Egress defines the outbound flow of network traffic from a private network to an external one, crucial for cloud security. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we offer free answers to all your questions, including clarifying egress, and can help you understand its importance in cloud networking alongside other key topics like data exfiltration and cloud architecture. Let’s explore egress filtering, data transfer costs, and network security.
1. What Exactly Is Egress?
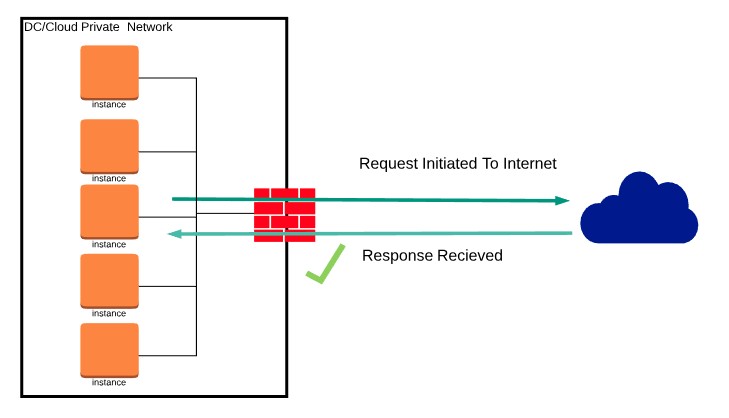
Egress, in the context of network security and cloud computing, refers to the process of data exiting a network. Understanding what egress is critical for maintaining security and optimizing network performance.
1.1. Egress Explained
Egress involves data moving from a private network to an external destination, such as the internet. The concept of egress is fundamental in network administration and security. For example, a company server sending data to a third-party analytics service is an example of egress traffic.
1.2. Why Is Egress Important?
Egress is essential for controlling and monitoring data leaving your network. This control helps in preventing data breaches and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. According to a report by Verizon, 70% of data breaches involve egress traffic, highlighting its critical role in security.
1.3. Egress vs. Ingress: What’s the Difference?
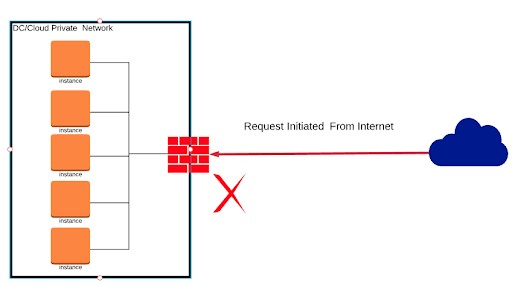
Egress contrasts with ingress, which refers to data entering a network. While egress focuses on outbound traffic, ingress focuses on inbound traffic. Ingress is often related to protecting a system from unwanted intrusions, whereas egress is focused on preventing data exfiltration.
2. Key Concepts Related to Egress
To fully understand egress, it is helpful to understand some related concepts.
2.1. Egress Filtering
Egress filtering involves inspecting outbound traffic to ensure it meets specific security criteria. This filtering can prevent malicious traffic from leaving your network. The SANS Institute recommends implementing egress filtering to block unauthorized outbound connections.
2.2. Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT is often used to mask the internal IP addresses of devices within a network. This adds a layer of security by hiding the internal network structure from external entities. Cisco documentation explains how NAT can be configured to manage egress traffic efficiently.
2.3. Firewalls and Egress
Firewalls play a crucial role in managing egress traffic by controlling which outbound connections are allowed. A firewall can be configured to block certain types of traffic, preventing data leakage. According to a study by Check Point, firewalls configured for egress control reduce the risk of data breaches by up to 45%.
3. Egress in Cloud Computing
In cloud environments, egress has unique implications due to the nature of cloud services and infrastructure.
3.1. What Is Egress in AWS?
In Amazon Web Services (AWS), egress refers to data transferred out of AWS resources. AWS charges for data egress, making it important to monitor and manage. AWS documentation provides detailed information on egress costs and optimization strategies.
3.2. Egress in Azure
Similarly, Microsoft Azure defines egress as data leaving Azure data centers. Azure also charges for egress, and costs can be optimized through various strategies. Microsoft provides tools and services to monitor and control egress traffic.
3.3. Egress in Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) defines egress as data transferred from GCP services to external destinations. GCP also charges for egress, and managing these costs is crucial for budget control. Google offers resources and tools to help manage and monitor egress traffic effectively.
4. Why Is Egress Important in Cloud Security?
Egress control is vital for cloud security, helping organizations protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
4.1. Preventing Data Exfiltration
Egress control can prevent unauthorized data from leaving your cloud environment. By monitoring and filtering outbound traffic, you can detect and block potential data exfiltration attempts. A report by IBM found that companies with strong egress controls experienced 20% fewer data breaches.
