Are you curious about generational classifications? What Generation Is 1996? This article from WHAT.EDU.VN explores how generational cohorts are defined, focusing on the 1996 birth year and its significance in distinguishing between Millennials and Generation Z. This exploration helps understand societal shifts and individual experiences, providing valuable insights. Discover generational differences and shared traits today.
1. The Significance of Generational Analysis
Generational analysis offers a unique perspective on understanding societal trends and individual attitudes. By examining groups of people born within a similar timeframe, we can gain insights into how shared experiences shape their worldviews. These experiences, such as major world events, technological advancements, and economic shifts, interact with the aging process to influence perspectives on various aspects of life. Understanding generational cohorts is useful for researchers, marketers, educators, and anyone interested in comprehending the evolving dynamics of society. This approach provides a tool for analyzing shifts in views over time and understanding the impact of formative experiences.
1.1. Why Study Generations?
Studying generations is essential for several reasons. It allows us to:
- Analyze Changes Over Time: Generational cohorts provide a framework for examining how opinions and behaviors evolve across different age groups.
- Understand Formative Experiences: By considering the major events and trends that shaped a generation’s youth, we can better understand their values and perspectives.
- Predict Future Trends: Generational analysis can offer insights into how different cohorts might approach future challenges and opportunities.
- Tailor Communication Strategies: Understanding generational differences is crucial for effective communication and marketing efforts.
- Bridge Generational Gaps: By recognizing the unique characteristics of each generation, we can foster understanding and collaboration between different age groups.
1.2. Pew Research Center’s Approach to Generations
Pew Research Center has long been committed to studying generational cohorts. Their research examines public attitudes on key issues, documenting differences across demographic groups. They use generations as a lens to understand Americans by their life cycle stage and membership in a cohort of individuals born at a similar time. Their approach considers the influence of formative experiences on shaping people’s views of the world. Pew Research Center’s work provides valuable insights into generational trends and their impact on society.
2. Defining the Millennial Generation
The Millennial generation, also known as Generation Y, has been a focal point of research for over a decade. It is generally defined as those born between 1981 and 1996. This generation came of age during a period of rapid technological advancement, globalization, and significant social and political changes. Key characteristics of Millennials include their comfort with technology, emphasis on work-life balance, and openness to diversity. However, as the oldest Millennials approached their late 30s, it became necessary to establish a cutoff point to distinguish them from the subsequent generation.
2.1. The 1981-1996 Birth Years
People born between 1981 and 1996 are considered Millennials. In 2019, this age group was between 23 and 38 years old. This timeframe encompasses a period of significant historical and technological shifts. Those born in the early 1980s experienced the rise of personal computers and the early internet, while those born in the mid-1990s grew up with mobile devices and social media as integral parts of their lives. The shared experiences of this generation, from economic booms to recessions, shaped their attitudes toward work, family, and society.
2.2. Key Traits and Experiences of Millennials
Millennials are often characterized by:
- Digital Natives: Growing up with technology has made them comfortable with computers, the internet, and mobile devices.
- Emphasis on Experiences: They value experiences over material possessions, often prioritizing travel, entertainment, and personal growth.
- Openness to Diversity: Millennials are generally more accepting of diverse cultures, lifestyles, and identities than previous generations.
- Work-Life Balance: They seek jobs that offer flexibility, purpose, and opportunities for personal fulfillment.
- Civic Engagement: Many Millennials are actively involved in social and political causes, advocating for change and progress.
3. The Emergence of Generation Z
As the Millennial generation matured, researchers began to focus on the cohort that followed. Born after 1996, this new generation has been labeled Generation Z. Growing up in an era of constant connectivity, social media, and on-demand entertainment, Gen Z has unique perspectives and behaviors. While they share some similarities with Millennials, they also exhibit distinct traits shaped by their formative experiences.
