Geofencing is a location-based technology that uses virtual boundaries to trigger actions when a device enters or exits a specific area, often used in location-based services. Discover how this technology works and its potential benefits at WHAT.EDU.VN. Learn about its possibilities, proximity marketing and location-based advertising.
1. Understanding Geofencing: The Basics
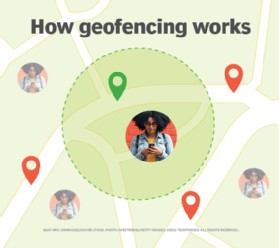
Geofencing is a technology that creates a virtual geographic boundary, enabling software to trigger a response when a device enters or exits that area. This boundary is known as a geofence and relies on technologies like GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi, or cellular data. Let’s delve deeper into the core aspects of geofencing.
1.1. How Does Geofencing Technology Work?
The functionality of geofencing relies on several key components working in harmony.
- Virtual Boundary Creation: An administrator or developer establishes a virtual perimeter around a specific location using GPS or RFID-enabled software.
- Technology Integration: Geofencing technology integrates communication technologies like GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi, and cellular data.
- Triggered Actions: Once set up, a preprogrammed action is triggered automatically when a mobile device or RFID tag crosses the geofence.
- Customization: Virtual boundaries can range from a small area like a building to a larger area such as a city.
1.2. Active vs. Passive Geofences
Geofences can operate in two primary modes: active and passive, each with its own set of requirements and capabilities.
- Active Geofences: Require the end-user to opt into location services and have the mobile app open.
- Passive Geofences: Operate in the background using Wi-Fi and cellular data, providing continuous monitoring.
1.3. User-Defined Geofencing
Beyond business applications, individual users can also set up geofencing in their mobile apps to trigger custom alerts or actions based on location.
- Users can program “if this, then that” commands to automate actions based on their location.
- Reminder apps can send alerts when a user approaches a specific location.
2. The Benefits of Geofencing for Businesses
Geofencing offers numerous advantages for businesses looking to enhance their marketing strategies and improve customer engagement.
2.1. Enhanced Customer Engagement
Geofencing enables businesses to target prospects with engaging messages and attractive offers based on their proximity to a specific location.
- Targets specific demographics within a defined geographical area.
- Enhances customer engagement through personalized and relevant offers.
2.2. Improved Ad Spend Effectiveness
Targeted advertising through geofencing can significantly improve the effectiveness of ad spending.
- Leads to higher engagement numbers due to the relevance of the advertisements.
- Optimizes ad spend by ensuring that ads are delivered to the most receptive audience.
2.3. Competitive Edge
Businesses can use geofencing to draw prospects away from competitors by offering enticing incentives when customers are near a competitor’s location.
- Boosts traffic and sales by attracting customers from competing businesses.
- Provides a unique way to stand out and capture the attention of potential customers.
2.4. Data-Driven Insights
Geofencing provides insightful data that helps marketers improve their campaigns by tracking foot traffic, stay durations, and conversions.
- Combines location data with user online activities and purchase habits for personalized campaigns.
- Enhances user experiences by tailoring offers based on user behavior and preferences.
2.5. Omnichannel Marketing Campaigns
Geofencing allows businesses to create omnichannel marketing campaigns to boost sales and revenues further.
- Integrates location-based marketing with other channels for a cohesive customer experience.
- Enhances overall marketing effectiveness by reaching customers through multiple touchpoints.
3. Real-World Applications of Geofencing
Geofencing has a wide range of applications beyond marketing, impacting various industries and sectors.
3.1. Marketing and Advertising
Geofencing is commonly used to attract more customers to brick-and-mortar businesses.
- Businesses can send in-app notifications when a user enters a geofenced area.
- Restaurants, movie theaters, and salons can send coupons via coupon apps.
- Social media apps and search engines can send targeted ads to users in predefined areas.
3.2. Drone Management
Geofencing can manage drone activity during events or secure sensitive areas.
- Creates temporary no-fly zones during sporting events to prevent drones from entering restricted areas.
- Secures airports, government buildings, and military camps by stopping unauthorized drones.
3.3. Event Engagement
Event organizers can use geofencing to engage with attendees before, during, and after the event.
- Sends notifications about schedules, special events, and networking opportunities.
- Enhances the overall event experience by providing relevant and timely information.
3.4. Shipping and Fleet Management
Geofencing alerts dispatchers when a truck deviates from its planned route.
- Monitors vehicle movements to ensure compliance with delivery schedules and routes.
