What Gas Is Lights Green? Discover the answer and explore the world of sustainable energy with WHAT.EDU.VN, your go-to resource for free answers to all your questions. We delve into renewable energy sources, focusing on options that are both environmentally friendly and economically viable, and explain how renewable energy certificates and solar tax incentives can impact your decisions. Find reliable insights and expert guidance to help you navigate the complexities of green energy solutions, including solar power and off-site renewable programs.
1. Understanding Green Power: An Overview
Green power refers to electricity generated from renewable and sustainable sources, such as solar, wind, and biomass. Unlike traditional fossil fuels like coal, green power produces minimal to no emissions, contributing to improved air quality and reduced dependence on non-renewable resources. This makes it a crucial component of sustainable energy strategies worldwide. The shift towards green power is driven by environmental concerns, government incentives, and technological advancements that are making renewable energy more accessible and affordable.
1.1. Key Benefits of Green Power
- Environmental Protection: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and minimizes air pollution.
- Resource Conservation: Utilizes renewable resources that are naturally replenished.
- Economic Growth: Creates jobs in the green energy sector and fosters innovation.
- Energy Independence: Decreases reliance on imported fossil fuels.
1.2. Common Types of Green Power
- Solar Power: Harnesses energy from the sun using photovoltaic (PV) panels.
- Wind Power: Converts wind energy into electricity using wind turbines.
- Biomass Energy: Burns organic matter to generate heat and electricity.
- Hydropower: Uses the energy of flowing water to produce electricity.
- Geothermal Energy: Taps into the Earth’s internal heat for power generation.
2. The Rise of Solar Power and Photovoltaics (PV)
Solar power, particularly through photovoltaics (PV), has become the most widespread form of renewable energy. Solar panels can be installed on individual homes and businesses or in large solar farms. The significant drop in the cost of solar installations, nearly 70% in the 2010s, has fueled its adoption across the nation. Federal tax credits have also played a vital role in making solar power more accessible.
2.1. Solar Power for Homes and Businesses
Installing solar panels on your property offers several benefits:
- Reduced Electricity Bills: Generate your own electricity and decrease your reliance on the grid.
- Environmental Impact: Lower your carbon footprint by using clean energy.
- Increased Property Value: Solar panels can increase the value of your home or business.
- Energy Independence: Gain more control over your energy supply.
2.2. Challenges and Considerations for Solar Power
Despite its advantages, solar power also faces certain challenges:
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of installing solar panels can be significant.
- Weather Dependency: Solar power generation depends on sunlight availability, which can vary by location and time of year.
- Space Requirements: Solar panels require sufficient roof or land space for installation.
- Energy Storage: Storing excess solar energy for use during cloudy days or at night requires batteries, which add to the overall cost.
3. Renewable Energy Options for MLGW Customers
Memphis Light, Gas and Water (MLGW) customers have two primary ways to benefit from renewable generation: participating in off-site renewable energy programs or installing on-site solar generation at their home or business. Understanding these options is essential for making informed decisions about green energy adoption.
3.1. Renewables Without an Upfront Investment (Off-Site)
Off-site renewable energy programs allow customers to support green energy without the need for an upfront investment in solar panels or other renewable energy systems. These programs typically involve purchasing Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs).
3.1.1. Green Flex Program
Green Flex provides large volumes of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) for businesses and organizations that need vast amounts to meet sustainability goals. These RECs are derived from midwestern wind farms, with bundled electricity imported into the Tennessee Valley. For calendar year 2023, each REC costs $3.00 (current pricing subject to change) and enables the buyer to claim 1 MWh of electricity usage as renewable. Eligible participants must consume at least 2,000,000 kWh (or 2,000 MWh) annually, across one or multiple sites within Shelby County.
