Are you puzzled about what a fuse is and how it safeguards your electrical devices? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we offer simple, free answers to all your questions. Discover the essential role of fuses in electrical safety and circuit protection. Learn about circuit protection, electrical safety, and overload protection to ensure your systems are secure.
1. Why Electrical Circuit Protection Matters
Electrical circuit protection is crucial. It identifies and resolves issues before they escalate into severe problems. Without it, minor electrical faults can lead to power outages, damaged equipment, or even fires. Think of it as a safety net, preventing small problems from becoming catastrophic.
- Prevents Power Loss: Circuit protection ensures a stable power supply by addressing minor issues before they cause a complete shutdown.
- Protects Equipment: Excessive current and heat can damage or destroy expensive equipment. Circuit protection prevents this, saving businesses and homeowners significant repair or replacement costs.
- Reduces Fire Risk: Faulty circuits can cause fires. Circuit protection intervenes early, preventing overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Avoids Arc Flash: Short circuits can lead to arc flashes, which are dangerous and can cause severe burns or even death. Proper circuit protection minimizes this risk.
Electrical circuit protection is a necessity for safe and reliable electricity use every day. If you have more questions about circuit protection and how to implement it in your home or business, visit WHAT.EDU.VN for free answers. Our experts are ready to help.
2. Defining an Electric Fuse
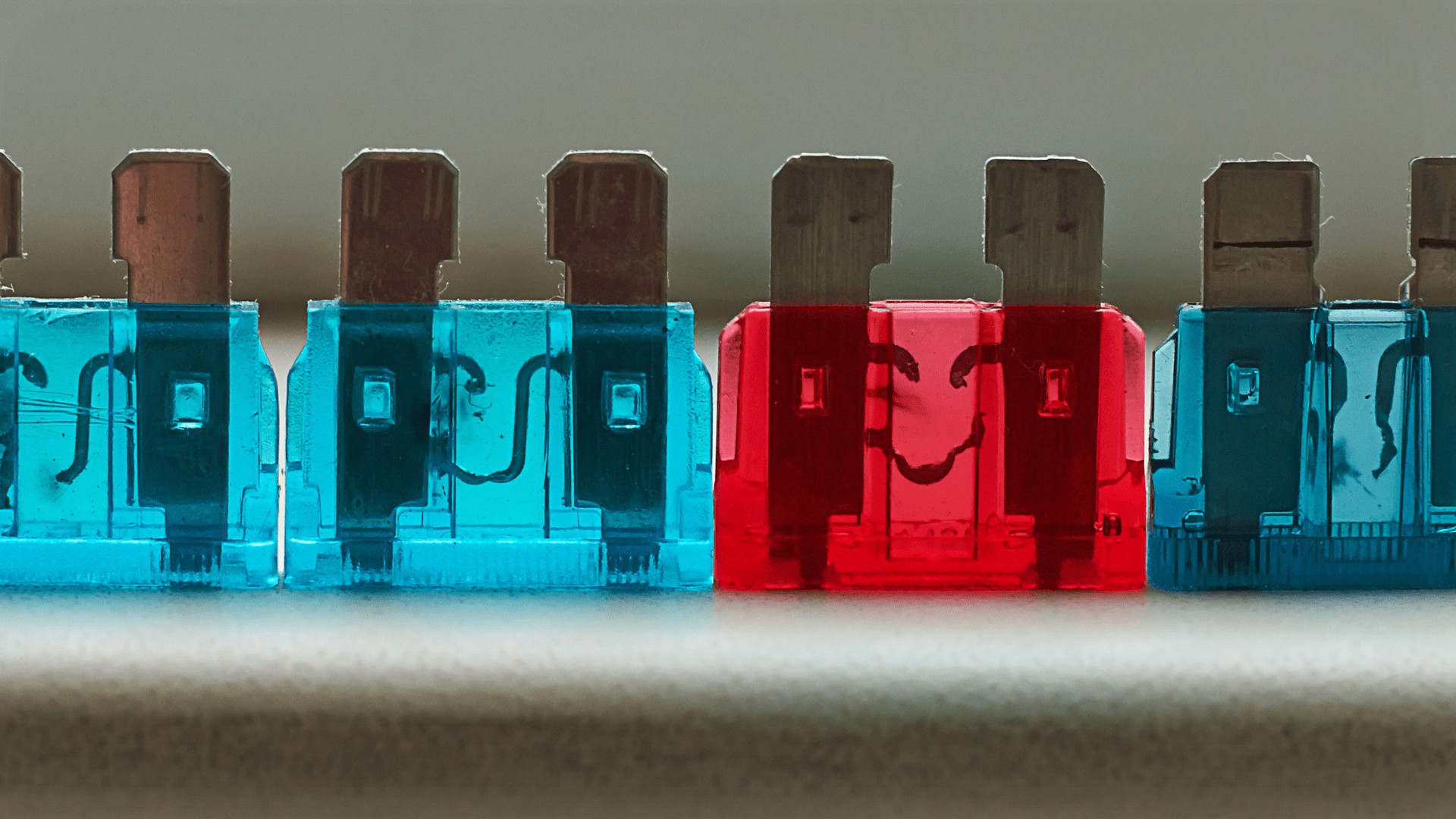
What Is A Fuse? An electric fuse is a safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from overcurrent. It contains a thin wire or strip of metal that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a safe level. This prevents damage to the circuit and connected devices.
- Simple Design: Fuses are intentionally designed as the weakest point in a circuit.
- Sacrificial Role: A fuse sacrifices itself to protect the rest of the circuit.
- Overcurrent Protection: When excessive current flows through the fuse, the wire inside melts, interrupting the current flow.
Fuses are commonly found in cars, appliances, and electronic devices. They are typically located near the power source to protect the wiring and components further down the line. If you’re unsure about the type of fuse your system needs, ask the experts at WHAT.EDU.VN for guidance.