3.1. Why 1996 as the Cutoff Year?
Pew Research Center designated 1996 as the last birth year for Millennials to maintain the analytical integrity of the Millennial generation and to begin exploring the unique characteristics of the next cohort. This decision was based on several factors, including key political, economic, and social events that significantly shaped the Millennial generation’s formative years. It allowed researchers to differentiate between those who came of age before the rise of social media and constant connectivity and those who grew up with these technologies as inherent parts of their lives.
3.2. Naming the Next Generation
Initially, there was hesitation in naming the generation after Millennials. Terms like “post-Millennials,” “iGeneration,” and “Homelanders” were considered. However, “Generation Z” gained traction in popular culture and journalism. Its widespread use by sources like Merriam-Webster, Oxford, and the Urban Dictionary, along with its dominance in Google searches, solidified its position as the accepted name for this cohort.
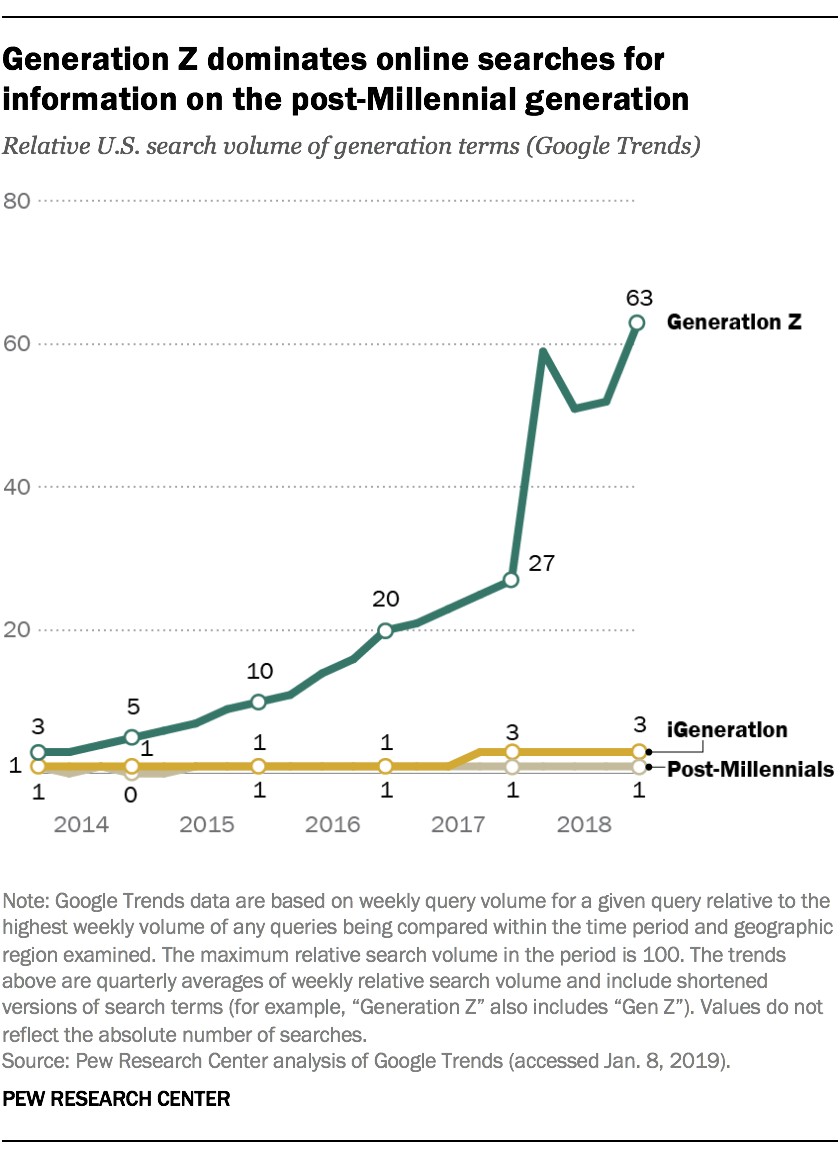 Generation dominates online searches for information on the post-Millennial generation
Generation dominates online searches for information on the post-Millennial generation
4. Key Defining Moments and Their Impact
Several key moments and trends differentiate Millennials from Generation Z. These include political events, economic shifts, and technological advancements that shaped their formative years. Understanding these differences provides insight into the unique characteristics and perspectives of each generation.
