What Is A Good Credit Rating? It’s a common question, and at WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide the answers you need to understand credit scores, creditworthiness, and how they impact your financial life. Discover the secrets to achieving a favorable credit rating and unlocking better financial opportunities. Let’s explore credit report, credit history and credit score range together.
1. Understanding Credit Scores: What Is a Good Credit Rating?
Credit scores are numerical representations of your creditworthiness, reflecting your ability to repay debts. Ranging from 300 to 850, these scores play a vital role in various financial decisions. But what exactly constitutes a good credit rating?
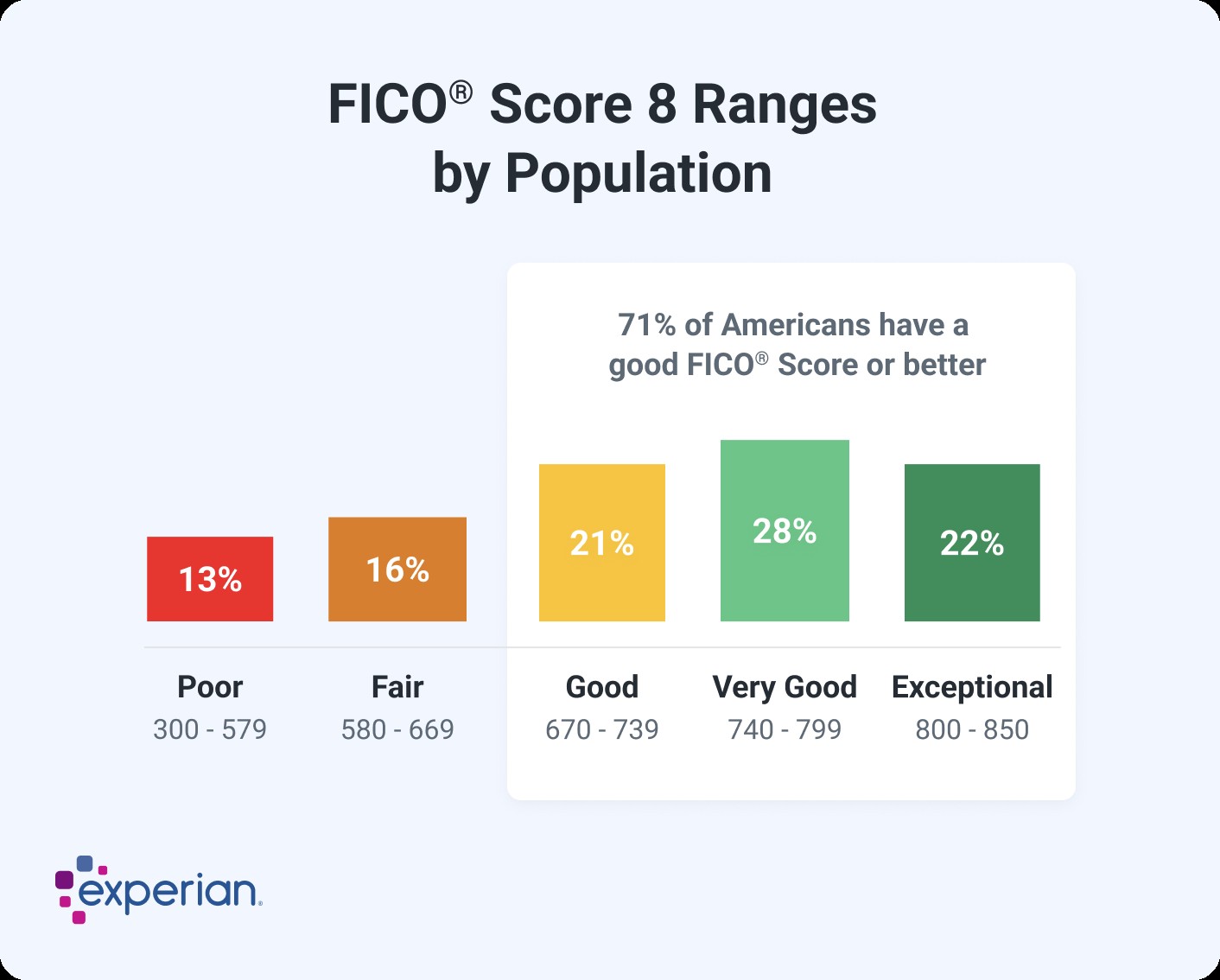
- FICO Scores: A FICO score between 670 and 739 is generally considered good.