3. Electric Fuse vs. Circuit Breaker
What is a fuse’s alternative? A circuit breaker is another type of protection device that can be used instead of a fuse. While both devices interrupt the flow of electricity when a fault occurs, they operate differently.
| Feature | Electric Fuse | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Melts and breaks the circuit | Opens a switch to interrupt the circuit |
| Sensitivity | More sensitive | Less sensitive |
| Reusability | Single-use; must be replaced after blowing | Reusable; can be reset after tripping |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Failure Rate | Less prone to failure | More prone to failure |
| Common Use Cases | Sensitive circuitry, energy sources like batteries | Homes, where resetting is convenient |
| Response Time | Faster | Slower |

While circuit breakers are more convenient due to their reusability, fuses offer faster and more sensitive protection. They are often preferred in applications where even minor overcurrents need to be detected quickly. Still have questions? WHAT.EDU.VN provides fast, free answers.
4. Ideal Applications for Fuses
Fuses are best used in scenarios where quick response and sensitivity are crucial. They are commonly placed near energy sources, such as batteries and solar panels, and in sensitive circuitry.
- Next to Energy Sources: Fuses protect against faults originating from batteries, solar panels, and grid connections.
- Sensitive Circuitry: Fuses react quickly to protect sensitive electronic devices from damage.
- Circuit Coordination: Using a fuse upstream from a smaller fuse ensures that the smaller fuse blows first, keeping the rest of the circuit online.
A well-coordinated circuit design uses fuses strategically to protect different components and ensure that only the necessary sections of the circuit are interrupted in the event of a fault.
5. How to Choose the Correct Fuse Size
Selecting the right fuse size is essential for effective circuit protection. An undersized fuse can cause unnecessary interruptions, while an oversized fuse may not provide adequate protection.
- Calculate Maximum Current: Determine the maximum current that the circuit will draw continuously.
- Apply Safety Factor: Multiply the maximum current by 1.25 to account for fluctuations.
- Select Fuse Size: Choose a fuse with a rating equal to or slightly higher than the calculated value.
- Consider Wire Size: Ensure the fuse size is appropriate for the wire gauge in the circuit.
