What Is A Good Cpu Temp? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of keeping your CPU running smoothly. Understanding optimal CPU temperatures and how to maintain them is crucial for peak performance and longevity. We’ll cover everything from identifying safe and dangerous temperature ranges to practical methods for monitoring and cooling your processor, ensuring your system remains efficient and reliable. Let’s dive into CPU temperature ranges, processor health, and cooling solutions.
1. Understanding Good CPU Temperature
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the brain of your computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. Like any engine, it generates heat. Maintaining a good operating temperature is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
1.1 What Is Considered a Normal CPU Temp?
Generally, a CPU should run at 30°C (86°F) to 40°C (104°F) when idle or under light use. This is the ideal temperature range for everyday tasks.
1.1.1 Defining Light Use
Light use typically means a CPU usage of 1% to 10%. You can check this using Task Manager on Windows:
- Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc).
- Close any unnecessary third-party programs.
- Click the Performance tab to view CPU usage.
- Wait for the temperature to stabilize and check the value.
Alt Text: Monitoring CPU temperature in a computer system to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating.
1.2 Average CPU Temp Under Load
Factors such as CPU type, cooling solutions, and ambient temperature influence the ideal temperature.
On a typical day, expect a temperature range of 30°C to 40°C (86°F to 104°F) at idle and 60°C to 70°C (140°F to 158°F) under load. The power consumption of the CPU determines the heat produced. Easier tasks require less power, while harder tasks demand more.
1.3 What is a Safe CPU Temp?
Most modern processors are designed to handle temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) without issue. However, maintaining a cooler temperature is always better for optimal performance and to extend the lifespan of your CPU.
1.4 When Does CPU Temp Become Too Hot?
Red flags appear when your CPU temperature consistently exceeds 80°C (176°F). Prolonged exposure to these high temperatures can cause performance degradation and potential long-term damage. Gamers and other users who put high demands on their CPUs should regularly monitor the temperature to ensure it remains within safe limits.
1.5 Optimal CPU Temp for Gaming/Streaming
During heavy loads such as gaming, video editing, or live streaming, temperatures can rise from 70°C (158°F) to 80°C (176°F). This is generally safe, but ensure temperatures do not exceed 90°C (194°F), as this can significantly reduce the lifespan of your CPU or cause immediate damage.
1.6 Key Takeaways for CPU Temperature
- Good CPU temperature: 30°C to 40°C (86°F to 104°F) under light use (1-10% CPU usage).
- Safe CPU temperature: Below 80°C (176°F).
- Dangerous CPU temperature: Above 80°C (176°F) consistently.
As long as your CPU temperature stays at or below 80°C (176°F), your processor is in good condition. Occasional spikes above this limit are acceptable, especially during demanding tasks. However, frequent high temperatures require attention.
2. Methods to Check CPU Temperature
Monitoring your CPU temperature is a proactive measure to prevent overheating. Here are several methods to check your CPU temperature.
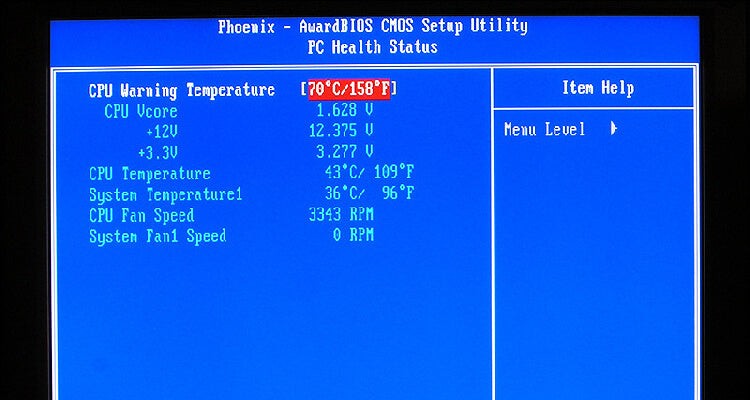
2.1 Using BIOS to Check CPU Temperature
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a built-in utility that checks the firmware, hardware, and software status of your computer, including CPU temperature.
Steps:
- Restart the PC. At the startup screen, press the designated key (usually F2, Delete, or Esc) to enter BIOS.
- Navigate to PC Status or Advanced Setup. Use the arrow keys to find the appropriate option and press Enter.
