In geometry, the radius is a fundamental concept for understanding circles and spheres. It’s a simple yet crucial measurement that unlocks the secrets of these shapes. Let’s delve into the world of radii, exploring what they are, how to calculate them, and why they are so important in mathematics and beyond.

What is a Radius?
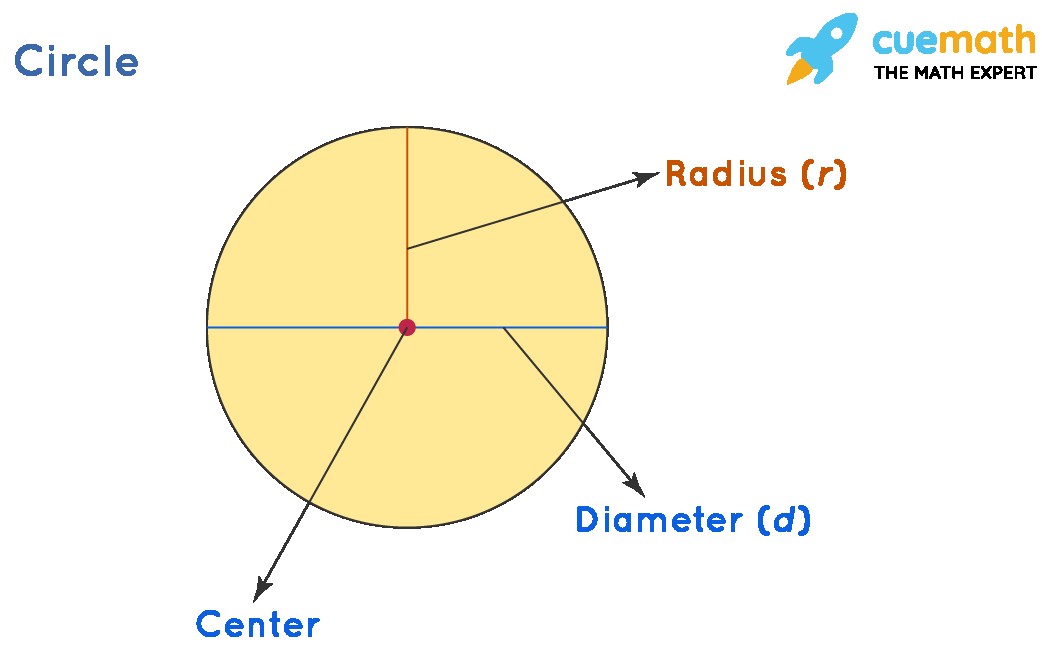
At its core, the radius of a circle (plural: radii) is a straight line segment that connects the very center of the circle to any point on its outer edge, known as the circumference. Think of it as a spoke in a wheel, extending from the hub (center) to the rim (circumference). This definition extends to spheres as well, where the radius connects the center of the sphere to any point on its surface. In mathematical notation, the radius is typically represented by the lowercase letter ‘r’.
Delving Deeper into the Meaning of Radius
The radius is more than just a line segment; it represents a fixed distance. No matter where you draw a line from the center of a perfect circle to its circumference, that length will always be the same – the radius. This consistent length is a defining characteristic of a circle. Furthermore, the radius has a direct and simple relationship with another key measurement of a circle: the diameter. The diameter is a line that passes straight through the center of the circle and touches two points on opposite sides of the circumference. As you might guess, the diameter is exactly twice the length of the radius. Conversely, the radius is always half the length of the diameter (r = d/2).
Now that we understand the fundamental definition of the radius, let’s explore the various formulas we can use to calculate it in different situations.
Formulas to Calculate the Radius of a Circle
Calculating the radius is straightforward, especially when you know other properties of the circle. Here are the most common formulas:
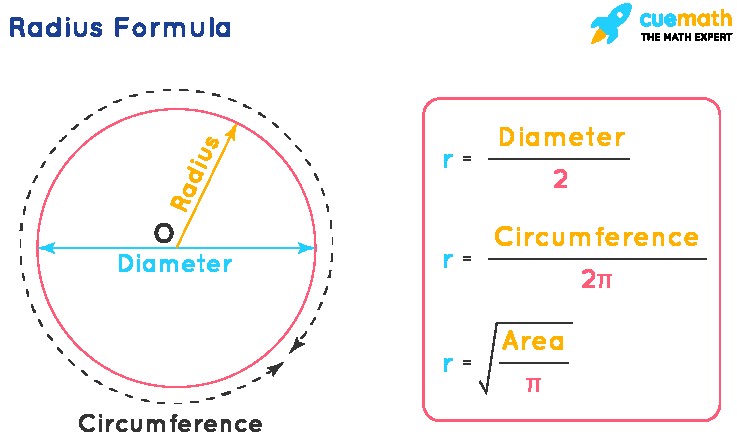
1. Radius Formula Using the Diameter
As we mentioned, the diameter (d) is twice the radius (r). This gives us the simplest formula for finding the radius:
Radius (r) = Diameter (d) ÷ 2
This formula is ideal when you already know the diameter of the circle.
