Are you curious about vehicle emissions and how they’re controlled? What Is A Catalytic Converter? WHAT.EDU.VN explains what it is, how it works, and why it’s crucial for reducing pollution from your car. We break down the science in a way that’s easy to understand, offering clear explanations and valuable insights into this essential automotive component. Learn about exhaust system, pollution control, and emission standards to understand its importance.
1. What Is a Catalytic Converter and Why Is It Important?
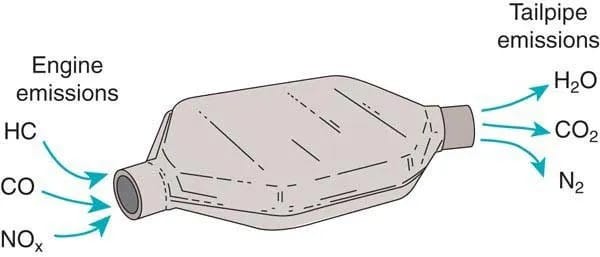
A catalytic converter is a vital component of your car’s exhaust system. It plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions. It transforms toxic gases produced by your engine into less harmful substances. These substances include water vapor and carbon dioxide. This process helps your vehicle meet emission standards and contributes to cleaner air. Understanding what a catalytic converter is and how it functions is essential for both environmental awareness and vehicle maintenance.
2. How Does a Catalytic Converter Work?
The catalytic converter is located beneath your vehicle. It looks like a metallic box with two pipes extending from it. It utilizes a catalyst to convert harmful emissions into safer gases, such as steam. Gases enter through the input pipe, connected to the engine. They then pass over the catalyst. This process triggers a chemical reaction, breaking down pollutants. The less harmful gases then exit through the output pipe, which leads to the car’s tailpipe. The effectiveness of the catalytic converter ensures that your vehicle complies with environmental regulations.
2.1 What is the Core Purpose of Catalytic Converters?
The main purpose of catalytic converters is to minimize the release of harmful pollutants. These pollutants come from the exhaust gases produced by an engine. By converting these gases into less harmful substances, catalytic converters significantly reduce air pollution. This process not only benefits the environment. It also helps maintain vehicle performance and ensures compliance with environmental standards. The role of catalytic converters is indispensable in modern automotive systems.
3. What Are the Components Inside a Catalytic Converter?
Inside a catalytic converter, the catalyst is generally composed of platinum or similar metals, such as rhodium or palladium. Gases pass through a ceramic honeycomb structure within the converter housing. This structure is lined with metals that perform specific tasks to reduce emissions.
3.1 Reduction Catalysts
Reduction catalysts are designed to decrease nitrogen oxide pollution. They achieve this by eliminating oxygen. Nitrogen oxides are broken down into harmless nitrogen and oxygen gases.
3.2 Oxidation Catalysts
Oxidation catalysts convert carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. This is achieved by adding oxygen.
Near the catalytic converter, an oxygen (O2) sensor is located. This sensor informs the car’s electronic control unit (ECU) about the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. This allows the engine to operate with a more efficient air/fuel ratio, ensuring the converter has enough oxygen for oxidation.
4. What Are the Different Types of Catalytic Converters?
There are two primary types of catalysts: reduction and oxidation. These catalysts are utilized within exhaust systems to handle specific gases. The presence of a reduction catalyst depends on the vehicle’s year and type of catalytic converter.
4.1 Two-Way Catalytic Converters
Two-way catalytic converters were used in vehicles in the United States until 1981. They solely consist of oxidation catalysts. These catalysts convert carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. They also convert hydrocarbons (unburned and partially burned fuel) into carbon dioxide and water.
4.2 Three-Way Catalytic Converters
Since 1981, three-way catalytic converters have been the standard. These perform the same functions as two-way converters but also include a reduction catalyst. As mentioned earlier, the reduction catalyst converts nitrogen oxides into nitrogen and oxygen gases.
Diesel engines utilize two-way catalysts. These converters are specifically designed to work with diesel exhausts. The converters target particulates known as soluble organic fractions. These are made from hydrocarbons attached to soot.
5. Who Invented the Catalytic Converter and When?
The catalytic converter’s origins can be traced to the late 19th century. Prototypes were developed in France during that time. In the mid-1950s, Eugene Houdry, a French mechanical engineer, patented catalytic converters for gasoline engines.
Houdry’s motivation stemmed from his concern about air pollution caused by smokestacks and automobile exhaust. He had observed studies in Los Angeles. He started working on converters for smokestacks.
Catalytic converters were further developed following emissions control regulations in the early 1960s. In 1973, the first production catalytic converter was created at Engelhard Corporation. Widespread use began around 1975.
6. How Can You Prevent Catalytic Converter Theft?
Catalytic converters are frequently targeted by thieves. This is because they contain valuable precious metals. Thefts commonly occur on vehicles with higher ground clearance. This makes the part easier to access.
Regardless of your vehicle type, you can take steps to deter theft:
- Park in well-lit areas near building entrances when secure garages are unavailable.
- Weld the catalytic converter to the vehicle frame. This makes removal more difficult.
- Consider purchasing an aftermarket part, like a metal cage, to cover the converter.
- Install a car alarm with a vibration alert sensor.