- VantageScores: A VantageScore between 661 and 780 is considered good.
Understanding these ranges is crucial for anyone looking to improve their financial standing and access better credit terms.
2. Decoding FICO Scores: A Deeper Dive into Credit Rating
The FICO score, developed by Fair Isaac Corporation, is one of the most widely used credit scoring models. It assesses your credit risk based on various factors.
2.1. FICO Score Ranges and Their Meanings
- Exceptional (800-850): This range indicates excellent credit management, opening doors to the best interest rates and loan terms.
- Very Good (740-799): A very good score demonstrates a strong credit history, making you a reliable borrower.
- Good (670-739): A good score means you’re a dependable borrower and likely to be approved for credit.
- Fair (580-669): A fair score may lead to higher interest rates and stricter loan terms.
- Poor (300-579): A poor score indicates significant credit risks, making it difficult to obtain credit.
2.2. Factors Influencing Your FICO Score
FICO scores consider several factors, each with varying degrees of influence:
- Payment History (35%): This is the most crucial factor, reflecting your track record of timely payments.
- Amounts Owed (30%): This assesses the amount of debt you owe relative to your available credit.
- Length of Credit History (15%): A longer credit history typically results in a higher score.
- Credit Mix (10%): Having a mix of credit accounts (e.g., credit cards, loans) can positively impact your score.
- New Credit (10%): Opening too many new accounts in a short period can lower your score.
Understanding these factors allows you to focus on areas that need improvement and strategically enhance your FICO score.
3. Exploring VantageScore: Another Perspective on Credit Rating
VantageScore is another popular credit scoring model, developed jointly by the three major credit bureaus: Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax. It offers a different perspective on creditworthiness.
3.1. VantageScore Ranges and Their Significance
- Super Prime (781-850): This range signifies exceptional creditworthiness, similar to FICO’s “Exceptional” range.
- Prime (661-780): A prime score indicates a solid credit history and responsible borrowing behavior.
- Near Prime (601-660): This range suggests moderate credit risk, potentially leading to less favorable terms.
- Subprime (300-600): A subprime score indicates significant credit risk, making it challenging to secure credit.
3.2. Factors Influencing Your VantageScore
VantageScore also considers various factors to determine your creditworthiness:
- Payment History: Extremely influential
- Total Credit Usage: Highly influential
- Credit Mix and Experience: Highly influential
- New Accounts Opened: Moderately influential
- Balances and Available Credit: Less influential
While the factors are similar to those used by FICO, the relative importance of each may vary.
4. Credit Score vs. Credit Rating: Is There a Difference?
The terms “credit score” and “credit rating” are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle distinction. A credit score is a specific numerical value assigned to your creditworthiness, while a credit rating is a broader assessment of your credit risk, often categorized into ranges like “good,” “fair,” or “poor.” Both provide insights into your ability to manage debt, but credit rating offers a more qualitative evaluation.
5. The Importance of a Good Credit Rating: Opening Doors to Opportunities
A good credit rating is essential for various financial endeavors. It not only affects your ability to obtain credit but also influences the terms and conditions you receive.
5.1. Securing Loans and Credit Cards
Lenders use credit ratings to assess risk when offering loans or credit cards. A good credit rating increases your chances of approval and can lead to lower interest rates and more favorable terms. Conversely, a poor credit rating may result in denial or higher costs.
5.2. Mortgage and Auto Loans
For significant purchases like homes or cars, a good credit rating is crucial. It can save you thousands of dollars in interest payments over the life of the loan. Lower interest rates translate to smaller monthly payments and reduced overall costs.