- Key Features of Green Flex:
- Certified Green-e Energy program
- TVA retires RECs in the name of each individual participant
- Limited enrollment based on REC availability
- Benefits:
- Supports renewable energy without upfront costs
- Helps businesses meet sustainability goals
- Reduces carbon footprint
- How to Participate:
- Contact MLGW to learn more about the program
- Ensure your business meets the minimum energy consumption requirements
- Purchase RECs annually through a separate invoice from MLGW
3.2. Renewables With an Upfront Investment (On-Site)
On-site renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, require an initial investment but offer long-term benefits in terms of reduced electricity bills and environmental impact. MLGW provides resources and guidance to help customers determine if on-site solar generation is right for them.
3.2.1. MLGW’s Five Tips for Considering On-Site Solar Generation
- Start with Efficiency:
- Make energy efficiency improvements to reduce overall electricity consumption.
- Replace aging heating, cooling, and water heating systems.
- Add insulation and weatherstripping.
- Install more efficient exterior doors and windows.
- Explore MLGW’s My Account Explore Usage section.
- Utilize the MLGW/TVA EnergyRight for Homes program.
- Consider the MLGW/TVA EnergyRight for Business & Industry program.
- Take advantage of federal tax incentives for qualified home and commercial building improvements.
- Consider Your Motivations:
- Environmental benefits and resiliency are strong reasons to consider solar.
- MLGW’s low electric rates and Shelby County’s below-average solar irradiance make it difficult to justify solar based on potential utility bill savings alone.
- Understand that financing a solar project involves lowering one expense (MLGW bill) while adding another (loan payment).
- Find the Right Installer:
- Use the Green Connect Quality Contractor Network for TVA-vetted residential installers.
- Look for credentials from the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP).
- Check multiple references, especially from clients with systems installed more than a year ago.
- Ask references about the installation process and the installer’s responsiveness.
- Be wary of installers who begin construction before MLGW has approved your application.
- Evaluate System Size:
- Consider available roof space (or land) and budget when determining system size.
- Avoid over-building; excess generation sold to TVA is valued below the retail electric rate.
- Aim for a system that provides most of your daytime electricity needs in Spring and Fall months.
- Adding battery storage can extend the hours your solar array supplies electricity (and provides limited backup power) but increases project cost.
- Use the My Meter Data feature in My Account to see your home’s electricity usage in 30-minute increments.
- Calculate Your Simple Payback:
- Estimate the number of years it will take to recover your solar project expense through utility bill savings and earnings from selling excess generation.
- Do the math yourself rather than relying on sales pitches.
- Consider MLGW’s low electric rates and the area’s below-average annual solar irradiance.
- Ensure your net average monthly electricity savings are greater than your loan payment if you plan to finance the system.
- Evaluate the cost and payback for solar arrays up to 50 kW generation capacity with TVA’s solar calculator.
4. Understanding Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are tradable instruments that represent the environmental attributes of electricity generated from renewable energy sources. Each REC represents one megawatt-hour (MWh) of renewable energy generated and delivered to the grid. RECs allow consumers and businesses to support renewable energy even if they cannot directly purchase it.
4.1. How RECs Work
- Generation: A renewable energy facility generates electricity and creates RECs.
- Tracking: RECs are tracked through a registry to ensure they are not double-counted.
- Purchase: Consumers and businesses purchase RECs to offset their electricity consumption.
- Retirement: The purchased RECs are retired, meaning they can no longer be used to make renewable energy claims.
4.2. Benefits of Purchasing RECs
- Supports Renewable Energy: Helps fund renewable energy projects and encourages their development.
- Meets Sustainability Goals: Allows businesses to meet their sustainability targets and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Flexible and Accessible: Provides a flexible way to support renewable energy, regardless of location or ability to install on-site systems.
- Credible Claims: Ensures that renewable energy claims are transparent and verifiable.
5. Federal Tax Incentives for Renewable Energy
Federal tax incentives play a significant role in making renewable energy more affordable and accessible for homeowners and businesses. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of installing solar panels and other renewable energy systems.
5.1. Residential Tax Incentives
The Residential Clean Energy Credit, previously known as the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), provides a tax credit for homeowners who install solar panels, solar water heaters, and other renewable energy systems.
- Key Features:
- Provides a credit for a percentage of the cost of the renewable energy system.