- Engrave your vehicle identification number (VIN) on the converter. This can deter resale and help identify it if stolen.
7. What Are the Signs of Catalytic Converter Issues?
When a catalytic converter malfunctions, several symptoms may arise, given its role in the exhaust system.
Some signs to watch for include:
- Declining Fuel Efficiency: A clogged catalytic converter can reduce airflow through the engine. The engine may burn more fuel, resulting in reduced fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: While a check engine light can indicate various issues, vehicles manufactured after 1996 have a diagnostic system that tests the catalytic converter. A malfunctioning converter can trigger the warning light. This is because the air-to-fuel ratio sensors detect issues.
- Smelling Rotten Eggs: Internal damage to the catalytic converter can hinder its ability to convert exhaust gases. This can result in a sulfuric “rotten egg” smell.
- Issues Starting the Engine: Exhaust gases need to escape. A clogged catalytic converter can impede this process. This can increase exhaust pressure, causing the car to sputter or stall during startup.
- Poor Acceleration: Trapped exhaust and increased pressure from a clogged converter can cause acceleration problems. You might experience jerking or stalling.
- Failed Emissions Test: Many states require regular emissions testing. Failing this test often indicates a problem with the catalytic converter. This may be accompanied by other symptoms.
8. Common Questions About Catalytic Converters
8.1 Why Are Catalytic Converters Stolen?
Catalytic converters are often stolen due to the valuable precious metals they contain. These metals, including platinum, palladium, and rhodium, can be sold to metal dealers. The high value of these materials makes catalytic converters a prime target for thieves. Protecting your catalytic converter is crucial to prevent theft and costly replacements.
8.2 What Materials Are Found Inside Catalytic Converters?
A standard catalytic converter typically contains between 3 to 7 grams of platinum. It also includes 2 to 7 grams of palladium and 1 to 2 grams of rhodium. These precious metals act as catalysts, facilitating the chemical reactions that convert harmful gases into less toxic substances. Their presence is essential for the converter’s functionality and efficiency.
8.3 What Is the Monetary Value of a Catalytic Converter?
A recycler may pay between $50 and $250 for a catalytic converter. Some, especially those from hybrid vehicles, can fetch $800 to $1,500. Replacing a stolen catalytic converter can cost around $2,000. This is a significant reason to take preventive measures against theft. The high replacement cost underscores the importance of protecting this vital automotive component.
8.4 How Long Does a Catalytic Converter Typically Last?
A catalytic converter typically lasts between 70,000 and 100,000 miles. However, its lifespan can vary depending on the vehicle type, usage patterns, and maintenance habits. Regular maintenance and careful driving can help extend the life of your catalytic converter. Monitoring its performance and addressing issues promptly can prevent costly replacements.
8.5 Can a Catalytic Converter Be Cleaned or Repaired?
Catalytic converters can often be cleaned. Repairing them, however, is generally not feasible due to their construction and materials. Cleaning involves specific chemical treatments. These remove carbon and other substance deposits.
This process can restore some functionality. This is particularly true if the converter is not heavily damaged. Physical damage or severe clogging often requires replacement. This clogging is often caused by internal melting or breakdown. Replacement becomes necessary in such cases.
9. Interested in Automotive Systems?
Are you fascinated by what goes on under the hood of a car? You might want to think about a future in the automotive industry.
At Universal Technical Institute, you can train to become an automotive technician in as little as 51 weeks in the Automotive Technology program. You’ll take courses that prepare you for roles that provide insight into catalytic converters, exhaust systems, and more.
Want to learn more? Request information here on our site. Or, call 1-800-834-7308. Start taking steps toward your future today]
10. WHAT.EDU.VN: Your Source for Free Answers
Navigating the complexities of automotive systems can be challenging. Finding reliable, quick, and free answers to your questions shouldn’t be a struggle. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand these challenges and provide a platform where you can ask any question and receive expert responses without any cost.
10.1 Facing Difficulties in Finding Answers?
Are you finding it hard to get clear, concise answers to your questions? Do you spend hours searching without success? WHAT.EDU.VN is here to change that. We offer a seamless way to ask questions and get the information you need quickly and easily.
10.2 Need Expert Advice Without the Cost?
Worried about expensive consultation fees? At WHAT.EDU.VN, you can access expert advice for free. Our platform connects you with knowledgeable professionals who are ready to answer your questions accurately and efficiently.
10.3 Join Our Community of Curious Minds
WHAT.EDU.VN is more than just a question-and-answer site; it’s a community. Connect with other users, share your knowledge, and learn from diverse perspectives. Our platform is designed to foster collaboration and continuous learning.
10.4 Easy Access to Knowledge
Our user-friendly interface ensures that asking questions and receiving answers is straightforward. Whether you’re using a computer or a mobile device, WHAT.EDU.VN provides a hassle-free experience.
10.5 We’re Here to Help
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing a reliable and accessible platform for everyone seeking answers. Our mission is to empower you with the knowledge you need, when you need it, without any barriers.
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the ease of getting free, expert advice.
Ready to get your questions answered?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN now and ask your question for free. Our team of experts is ready to provide you with the answers you need.
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Let what.edu.vn be your go-to resource for all your questions. We’re here to help you find the answers you’re looking for, quickly and easily.