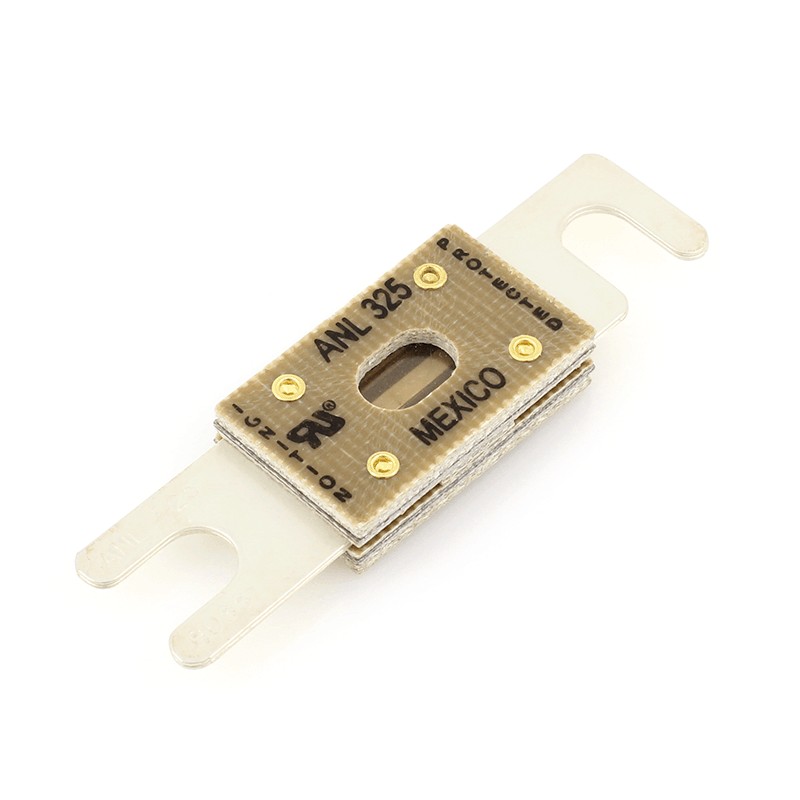
For example, if you are using a 3000-watt, 12-volt inverter, it will draw a maximum of 250 amps (3000 W / 12 V = 250 A). To select the right fuse, multiply 250 amps by 1.25, resulting in 312.5 amps. Choose a 325-amp fuse or the next available size.
Confused about these calculations? Get free assistance from the experts at WHAT.EDU.VN.
6. Ensuring Safety with Properly Installed Fuses
Correctly installed fuses are a critical safety component in any electrical system. They prevent overheating and potential hazards by interrupting the current flow when a fault occurs.
- Overload Protection: A correctly fused circuit will not overheat during an overload.
- Preventing Heat and Explosions: Fuses stop the flow of current, preventing excessive heat or explosions.
- Importance of Quality: Don’t compromise on quality when selecting fuses. They are a vital part of your electrical system’s safety.
Regularly inspect your fuses to ensure they are in good condition and properly sized for your circuits. If you have any concerns or questions about fuse installation, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide the answers you need, absolutely free.
7. FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About Fuses
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary function of a fuse? | The primary function of a fuse is to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent by interrupting the flow of electricity when the current exceeds a safe level, preventing damage to equipment and reducing the risk of fires. |
| How does a fuse work? | A fuse contains a thin strip of metal that melts and breaks the circuit when excessive current flows through it. This sacrificial action prevents further damage by stopping the current. |
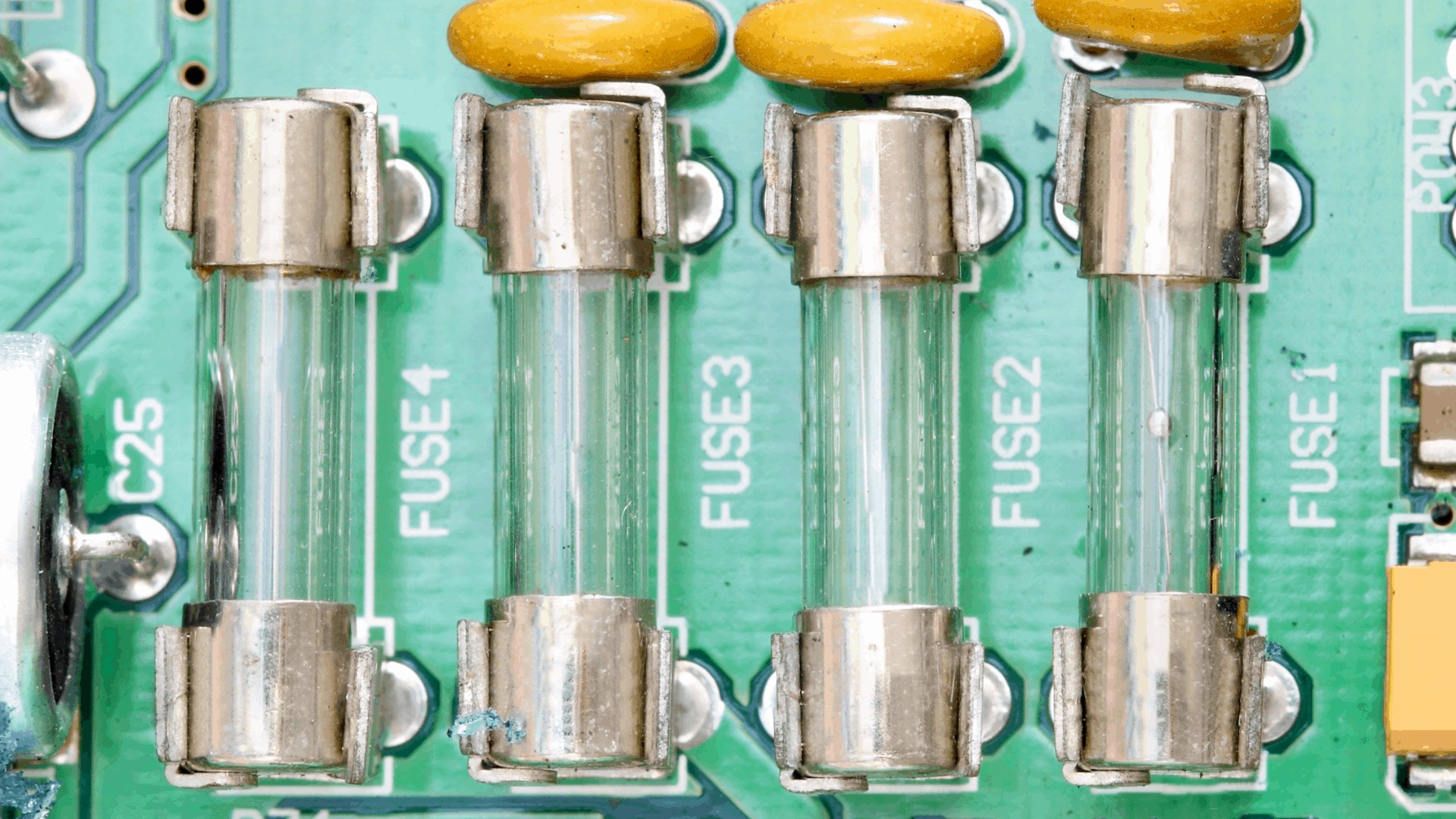
| What are the different types of fuses? | There are various types of fuses, including cartridge fuses, blade fuses (ATO/ATC), glass tube fuses, and ceramic fuses, each designed for specific applications and voltage/current ratings. |