- The credit can be claimed in the year the system is “placed into service.”
- Consult your tax advisor for specific advice.
5.2. Non-Residential Tax Incentives
Non-residential tax incentives, such as the Business Energy Investment Tax Credit (ITC), offer similar benefits for businesses that invest in renewable energy systems.
- Key Features:
- Provides a credit for a percentage of the cost of the renewable energy system.
- The credit can be claimed in the year the system is “placed into service.”
- Consult your tax advisor for specific advice.
6. Solar Generation Technology, Costs, and Output
Understanding the technology, costs, and output of solar generation systems is crucial for making informed decisions. This knowledge helps you set realistic expectations and avoid surprises later.
6.1. Solar Panel Technology
Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into electricity. There are several types of solar panels, including:
- Monocrystalline: Made from a single crystal of silicon, offering high efficiency and a sleek appearance.
- Polycrystalline: Made from multiple silicon crystals, less efficient than monocrystalline but more affordable.
- Thin-Film: Made from thin layers of semiconductor materials, flexible and lightweight but less efficient.
6.2. Factors Affecting Solar Panel Output
- Sunlight Availability: The amount of sunlight a location receives directly affects solar panel output.
- Panel Angle and Orientation: The angle and orientation of solar panels should be optimized to maximize sunlight capture.
- Panel Efficiency: Higher efficiency panels produce more electricity per square foot.
- Temperature: Solar panels perform best at cooler temperatures; high temperatures can reduce efficiency.
6.3. Cost Considerations for Solar Panels
- Equipment Costs: Solar panels, inverters, racking, and other components.
- Installation Costs: Labor, permits, and other installation expenses.
- Maintenance Costs: Cleaning and occasional repairs.
7. Exploring the Role of TVA and Green Connect
TVA (Tennessee Valley Authority) and its Green Connect program are pivotal in advancing renewable energy adoption in the region. They provide resources, education, and contractor networks to support customers in their green energy journey.
7.1. TVA’s Contribution to Renewable Energy
TVA plays a crucial role in promoting renewable energy through various initiatives:
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): TVA enters into PPAs with renewable energy developers to purchase electricity generated from solar farms and other renewable energy facilities.
- Green Connect Program: TVA’s Green Connect program offers residential solar education resources and a Qualified Contractor Network of TVA-vetted solar installers.
- Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs): TVA supports the REC market by purchasing and retiring RECs on behalf of its customers.
7.2. Benefits of Using TVA’s Green Connect Program
- Education Resources: Access to information about solar technology, costs, and benefits.
- Qualified Contractor Network: A list of TVA-vetted solar installers who have the required licenses, industry-leading certifications, and program training.
- Fair Business Practices: Assurance that installers operate using fair business practices for sales and high-quality workmanship.
8. Integrating Battery Storage with Solar Systems
Battery storage is an increasingly popular addition to solar systems, allowing homeowners and businesses to store excess solar energy for later use. This can increase energy independence and provide backup power during grid outages.
8.1. Advantages of Battery Storage
- Increased Energy Independence: Store excess solar energy for use during cloudy days or at night.
- Backup Power: Provide backup power during grid outages, ensuring essential appliances and systems continue to function.
- Reduced Peak Demand Charges: Reduce peak demand charges by using stored energy during peak hours.
- Grid Stabilization: Help stabilize the grid by providing energy storage and reducing the need for fossil fuel power plants.
8.2. Types of Battery Storage Systems
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: The most common type of battery storage, offering high energy density, long lifespan, and relatively low cost.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: A more traditional battery storage option, less expensive than lithium-ion but with lower energy density and shorter lifespan.
- Flow Batteries: An emerging battery storage technology that uses liquid electrolytes to store energy, offering long lifespan and scalability.