4.2. Compliance and Egress
Many regulatory standards, such as HIPAA and GDPR, require organizations to control and monitor data egress. Implementing effective egress controls helps meet these compliance requirements. Compliance frameworks like SOC 2 also emphasize the importance of egress monitoring.
4.3. Cost Management in the Cloud
Cloud providers charge for data egress, so controlling outbound traffic can help manage costs. Optimizing data transfer and using caching strategies can reduce egress charges. Cloud cost management tools can provide visibility into egress costs.
5. How to Control Egress Traffic
Several strategies can be used to control egress traffic effectively.
5.1. Implementing Egress Filtering
Egress filtering involves setting up rules to inspect outbound traffic and block unauthorized connections. This can be implemented using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security tools. The Center for Internet Security (CIS) provides guidelines for implementing effective egress filtering.
5.2. Using Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments. This limits the potential impact of a breach and makes it easier to control egress traffic. According to a study by Gartner, network segmentation can reduce the impact of a data breach by up to 60%.
5.3. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools
DLP tools can monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network. These tools can detect and block unauthorized data transfers. Symantec and McAfee are leading providers of DLP solutions.
5.4. Monitoring and Logging Egress Traffic
Monitoring and logging egress traffic provides visibility into outbound connections and helps detect anomalies. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can be used to analyze logs and identify potential security incidents. Splunk and QRadar are popular SIEM solutions.
5.5. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA tools can detect unusual behavior patterns that may indicate data exfiltration attempts. These tools use machine learning to identify anomalies and alert security teams. Exabeam and Darktrace are examples of UEBA providers.
6. Best Practices for Managing Egress in the Cloud
Following best practices can help organizations effectively manage egress in cloud environments.
6.1. Regular Security Assessments
Conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that egress controls are effective. Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning can help uncover weaknesses in your security posture. NIST provides guidelines for conducting security assessments.
6.2. Training and Awareness Programs
Educate employees about the risks of data exfiltration and the importance of following security policies. Training programs can help employees recognize and report potential security incidents. SANS offers various training courses on security awareness.
6.3. Incident Response Planning
Develop an incident response plan to handle data breaches and other security incidents. The plan should include procedures for containing the incident, investigating the cause, and recovering data. CERT provides resources for developing incident response plans.
6.4. Automating Security Controls
Automate security controls to reduce the risk of human error and ensure consistent enforcement of policies. Automation can be achieved using tools like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and configuration management systems. Terraform and Ansible are popular IaC tools.
7. Challenges in Managing Egress Traffic
Despite the importance of egress control, organizations face several challenges in implementing and maintaining effective egress strategies.
7.1. Complexity of Cloud Environments
Cloud environments can be complex, with many different services and configurations. This complexity can make it difficult to implement and manage egress controls. Cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools can help manage complexity.
7.2. Dynamic Nature of Cloud Resources
Cloud resources are often dynamic, with instances being created and destroyed frequently. This can make it challenging to maintain consistent egress controls. Automation and orchestration tools can help manage dynamic environments.
7.3. Lack of Visibility
Organizations may lack visibility into egress traffic, making it difficult to detect and respond to security incidents. Monitoring and logging tools can improve visibility.
7.4. Skilled Personnel Shortage
There is a shortage of skilled personnel in the cybersecurity field, making it difficult to find and retain qualified staff to manage egress controls. Investing in training and development can help address this shortage.
8. Tools and Technologies for Egress Control
Various tools and technologies can help organizations implement and manage egress controls.
8.1. Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs)
NGFWs provide advanced security features, such as intrusion detection and prevention, application control, and threat intelligence. These features can help control egress traffic effectively. Palo Alto Networks and Fortinet are leading NGFW providers.
8.2. Secure Web Gateways (SWGs)
SWGs filter web traffic and protect users from web-based threats. These gateways can control egress traffic by blocking access to malicious websites and preventing data exfiltration. Cisco and Symantec offer SWG solutions.
8.3. Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
CASBs provide visibility and control over cloud applications. These tools can monitor and control egress traffic to and from cloud services, preventing data leakage. McAfee and Netskope are CASB providers.
8.4. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS monitor network traffic for malicious activity and take action to prevent or mitigate threats. These systems can detect and block unauthorized egress traffic. Snort and Suricata are open-source IDPS solutions.
8.5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Systems
DLP systems monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network. These systems can detect and block unauthorized data transfers, such as files containing confidential information. Digital Guardian and Forcepoint are DLP providers.
9. Future Trends in Egress Security
Egress security is an evolving field, with new trends and technologies emerging.
9.1. Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no user or device is trusted by default. This model requires strict authentication and authorization for all network traffic, including egress. Implementing Zero Trust can improve egress security by limiting access to sensitive data. According to Forrester, Zero Trust is becoming the new standard for security.