4.1. 9/11 and Its Aftermath
Most Millennials were between 5 and 20 years old when the 9/11 terrorist attacks occurred. Many were old enough to grasp the historical significance of this event. In contrast, most members of Gen Z have little or no memory of 9/11. The attacks and subsequent wars in Iraq and Afghanistan significantly impacted the political views and awareness of Millennials.
4.2. The 2008 Election and Political Polarization
The 2008 election, which saw the election of the first black president, was a pivotal moment for Millennials. They were between 12 and 27 years old at the time, and the youth vote played a significant role in the outcome. This event, along with the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, contributed to increased political polarization, shaping the political environment in which Millennials came of age.
4.3. The Economic Recession of 2008
The economic recession of 2008 had a profound impact on Millennials, many of whom were entering the workforce or starting their careers during this period. The recession affected their life choices, future earnings, and entry into adulthood. The long-term effects of this “slow start” continue to shape American society.
5. Technology and Generational Identity
Technology has played a significant role in shaping generational identities. Each generation has experienced unique technological advancements that have influenced their lifestyles, communication patterns, and connection to the world. For Gen Z, growing up in an “always on” technological environment has had profound implications.
5.1. The “Always On” Environment
Gen Z has grown up in an environment where social media, constant connectivity, and on-demand entertainment and communication are the norm. The iPhone launched in 2007, when the oldest Gen Zers were 10 years old. By their teens, mobile devices, Wi-Fi, and high-bandwidth cellular service were the primary means of accessing the internet. These technologies have shaped their behaviors, attitudes, and lifestyles in both positive and concerning ways.
5.2. Implications of Constant Connectivity
The implications of growing up in an “always on” technological environment are still emerging. Recent research indicates significant shifts in youth behaviors, attitudes, and lifestyles. The question remains whether these are lasting generational imprints or characteristics of adolescence that will fade over time. Tracking this new generation over time is of significant importance.
6. Beyond the Cutoff: The Continuum of Generations
While generational cutoff points provide a useful framework for analysis, it’s crucial to recognize that these boundaries are not absolute. Generational classifications should be viewed as tools that allow for specific types of analysis. The differences within a generation can be as significant as the differences between generations. The youngest and oldest members of a cohort may feel more connected to bordering generations than their own.
6.1. Diversity Within Generations
Generations are inherently diverse and complex groups, not simple caricatures. Factors such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and geographic location can contribute to significant differences within a generation. Recognizing this diversity is essential for avoiding generalizations and understanding the nuances of individual experiences.
6.2. Overlapping Traits and Shared Experiences
Despite the cutoff points, generations often share overlapping traits and experiences. Individuals born near the boundaries of two generations may identify with aspects of both. Understanding these shared connections is crucial for bridging generational gaps and fostering collaboration.
7. The Future of Generational Research
Generational research continues to evolve as society changes. Future studies will focus on tracking Generation Z as they enter adulthood. This includes examining their views on social and political issues, their demographic and economic dynamics, and their daily lives and aspirations. It’s essential to remain cautious about projecting onto a generation while they are still young, recognizing that their views and behaviors may evolve over time.
7.1. Key Areas of Focus
Future research will likely focus on:
- Social and Political Views: Examining how Gen Z views key social and political issues and how their views compare to those of older generations.
- Demographic and Economic Dynamics: Comparing Millennials to previous generations at the same stage in their life cycle to identify unique demographic, economic, and household dynamics.
- Technology Use: Exploring the daily lives, aspirations, and pressures faced by teenagers as they navigate the teenage years in an increasingly digital world.
- Impact of Current Events: Assessing how current political and social events shape the attitudes and engagement of Generation Z.