- View CPU Temperature. The temperature should be listed in this section.
Note: The specific key to enter BIOS varies by manufacturer, model, and version. Consult your PC’s manual or manufacturer’s website for the correct key combination.
While BIOS is free, it is not ideal for regular monitoring as it requires restarting your computer each time. Additionally, it cannot provide peak temperatures or track temperature changes over time.
Alt Text: Accessing BIOS settings to monitor CPU temperature on a computer system.
2.2 Utilizing CPU Temperature Monitoring Software
Many third-party CPU monitoring software programs are available online. These tools provide real-time temperature readings and can log data for later analysis.
Example: Core Temp
Core Temp is a free and easy-to-use software for monitoring CPU temperature. Simply download and install it on your Windows PC to begin monitoring.
Considerations:
CPU monitoring programs consume CPU resources. Choose a lightweight program to minimize the impact on performance, especially during demanding tasks like gaming.
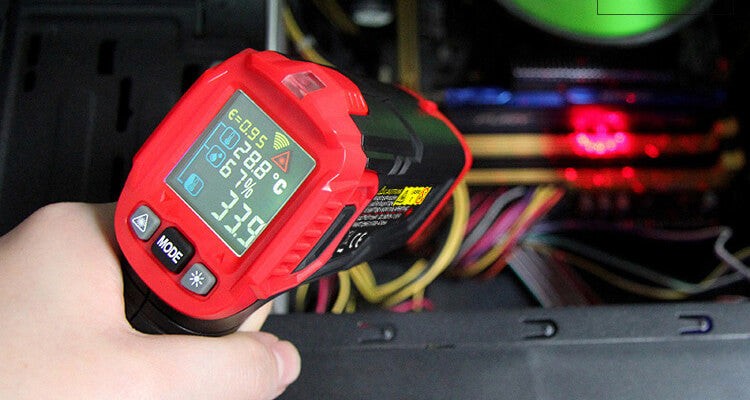
2.3 Employing an Infrared Thermometer
An infrared (IR) thermometer offers a quick and easy way to check CPU temperature by measuring thermal radiation.
Advantages:
- Data Logging: Many IR thermometers support data saving, allowing you to track CPU temperature over time.
- Real-Time Measurement: IR thermometers provide real-time temperature readings without impacting CPU usage.
- Universal Compatibility: They work with any brand, version, and model of CPU.
- Ease of Use: No complex setups are required.
2.4 Selecting the Right IR Thermometer
Two primary options are available: handheld IR thermometers and thermal imaging guns.
2.4.1 Handheld IR Thermometer
A handheld IR thermometer, such as the NF-HT650C, provides accurate and simple CPU temperature monitoring.
Features of NF-HT650C:
- Single-press, one-hand operation
- Accuracy over 98%
- Measurement range: -50°C to 800°C (-58°F to 1472°F)
This device allows you to quickly assess the CPU status.
Alt Text: Checking CPU temperature using the NF-HT650C infrared thermometer for accurate readings.
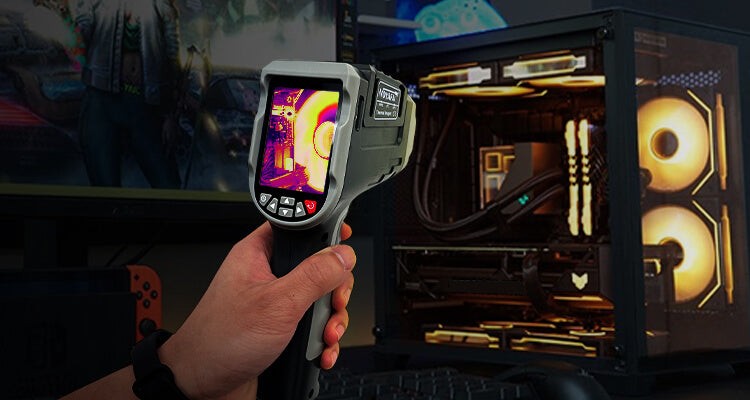
2.4.2 IR Imaging Gun
An IR imaging gun, like the NF-521S, is a more advanced option that displays live thermal images.
Advantages of NF-521S:
- Live Thermal Images: Displays temperature distribution across the CPU and surrounding components.
- Video Recording: Records the processor’s status during gaming or streaming for later analysis.