5.3. Renting an Apartment
Landlords often check credit ratings to assess the reliability of potential tenants. A good credit rating demonstrates financial responsibility and increases your chances of securing your desired apartment.
5.4. Insurance Premiums
In many states, insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores to determine premiums for auto, home, and life insurance. A good credit rating can lead to lower insurance rates, saving you money on your monthly bills.
5.5. Employment Opportunities
Some employers may review credit reports (but not credit scores) as part of their hiring process. A good credit rating can reflect positively on your responsibility and financial stability, enhancing your employment prospects.
6. What Is Considered a Bad Credit Rating?
A bad credit rating is characterized by low credit scores, typically below 600 for both FICO and VantageScore models. This rating indicates a high risk of default, making it difficult to obtain credit or secure favorable terms.
6.1. Impact of a Bad Credit Rating
- Difficulty Obtaining Credit: Lenders are hesitant to offer credit to individuals with bad credit, limiting their access to loans and credit cards.
- High Interest Rates: If approved for credit, individuals with bad credit often face high interest rates, increasing the cost of borrowing.
- Limited Loan Amounts: Lenders may offer smaller loan amounts to those with bad credit, restricting their purchasing power.
- Higher Insurance Premiums: As mentioned earlier, a bad credit rating can lead to higher insurance rates.
- Rental Challenges: Landlords may deny rental applications based on poor credit history.
6.2. Strategies to Improve a Bad Credit Rating
- Pay Bills on Time: Consistent, timely payments are crucial for improving your credit rating.
- Reduce Credit Balances: Lowering your credit utilization ratio can significantly boost your score.
- Dispute Errors: Review your credit reports for inaccuracies and dispute them promptly.
- Avoid New Credit: Refrain from opening new credit accounts until your score improves.
- Consider Secured Credit Cards: These cards can help you rebuild credit with responsible use.
7. What Is a Good Credit Rating for Buying a House?
For purchasing a home, a credit score of 670 or higher is generally considered good. This score can help you qualify for a mortgage with a lower interest rate.
7.1. Credit Score Requirements for Mortgages
- Conventional Mortgages: Many lenders require a minimum credit score of 620.
- FHA Loans: Credit score requirements range from 500 to 579 with a 10% down payment, or 580+ with a 3.5% down payment.
- USDA Loans: Lenders may require a credit score between 580 and 620, although there is no set minimum.
- VA Loans: Lenders generally require a credit score of 620 or higher.
7.2. Benefits of a Good Credit Rating for Mortgages
- Lower Interest Rates: A good credit rating can secure lower interest rates, saving you thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
- Better Loan Terms: Lenders are more likely to offer favorable terms to borrowers with good credit.
- Higher Approval Odds: A good credit rating increases your chances of mortgage approval.
8. What Is a Good Credit Rating for Buying a Car?
While there isn’t a strict minimum, a VantageScore of 661 or higher is generally considered a good credit rating for buying a car.
8.1. Impact of Credit Score on Auto Loan Terms
- Good Credit: Higher credit scores typically lead to better auto loan terms and lower interest rates.
- Poor Credit: Lower credit scores may result in higher interest rates and less favorable terms.
8.2. Tips for Securing an Auto Loan with a Good Credit Rating
- Check Your Credit Report: Review your credit report for errors before applying for a loan.
- Shop Around: Compare offers from multiple lenders to find the best rates.
- Make a Larger Down Payment: A larger down payment can lower your loan amount and monthly payments.
9. Common Misconceptions About Credit Ratings
There are several myths surrounding credit ratings that can lead to confusion and poor financial decisions.
9.1. Myth: Checking Your Credit Score Will Lower It
Fact: Checking your own credit score does not negatively impact it. These are considered “soft inquiries” and do not affect your credit rating.
9.2. Myth: Closing Credit Cards Improves Your Score
Fact: Closing credit cards can actually lower your score, especially if it reduces your overall available credit.
9.3. Myth: Credit Scores Only Matter for Loans
Fact: Credit scores are used for various purposes, including renting apartments, securing insurance, and even employment decisions.