- Improves logistics and reduces the risk of delays or unauthorized deviations.
3.5. Human Resource Security
Geofencing enhances security by monitoring employee access to restricted areas.
- Sends alerts if an employee attempts to enter an unauthorized geofenced area.
- Ensures that employees only access areas relevant to their job responsibilities.
3.6. Time Management
Geofencing-enabled software tracks employee time and resource use.
- Monitors when employees enter and exit work zones, providing accurate time tracking.
- Improves productivity and accountability by ensuring that employees are present when needed.
3.7. Compliance Management
Geofence crossings can be recorded to document device usage and confirm compliance with established policies.
- Provides a log of when and where devices are used, ensuring adherence to company policies.
- Facilitates audits and helps maintain regulatory compliance.
3.8. Asset Management
Geofencing alerts administrators when company-owned devices leave the premises.
- Locates and secures devices to prevent misuse by unauthorized users.
- Reduces the risk of theft or loss of valuable company assets.
3.9. Law Enforcement
Ankle bracelets use geofencing to alert authorities if an individual under house arrest leaves the premises.
- Monitors the movement of individuals to ensure compliance with court orders.
- Enhances public safety by preventing unauthorized departures.
3.10. Home Automation
When a homeowner’s smartphone enters the home’s geofenced perimeter, the thermostat adjusts itself, or the lights turn on automatically.
- Automates home functions based on proximity, improving comfort and energy efficiency.
- Creates a personalized living environment that responds to the homeowner’s needs.
3.11. Animal Tracking
Pet owners and farmers can set up geofences to alert them when an animal leaves the boundary.
- Tracks animals to prevent them from getting lost or wandering into dangerous areas.
- Provides peace of mind and reduces the risk of animal-related incidents.
4. Setting Up a Geofence: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a geofence involves several steps to ensure that it functions correctly and meets your specific needs.
4.1. Choosing the Right Software
Select geofencing software that aligns with your objectives and technical capabilities.
- Consider ease of use, integration with existing systems, and customization options.
- Evaluate the software’s ability to handle the required number of geofences and devices.
4.2. Defining the Geographical Boundary
Establish the virtual boundary by drawing a circle or polygon around the desired location using mapping tools.
- Use Google Maps API or other mapping platforms to define the geofence accurately.
- Ensure the boundary covers the intended area without unnecessary overlap.
4.3. Configuring Triggers and Actions
Program the actions that will be triggered when a device enters or exits the geofence.
- Set up notifications, alerts, or automated tasks that align with your objectives.
- Customize the triggers to respond to specific events, such as entry, exit, or dwell time.
4.4. Testing and Optimization
Thoroughly test the geofence to ensure it functions correctly and optimize its performance.
- Verify that triggers are firing as expected and that notifications are being delivered accurately.
- Adjust the geofence size and settings as needed to achieve optimal results.
4.5. Monitoring and Maintenance
Continuously monitor the geofence to ensure it remains effective and make adjustments as needed.
- Track performance metrics such as trigger rates and user engagement.
- Update the geofence as needed to reflect changes in the environment or business objectives.
5. Geofencing Technologies and Techniques
Geofencing leverages various technologies and techniques to create and manage virtual boundaries.
5.1. GPS (Global Positioning System)
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information for devices anywhere on Earth.
- Accurately determines the position of a device within a geofenced area.
- Relies on signals from multiple satellites to calculate location with high precision.
5.2. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects.
- Enables geofencing in environments where GPS signals may be unreliable.
- Ideal for tracking assets within a defined area, such as a warehouse or retail store.
5.3. Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi positioning uses the signal strength of nearby Wi-Fi networks to estimate a device’s location.
- Provides location data indoors where GPS signals may be weak.
- Enhances the accuracy of geofencing in urban environments with dense Wi-Fi coverage.
5.4. Cellular Data
Cellular data networks provide location information based on the device’s connection to cell towers.
- Offers a broad estimate of location, suitable for large-scale geofencing applications.
- Requires minimal power consumption, making it ideal for passive geofencing.
6. The Future of Geofencing
Geofencing is continuously evolving, with new technologies and applications emerging regularly.
6.1. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things)
Geofencing is increasingly integrated with IoT devices, enabling new possibilities for automation and control.
- Smart home devices can respond to geofencing triggers, creating a seamless and personalized experience.
- Industrial IoT devices can be monitored and managed based on their location within a geofenced area.
6.2. Enhanced Location Accuracy
Advances in location technology are improving the accuracy of geofencing, enabling more precise targeting and triggering.
