LinkedIn stands as a premier social networking platform, uniquely tailored for the global business and professional community. At its core, Linked In Is What connects individuals to establish and strengthen their professional networks, documenting relationships built on trust and industry relevance.
More than just connections, LinkedIn serves as a vital hub for professionals seeking career advancement, company insights, and industry-specific news. It empowers users to explore job opportunities, conduct in-depth company research, and stay informed about the latest trends within their professional spheres and among their business contacts.
Furthermore, LinkedIn leverages the vast data aggregated across its user profiles to furnish crucial, data-driven insights. These insights are invaluable for policymakers, employers, workers, and educators alike, aiding in the crucial task of aligning workforce supply with global demand. LinkedIn’s data reveals significant patterns, such as typical career transition timelines, workforce migration trends across regions, critical skill gaps within specific industries, and the “stickiness” of certain cities – indicating areas where employees demonstrate higher retention rates.
LinkedIn’s Distinct Position in the Social Media Landscape
Understanding linked in is what it offers requires differentiating it from other prevalent social media platforms. Unlike broad-spectrum social networks like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, LinkedIn is purposefully engineered for professional networking and business engagement.
It operates as a more curated and focused network. Users primarily connect with individuals they have pre-existing professional relationships with or those introduced through mutual connections. This structure positions LinkedIn as the ideal environment for cultivating and nurturing professional relationships, contrasting with the more personal focus of other social media channels.
While maintaining its professional core, LinkedIn incorporates features familiar to users of other social networks, such as specialized groups and dynamic discussion forums. These features enhance engagement and facilitate knowledge sharing within professional communities.
The Genesis of LinkedIn: Who Founded It?
LinkedIn was brought to life through the vision and collaborative efforts of several founders, with Reid Hoffman, formerly a key executive at PayPal as Executive Vice President overseeing business and corporate development, playing a pivotal role.
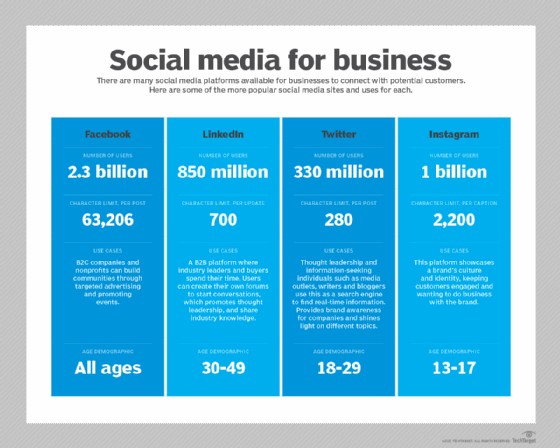
Launched in May 2003, LinkedIn has experienced exponential growth, now boasting over 850 million members globally. A significant portion, approximately 191 million, are based in the United States, with a further 58 million registered across more than 200 countries and territories. Notably, as highlighted by Reid Hoffman, recruiters constitute nearly 30% of LinkedIn’s extensive user base.
In a landmark acquisition in June 2016, Microsoft acquired LinkedIn for $26.2 billion. Industry experts widely consider this acquisition a strategic masterstroke, largely due to the immense value inherent in LinkedIn’s rich repositories of semi-structured data. This data, voluntarily contributed by members – encompassing job titles, geographic locations, industry affiliations, and skill sets – provides unparalleled insights into the professional world, making the acquisition exceptionally valuable for Microsoft despite its significant cost.
Unpacking the Utility: Why Leverage LinkedIn?
The utility of linked in is what it provides is primarily harnessed by three key demographics: individual professionals, sales professionals, and recruiters. Each group leverages LinkedIn’s functionalities to achieve distinct objectives:
- For Individual Professionals: LinkedIn emerges as an indispensable tool for career management and advancement. It facilitates job searching, in-depth company research, connection building with industry peers, and staying abreast of industry news.