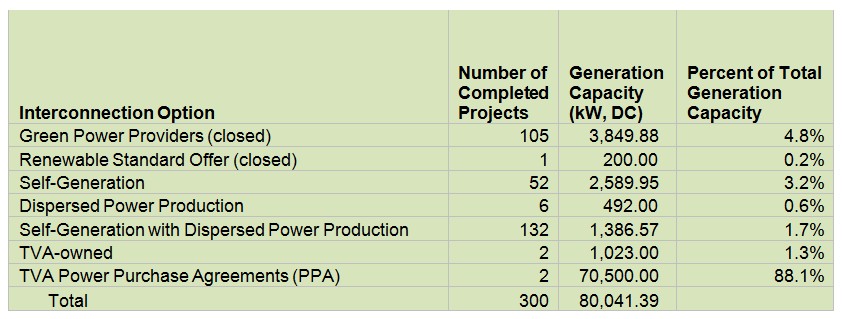
9. Navigating MLGW’s Interconnection Process
Connecting your on-site solar generation system to the MLGW grid requires following a specific interconnection process. Understanding this process is essential for a smooth and successful installation.
9.1. Key Steps in MLGW’s Interconnection Process
- Choose an Interconnection Option: Select the appropriate interconnection option based on your needs and system size.
- Submit an Application: Complete and submit the MLGW Application for Interconnection of Distributed Generation.
- System Review: MLGW reviews the application and system design to ensure compliance with safety and technical standards.
- Installation: Install the solar generation system according to the approved design.
- Inspection: MLGW inspects the system to ensure it meets all requirements.
- System Acceptance Test: MLGW performs a system acceptance test to verify proper operation.
- Interconnection Agreement: Sign an interconnection agreement with MLGW.
- Permission to Operate: Receive permission to operate the solar generation system and connect it to the grid.
9.2. Common Challenges in the Interconnection Process
- Application Delays: Processing times for interconnection applications can vary.
- Technical Requirements: Meeting MLGW’s technical requirements for system design and operation.
- Inspection Issues: Addressing any issues identified during the inspection process.
10. Exploring Alternative Renewable Energy Sources
While solar power is a prominent renewable energy source, it’s essential to explore other alternatives that can contribute to a diversified and sustainable energy mix.
10.1. Wind Energy
Wind energy converts the kinetic energy of wind into electricity using wind turbines. Wind farms can generate significant amounts of electricity and are often located in areas with consistent wind patterns.
- Advantages:
- Clean and renewable energy source
- Low operating costs
- Creates jobs in the wind energy sector
- Challenges:
- Intermittent energy source
- Visual impact on the landscape
- Potential impact on wildlife
10.2. Hydropower
Hydropower uses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. Hydropower plants can be large dams or smaller run-of-river facilities.
- Advantages:
- Reliable and predictable energy source
- Long lifespan
- Provides water storage and flood control
- Challenges:
- Environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems
- Limited availability of suitable sites
- High upfront costs
10.3. Biomass Energy
Biomass energy involves burning organic matter, such as wood, crops, and waste, to generate heat and electricity.
- Advantages:
- Renewable energy source if managed sustainably
- Reduces waste and landfill space
- Can be used for heating, electricity, and transportation fuels
- Challenges:
- Air pollution from combustion
- Potential impact on forests and land use
- Sustainability concerns
10.4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity and heat buildings.