- New algorithms and sensors are reducing location errors, resulting in more reliable geofencing performance.
- High-precision geofencing opens up new opportunities for applications that require pinpoint accuracy.
6.3. Personalized Customer Experiences
Geofencing is playing a key role in creating personalized customer experiences by delivering relevant content and offers based on location.
- Retailers can use geofencing to send personalized promotions to customers as they browse the store.
- Restaurants can offer customized menus and recommendations based on the customer’s location and preferences.
6.4. Increased Adoption in Various Industries
Geofencing is being adopted in a wide range of industries, from healthcare to transportation, to improve efficiency and enhance services.
- Hospitals can use geofencing to track patients and equipment, ensuring timely care and optimal resource utilization.
- Transportation companies can use geofencing to monitor vehicle movements and optimize delivery routes.
6.5. Growing Privacy Concerns
As geofencing becomes more prevalent, there are growing concerns about privacy and data security.
- Businesses must be transparent about how they collect and use location data.
- Users should have control over their location data and be able to opt-out of geofencing services.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Geofencing
To provide further clarity on the topic, here are some frequently asked questions about geofencing.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the typical range of a geofence? | The range can vary from a few meters to several kilometers, depending on the application and technology used. |
| Is geofencing accurate indoors? | Geofencing can be less accurate indoors due to weaker GPS signals, but technologies like Wi-Fi positioning can improve accuracy. |
| Does geofencing drain battery life? | Yes, geofencing can drain battery life, especially if it relies on continuous GPS tracking. However, optimized algorithms and passive geofencing can minimize battery drain. |
| Can I use geofencing without a mobile app? | Yes, geofencing can be implemented through other means, such as cellular data or Wi-Fi positioning, without requiring a dedicated mobile app. |
| How secure is geofencing? | The security of geofencing depends on the measures taken to protect location data and prevent unauthorized access. Encryption and secure authentication protocols are essential for ensuring the security of geofencing applications. |
| What are the privacy implications of geofencing? | Geofencing raises privacy concerns because it involves collecting and tracking location data. Businesses must be transparent about their data practices and provide users with control over their location data. |
| How can I optimize geofencing for my business? | To optimize geofencing, define clear objectives, choose the right technology, create engaging triggers, and continuously monitor and analyze performance. |
| What are the best practices for geofencing notifications? | Best practices include sending timely, relevant, and personalized notifications that provide value to the user. Avoid sending excessive or intrusive notifications that can annoy users and lead them to opt-out of geofencing services. |
| Can geofencing be used for security purposes? | Yes, geofencing can be used for security purposes, such as monitoring access to restricted areas or tracking the location of valuable assets. It can also be used to detect and respond to security breaches or unauthorized activities. |
| What is the cost of implementing geofencing? | The cost of implementing geofencing varies depending on the complexity of the application, the technology used, and the scale of the deployment. It can range from a few dollars per month for basic services to thousands of dollars for custom solutions. |
| Is geofencing legal? | Geofencing is generally legal, but businesses must comply with privacy laws and regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, when collecting and using location data. Transparency and user consent are essential for ensuring the legality of geofencing practices. According to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) businesses are obligated to protect personal data. |
8. How to Choose the Right Geofencing Provider
Selecting the appropriate geofencing provider is essential for achieving your business objectives.
8.1. Evaluate Features and Capabilities
Assess the features and capabilities offered by different providers to ensure they meet your specific requirements.
- Look for providers that offer customizable geofences, real-time tracking, and advanced analytics.
- Consider the provider’s ability to integrate with your existing systems and platforms.
8.2. Consider Pricing and Support
Compare the pricing models and support options offered by different providers to find the best value.
- Evaluate the provider’s pricing structure, including setup fees, monthly fees, and usage-based charges.
- Ensure the provider offers reliable technical support and documentation.
8.3. Check Reviews and Testimonials
Read reviews and testimonials from other businesses to get an idea of the provider’s reputation and performance.
- Look for providers with positive reviews and a track record of delivering successful geofencing solutions.
- Consider reaching out to existing customers to get their feedback and insights.
8.4. Request a Demo or Trial
Request a demo or trial of the provider’s geofencing platform to see how it works in practice.
- Test the platform’s features and capabilities to ensure it meets your needs.
- Evaluate the user interface and overall ease of use.
8.5. Assess Scalability and Reliability
Ensure the provider’s geofencing platform can scale to meet your growing needs and offers reliable performance.
- Look for providers with robust infrastructure and a proven track record of uptime and availability.
