What is an adjective with examples? An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun, adding detail and color to our language. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of clear and accessible information. This guide will explore adjectives, their functions, and provide many examples, helping you master their usage. Discover the power of descriptive words with us and enhance your understanding. Explore how adjectives function, their different forms, and improve your writing today with our guide.
1. Adjective Definition
An adjective is a word that modifies a noun or pronoun, providing extra information about its qualities, characteristics, or attributes. They can describe size, shape, color, origin, and many other qualities. For instance, in the phrase “the blue car,” the adjective blue describes the color of the car. Adjectives enhance the meaning of nouns and pronouns they accompany.
2. How to Use Adjectives Effectively
Adjectives help readers understand what kind or how much/many of something you’re referring to.
Example: Use five red roses in the bouquet.
Here, five and red are adjectives modifying roses.
When using multiple adjectives, separate them with a comma or conjunction.
Example: I want a small, friendly dog.
My dog is small and friendly.
3. Adjectives Modify Nouns
Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns. They don’t modify verbs, adverbs, or other adjectives.
Example: She wore a beautiful dress to the party.
Furry cats need regular grooming.
I need ten apples for the pie.
The tallest building in the city is the Empire State Building.
Adjectives usually appear before the nouns they modify, but they can also modify nouns without directly preceding them. This occurs with linking verbs and predicate adjectives.
A linking verb (like to be, to feel, to seem) describes a state of being or sensory experience rather than an action.
Example: The sky is blue.
It smells delicious in here.
Driving is faster than biking.
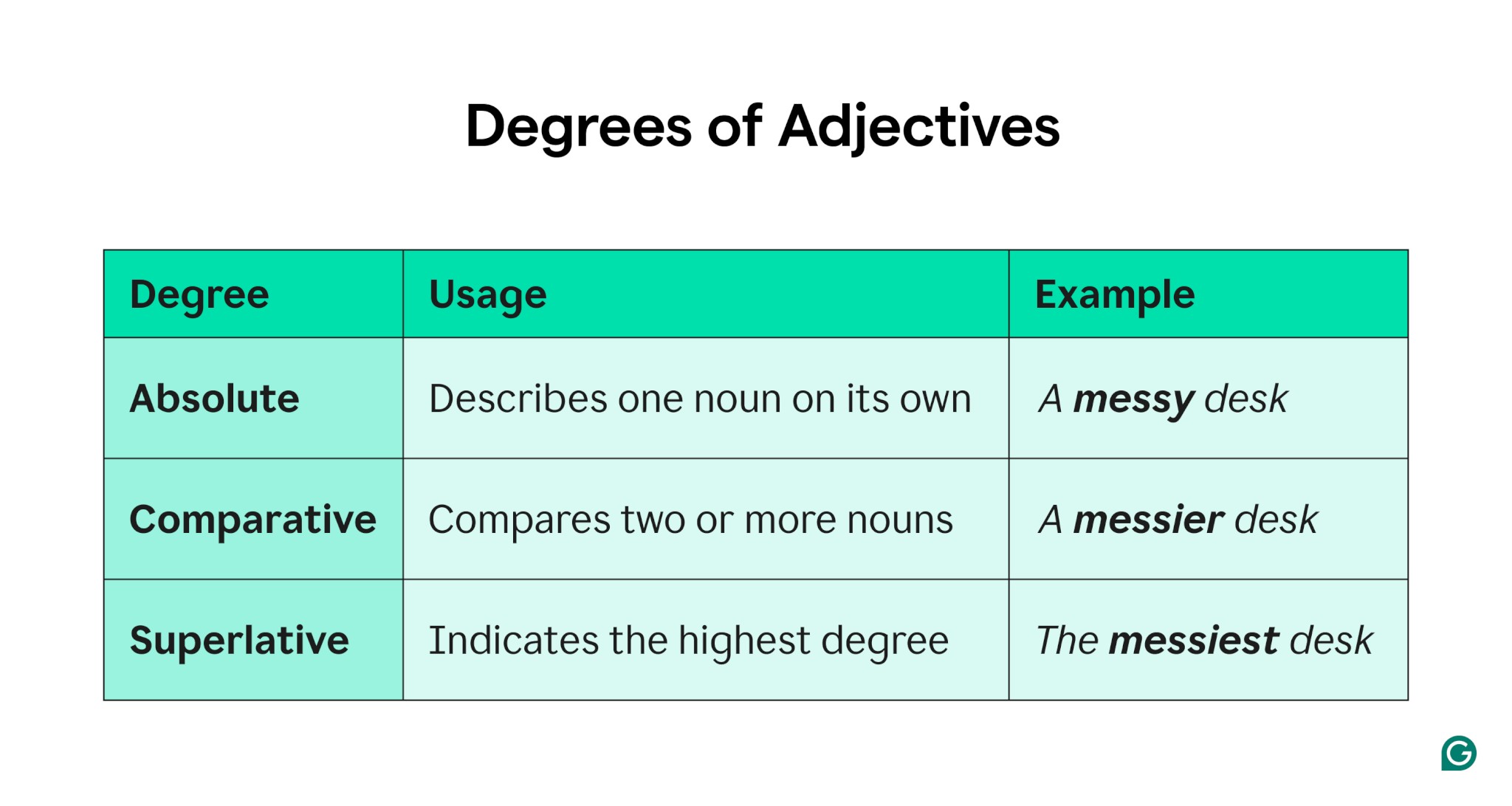
4. Degrees of Adjectives
Adjectives have three degrees: absolute, comparative, and superlative.
