Adderall, a prescription medication, impacts brain chemistry. WHAT.EDU.VN explains the uses, side effects, and risks of Adderall. Find clarity and answers here regarding dopamine regulation and cognitive enhancement.
1. What Is Adderall Used For Medically?
Adderall, a combination of amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, is primarily prescribed to treat two medical conditions: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved it for these specific uses.
1.1. Adderall for ADHD Treatment
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. People with ADHD often struggle with focusing on tasks, sitting still, and controlling impulsive behaviors. Adderall helps manage these symptoms by affecting the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. According to the American Psychiatric Association, stimulant medications like Adderall are often the first-line treatment for ADHD, improving focus and reducing hyperactivity in many individuals.
1.2. Adderall for Narcolepsy Treatment
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to control sleep-wake cycles. People with narcolepsy experience excessive daytime sleepiness and may involuntarily fall asleep during the day. Adderall can help promote wakefulness and reduce daytime sleepiness in individuals with narcolepsy. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) notes that stimulants like Adderall are used to manage the symptoms of narcolepsy and improve the quality of life for those affected.
2. How Does Adderall Work in the Brain?
To understand what Adderall does, it’s crucial to know how it affects the brain. Adderall primarily works by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters, specifically dopamine, norepinephrine, and to a lesser extent, serotonin, in the brain.
2.1. The Role of Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells (neurons) in the brain. They play a vital role in regulating various functions, including mood, attention, focus, and alertness.
-
Dopamine: Often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, dopamine is associated with pleasure, motivation, and reward. It plays a crucial role in attention, focus, and movement.
-
Norepinephrine: Also known as noradrenaline, norepinephrine is involved in alertness, arousal, and the “fight-or-flight” response. It helps regulate attention, focus, and energy levels.
-
Serotonin: This neurotransmitter affects mood, appetite, and sleep. While Adderall has a smaller impact on serotonin levels compared to dopamine and norepinephrine, it can still influence mood and behavior.
2.2. Adderall’s Mechanism of Action
Adderall works through several mechanisms to increase the availability of these neurotransmitters in the brain:
-
Reuptake Inhibition: Adderall blocks the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine. Normally, after a neurotransmitter is released into the synapse (the space between neurons), it is reabsorbed back into the releasing neuron. By blocking this reuptake process, Adderall allows these neurotransmitters to remain in the synapse for a longer period, increasing their availability to bind to receptors on the receiving neuron.
-
Release Enhancement: Adderall also promotes the release of dopamine and norepinephrine from nerve terminals. This means that more of these neurotransmitters are available to be released into the synapse, further increasing their concentration and effects.
2.3. Impact on Brain Activity
By increasing the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine, Adderall enhances neuronal signaling in brain regions responsible for attention, focus, and executive functions. This can lead to improvements in concentration, reduced impulsivity, and increased alertness, particularly in individuals with ADHD.
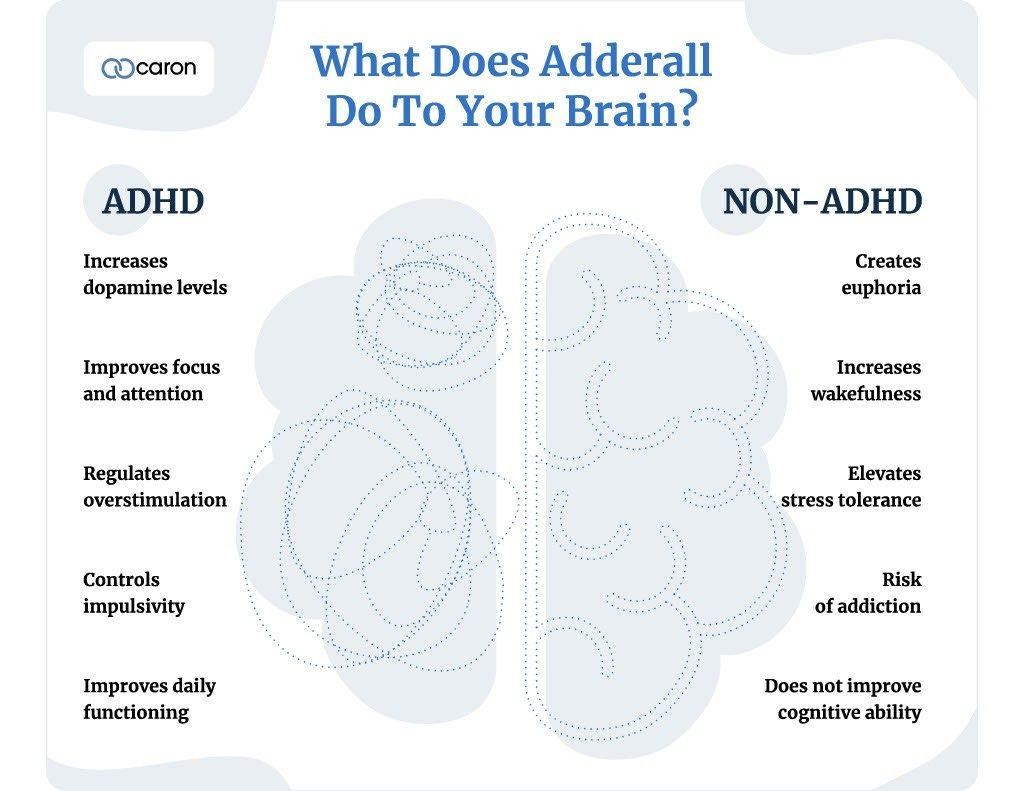 Adderall effects on the brain
Adderall effects on the brain
3. What Does Adderall Do for People With ADHD?