2. Radius Formula Using the Circumference
The circumference (C) is the distance around the circle, essentially its perimeter. The formula for circumference is C = 2πr, where π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. We can rearrange this formula to solve for the radius:
Radius (r) = Circumference (C) / (2π)
This formula is useful when you know the circumference of the circle, for example, if you’ve measured around a circular object.
3. Radius Formula Using the Area
The area (A) of a circle is the space enclosed within its circumference. The formula for the area of a circle is A = πr². Again, we can rearrange this to find the radius:
Radius (r) = √(Area (A) / π)
Here, √ indicates the square root. This formula is helpful when you know the area of the circle.
Exploring the Radius of a Circle
The radius is not just a calculation tool; it’s a fundamental property that defines a circle. Consider these key aspects:
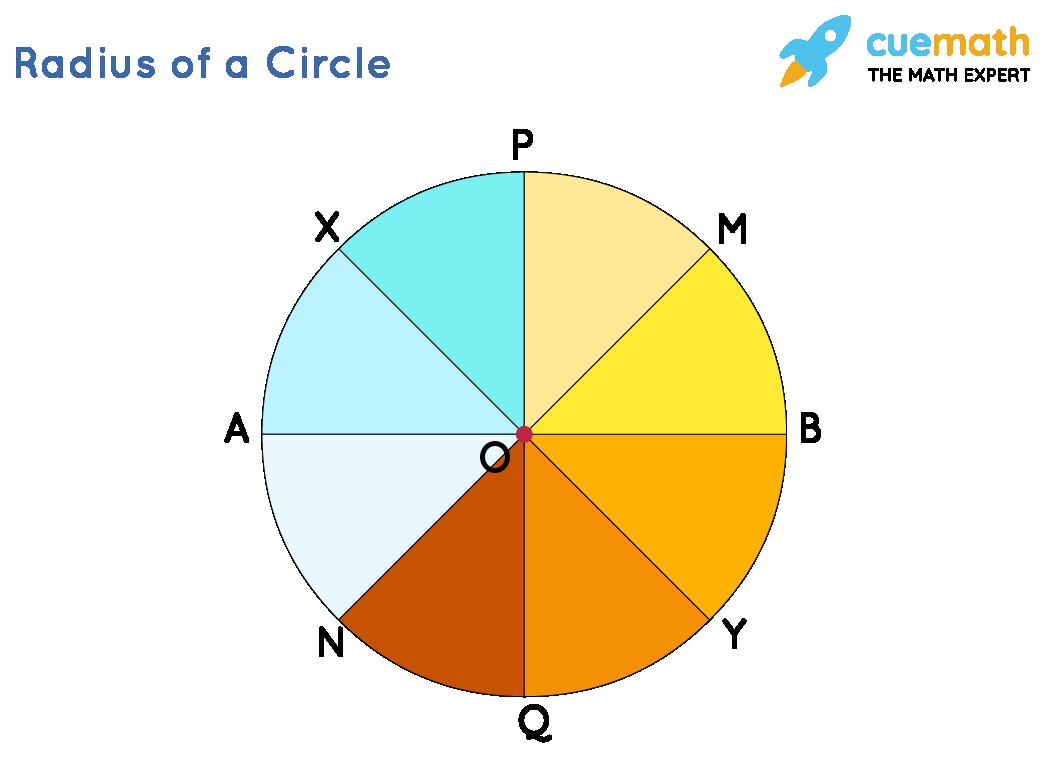
- Infinite Radii: A circle can have an infinite number of radii. You can draw a radius from the center to any of the countless points on the circumference.
- Equal Length: All radii within the same circle are of equal length. This is a defining characteristic of a circle – consistent distance from the center to the edge.
- Determines Circle Size: The length of the radius directly dictates the size of the circle. A longer radius means a larger circle, and a shorter radius means a smaller circle.
Imagine a point in the center and then visualize extending lines outwards in all directions, all stopping at the same distance. The endpoints of these lines form the circumference, and the length of each line is the radius.
In the diagram below, points A, B, M, N, P, Q, X, and Y all lie on the circumference. Each line segment from the center O to these points (OA, OB, OM, etc.) is a radius, and they are all equal in length.
Step-by-Step Guide: Finding the Radius
Let’s walk through how to find the radius using the formulas we discussed, with practical examples:
1. Finding the Radius When You Know the Diameter:
- Formula: Radius = Diameter / 2
- Example: If the diameter of a circle is 30 inches, then the radius is:
Radius = 30 inches / 2 = 15 inches
2. Finding the Radius When You Know the Circumference:
- Formula: Radius = Circumference / (2π)
- Example: If the circumference of a circle is 62.8 units, then the radius is approximately:
Radius = 62.8 units / (2 * 3.14) = 62.8 / 6.28 = 10 units
3. Finding the Radius When You Know the Area:
- Formula: Radius = √(Area / π)
- Example: If the area of a circle is 154 square meters, then the radius is approximately:
Radius = √(154 square meters / 3.14) = √(49.04) ≈ 7 meters
The Radius in the Equation of a Circle
The radius plays a crucial role in defining the equation of a circle in the Cartesian plane. The standard equation of a circle with center at point (h, k) and radius ‘r’ is:
(x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
Here, (x, y) represents any point on the circumference of the circle. If the center of the circle is at the origin (0, 0), the equation simplifies to:
x² + y² = r²
This equation tells us that for any point (x, y) on the circle, its distance from the center (h, k) or (0,0) is always equal to the radius ‘r’. The radius essentially fixes the size of the circle in the coordinate system.