4.1. Absolute Adjectives
Absolute adjectives describe a quality in an absolute sense, without comparison. These qualities generally can’t be modified or intensified.
Examples:
- A unique experience
- A perfect score
- A round ball
- An empty glass
- A wooden table
- A daily routine
4.2. Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives compare two or more things.
- For one-syllable adjectives, add -er.
- For two-syllable adjectives, some use -er, others use more. Adjectives ending in -er, -le, -ow, -ure, or -y usually use -er (changing y to -ier).
- For three or more syllables, use more.
Examples:
- A larger car
- A happier person
- A more beautiful painting
- A more interesting book
- A wider road
- A busier street
4.3. Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives indicate the highest degree of a quality.
- One-syllable adjectives add -est.
- Some two-syllable adjectives use -est, others use most. Adjectives ending in -y usually change -y to -iest.
- Adjectives with three or more syllables use most.
- Superlative adjectives usually use the definite article the.
Examples:
- The largest house
- The happiest day
- The most beautiful flower
- The most interesting movie
- The widest river
- The busiest city
5. Coordinate Adjectives
Coordinate adjectives modify the same noun equally and are separated by a comma or the word and.
Example: It was a long, cold winter.
Her tireless and dedicated work made a difference.
Sometimes, adjectives form a single semantic unit with the noun, and no comma is needed.
Example: My favorite blue shirt is torn.
He found an old silver coin.
To test if adjectives are coordinate:
- Insert and between the adjectives. If it sounds natural, they are coordinate.
- Switch the order of the adjectives. If the phrase still works, they are coordinate.
6. Order of Adjectives
Adjectives follow a specific order in a sentence.
The general order is:
- Quantity or Number
- Quality or Opinion
- Size
- Age
- Shape
- Color
- Origin
- Material
- Type
- Purpose
Example: the two beautiful small old round blue French cotton shirts
7. Compound Adjectives
Compound adjectives combine two or more words, often linked with hyphens, to describe a noun.
Examples:
- A well-written essay
- A fast-paced game
- A blue-eyed child
When the compound adjective follows the noun, the hyphen is usually dropped.
Example: The essay was well written.
Adverbs modifying adjectives are not hyphenated.
Example: A very well written essay.
Common compound adjective forms:
8. Adjectives vs. Adverbs
Adjectives modify nouns; adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs.
A common mistake is using an adverb when a predicate adjective is needed.
Example:
Incorrect: I feel badly.
Correct: I feel bad.
Feel is a linking verb, so it requires an adjective to describe what you feel, not how you feel the action of feeling.
Example showing the distinction:
Max smells badly (Max has a weak sense of smell).
Max smells bad (Max has an unpleasant odor).
9. Nouns as Adjectives and Adjectives as Nouns
Sometimes, nouns can function as adjectives, and adjectives can function as nouns.
Noun as adjective:
Example: A history book.
Adjective as noun (often with the):
Example: The poor need our help.
Other examples:
Our English class took our final this morning.
Camille tends to focus on intangibles like communication style and a sense of camaraderie when deciding whether to accept a job offer.
10. Adjective Usage Advice
Use adjectives to be precise, but avoid unnecessary adjectives. Good writing is concise. Choose the right noun to eliminate unnecessary adjectives.