9.2. Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP)
SDP creates a secure perimeter around applications and data, regardless of location. This technology can control access to resources and prevent unauthorized egress. Implementing SDP can improve egress security in cloud and hybrid environments. Gartner predicts that SDP will be adopted by 60% of enterprises by 2025.
9.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML can be used to analyze egress traffic and detect anomalies that may indicate a security incident. These technologies can automate threat detection and response, improving egress security. Darktrace and Cylance are using AI and ML to enhance security.
9.4. Security Automation and Orchestration (SAO)
SAO automates security tasks and workflows, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of human error. This technology can automate egress controls, ensuring consistent enforcement of policies. Swimlane and Demisto are SAO providers.
10. Egress Use Cases
Understanding specific use cases can help illustrate the importance and application of egress controls.
10.1. Protecting Intellectual Property
Egress controls can prevent employees from sending confidential information, such as trade secrets and patents, outside the organization. This helps protect intellectual property and maintain a competitive advantage.
10.2. Preventing Financial Fraud
Egress controls can prevent attackers from exfiltrating financial data and using it for fraudulent purposes. This helps protect the organization’s assets and reputation.
10.3. Complying with Healthcare Regulations
Egress controls can help healthcare organizations comply with HIPAA by preventing unauthorized disclosure of protected health information (PHI). This helps protect patient privacy and avoid costly penalties.
10.4. Securing Government Data
Egress controls can help government agencies protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and disclosure. This is particularly important for classified information and national security data.
10.5. Controlling Cloud Costs
Egress controls can help organizations manage cloud costs by optimizing data transfer and preventing unnecessary egress traffic. This helps reduce cloud spending and improve budget control.
By implementing robust egress controls, organizations can enhance their security posture, comply with regulatory requirements, and manage cloud costs effectively. For more insights and assistance on securing your network and cloud infrastructure, visit WHAT.EDU.VN, where we provide free answers to your questions and expert guidance on egress security and other critical topics.
Understanding egress is more than just knowing a definition; it’s about understanding how to protect your data as it leaves your network. With the right strategies and tools, you can effectively manage egress traffic, prevent data breaches, and maintain compliance. Do you have more questions about egress or other network security topics? Ask them for free at WHAT.EDU.VN. We’re here to help!
Remember, securing your network is an ongoing process. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and leverage the resources available at WHAT.EDU.VN to keep your data safe. For personalized assistance and expert advice, contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. We are committed to providing you with the knowledge and support you need to succeed in today’s complex digital landscape. Explore related topics such as network architecture and data governance for a more holistic approach to data security.
FAQ: Egress Explained
Here are some frequently asked questions about egress, covering various aspects and concerns.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary goal of egress filtering? | The primary goal is to prevent malicious or unauthorized traffic from leaving your network, thereby protecting against data exfiltration and further compromise. |
| How does NAT relate to egress? | NAT masks internal IP addresses, providing an additional layer of security for egress traffic by hiding the internal network structure from external entities. |
| What are the cost implications of egress in AWS? | AWS charges for data egress, meaning you pay for data transferred out of AWS resources. Monitoring and managing this traffic is crucial for cost optimization. |
| Can DLP tools help with egress control? | Yes, DLP tools monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network, detecting and blocking unauthorized data transfers to prevent data leakage. |
| Why is monitoring egress traffic important? | Monitoring egress traffic provides visibility into outbound connections, helping detect anomalies and potential security incidents that might indicate data exfiltration attempts. |
| What role do firewalls play in egress? | Firewalls are essential for controlling egress traffic, allowing you to specify which outbound connections are permitted and blocking potentially harmful or unauthorized traffic. |
| How does network segmentation improve egress security? | Network segmentation divides the network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting the impact of a breach and making it easier to control and monitor egress traffic in specific areas, reducing the overall risk. |
| What is Zero Trust Architecture, and how does it affect egress? | Zero Trust Architecture assumes no user or device is trusted by default, requiring strict authentication and authorization for all network traffic, including egress, enhancing security by limiting access and potential exfiltration points. |
| How can AI and ML enhance egress security? | AI and ML can analyze egress traffic to detect anomalies and potential security incidents, automating threat detection and response and improving overall egress security through intelligent monitoring. |
| What are some common challenges in managing egress traffic? | Common challenges include the complexity of cloud environments, the dynamic nature of cloud resources, a lack of visibility into egress traffic, and a shortage of skilled personnel to manage and monitor egress controls effectively. |
Call to Action
Do you have more questions about what egress is, how to control it, or any other tech-related topic? Don’t hesitate to ask for free at what.edu.vn. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with the answers and guidance you need. Visit our website or contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Get the clarity you deserve today!