7.2. Remaining Open to Recalibration
As more data is collected over time, a clearer delineation between generations may emerge. Researchers should remain open to recalibrating generational boundaries if necessary. However, it’s more likely that historical, technological, behavioral, and attitudinal data will reveal a continuum across generations rather than a sharp threshold.
8. Understanding Generation Z
Generation Z, born after 1996, is the newest generation to come of age. They are characterized by their digital fluency, entrepreneurial spirit, and focus on social justice. Growing up in a world of constant connectivity, they are adept at navigating online platforms and using technology to express themselves and connect with others.
8.1. Defining Characteristics
Some of the defining characteristics of Generation Z include:
- Digital Natives: They have never known a world without the internet or mobile devices.
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: Many Gen Zers are interested in starting their own businesses and creating their own opportunities.
- Focus on Social Justice: They are passionate about addressing social and environmental issues and advocating for change.
- Value Authenticity: They appreciate transparency and honesty in their interactions with brands and individuals.
- Independent and Self-Reliant: They are comfortable learning on their own and finding solutions to problems independently.
8.2. How Gen Z Differs from Millennials
While Gen Z shares some similarities with Millennials, there are also key differences. Gen Z tends to be more pragmatic and financially conservative than Millennials. They are also more focused on individual achievement and less likely to identify with group labels. Additionally, they are more adept at filtering information and discerning between credible and unreliable sources.
9. Practical Applications of Generational Understanding
Understanding generational differences has numerous practical applications in various fields, including marketing, education, and workplace management. By tailoring strategies to the unique characteristics and preferences of each generation, organizations can improve communication, engagement, and overall effectiveness.
9.1. Marketing Strategies
Marketers can use generational insights to develop targeted campaigns that resonate with specific age groups. For example, Millennials may respond well to authentic, socially conscious messaging, while Gen Z may be more receptive to influencer marketing and user-generated content. Understanding the media consumption habits and online behaviors of each generation is crucial for effective marketing.
9.2. Educational Approaches
Educators can adapt their teaching methods to accommodate the learning styles and preferences of different generations. Millennials may benefit from collaborative projects and technology-enhanced learning, while Gen Z may thrive in more self-directed, personalized learning environments. Understanding the motivations and aspirations of each generation can help educators create more engaging and relevant learning experiences.
9.3. Workplace Dynamics
Understanding generational differences is essential for effective workplace management. Creating a work environment that values diversity, inclusivity, and collaboration can help bridge generational gaps and foster positive relationships between employees of different ages. Recognizing the unique skills and perspectives that each generation brings to the table can enhance innovation and productivity.
10. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Generations
It’s important to address common misconceptions about generations to avoid stereotypes and promote understanding. Not all members of a generation fit neatly into predefined categories. Individual experiences and circumstances play a significant role in shaping their identities and behaviors.
10.1. Avoiding Stereotypes
Stereotyping generations can lead to inaccurate assumptions and unfair judgments. It’s important to recognize that each generation is diverse and complex. Generalizations should be used cautiously and should not be applied to individuals without considering their unique circumstances.
10.2. Recognizing Individual Differences
Individual differences within a generation are often as significant as the differences between generations. Factors such as personality, values, and life experiences can shape an individual’s attitudes and behaviors. It’s crucial to treat each person as an individual and avoid making assumptions based solely on their generational affiliation.
11. The Role of External Factors
External factors, such as economic conditions, social movements, and global events, can significantly impact the development of a generation. These factors can shape their values, attitudes, and behaviors, influencing their perspectives on the world.
11.1. Economic Influences
Economic conditions can have a profound impact on a generation’s financial security, career opportunities, and overall outlook on life. Generations that come of age during periods of economic prosperity may have different priorities and values than those who experience economic hardship.
11.2. Social and Political Movements
Social and political movements can shape a generation’s sense of identity and purpose. Generations that participate in significant social movements may be more likely to engage in activism and advocacy.