9.4. Myth: Paying Off a Loan Always Improves Your Score
Fact: While paying off a loan is generally positive, it can sometimes lead to a temporary score drop if it was the only open installment account on your credit report.
10. Building and Maintaining a Good Credit Rating: Long-Term Strategies
Building and maintaining a good credit rating requires consistent effort and responsible financial habits.
10.1. Establishing Credit
If you have no credit history, consider these steps to establish credit:
- Secured Credit Card: Obtain a secured credit card by providing a cash deposit as collateral.
- Credit-Builder Loan: Take out a credit-builder loan, where the funds are held in an account until you repay the loan.
- Become an Authorized User: Ask a trusted friend or family member to add you as an authorized user on their credit card.
10.2. Maintaining a Good Credit Rating
- Pay Bills on Time: Always pay your bills on time, every time.
- Keep Credit Balances Low: Aim to keep your credit utilization ratio below 30%.
- Monitor Your Credit Reports: Regularly check your credit reports for errors and suspicious activity.
- Avoid Maxing Out Credit Cards: Maxing out your credit cards can significantly lower your score.
- Diversify Your Credit Mix: Having a mix of credit accounts can positively impact your score.
11. What to Do if Your Credit Score Drops: Addressing the Issues
If your credit score drops, it’s essential to identify the cause and take corrective action.
11.1. Common Reasons for a Credit Score Drop
- Late Payments: Missing payments can significantly lower your score.
- High Credit Utilization: Using a large portion of your available credit can negatively impact your score.
- New Credit Accounts: Opening too many new accounts in a short period can lower your score.
- Collections Accounts: Unpaid debt sent to collections can severely damage your credit.
- Public Records: Bankruptcies and other public records can have a significant negative impact.
11.2. Steps to Take After a Credit Score Drop
- Identify the Cause: Review your credit reports to determine the reason for the score drop.
- Dispute Errors: If you find errors, dispute them with the credit bureaus.
- Pay Down Debt: Reduce your credit balances to improve your credit utilization ratio.
- Catch Up on Payments: Bring any past-due accounts current.
- Seek Professional Help: If needed, consult with a credit counselor for guidance.
12. Credit Monitoring Services: Staying Informed About Your Credit Health
Credit monitoring services provide real-time alerts about changes to your credit reports and scores.
12.1. Benefits of Credit Monitoring
- Early Fraud Detection: Receive alerts about suspicious activity that could indicate fraud.
- Score Tracking: Monitor your credit score over time and track your progress.
- Report Access: Access your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus.
- Identity Theft Protection: Some services offer identity theft protection features.
12.2. Popular Credit Monitoring Services
- Experian: Offers free credit monitoring with daily updates and real-time alerts.
- TransUnion: Provides credit monitoring services with various subscription options.
- Equifax: Offers credit monitoring and identity theft protection services.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Credit Ratings
13.1. What Is the Highest Credit Score Possible?
The highest possible credit score is 850, for both FICO and VantageScore models.
13.2. How Often Should I Check My Credit Score?
It’s recommended to check your credit score at least once a year, or more frequently if you’re planning a major financial transaction.
13.3. Does Income Affect My Credit Score?
No, income is not a factor in determining your credit score. Credit scores are based on your credit history and payment behavior.
13.4. How Long Does It Take to Rebuild Credit?
The time it takes to rebuild credit varies depending on the severity of the damage and your efforts to improve your credit habits. It can take several months to several years.
13.5. Can I Get a Loan with No Credit History?
It can be challenging to get a loan with no credit history, but there are options like secured loans and credit-builder loans.
14. Navigating Credit Rating Systems: A Global Perspective
Credit rating systems vary across the globe, with different scoring models and factors considered. Understanding these differences is crucial for individuals moving or conducting business internationally.
14.1. United States
The United States primarily uses FICO and VantageScore models. Credit history and payment behavior are heavily weighted.
14.2. Canada
Canada uses credit scores ranging from 300 to 900. Equifax and TransUnion are the main credit bureaus.
14.3. United Kingdom
The UK uses credit scores ranging from 0 to 999. Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion are the primary credit reference agencies.