- Hot and Cold Spot Identification: Highlights areas of high and low temperature, making it easy to identify potential issues.
This tool provides a comprehensive view of the CPU’s thermal performance and the effectiveness of the cooling system.
Alt Text: Monitoring CPU temperature with the NF-521S thermal imaging camera for detailed thermal analysis.
3. Common Causes of High CPU Temperature
A CPU can overheat due to several factors. Identifying these causes is the first step in resolving the issue.
3.1 Dust Accumulation
Dust buildup on components is a common culprit. Dust can block fans and airflow pathways, reducing the cooling efficiency of the system.
3.2 Inadequate Cooling and Poor Ventilation
Insufficient or malfunctioning cooling systems, such as fans or heat sinks, can lead to poor heat dissipation. Additionally, old or poorly applied thermal paste between the CPU and cooler can reduce heat transfer efficiency.
Alt Text: A typical cooling system inside a PC case, illustrating the importance of proper heat dissipation.
3.3 Overclocking
Overclocking pushes the CPU beyond its standard operating conditions, increasing heat output. While it can improve performance, it also increases the risk of overheating.
4. Practical Solutions to Cool Down an Overheated CPU
If your CPU is running too hot, immediate action is needed to prevent damage. Here are several effective methods to cool it down.
4.1 Enhance the Cooling System
The most effective solution is to improve your system’s cooling capabilities.
- Clean Dust: Regularly clean dust from inside your computer, especially from fans and heat sinks.
- Reapply Thermal Paste: Reapply high-quality thermal paste between the CPU and cooler to improve heat transfer.
- Upgrade Cooling: Consider upgrading to a high-end air or liquid cooling solution, especially for high-performance CPUs or overclocking.
- Improve Airflow: Rearrange internal components or add more or better-placed fans to improve airflow.
Alt Text: Reinstalling a PC case to improve airflow and cooling for the CPU and GPU.
4.2 Maintain a Cool Room Environment
Running a computer in a hot room will increase CPU temperature. Use air conditioning to keep the room cool, especially during heavy use.
4.3 Reduce Demanding Tasks
Avoid running multiple demanding programs simultaneously. Close unnecessary applications and limit the duration of high-intensity tasks. Keep your software and firmware updated.
4.4 Consider a CPU Upgrade
If your current CPU cannot handle your gaming or streaming needs, consider upgrading to a more powerful processor.
Note for Mac Users:
Upgrading the CPU in a Mac is not possible. The only option is to purchase a new model.
Check the game company’s official website for recommended CPU specifications for the best gaming experience. Also, ensure the new CPU is compatible with your motherboard.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About CPU Temperature
To provide a comprehensive understanding, here are some frequently asked questions about CPU temperature, along with answers to address common concerns.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the ideal CPU temperature for gaming? | The ideal CPU temperature while gaming should be below 80°C (176°F). Temperatures between 70°C (158°F) and 80°C (176°F) are generally safe and normal, but avoid exceeding 90°C (194°F). |
| How does ambient temperature affect CPU temp? | Ambient temperature significantly impacts CPU temperature. Higher ambient temperatures reduce the effectiveness of cooling solutions, leading to higher CPU temperatures. |
| Can overclocking cause CPU overheating? | Yes, overclocking increases the CPU’s heat output, which can lead to overheating if the cooling system is not adequate. Always monitor temperatures closely when overclocking. |
| How often should I check my CPU temperature? | Regularly check your CPU temperature, especially during heavy use like gaming or video editing. Monitoring once a month is generally sufficient for regular use. |
| What type of cooling is best for a CPU? | Both air and liquid cooling can be effective. Liquid cooling is generally more efficient and quieter but also more expensive. Air cooling is a reliable and cost-effective solution for most users. |
| Can dust buildup really affect CPU temperature? | Yes, dust buildup can block airflow and reduce the efficiency of cooling fans and heat sinks, leading to higher CPU temperatures. Regular cleaning is essential. |
| Is it safe to run my CPU at 75°C? | Yes, running your CPU at 75°C (167°F) is generally safe. Most modern CPUs are designed to operate safely up to 80°C (176°F). |
| What is thermal throttling? | Thermal throttling is a safety mechanism that reduces the CPU’s clock speed when it reaches a critical temperature. This prevents overheating but also reduces performance. |
| What are the signs of CPU overheating? | Signs include system crashes, blue screens, reduced performance, and the computer shutting down unexpectedly. Monitoring your CPU temperature can help prevent these issues. |
| Does CPU usage affect CPU temperature? | Yes, higher CPU usage generates more heat. Running demanding applications or multitasking can increase CPU temperature. |




6. Expert Tips for Maintaining Optimal CPU Temperature
Here are some expert tips to keep your CPU running cool and efficiently, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
6.1 Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular cleaning is crucial for maintaining optimal CPU temperature. Dust accumulation can significantly impede airflow and reduce the effectiveness of cooling solutions. Aim to clean the inside of your computer every 3-6 months, depending on the environment.