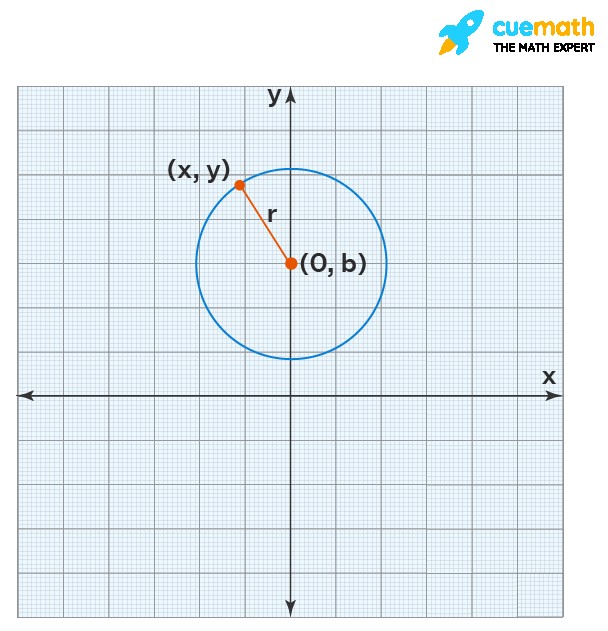
Consider a circle on the Cartesian plane with its center at (0, b). The equation to describe this circle and incorporate its radius ‘r’ would be:
(x − 0)² + (y − b)² = r² which simplifies to x² + (y − b)² = r²
Radius in 3D: Spheres
The concept of radius extends seamlessly to three-dimensional shapes, specifically spheres. A sphere is essentially a 3D circle – all points on its surface are equidistant from a central point. Just like with circles, the radius of a sphere is the distance from the center to any point on its surface.
The radius is equally important for spheres as it is for circles. It determines the size of the sphere, and it’s essential for calculating other properties like volume and surface area.
Formulas for Radius of a Sphere:
- From Volume (V): Radius (r) = ³√(3V / (4π)) (where ³√ denotes the cube root)
- From Surface Area (A): Radius (r) = √(A / (4π))
You can also use online calculators to quickly find the radius of a sphere if you know its volume, surface area, or diameter.
Related Articles:
[Links to related articles on circles, spheres, and geometry concepts on what.edu.vn would be listed here]
Radius Examples in Practice
Example 1: A circle has its center at (3, -2) on a Cartesian plane, and a point on its circumference is (7, 1). Find the radius.
Solution: Using the distance formula (derived from the circle equation), or directly applying the circle equation:
r² = (7 – 3)² + (1 – (-2))² = 4² + 3² = 16 + 9 = 25
r = √25 = 5 units
Example 2: A circular garden has a circumference of 50 feet. What is its radius?
Solution: Using the circumference formula:
r = Circumference / (2π) = 50 feet / (2 * 3.14159) ≈ 7.96 feet
Example 3: The area of a circular tabletop is 2 square meters. What is the radius?
Solution: Using the area formula:
r = √(Area / π) = √(2 square meters / 3.14159) ≈ 0.798 meters
[Button/Link to practice questions on radius calculations]
[Button/Link to interactive radius calculator]
Frequently Asked Questions about Radii
Q1: What is the radius of a circle in geometry?
A: In geometry, the radius of a circle is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. It’s half the length of the diameter and is constant for any given circle.
Q2: How is the diameter related to the radius of a circle?
A: The diameter of a circle is always twice the length of its radius. The formula is: Diameter = 2 × Radius. Conversely, Radius = Diameter / 2.
Q3: How do I find the radius from the circumference of a circle?
A: You can find the radius using the formula: Radius = Circumference / (2π). Divide the circumference by 2π (approximately 6.28318) to get the radius.
Q4: What are the different formulas to calculate the radius?
A: The main formulas are:
- Radius = Diameter / 2
- Radius = Circumference / (2π)
- Radius = √(Area / π)
Q5: Can I use a calculator to find the radius of a circle?
A: Yes! There are many online radius calculators available. You can also use a standard calculator and the formulas provided to calculate the radius yourself.
Q6: How do I find the radius of a circle if I know its area?
A: Use the formula: Radius = √(Area / π). Divide the area by π and then take the square root of the result to find the radius.
Q7: How do I calculate the radius if I only know the diameter?
A: This is the simplest calculation! Just divide the diameter by 2: Radius = Diameter / 2.