| How do I know when a fuse is blown? | A blown fuse typically shows a visible break in the metal strip inside the fuse. Some fuses have a clear window for easy inspection. You can also use a multimeter to test for continuity. |
| Can I replace a fuse with a higher amperage fuse? | No, never replace a fuse with a higher amperage fuse. Doing so can bypass the circuit’s intended protection and lead to overheating, damage to equipment, or even a fire. Always use a fuse with the same or lower amperage rating. |
| What is the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker? | A fuse is a one-time-use device that melts to break a circuit, while a circuit breaker is a reusable switch that trips to interrupt the circuit. Fuses are generally faster and more sensitive but must be replaced after use, whereas circuit breakers can be reset. |
| Where are fuses commonly used? | Fuses are commonly used in cars, appliances, electronic devices, and electrical panels to protect circuits from overcurrent. They are often located near power sources such as batteries and solar panels. |
| How do I choose the correct fuse size? | To choose the correct fuse size, determine the maximum current the circuit will draw continuously, multiply that value by 1.25, and select a fuse with a rating equal to or slightly higher than the result. Also, ensure the fuse size is appropriate for the wire gauge in the circuit. |
| What happens if I use the wrong size fuse? | Using an undersized fuse can cause nuisance tripping, interrupting the circuit unnecessarily. Using an oversized fuse can bypass the circuit’s protection, leading to overheating, damage to equipment, or a fire. |
| How do I install a fuse correctly? | To install a fuse correctly, ensure the power is off, remove the old fuse, and replace it with a new fuse of the correct size and type. Make sure the fuse is firmly seated in the fuse holder. |
Still have more questions about electrical fuses or circuit protection? Don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN. Our experts are here to provide clear, helpful answers for free.