For individuals with ADHD, Adderall can have a significant impact on their ability to function in daily life. It helps manage the core symptoms of ADHD, leading to improved focus, attention span, and impulse control.
3.1. Improved Focus and Attention Span
One of the primary benefits of Adderall for people with ADHD is its ability to enhance focus and attention span. By increasing dopamine and norepinephrine levels, Adderall helps regulate brain activity in areas responsible for attention. This allows individuals with ADHD to concentrate on tasks more effectively, filter out distractions, and maintain focus for longer periods.
3.2. Reduced Hyperactivity and Impulsivity
Adderall can also help reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity, which are common symptoms of ADHD. By modulating neurotransmitter levels, Adderall helps regulate behavior and improve impulse control. This can lead to decreased restlessness, fidgeting, and impulsive decision-making.
3.3. Enhanced Executive Function
Executive function refers to a set of cognitive skills that are essential for planning, organizing, and managing tasks. People with ADHD often struggle with executive function deficits. Adderall can improve executive function by enhancing brain activity in the prefrontal cortex, a region responsible for these skills. This can lead to better time management, organization, and task completion.
3.4. Emotional Regulation
Some individuals with ADHD experience difficulties with emotional regulation, such as increased irritability, mood swings, and difficulty managing frustration. Adderall may help stabilize mood and improve emotional regulation by affecting neurotransmitter systems involved in emotional processing.
4. What Does Adderall Do to Someone Without ADHD?
While Adderall can be beneficial for people with ADHD, its effects on individuals without ADHD can be quite different and potentially harmful. The increase in dopamine and norepinephrine can lead to a range of effects, some of which may be perceived as positive in the short term but can have negative consequences in the long run.
4.1. Increased Alertness and Wakefulness
Adderall is a stimulant, and one of its primary effects is to increase alertness and wakefulness. People without ADHD may experience a heightened sense of energy, reduced fatigue, and an increased ability to stay awake for extended periods. This is why Adderall is sometimes misused by students who are trying to cram for exams or by individuals who need to stay awake for work.
4.2. Enhanced Focus and Concentration
Similar to its effects on people with ADHD, Adderall can also enhance focus and concentration in individuals without ADHD. They may find it easier to concentrate on tasks, filter out distractions, and maintain attention for longer periods. However, this effect is not the same as restoring normal brain function; rather, it’s an artificial boost that can lead to dependency and other adverse effects.
4.3. Euphoria and Elevated Mood
Adderall can stimulate the release of dopamine, leading to feelings of euphoria and elevated mood. This can be particularly pronounced in people without ADHD, as their brains are not deficient in dopamine to begin with. The euphoric effects of Adderall can be highly addictive and contribute to its misuse.
4.4. Physiological Effects
Adderall can cause several physiological effects, including increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and decreased appetite. These effects can be particularly risky for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
4.5. Potential Risks and Side Effects
It’s important to recognize that using Adderall without ADHD can carry significant risks and side effects. These can include:
- Anxiety and Irritability: While Adderall can improve focus, it can also lead to increased anxiety, nervousness, and irritability, particularly as the drug wears off.