11.3. Global Events
Global events, such as wars, pandemics, and environmental disasters, can have a lasting impact on a generation’s worldview. These events can shape their attitudes toward international relations, security, and environmental sustainability.
12. How WHAT.EDU.VN Can Help You Understand Generations
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of staying informed and up-to-date on the latest trends and insights. That’s why we offer a comprehensive platform where you can ask any question and receive accurate, reliable answers from knowledgeable experts. Whether you’re curious about generational differences, technological advancements, or any other topic, we’re here to provide you with the information you need.
12.1. Ask Any Question, Get Free Answers
Do you have questions about what generation is 1996, or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask. Our platform is designed to provide you with fast, accurate answers from experts in various fields. Best of all, it’s completely free.
12.2. Easy-to-Use Platform
Our platform is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to everyone. Simply type your question into the search bar and let our experts provide you with the answers you need.
12.3. Stay Informed and Up-to-Date
With WHAT.EDU.VN, you can stay informed and up-to-date on the latest trends and insights in various fields. Our platform is constantly updated with new information and expert answers, ensuring that you have access to the most current knowledge.
13. Why Ask Questions on WHAT.EDU.VN?
Are you struggling to find reliable answers to your questions? Do you feel overwhelmed by the amount of information available online? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a simple, convenient, and free solution to all your information needs.
13.1. Overcome Information Overload
With so much information available online, it can be difficult to sort through the noise and find accurate, reliable answers. WHAT.EDU.VN simplifies the process by providing you with expert answers in a clear, concise format.
13.2. Get Answers from Knowledgeable Experts
Our platform connects you with knowledgeable experts who are passionate about sharing their expertise. You can trust that the answers you receive on WHAT.EDU.VN are accurate, reliable, and up-to-date.
13.3. Free and Convenient Access
Accessing reliable information shouldn’t be expensive or time-consuming. WHAT.EDU.VN offers free and convenient access to expert answers, allowing you to get the information you need quickly and easily.
14. Embrace Lifelong Learning with WHAT.EDU.VN
In today’s rapidly changing world, lifelong learning is essential for personal and professional growth. WHAT.EDU.VN empowers you to embrace lifelong learning by providing you with a platform to ask questions, explore new topics, and expand your knowledge.
14.1. Unlock Your Potential
Learning new things can open doors to new opportunities and help you achieve your goals. WHAT.EDU.VN provides you with the resources and support you need to unlock your full potential.
14.2. Stay Curious and Engaged
Curiosity is a powerful motivator for learning. WHAT.EDU.VN encourages you to stay curious and engaged by providing you with a platform to explore your interests and discover new passions.
14.3. Join a Community of Learners
When you use WHAT.EDU.VN, you become part of a community of learners who are passionate about knowledge and discovery. Connect with others, share your insights, and learn from each other.
15. Take the Next Step: Ask Your Question Today
Ready to start your journey of discovery? Don’t wait any longer. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question. Our experts are standing by to provide you with the answers you need.
15.1. Empower Yourself with Knowledge
Knowledge is power. By asking questions and seeking answers, you empower yourself to make informed decisions, solve problems, and achieve your goals.
15.2. Join the WHAT.EDU.VN Community
Join our growing community of curious minds and knowledge seekers. Together, we can explore the world, discover new insights, and make a positive impact on society.
15.3. Your Questions, Our Answers
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with the answers you need. No question is too big or too small. Ask away, and let us help you on your journey of learning and discovery.
Understanding generational cohorts provides valuable insights into societal trends and individual experiences. Knowing what generation is 1996 helps clarify the distinction between Millennials and Generation Z, enhancing our understanding of their unique characteristics and perspectives. Explore these concepts further and get your questions answered at WHAT.EDU.VN, your go-to source for free and reliable information.
Ready to explore further? Visit what.edu.vn today to ask your questions and connect with our community of experts. We are located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Let us help you find the answers you’re looking for.