Examples:
Instead of “a big house,” use “a mansion.”
Instead of “a large crowd,” use “a throng.”
Instead of “a mixed-breed dog,” use “a mutt.”
11. Examples of Adjectives
To provide a comprehensive understanding, let’s explore various categories of adjectives with examples:
11.1. Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives provide information about the qualities or characteristics of a noun.
- Color: red, blue, green, yellow, purple
- Size: big, small, large, tiny, huge
- Shape: round, square, triangular, oval
- Texture: smooth, rough, soft, hard
- Taste: sweet, sour, bitter, salty
- Smell: fragrant, pungent, musty, fresh
- Sound: loud, quiet, noisy, silent
- Appearance: beautiful, ugly, pretty, handsome
- Personality: kind, cruel, friendly, shy
- Condition: healthy, sick, broken, repaired
- Origin: American, Italian, Chinese, French
Examples in sentences:
- The red rose smelled fragrant.
- A large and round table stood in the center of the room.
- The smooth stone felt cool to the touch.
- She had a friendly and outgoing personality.
- He enjoyed Italian food.
11.2. Quantitative Adjectives
Quantitative adjectives indicate the quantity or amount of a noun.
- Numbers: one, two, three, four, five
- General Quantities: some, many, few, several, all
- Indefinite Quantities: much, little, enough, plenty
Examples in sentences:
- I have three apples.
- Many people attended the concert.
- She has few friends.
- He drank much water after the race.
- There is enough food for everyone.
11.3. Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives point out specific nouns. They include this, that, these, and those.
- This: Used for singular nouns that are near.
- That: Used for singular nouns that are far.
- These: Used for plural nouns that are near.
- Those: Used for plural nouns that are far.
Examples in sentences:
- This book is interesting.
- That car is fast.
- These flowers are beautiful.
- Those birds are singing.
11.4. Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives show ownership or possession. They include my, your, his, her, its, our, and their.
- My: Belonging to me.
- Your: Belonging to you.
- His: Belonging to him.
- Her: Belonging to her.
- Its: Belonging to it.
- Our: Belonging to us.
- Their: Belonging to them.
Examples in sentences:
- My car is blue.
- Your house is big.
- His job is interesting.
- Her dress is beautiful.
- The dog wagged its tail.
- Our team won the game.
- Their parents are kind.
11.5. Interrogative Adjectives
Interrogative adjectives are used to ask questions about nouns. They include what, which, and whose.
- What: Used to ask about the identity or nature of something.
- Which: Used to ask about a choice between options.
- Whose: Used to ask about ownership.
Examples in sentences:
- What book are you reading?
- Which car is yours?
- Whose pen is this?
11.6. Distributive Adjectives
Distributive adjectives refer to individual members of a group. They include each, every, either, and neither.
- Each: Refers to individual items in a group.
- Every: Refers to all items in a group collectively.
- Either: Refers to one of two options.
- Neither: Refers to none of two options.
Examples in sentences:
- Each student received a prize.
- Every dog needs love.
- You can choose either option.
- Neither answer is correct.
11.7. Proper Adjectives
Proper adjectives are formed from proper nouns and modify other nouns. They are always capitalized.
Examples:
- American history
- Italian food
- Shakespearean drama
- Victorian architecture
- Christian values
11.8. Adjectives of Time
Adjectives of time describe when something happens or its duration.
- Daily routine
- Weekly meeting
- Monthly report
- Annual event
- Ancient history
- Modern art
11.9. Adjectives of Measurement
Adjectives of measurement describe the size, weight, or capacity of a noun.
- Long road
- Short distance
- Heavy box
- Light load
- Wide river
- Narrow path
11.10. Evaluative Adjectives
Evaluative adjectives express an opinion or judgment about a noun.
- Good idea
- Bad decision
- Excellent performance
- Terrible mistake
- Wonderful experience
- Awful weather
Understanding and using these different types of adjectives can greatly improve your writing and communication skills.
12. Common Mistakes in Adjective Usage
Even with a good understanding of adjectives, some common mistakes can occur. Here are a few to watch out for:
- Misusing Adjectives and Adverbs: As mentioned earlier, confusing adjectives and adverbs is a common mistake. Remember that adjectives modify nouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
- Incorrect Comparative and Superlative Forms: Make sure to use the correct comparative and superlative forms of adjectives. For example, “good” becomes “better” (comparative) and “best” (superlative), not “gooder” and “goodest.”