- Insomnia: The stimulant effects of Adderall can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to insomnia.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Adderall can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be dangerous for individuals with heart problems.
- Addiction: Using Adderall without a prescription can lead to addiction and dependence. Over time, the brain may adapt to the presence of the drug, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects.
- Psychiatric Problems: In some cases, Adderall can trigger or worsen psychiatric problems, such as anxiety disorders, depression, and psychosis.
5. Does Adderall Make You Smarter?
A common misconception is that Adderall can make you smarter or improve cognitive abilities beyond what is typical for an individual. However, scientific evidence does not support this claim.
5.1. Studies on Cognitive Enhancement
Research has shown that Adderall does not significantly enhance cognitive performance in people without ADHD. While it may improve focus and attention, it does not boost intelligence, memory, or problem-solving skills. A review published in the journal Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews concluded that stimulant medications like Adderall do not enhance cognitive function in healthy individuals.
5.2. The Illusion of Enhanced Performance
The perception that Adderall makes you smarter may arise from the fact that it can improve focus and attention, allowing individuals to concentrate on tasks more effectively. This can lead to a temporary sense of enhanced performance, particularly in academic or work settings. However, this is not the same as true cognitive enhancement.
5.3. Dependence and Tolerance
Over time, regular use of Adderall can lead to tolerance, meaning that the brain adapts to the drug’s effects and requires higher doses to achieve the same level of focus and concentration. This can create a cycle of dependence and addiction.
5.4. Ethical Considerations
Using Adderall as a cognitive enhancer also raises ethical concerns. It creates an unfair advantage for those who have access to the drug, potentially disadvantaging those who do not. It also normalizes the use of medication for non-medical purposes, which can have broader societal implications.
6. What Are the Side Effects of Adderall?
Adderall can cause a range of side effects, both physical and psychological. The severity and likelihood of these side effects can vary depending on the individual, dosage, and duration of use.
6.1. Common Side Effects
Some of the most common side effects of Adderall include:
-
Loss of Appetite: Adderall can suppress appetite, leading to weight loss.
-
Insomnia: The stimulant effects of Adderall can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
-
Dry Mouth: Adderall can reduce saliva production, leading to dry mouth.
-
Headache: Headaches are a common side effect of Adderall.
-
Stomach Upset: Adderall can cause stomach pain, nausea, or diarrhea.
-
Anxiety and Nervousness: Adderall can increase anxiety, nervousness, and irritability.
-
Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Adderall can elevate heart rate and blood pressure, which can be dangerous for individuals with cardiovascular conditions.
6.2. Less Common Side Effects
Less common but more serious side effects of Adderall can include:
-
Cardiovascular Problems: In rare cases, Adderall can cause serious cardiovascular problems, such as heart attack, stroke, and sudden death, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
-
Psychiatric Problems: Adderall can trigger or worsen psychiatric problems, such as anxiety disorders, depression, psychosis, and mania.
-
Seizures: Adderall can increase the risk of seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of seizures.
-
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to Adderall, which can include rash, hives, itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing.
6.3. Long-Term Side Effects
Long-term use of Adderall can lead to several potential side effects, including:
-
Dependence and Addiction: Regular use of Adderall can lead to dependence and addiction, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects and experiencing withdrawal symptoms when the drug is stopped.
-
Tolerance: Over time, the brain may adapt to the presence of Adderall, requiring higher doses to achieve the same level of focus and concentration.
-
Growth Suppression: In children and adolescents, Adderall can slow down growth and development.
-
Mood Changes: Long-term use of Adderall can lead to mood changes, such as depression, anxiety, and irritability.
7. What Are the Risks of Adderall Misuse?
Misusing Adderall, either by taking it without a prescription or taking more than prescribed, can lead to a range of serious health risks.
7.1. Addiction and Dependence
One of the most significant risks of Adderall misuse is addiction. Adderall is a Schedule II controlled substance, meaning it has a high potential for abuse and dependence. People who misuse Adderall may develop a psychological or physical dependence on the drug, leading to compulsive drug-seeking behavior and withdrawal symptoms when the drug is stopped.
7.2. Cardiovascular Problems
Adderall can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be particularly dangerous for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Misuse of Adderall can lead to serious cardiovascular problems, such as heart attack, stroke, and sudden death.