8. Common Fuse Types and Their Applications
Understanding the different types of fuses and their applications can help you choose the right fuse for your needs. Here are some of the most common types:
| Fuse Type | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Cartridge Fuses | Cylindrical fuses with metal caps on each end, available in various sizes and amperage ratings. | Automotive, appliances, and industrial equipment. |
| Blade Fuses (ATO/ATC) | Plastic body with exposed blades that plug into a fuse block, commonly used in automotive applications. | Automotive electrical systems. |
| Glass Tube Fuses | Fuses enclosed in a glass tube, allowing visual inspection of the fuse element. | Electronic devices, low-voltage circuits. |
| Ceramic Fuses | Fuses enclosed in a ceramic body, providing higher temperature and current ratings than glass tube fuses. | High-power electronic devices, industrial equipment. |
| Surface Mount Fuses (SMD) | Small, rectangular fuses designed to be mounted directly on printed circuit boards. | Circuit protection for PCBs. |
Each type of fuse is designed for specific applications and has different voltage and current ratings. Selecting the right fuse type ensures optimal protection for your electrical circuits.
9. Troubleshooting Common Fuse Problems
Understanding common fuse problems and how to troubleshoot them can save you time and money. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Blown Fuse: If a fuse blows repeatedly, there may be an underlying issue such as an overcurrent or short circuit. Investigate the cause before replacing the fuse.
- Nuisance Tripping: If a fuse trips frequently without an apparent cause, it may be undersized or faulty. Check the fuse rating and consider replacing it with a higher quality fuse.
- Fuse Not Making Contact: Sometimes, a fuse may not make proper contact with the fuse holder, causing intermittent issues. Clean the contacts and ensure the fuse is firmly seated.
By understanding these common problems, you can quickly diagnose and resolve fuse-related issues in your electrical systems.
10. The Future of Fuse Technology
Fuse technology continues to evolve, with advancements in materials, design, and functionality. Some of the latest developments include:
- Smart Fuses: Fuses with built-in monitoring and communication capabilities, allowing for remote monitoring and control.
- Solid-State Fuses: Fuses that use solid-state components to interrupt the current flow, offering faster response times and improved reliability.
- Self-Resetting Fuses: Fuses that automatically reset after a fault condition is cleared, eliminating the need for manual replacement.
These innovations are paving the way for more efficient, reliable, and intelligent circuit protection in the future.
11. E-E-A-T and YMYL Compliance for Fuse Information
When providing information about electrical fuses, it is essential to adhere to E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) and YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) guidelines. This ensures that the information is accurate, reliable, and safe for users.
- Experience: Information should be based on practical experience and real-world testing.
- Expertise: Content should be created by knowledgeable experts in the field of electrical engineering.
- Authoritativeness: Sources should be credible and authoritative, such as industry standards and reputable manufacturers.
- Trustworthiness: Information should be transparent, unbiased, and regularly updated to reflect the latest best practices.
By following these guidelines, we can provide users with trustworthy and reliable information about electrical fuses and circuit protection.
12. The Convenience of Free Answers at WHAT.EDU.VN
Navigating the world of electrical systems can be daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. WHAT.EDU.VN offers a convenient and free platform for asking any questions you may have about fuses, circuit protection, or any other electrical topic. Our goal is to provide you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions and stay safe.