- Using Double Negatives: Avoid using double negatives with adjectives. For example, instead of saying “He is not unkind,” say “He is kind.”
- Incorrect Order of Adjectives: Be mindful of the correct order of adjectives when using multiple adjectives to describe a noun.
- Redundant Adjectives: Avoid using adjectives that add no new information or are already implied by the noun. For example, saying “a round circle” is redundant because all circles are round.
- Misplaced Adjectives: Ensure that adjectives are placed close to the nouns they modify to avoid confusion. For example, instead of saying “I saw a dog running down the street, which was small,” say “I saw a small dog running down the street.”
- Using “Real” vs. “Really”: “Real” is an adjective, while “really” is an adverb. Avoid using “real” to modify a verb or adjective. For example, say “I am really tired,” not “I am real tired.”
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can improve the accuracy and clarity of your writing.
13. How to Improve Your Adjective Usage
Improving your adjective usage involves expanding your vocabulary, practicing writing, and seeking feedback. Here are some tips to help you enhance your skills:
- Read Widely: Reading a variety of texts exposes you to different writing styles and a wide range of adjectives. Pay attention to how authors use adjectives to create vivid descriptions and convey specific meanings.
- Use a Thesaurus: A thesaurus can help you find synonyms for common adjectives, allowing you to add variety and precision to your writing.
- Practice Writing Regularly: The more you write, the more comfortable you will become with using adjectives effectively. Try writing descriptive paragraphs or short stories and focus on incorporating a variety of adjectives.
- Seek Feedback: Ask friends, teachers, or writing partners to review your work and provide feedback on your adjective usage. They can help you identify areas where you can improve and offer suggestions for better word choices.
- Keep a Vocabulary Journal: Write down new adjectives you encounter in your reading, along with their definitions and example sentences. Review your journal regularly to reinforce your learning.
- Play Word Games: Word games like Scrabble and Boggle can help you expand your vocabulary and improve your ability to think of descriptive words quickly.
- Use Online Resources: Many websites and apps offer exercises and quizzes to help you practice using adjectives correctly.
14. Adjective FAQs
14.1. What is an adjective?
An adjective is a word that describes the traits, qualities, or number of a noun.
14.2. What are examples of adjectives?
Descriptive words like beautiful, smooth, and heavy are all adjectives, as are numbers (twelve eggs).
14.3. What is the difference between adjectives and adverbs?
Adjectives modify nouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. For example, in the phrase very funny movie, funny is an adjective describing the noun movie, and very is an adverb describing the adjective funny.
14.4. Can adjectives modify adverbs?
Adjectives can modify only nouns. Only adverbs can modify other adverbs.
15. Need More Help? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
Do you have questions about adjectives or any other topic? Don’t struggle alone! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a free platform where you can ask any question and receive quick, accurate answers from knowledgeable individuals. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, we’re here to help.
15.1. Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free: Ask as many questions as you like without any cost.
- Fast: Get answers quickly from our community of experts.
- Accurate: Receive reliable information from knowledgeable sources.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is simple and intuitive to navigate.
- Comprehensive: Ask about any topic, from grammar to science to history.
15.2. How to Get Started
- Visit our website at WHAT.EDU.VN.
- Create a free account.
- Ask your question in the designated area.
- Receive answers from our community of experts.
15.3. Example Questions
- What is the difference between a simile and a metaphor?
- How do I calculate the area of a triangle?
- What are the main causes of climate change?
- Can someone explain the theory of relativity in simple terms?
No matter what your question is, we’re here to help you find the answers you need.
16. Conclusion
Adjectives are essential for adding detail and clarity to your writing. By understanding their functions, degrees, and proper usage, you can significantly improve your communication skills. Remember to use adjectives purposefully, choose the right words, and avoid common mistakes. And if you ever need help with adjectives or any other topic, don’t hesitate to ask WHAT.EDU.VN. We’re here to provide you with the free, accurate, and fast answers you need. Visit us today at WHAT.EDU.VN and start asking your questions!
For further assistance, contact us at:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
We are here to provide you with fast, reliable, and cost-free answers to all of your questions. We understand the challenges you encounter when seeking quick solutions. That’s why WHAT.EDU.VN is committed to offering a user-friendly platform where you can easily post your questions and receive prompt responses from knowledgeable community members. Don’t hesitate any longer—visit what.edu.vn today and pose your questions. Our team is ready to support you!