- Advantages:
- Reliable and consistent energy source
- Low emissions
- Can be used for heating, electricity, and direct-use applications
- Challenges:
- Limited availability of suitable sites
- High upfront costs
- Potential for induced seismicity
11. FAQ: Common Questions About Green Power
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is green power? | Green power is electricity generated from renewable and sustainable resources like solar, wind, and biomass, producing minimal emissions. |
| How does solar power work? | Solar power harnesses energy from the sun using photovoltaic (PV) panels, which convert sunlight into electricity. |
| What are Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)? | RECs are tradable instruments representing the environmental attributes of electricity generated from renewable energy sources. Each REC represents one megawatt-hour (MWh) of renewable energy. |
| What is the Green Flex program? | Green Flex provides large volumes of RECs for businesses and organizations needing to meet sustainability goals, derived from midwestern wind farms. |
| What are the benefits of on-site solar generation? | On-site solar generation reduces electricity bills, lowers your carbon footprint, increases property value, and provides greater energy independence. |
| How can I find a reliable solar installer? | Look for TVA-vetted installers through the Green Connect Quality Contractor Network and ensure they have credentials from the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP). |
| What factors affect the output of solar panels? | Sunlight availability, panel angle and orientation, panel efficiency, and temperature all affect solar panel output. |
| What are the advantages of battery storage with solar systems? | Battery storage increases energy independence, provides backup power during grid outages, reduces peak demand charges, and helps stabilize the grid. |
| What are the steps in MLGW’s interconnection process? | The process includes choosing an interconnection option, submitting an application, system review, installation, inspection, system acceptance test, signing an interconnection agreement, and receiving permission to operate. |
| What are some alternative renewable energy sources? | Alternative sources include wind energy, hydropower, biomass energy, and geothermal energy, each with its own advantages and challenges. |
12. The Future of Green Power and Renewable Energy
The future of green power and renewable energy is promising, with continued technological advancements, decreasing costs, and increasing government support. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy future, green power will play a vital role in reducing carbon emissions, protecting the environment, and ensuring energy security.
12.1. Emerging Trends in Renewable Energy
- Advanced Solar Technologies: Development of more efficient and cost-effective solar panels, such as perovskite solar cells and bifacial panels.
- Offshore Wind Energy: Expansion of offshore wind farms, which can harness stronger and more consistent winds.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Advancements in battery storage technologies, including longer-lasting and more affordable batteries.
- Smart Grids: Integration of smart grid technologies to improve the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy systems.
- Green Hydrogen: Production of hydrogen using renewable energy sources, which can be used as a clean fuel for transportation and industry.
12.2. The Role of Policy and Regulation
Government policies and regulations play a critical role in driving the adoption of green power and renewable energy. These policies can include:
- Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): Requiring utilities to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources.
- Tax Incentives: Providing tax credits and other incentives for renewable energy projects.
- Carbon Pricing: Implementing carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems to make fossil fuels more expensive.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Setting energy efficiency standards for buildings and appliances to reduce overall energy consumption.
- Grid Modernization: Investing in grid modernization to support the integration of renewable energy sources.
13. Case Studies: Successful Green Power Initiatives
Examining successful green power initiatives can provide valuable insights and inspiration for individuals and organizations looking to adopt renewable energy solutions.
13.1. City of Greensburg, Kansas
After being devastated by a tornado in 2007, the city of Greensburg, Kansas, rebuilt itself as a model of sustainability. The city committed to using 100% renewable energy and implemented various green building practices.
- Key Achievements:
- All city buildings are LEED-certified.
- The city uses wind energy to power its operations.
- Residents have access to renewable energy options.
- Greensburg has become a national leader in sustainability.
13.2. Apple’s Renewable Energy Initiatives
Apple has made significant investments in renewable energy to power its data centers, retail stores, and corporate offices. The company has also worked with its suppliers to encourage them to adopt renewable energy.
- Key Achievements:
- Apple is powered by 100% renewable energy globally.
- The company has invested in large-scale solar and wind projects.
- Apple has reduced its carbon footprint significantly.
14. Take the Next Step Towards Green Energy
Ready to explore green power options for your home or business? With the help of WHAT.EDU.VN, you can find the information and resources you need to make informed decisions and take action.
14.1. Call to Action: Explore Your Options with WHAT.EDU.VN
Do you have any burning questions about green energy, solar power, or renewable energy certificates? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your questions for free! Our experts are ready to provide you with the answers you need to make informed decisions about sustainable energy.
14.2. Contact Us for More Information
For personalized assistance and answers to your specific questions, contact us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Let what.edu.vn be your trusted resource for all things green energy! Whether you’re curious about the environmental impact of solar panels, the financial benefits of renewable energy, or the latest advancements in sustainable technology, we’re here to help. Start your journey towards a cleaner, greener future today!
 Solar panels on a rooftop
Solar panels on a rooftop