- For Sales Professionals: LinkedIn transforms into a powerful platform for lead generation and relationship building with prospective clients. It enables targeted outreach and engagement, fostering connections that can convert into business opportunities.
- For Recruiters: LinkedIn becomes a critical resource for talent acquisition. Recruiters utilize it to identify potential candidates for open positions, conduct comprehensive company research, and directly connect with individuals who match their recruitment needs.
Navigating LinkedIn Membership: Basic and Beyond
Understanding linked in is what membership entails begins with recognizing its structure. A LinkedIn member’s profile page is designed to be a comprehensive professional snapshot, prominently featuring skills, employment history, and educational background. It integrates professional network news feeds and customizable modules that allow users to effectively showcase their competencies, qualifications, career trajectory, and endorsements from colleagues and former employers.
Basic LinkedIn membership is available without charge. Members within the network are termed “connections,” and unlike many other free social networking platforms, LinkedIn encourages connections to be based on genuine, pre-existing professional relationships.
Exploring LinkedIn Premium: Enhanced Features for Career Advancement
Beyond the foundational features of basic membership, linked in is what LinkedIn Premium offers lies in its enhanced functionalities designed to propel career productivity and success. Premium subscriptions unlock a suite of advanced tools and capabilities, including:
- InMail Messages: This feature enables direct communication with any LinkedIn member, regardless of connection status. It’s an especially valuable asset for recruiters needing to contact potential candidates outside their immediate network.
- Advanced Search Filters: Premium users benefit from refined search capabilities, allowing for precise filtering of search results to pinpoint ideal professional contacts and opportunities.
- Profile Views: This feature provides insights into who has viewed your profile and when. It is particularly useful for job seekers to gauge interest from potential employers reviewing their profiles.
- Sales Navigator: Tailored for sales professionals, Sales Navigator is a specialized tool providing enhanced access to leads, detailed account information, and critical contact details, streamlining sales outreach and relationship management.
Getting Started: How to Sign Up for LinkedIn
Embarking on your LinkedIn journey is straightforward. To understand linked in is what it takes to join, follow these step-by-step instructions to create your LinkedIn account:
- Navigate to linkedin.com and select Join now. You will be prompted to enter your first name, last name, email address, and create a secure password. You’ll also need to specify your country/region and preferred language.
- After completing the required fields, click Join LinkedIn. This action will direct you to your profile page, where you can begin populating it with details about your professional experience, educational background, skills, and interests.
- Once your profile is set up, you can start expanding your network by connecting with other LinkedIn members and exploring the platform’s vast professional community.
Best Practices for Crafting an Effective LinkedIn Profile
While the process to sign up and understand linked in is what a good profile looks like is simple, creating a truly impactful LinkedIn profile requires attention to best practices. Consider these key recommendations:
- Use a Professional Profile Photo: Your profile picture is often the first impression you make. Opt for a professional, high-quality headshot.
- Develop a Compelling ‘About’ Section: Utilize the ‘About’ section to provide a concise and engaging overview of your professional background, key skills, and career aspirations.
- Detail Your Experience in the ‘Experience’ Section: Thoroughly list all relevant work experiences, including job titles, employment dates, and detailed descriptions of your responsibilities and achievements.
- Complete the ‘Education’ Section: Include all relevant educational qualifications, degrees, and any pertinent coursework or certifications.
- Strategically List Skills in the ‘Skills’ Section: Populate the ‘Skills’ section with relevant skills and competencies, including software proficiencies or language skills.
- Actively Build Your Network: Connect with colleagues, industry peers, and professionals you know and trust to expand your network and visibility.
- Maintain and Regularly Update Your Profile: Keep your LinkedIn profile current by updating it as your experience and skills evolve. Seek endorsements from colleagues and reciprocate, ensuring your profile remains dynamic and impactful.
By understanding linked in is what it offers and how to effectively utilize its features, professionals can leverage this powerful platform for career growth, networking, and industry engagement.