- Consider the provider’s ability to handle large volumes of data and traffic.
 Geofencing applications in various industries
Geofencing applications in various industries
9. Overcoming Common Challenges in Geofencing
While geofencing offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges that businesses need to address.
9.1. Ensuring Location Accuracy
Maintaining accurate location data is critical for the success of geofencing applications.
- Use high-quality location data sources and implement filtering techniques to reduce errors.
- Regularly calibrate and test your geofences to ensure they are functioning correctly.
9.2. Managing Battery Drain
Geofencing can drain battery life, especially if it relies on continuous GPS tracking.
- Optimize your geofencing implementation to minimize battery consumption.
- Use passive geofencing techniques and reduce the frequency of location updates.
9.3. Protecting User Privacy
Protecting user privacy is essential for maintaining trust and complying with privacy regulations.
- Be transparent about how you collect and use location data.
- Provide users with control over their location data and offer opt-out options.
9.4. Avoiding Notification Fatigue
Sending too many notifications can annoy users and lead them to opt-out of geofencing services.
- Send timely, relevant, and personalized notifications that provide value to the user.
- Limit the frequency of notifications and allow users to customize their notification preferences.
9.5. Integrating with Existing Systems
Integrating geofencing with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Choose a geofencing provider that offers seamless integration with your existing systems and platforms.
- Work with experienced developers and consultants to ensure a smooth and successful integration.
10. The Impact of Geofencing on Various Sectors
Geofencing is making a significant impact on various sectors, transforming the way businesses operate and interact with customers.
10.1. Retail
Retailers are using geofencing to enhance the shopping experience and drive sales.
- Sending personalized promotions to customers as they browse the store.
- Offering loyalty rewards and discounts to customers who enter the store.
10.2. Hospitality
Hospitality businesses are using geofencing to improve customer service and increase revenue.
- Offering personalized recommendations and promotions to guests as they arrive at the hotel.
- Providing location-based information about nearby attractions and activities.
10.3. Healthcare
Healthcare providers are using geofencing to improve patient care and optimize operations.
- Tracking patients and equipment to ensure timely care and optimal resource utilization.
- Monitoring staff movements to improve efficiency and compliance.
10.4. Transportation
Transportation companies are using geofencing to optimize delivery routes and improve customer satisfaction.
- Tracking vehicle movements to ensure timely deliveries and prevent delays.
- Providing real-time updates to customers about the location of their packages.
10.5. Education
Educational institutions are using geofencing to improve security and enhance the student experience.
- Monitoring access to restricted areas and preventing unauthorized entry.
- Providing location-based information about campus events and activities.
11. Geofencing and Proximity Marketing
Geofencing is a powerful tool for proximity marketing, allowing businesses to target customers who are in close proximity to their locations.
11.1. Enhancing Customer Engagement
Proximity marketing enhances customer engagement by delivering relevant and personalized content based on location.
- Sending targeted offers and promotions to customers as they enter a geofenced area.
- Providing location-based information about nearby products and services.
11.2. Driving Foot Traffic
Proximity marketing drives foot traffic by enticing customers to visit your store or business.
- Offering special discounts and promotions to customers who are nearby.
- Providing directions and other helpful information to guide customers to your location.
11.3. Improving Brand Awareness
Proximity marketing improves brand awareness by increasing visibility and exposure in the local community.
- Reaching a wider audience with targeted ads and promotions.
- Creating a positive impression by providing valuable and relevant information.
11.4. Increasing Sales
Proximity marketing increases sales by driving more customers to your store and encouraging them to make a purchase.
- Offering incentives to customers who visit your store and make a purchase.
- Providing a seamless and convenient shopping experience.
11.5. Measuring Effectiveness
Proximity marketing allows you to measure the effectiveness of your campaigns by tracking key metrics such as foot traffic, engagement, and sales.
- Analyzing data to identify what’s working and what’s not.
- Making adjustments to your campaigns to improve performance.
12. The Ethical Considerations of Geofencing
Geofencing raises several ethical considerations that businesses need to address to maintain trust and comply with regulations.
12.1. Transparency
Be transparent about how you collect and use location data.
- Clearly explain your geofencing practices in your privacy policy.
- Provide users with easy-to-understand information about how their location data is being used.
12.2. Consent
Obtain explicit consent from users before collecting their location data.
- Use clear and concise language to explain what users are consenting to.
- Provide users with the option to opt-in or opt-out of geofencing services.
12.3. Data Minimization
Collect only the minimum amount of location data necessary to achieve your objectives.
