astronomy.
- ‘Alae Crater: Features ancient petroglyphs.
- Various local cultural centers and museums: Provide insights into Hawaiian traditions.
5.3 What Role Did King Kamehameha I Play On The Big Island?
King Kamehameha I was born on the Big Island and began his quest to unite the Hawaiian Islands there. He built Pu’ukoholā Heiau to seek divine favor in his endeavors.
5.4 Are There Any Ancient Temples (Heiau) To Visit?
Yes, several heiau can be visited:
- Pu’ukoholā Heiau National Historic Site
- Mo’okini Heiau State Historic Site
- Ahuena Heiau
6. What Activities And Attractions Are Unique To The Big Island?
The Big Island offers a range of unique activities and attractions, from stargazing on Mauna Kea to exploring active volcanoes.
6.1 Where Can You Go Stargazing?
Mauna Kea is one of the best places in the world for stargazing due to its high altitude, dry climate, and minimal light pollution. The Mauna Kea Observatories offer guided tours and stargazing programs.
6.2 Can You Safely View Active Volcanoes?
Yes, you can safely view active volcanoes at Hawai’i Volcanoes National Park. The park offers various viewing points and guided tours to observe Kilauea’s volcanic activity. However, always follow park guidelines and safety precautions.
6.3 Are There Opportunities For Adventure Activities?
Yes, the Big Island offers many adventure activities:
- Ziplining: Experience the rainforest canopy from above.
- Helicopter Tours: Get a bird’s-eye view of the island’s diverse landscapes.
- Snorkeling and Diving: Explore vibrant coral reefs.
- Hiking: Discover hidden waterfalls and scenic trails.
6.4 What Unique Wildlife Can You See?
- Sea Turtles: Often seen on black sand beaches.
- Manta Rays: Nighttime manta ray snorkeling tours are popular.
- Hawaiian Monk Seals: An endangered species often found resting on beaches.
- Native Birds: Including the ‘Io (Hawaiian hawk) and Nene (Hawaiian goose).
7. What Are The Best Ways To Explore The Big Island?
Exploring the Big Island requires careful planning due to its size and diverse landscapes.
7.1 Should You Rent A Car?
Yes, renting a car is highly recommended to explore the Big Island. Public transportation is limited, and many attractions are spread out across the island.
7.2 What Are The Must-Drive Scenic Routes?
- Hamakua Heritage Corridor: Offers stunning views of waterfalls and lush valleys.
- Chain of Craters Road: A drive through Hawai’i Volcanoes National Park.
- Kona Coast: Scenic coastal drive with beautiful beaches.
7.3 How Should You Plan Your Itinerary?
- Divide The Island: Focus on exploring one side (east or west) at a time.
- Prioritize Attractions: Identify key attractions and plan accordingly.
- Allow Ample Travel Time: Distances can be deceiving, so allow extra time for driving.
7.4 Are There Guided Tours Available?
Yes, many guided tours are available:
- Volcano Tours: Led by experts who provide insights into volcanic activity.
- Stargazing Tours: To Mauna Kea, offering access to observatories.
- Cultural Tours: Exploring historical sites and Hawaiian traditions.
- Adventure Tours: Including ziplining, hiking, and snorkeling.
8. What Are Some Lesser-Known Facts About The Big Island?
Delve into some intriguing and less commonly known aspects of the Big Island.
8.1 Is The Big Island Still Growing?
Yes, the Big Island is still growing due to ongoing volcanic activity, particularly from Kilauea. Lava flows continuously add new land to the island’s coastline.
8.2 What Is Kona Coffee Known For?
Kona coffee is renowned for its rich flavor and smooth taste, grown on the slopes of Hualalai and Mauna Loa. The unique climate and volcanic soil contribute to its distinctive characteristics.
8.3 Does The Big Island Have A Desert?
Yes, the Ka’u Desert is a barren, arid region on the Big Island, characterized by volcanic ash and limited vegetation.
8.4 How Does The Big Island Support Astronomy?
Mauna Kea’s summit is home to some of the world’s most advanced astronomical observatories. The clear skies, high altitude, and minimal light pollution make it an ideal location for studying the universe.
9. How Does The Big Island Contribute To Scientific Research?
The Big Island serves as a natural laboratory for various scientific disciplines, including volcanology, astronomy, and ecology.
9.1 What Kind Of Volcanology Research Is Conducted?
The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) conducts ongoing research on volcanic activity, monitoring eruptions, studying lava flows, and assessing volcanic hazards.
9.2 What Role Does The Island Play In Astronomy?
Mauna Kea’s observatories contribute significantly to astronomical research, enabling scientists to study distant galaxies, black holes, and the origins of the universe.
9.3 How Is The Big Island Used For Ecological Studies?
The Big Island’s diverse ecosystems provide opportunities for ecological studies, including research on native species, invasive species, and the impact of climate change.
9.4 Are There Renewable Energy Initiatives On The Island?
Yes, the Big Island is at the forefront of renewable energy initiatives, including geothermal, solar, wind, and hydropower projects. These efforts aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote sustainable energy practices.
10. What Should You Know Before Visiting The Big Island?
Planning a trip to the Big Island requires considering its unique characteristics and diverse offerings.
10.1 What Are The Best Times To Visit?
The best times to visit are during the shoulder seasons (April-May and September-October) when the weather is pleasant, and the crowds are smaller.
10.2 What Should You Pack?
- Light Clothing: For warm, tropical weather.
- Rain Gear: Especially if visiting the Hilo side.
- Hiking Shoes: For exploring trails and volcanic landscapes.
- Sunscreen: To protect against the strong sun.
- Swimsuit: For enjoying the beaches.
10.3 How Can You Respect Local Culture?
- Learn Basic Hawaiian Phrases: Such as “Aloha” and “Mahalo.”
- Respect Sacred Sites: Follow guidelines at historical and cultural landmarks.
- Support Local Businesses: Shop at local markets and eat at local restaurants.
- Be Mindful Of The Environment: Avoid touching coral reefs and dispose of waste properly.
10.4 What Safety Precautions Should You Take?
- Volcanic Hazards: Stay informed about volcanic activity and follow park guidelines.
- Ocean Safety: Be aware of currents and surf conditions.
- Hiking Safety: Stay on marked trails and bring plenty of water.
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen and wear a hat.
The Big Island in Hawaii is a land of contrasts and wonders, offering an unparalleled experience for visitors seeking adventure, relaxation, and cultural immersion. Ready to explore this incredible island?
Do you have more questions about the Big Island? Don’t struggle to find answers elsewhere; visit WHAT.EDU.VN and ask your questions for free! Our community of experts is ready to provide you with fast, accurate, and helpful information. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit our website at what.edu.vn and ask away!