7.3. Psychiatric Problems
Adderall misuse can trigger or worsen psychiatric problems, such as anxiety disorders, depression, psychosis, and mania. People with a history of mental health issues are particularly vulnerable to these effects.
7.4. Overdose
Taking too much Adderall can lead to an overdose, which can be life-threatening. Symptoms of an Adderall overdose can include:
- Agitation
- Tremors
- Seizures
- Rapid heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Hyperthermia (high body temperature)
- Hallucinations
- Coma
If you suspect someone has overdosed on Adderall, seek immediate medical attention.
7.5. Drug Interactions
Adderall can interact with other medications, potentially leading to dangerous side effects. It’s important to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Adderall.
8. How to Recognize Adderall Addiction?
Recognizing the signs of Adderall addiction is crucial for seeking help and preventing further harm. Some common signs of Adderall addiction include:
8.1. Compulsive Drug-Seeking Behavior
People who are addicted to Adderall may spend a significant amount of time and energy obtaining the drug, even if it means engaging in risky or illegal behavior.
8.2. Loss of Control
They may have difficulty controlling their use of Adderall, taking more than intended or using it for longer periods than planned.
8.3. Neglecting Responsibilities
Adderall addiction can lead to neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home.
8.4. Continued Use Despite Negative Consequences
They may continue to use Adderall despite experiencing negative consequences, such as health problems, relationship issues, or legal troubles.
8.5. Withdrawal Symptoms
When they stop using Adderall, they may experience withdrawal symptoms, such as fatigue, depression, anxiety, irritability, and sleep disturbances.
9. What Are the Alternatives to Adderall?
For individuals seeking alternatives to Adderall for managing ADHD or other conditions, several options are available.
9.1. Non-Stimulant Medications
Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine (Strattera), guanfacine (Intuniv), and clonidine (Kapvay), can be effective in treating ADHD without the risk of addiction associated with stimulants. These medications work differently than stimulants and may have fewer side effects for some individuals.
9.2. Therapy and Counseling
Therapy and counseling can be valuable tools for managing ADHD symptoms and improving overall functioning. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals develop coping strategies for managing impulsivity, inattention, and other ADHD-related challenges.
9.3. Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle modifications can also help manage ADHD symptoms. These can include:
- Regular exercise
- A healthy diet
- Sufficient sleep
- Stress management techniques
9.4. Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback that involves training the brain to regulate its own activity. It has been shown to be effective in reducing ADHD symptoms in some individuals.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Adderall
To provide more clarity on the topic, here are some frequently asked questions about Adderall.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is Adderall addictive? | Yes, Adderall has a high potential for abuse and dependence, especially when misused. |
| Can Adderall cause anxiety? | Yes, Adderall can cause anxiety, nervousness, and irritability, particularly as the drug wears off. |
| Is it safe to take Adderall every day? | Adderall should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Daily use can lead to dependence and tolerance. |
| What are the long-term effects of Adderall? | Long-term use of Adderall can lead to dependence, tolerance, mood changes, growth suppression in children, and cardiovascular problems. |
| Can Adderall cause weight loss? | Yes, Adderall can suppress appetite, leading to weight loss. |
| What happens if you stop taking Adderall suddenly? | Suddenly stopping Adderall can lead to withdrawal symptoms, such as fatigue, depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. |
| Can Adderall affect your mood? | Yes, Adderall can affect your mood, causing anxiety, irritability, and in some cases, depression. |
| Is Adderall safe for children? | Adderall can be safe for children with ADHD when prescribed and monitored by a doctor. However, it can have side effects and risks. |
| Can Adderall cause heart problems? | Yes, Adderall can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be dangerous for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. |
| What should I do if I think I’m addicted to Adderall? | If you think you’re addicted to Adderall, seek help from a doctor or addiction specialist. Treatment options include therapy, counseling, and medication. You can also reach out to WHAT.EDU.VN for guidance. |
Do you have more questions about Adderall or any other topic? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding quick and reliable answers can be challenging. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive free, accurate responses from knowledgeable individuals.
Are you struggling to find answers to your questions? Do you need expert advice without the high cost of consulting fees? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a free platform where you can ask any question and get reliable answers quickly. Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today, located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Our website, what.edu.vn, is your gateway to a wealth of knowledge, all at your fingertips. Ask away, and let us help you find the answers you need