Steps for Cleaning:
- Power Down: Turn off your computer and unplug it from the power source.
- Open the Case: Open the computer case to access internal components.
- Use Compressed Air: Use compressed air to gently blow dust away from fans, heat sinks, and other components.
- Clean Fans: Use a soft brush to clean fan blades, removing any stubborn dust particles.
- Reassemble: Close the case and ensure all components are securely in place.
6.2 Optimize Airflow
Proper airflow is essential for efficient cooling. Ensure that your computer case has adequate ventilation and that fans are correctly positioned to promote airflow.
Tips for Optimizing Airflow:
- Fan Placement: Position intake fans at the front and bottom of the case to draw in cool air, and exhaust fans at the rear and top to expel hot air.
- Cable Management: Neatly organize cables to prevent them from blocking airflow.
- Component Placement: Ensure that components are not positioned too close together, allowing for adequate space for airflow.
6.3 Upgrade Cooling Solutions
If you consistently experience high CPU temperatures, consider upgrading your cooling solution. There are several options available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Types of Cooling Solutions:
- Air Coolers: Air coolers are a cost-effective and reliable option for most users. They consist of a heat sink and fan that dissipate heat away from the CPU.
- Liquid Coolers: Liquid coolers are more efficient and quieter than air coolers. They use a liquid coolant to transfer heat away from the CPU to a radiator, where it is dissipated by fans.
- Custom Loop Cooling: Custom loop cooling systems are the most advanced and customizable option. They allow you to design a cooling system tailored to your specific needs and components.
6.4 Monitor CPU Usage
High CPU usage can lead to increased temperatures. Monitor your CPU usage regularly to identify applications or processes that are consuming excessive resources.
Tools for Monitoring CPU Usage:
- Task Manager (Windows): Task Manager provides real-time information about CPU usage, memory usage, and disk activity.
- Activity Monitor (macOS): Activity Monitor provides similar functionality to Task Manager, allowing you to monitor CPU usage and identify resource-intensive processes.
6.5 Update BIOS and Drivers
Keeping your BIOS and drivers up to date can improve system stability and performance, which can indirectly affect CPU temperature.
How to Update BIOS and Drivers:
- BIOS: Check the manufacturer’s website for BIOS updates and follow their instructions for installation.
- Drivers: Use the Device Manager to update drivers for your CPU, motherboard, and other components.
6.6 Consider Undervolting
Undervolting involves reducing the voltage supplied to the CPU, which can lower its temperature without significantly impacting performance.
How to Undervolt:
- Use BIOS Settings: Access the BIOS settings and look for options to adjust CPU voltage.
- Use Software Tools: Use software tools like Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) or AMD Ryzen Master to undervolt your CPU.
6.7 Avoid Overclocking If Not Necessary
Overclocking can significantly increase CPU temperature. If you don’t need the extra performance, avoid overclocking your CPU.
7. Let WHAT.EDU.VN Answer Your Questions for Free
Monitoring and maintaining your CPU temperature is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your computer. By understanding safe temperature ranges, employing effective monitoring techniques, and implementing practical cooling solutions, you can keep your CPU running smoothly. Remember, regular maintenance and proactive measures are key to preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
Do you have more questions about CPU temperatures or other tech-related topics? Don’t hesitate to ask WHAT.EDU.VN! We offer a free platform where you can get answers to all your questions. Our community of experts is ready to help you with any issue you might be facing.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t struggle with unanswered questions. Visit what.edu.vn today and get the answers you need quickly and easily. Our team is dedicated to providing you with the best possible information and support. Ask your question now and experience the convenience of free, expert advice!