- Avoid collecting unnecessary or irrelevant data.
- Limit the duration of data retention.
12.4. Data Security
Protect user location data from unauthorized access and disclosure.
- Implement robust security measures to safeguard data.
- Comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
12.5. User Control
Provide users with control over their location data and allow them to opt-out of geofencing services at any time.
- Make it easy for users to access, modify, or delete their location data.
- Honor opt-out requests promptly and without penalty.
13. Geofencing in Smart Cities
Geofencing is playing a key role in the development of smart cities by enabling a wide range of applications and services.
13.1. Public Safety
Geofencing is used to enhance public safety by monitoring and managing access to restricted areas.
- Creating virtual perimeters around sensitive locations such as government buildings and critical infrastructure.
- Alerting authorities when unauthorized individuals enter restricted areas.
13.2. Traffic Management
Geofencing is used to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Monitoring traffic patterns and adjusting traffic signals in real-time.
- Providing drivers with real-time information about traffic conditions and alternative routes.
13.3. Waste Management
Geofencing is used to optimize waste collection and improve efficiency.
- Tracking waste collection vehicles and optimizing routes.
- Monitoring waste levels in containers and alerting collection crews when they need to be emptied.
13.4. Emergency Response
Geofencing is used to improve emergency response times and coordination.
- Tracking the location of emergency vehicles and personnel.
- Providing first responders with real-time information about the location of incidents.
13.5. Environmental Monitoring
Geofencing is used to monitor environmental conditions and detect pollution.
- Tracking air and water quality levels in real-time.
- Alerting authorities when pollution levels exceed safe limits.
14. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Geofencing
To maximize the effectiveness of your geofencing campaigns, avoid these common mistakes.
14.1. Neglecting Location Accuracy
Failing to ensure accurate location data can lead to ineffective campaigns and frustrated customers.
- Use high-quality location data sources and implement filtering techniques to reduce errors.
- Regularly calibrate and test your geofences to ensure they are functioning correctly.
14.2. Overlooking User Privacy
Disregarding user privacy can damage your reputation and lead to legal issues.
- Be transparent about how you collect and use location data.
- Provide users with control over their location data and offer opt-out options.
14.3. Sending Irrelevant Notifications
Sending irrelevant or poorly targeted notifications can annoy users and lead them to opt-out of your services.
- Send timely, relevant, and personalized notifications that provide value to the user.
- Limit the frequency of notifications and allow users to customize their notification preferences.
14.4. Ignoring Analytics
Failing to track and analyze your geofencing campaigns can prevent you from optimizing your performance.
- Monitor key metrics such as foot traffic, engagement, and sales.
- Analyze data to identify what’s working and what’s not, and make adjustments accordingly.
14.5. Lack of Testing
Failing to thoroughly test your geofencing campaigns can lead to unexpected issues and poor results.
- Test your geofences on a variety of devices and in different locations.
- Verify that notifications are being delivered accurately and that triggers are firing as expected.
15. Optimizing Geofencing for Different Mobile Platforms
To maximize the reach and effectiveness of your geofencing campaigns, it’s important to optimize them for different mobile platforms.
15.1. iOS Optimization
Optimize your geofencing implementation for iOS devices by following Apple’s guidelines.
- Use the Core Location framework to implement geofencing.
- Request location permissions from users and explain why you need their location data.
15.2. Android Optimization
Optimize your geofencing implementation for Android devices by following Google’s best practices.
- Use the Geofencing API to implement geofencing.
- Request location permissions from users and explain why you need their location data.
15.3. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Ensure your geofencing implementation is compatible with both iOS and Android devices.
- Use a cross-platform development framework or library to simplify development.
- Test your geofences on a variety of devices and operating systems to ensure compatibility.
15.4. Battery Management
Optimize your geofencing implementation to minimize battery consumption on both iOS and Android devices.
- Use passive geofencing techniques and reduce the frequency of location updates.
- Avoid using continuous GPS tracking unless it’s absolutely necessary.
15.5. Location Accuracy
Maximize location accuracy on both iOS and Android devices by using the most appropriate location services.
- Use GPS for outdoor location tracking and Wi-Fi positioning for indoor location tracking.
- Implement filtering techniques to reduce location errors and improve accuracy.
Do you have more questions about geofencing or location-based services? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask our experts for free. Our community is ready to provide quick and accurate answers to all your questions. Don’t hesitate, connect with us now at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Let what.edu.vn be your go-to resource for knowledge and support.