14.4. Australia
Australia uses credit scores ranging from 0 to 1,200. Experian and Equifax are the main credit bureaus.
14.5. Germany
Germany uses a credit scoring system called SCHUFA, which assesses creditworthiness based on various factors.
15. The Future of Credit Ratings: Emerging Trends and Technologies
The credit rating landscape is evolving with new technologies and data sources.
15.1. Alternative Data
Alternative data, such as utility payments and rental history, is increasingly being used to assess creditworthiness, especially for individuals with limited credit history.
15.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to develop more sophisticated credit scoring models that can better predict risk.
15.3. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is being explored as a way to create more secure and transparent credit rating systems.
16. Expert Tips for Maintaining an Excellent Credit Rating
Maintaining an excellent credit rating requires ongoing effort and diligence.
16.1. Set Up Automatic Payments
Automate your bill payments to avoid missing due dates.
16.2. Monitor Your Credit Utilization Ratio
Keep your credit utilization ratio below 30% by paying down balances regularly.
16.3. Review Your Credit Reports Regularly
Check your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus at least once a year.
16.4. Avoid Applying for Too Much Credit at Once
Spreading out credit applications can prevent a negative impact on your score.
16.5. Be Mindful of Your Credit Mix
Having a mix of credit accounts can demonstrate responsible credit management.
17. Personal Stories: Real-Life Impact of Credit Ratings
Hearing real-life stories can illustrate the profound impact of credit ratings.
17.1. Sarah’s Story
Sarah, a recent college graduate, struggled to find an apartment due to her limited credit history. By becoming an authorized user on her mother’s credit card and diligently paying her bills, she improved her credit score and secured her dream apartment.
17.2. John’s Story
John’s credit score plummeted after he missed several credit card payments due to a job loss. He worked with a credit counselor, paid down his debt, and gradually rebuilt his credit score. Today, he owns a home and enjoys financial stability.
18. Tools and Resources for Managing Your Credit
Several tools and resources can help you manage your credit effectively.
18.1. Credit Score Simulators
These tools allow you to estimate how certain actions, such as paying off debt or opening a new account, will impact your credit score.
18.2. Budgeting Apps
Budgeting apps can help you track your spending, manage your bills, and avoid late payments.
18.3. Credit Counseling Services
Nonprofit credit counseling agencies offer free or low-cost advice and assistance with debt management.
19. Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Credit Rating
Understanding what is a good credit rating and how to achieve it is essential for financial success. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can take control of your credit and unlock a world of opportunities. Whether you’re looking to buy a home, secure a loan, or simply improve your financial standing, a good credit rating is your key to a brighter future.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that navigating the complexities of credit can be overwhelming. That’s why we’re here to provide you with the information and resources you need to make informed decisions. If you have any questions or need personalized advice, don’t hesitate to reach out. We’re committed to helping you achieve your financial goals. Remember, building a good credit rating is a journey, not a destination. Stay informed, stay diligent, and watch your credit score soar.
20. Have More Questions? Ask Us at WHAT.EDU.VN!
Do you have any more burning questions about credit scores, credit reports, or anything else related to personal finance? Don’t hesitate to ask! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a free platform for you to ask any question and receive answers from knowledgeable experts. We understand that everyone has unique circumstances and challenges, and we’re here to provide personalized guidance to help you achieve your financial goals. Whether you’re wondering how to improve your credit score, how to budget effectively, or how to invest wisely, we’ve got you covered.
20.1. Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Service: Our question-and-answer platform is completely free to use.
- Expert Advice: Get answers from experienced professionals in various fields.
- Quick Responses: Receive timely responses to your questions.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is user-friendly and easy to navigate.
- Community Support: Connect with a supportive community of learners and experts.
20.2. How to Ask a Question on WHAT.EDU.VN
- Visit our website: Go to WHAT.EDU.VN.
- Create an account: Sign up for a free account.
- Ask your question: Type your question in the search bar and submit.
- Receive answers: Our experts will provide you with detailed, helpful answers.
20.3. Contact Us
If you have any questions or need assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn
We’re here to help you every step of the way. Ask your question today and take control of your financial future!