- Free Access: Our services are completely free, making expert advice accessible to everyone.
- Fast Answers: Get quick and accurate answers to your questions from experienced professionals.
- Comprehensive Information: Explore a wide range of topics related to electrical systems and safety.
Don’t let confusion or uncertainty compromise your safety. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get the answers you need to protect your home, business, and loved ones.
13. Real-World Examples of Fuse Protection
To better illustrate the importance of fuses, here are a few real-world examples of how they protect electrical systems:
- Automotive: In a car, fuses protect the various electrical circuits, such as headlights, taillights, and the radio. If there’s a short circuit in the headlight wiring, the fuse will blow, preventing damage to the entire electrical system.
- Home Appliances: Fuses in appliances like refrigerators and washing machines protect against overloads. If the motor starts drawing excessive current, the fuse will blow, preventing the motor from burning out.
- Electronics: Fuses in electronic devices like computers and TVs protect sensitive components from power surges. If there’s a surge, the fuse will blow, preventing damage to the internal circuitry.
- Solar Power Systems: Fuses are crucial in solar power systems to protect against overcurrents and short circuits. They protect the expensive batteries and inverters from damage.
These examples highlight the vital role that fuses play in safeguarding electrical systems in various applications.
14. How to Test a Fuse with a Multimeter
Testing a fuse with a multimeter is a simple process that can help you determine if it’s blown. Here’s how:
- Set the Multimeter: Set your multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a sound wave symbol).
- Power Off: Ensure the circuit is de-energized before testing the fuse.
- Remove the Fuse: Remove the fuse from its holder.
- Connect Probes: Place one probe of the multimeter on each end of the fuse.
- Check for Continuity: If the multimeter beeps or displays a value close to zero ohms, the fuse is good. If it doesn’t beep or displays an infinite resistance, the fuse is blown.
This simple test can quickly tell you whether a fuse needs to be replaced.
15. Safety Precautions When Working with Fuses
When working with fuses, it’s essential to follow safety precautions to prevent electrical shock and injury:
- De-Energize the Circuit: Always turn off the power to the circuit before working with fuses.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools to handle fuses and avoid contact with live wires.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from sparks or debris.
- Follow Instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when installing or replacing fuses.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of electrical accidents.
16. Fuse Standards and Certifications
Fuses are subject to various industry standards and certifications to ensure their quality and safety. Some of the most common standards include:
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories): UL certification indicates that a fuse has been tested and meets safety requirements.
- CSA (Canadian Standards Association): CSA certification indicates that a fuse meets Canadian safety standards.
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): IEC standards provide a global framework for fuse design and performance.
When selecting fuses, look for products that are certified by these organizations to ensure they meet industry standards.
17. Environmental Considerations for Fuse Disposal
Fuses contain small amounts of metal and other materials that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. Follow these guidelines for environmentally responsible fuse disposal:
- Recycle Metal Components: If possible, recycle the metal components of the fuse.
- Dispose of Properly: Dispose of the fuse in accordance with local regulations for electronic waste.
- Avoid Landfills: Avoid disposing of fuses in landfills, where they can leach harmful substances into the soil and water.
By following these guidelines, you can minimize the environmental impact of fuse disposal.
18. Ask Your Questions at WHAT.EDU.VN
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding reliable answers to your questions can be challenging. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive free, expert advice. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, we’re here to help.
- Completely Free: Our services are 100% free, with no hidden fees or subscriptions.
- Expert Advice: Get answers from experienced professionals who are passionate about sharing their knowledge.
- Easy to Use: Our website is easy to navigate, making it simple to find the information you need.
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get the answers you deserve. Our address is 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us on Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Our website is WHAT.EDU.VN.
19. How Fuses Contribute to Home Safety
Fuses are a critical component of home safety, preventing electrical fires and protecting valuable appliances and electronics. By interrupting the flow of electricity during an overload or short circuit, fuses minimize the risk of overheating and potential hazards.
- Preventing Electrical Fires: Fuses prevent electrical fires by stopping the flow of current when a fault occurs.
- Protecting Appliances: Fuses protect appliances from damage by preventing excessive current from reaching sensitive components.
- Ensuring Family Safety: Fuses help ensure the safety of your family by minimizing the risk of electrical accidents.
Regularly check your home’s fuses to ensure they are in good condition and properly sized for your circuits.
20. Fuses in Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power, rely heavily on fuses to protect their sensitive components. Fuses safeguard batteries, inverters, and other equipment from overcurrents and short circuits, ensuring the reliable operation of these systems.
- Protecting Batteries: Fuses protect batteries from damage by preventing excessive current from flowing during charging and discharging.
- Safeguarding Inverters: Fuses safeguard inverters from power surges and overloads, ensuring a stable and consistent power supply.
- Ensuring System Reliability: Fuses help ensure the overall reliability of renewable energy systems by minimizing the risk of electrical faults.
By using the correct fuses in your renewable energy system, you can protect your investment and ensure its long-term performance.
21. Understanding Fuse Markings and Ratings
Fuses have various markings and ratings that provide important information about their characteristics and performance. Understanding these markings can help you select the right fuse for your application.
- Amperage Rating: Indicates the maximum current that the fuse can carry before blowing.
- Voltage Rating: Indicates the maximum voltage that the fuse can safely interrupt.
- Time-Delay Characteristics: Indicates how quickly the fuse will blow under different overload conditions (e.g., fast-acting, time-delay).
- Interrupting Capacity: Indicates the maximum fault current that the fuse can safely interrupt.
Refer to the fuse’s markings and ratings to ensure it is suitable for your specific circuit and application.
22. The Role of Fuses in Industrial Equipment
Industrial equipment relies heavily on fuses to protect its complex electrical systems. Fuses safeguard motors, transformers, and other critical components from overcurrents and short circuits, preventing costly downtime and ensuring worker safety.
- Protecting Motors: Fuses protect motors from damage by preventing excessive current from flowing during start-up and operation.
- Safeguarding Transformers: Fuses safeguard transformers from power surges and overloads, ensuring a stable and consistent power supply.
- Ensuring Worker Safety: Fuses help ensure worker safety by minimizing the risk of electrical accidents in industrial environments.
By using the correct fuses in your industrial equipment, you can protect your investment and ensure a safe working environment.
23. Don’t Know Who to Ask? Try WHAT.EDU.VN!
Are you struggling to find the answers you need? Don’t know who to ask? WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help! Our platform provides a convenient and free way to get expert advice on any topic. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, we’re here to provide you with the information you need.
- Ask Anything: Ask any question, no matter how simple or complex.
- Get Expert Answers: Receive answers from experienced professionals in various fields.
- Free and Convenient: Our services are completely free and easy to use.
Stop struggling and start getting the answers you need. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question!
24. Upgrading Your Fuse Protection System
Upgrading your fuse protection system can improve the safety and reliability of your electrical circuits. Consider these upgrades to enhance your system:
- Replace Old Fuses: Replace old and outdated fuses with new, high-quality fuses that meet current safety standards.
- Install Fuse Blocks: Install fuse blocks to provide a secure and organized way to manage your fuses.
- Add Surge Protection: Add surge protection devices to protect your circuits from power surges and transient voltages.
- Use Smart Fuses: Consider using smart fuses with built-in monitoring and communication capabilities for advanced protection.
By upgrading your fuse protection system, you can enhance the safety and reliability of your electrical circuits.
25. Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN for Your Questions?
There are many sources of information available online, but WHAT.EDU.VN stands out as a reliable and trustworthy platform for getting your questions answered. Here’s why you should choose us:
- Free Expert Advice: We provide free access to expert advice from experienced professionals.
- Comprehensive Coverage: We cover a wide range of topics, from electrical systems to renewable energy.
- Easy to Use: Our website is easy to navigate and provides a seamless user experience.
- Community Support: We foster a supportive community where you can connect with other learners and experts.
Choose WHAT.EDU.VN for your questions and experience the difference! We’re located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Contact us on Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890, or visit our website at WHAT.EDU.VN.
Do you need quick, free answers to your burning questions? Visit what.edu.vn now to ask your question and receive expert advice! Don’t wait – your answer is just a click away. Benefit from circuit safeguard, electrical component knowledge, and fuse selection expertise today.
