What Is A Hemi Engine? It’s a combustion engine with a hemispherical combustion chamber, and at WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide easy answers to your questions. Delve into its workings, advantages, and disadvantages. Discover what makes it unique. Hemi engines deliver superior performance, efficient fuel burning, and reduced heat loss.
1. What is a Hemi Engine? Understanding the Basics
The Hemi engine, short for hemispherical engine, gets its name from the shape of its combustion chamber. Unlike traditional flathead engines, the Hemi features a dome-shaped (hemispherical) combustion chamber, which offers several performance advantages.
- Hemispherical Combustion Chamber: This unique design allows for larger valves and better airflow compared to other engine designs.
- Valve Placement: The valves are positioned on opposite sides of the combustion chamber, allowing for a more direct path for air and fuel to enter and exit the cylinder.
- Spark Plug Location: The spark plug is typically located at the top center of the hemisphere, ensuring optimal ignition of the air-fuel mixture.
2. The History of the Hemi Engine
The Hemi engine has a rich history, dating back to the early 20th century. While Chrysler is most famously associated with the Hemi, the concept of a hemispherical combustion chamber predates their involvement.
- Early Innovations: The first known use of a hemispherical combustion chamber was in 1901 in a Belgian car.
- Chrysler’s Introduction: Chrysler introduced its first Hemi engine in 1951 with the 331 cubic inch FirePower V8. This engine quickly gained fame for its power and efficiency.
- Racing Success: The Hemi engine became a dominant force in motorsports, particularly in NASCAR and drag racing, throughout the 1960s and 1970s.
- Modern Hemi Engines: Chrysler has continued to produce Hemi engines in various forms, including the modern 5.7-liter, 6.1-liter, 6.4-liter, and the supercharged 6.2-liter Hellcat engines.
3. How Does a Hemi Engine Work?
The Hemi engine operates on the same four-stroke principle as other internal combustion engines: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. However, the Hemi’s unique design enhances each of these strokes.
- Intake Stroke: The piston moves down, creating a vacuum that draws the air-fuel mixture into the cylinder through the intake valve.
- Compression Stroke: The piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture. The hemispherical chamber allows for a high compression ratio, which increases power.
- Combustion Stroke: The spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing a rapid expansion of gases that pushes the piston down.
- Exhaust Stroke: The piston moves up again, pushing the exhaust gases out of the cylinder through the exhaust valve.
4. Advantages of a Hemi Engine
Hemi engines offer several distinct advantages over other engine designs, contributing to their reputation for power and performance.
- Improved Airflow: The hemispherical combustion chamber and large valves allow for better airflow into and out of the cylinder. This improves the engine’s ability to breathe, resulting in increased power.
- Efficient Combustion: The spark plug’s central location ensures a more complete and efficient combustion of the air-fuel mixture. This results in more power and reduced emissions.
- High Compression Ratio: The Hemi design allows for a higher compression ratio, which increases the engine’s thermal efficiency and power output.
- Reduced Heat Loss: The smaller surface area-to-volume ratio of the hemispherical chamber reduces heat loss during combustion, leading to higher peak pressures and more power.
- Greater Valve Size: The arrangement of valves on opposite sides of the head allows for greater valve size, further improving the airflow through the engine.
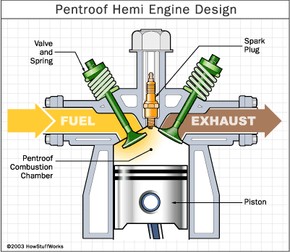 Hemi Engine Combustion Chamber
Hemi Engine Combustion Chamber
5. Disadvantages of a Hemi Engine
Despite their advantages, Hemi engines also have some drawbacks compared to more modern engine designs.
- Complex Design: The hemispherical head design is more complex and expensive to manufacture than other designs.
- Larger Size: Hemi engines tend to be physically larger than other engines with similar displacement, which can limit their use in certain vehicles.
- Two-Valve Configuration: Traditional Hemi engines typically use only two valves per cylinder, which can limit their ability to breathe at high RPMs compared to engines with four valves per cylinder.
- Combustion Chamber Shape: The hemispherical shape can sometimes lead to slower flame propagation, especially in larger engines.
- Weight: Hemi engines can be heavier than comparable engines due to the larger heads and components.
6. Key Components of a Hemi Engine
Several key components contribute to the Hemi engine’s unique performance characteristics.
- Hemispherical Heads: The defining feature of the Hemi engine, the hemispherical heads provide the combustion chamber’s distinctive shape.
- Large Valves: The large intake and exhaust valves allow for optimal airflow into and out of the cylinder.
- Spark Plug Location: The centrally located spark plug ensures efficient ignition of the air-fuel mixture.
- High-Performance Camshaft: The camshaft is designed to maximize valve lift and duration, further enhancing the engine’s performance.
- Reinforced Engine Block: The engine block is typically reinforced to withstand the high pressures and stresses generated by the Hemi’s powerful combustion.
7. Applications of Hemi Engines
Hemi engines have been used in a variety of applications, from passenger cars to racing vehicles.
- Passenger Cars: Chrysler has used Hemi engines in various passenger cars, including the Chrysler 300, Dodge Charger, and Dodge Challenger.
- Trucks and SUVs: Hemi engines are also found in trucks and SUVs, such as the Ram 1500, 2500, and 3500.
- Motorsports: Hemi engines have a long and successful history in motorsports, particularly in NASCAR and drag racing.
- Marine Applications: Some Hemi engines have been used in marine applications, powering boats and other watercraft.
8. Hemi vs. Other Engine Designs
Comparing the Hemi engine to other engine designs highlights its unique strengths and weaknesses.
- Hemi vs. Flathead: The Hemi offers significantly better airflow and combustion efficiency compared to flathead engines, resulting in much higher power output.
- Hemi vs. Wedge: Wedge-shaped combustion chambers are more compact but don’t offer the same airflow advantages as the Hemi.
- Hemi vs. Pentroof: Pentroof designs, which accommodate four valves per cylinder, can offer better breathing at high RPMs but may not match the Hemi’s low-end torque.
9. Modern Hemi Engines: Technology and Innovations
Modern Hemi engines incorporate advanced technology to improve performance, efficiency, and emissions.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT): VVT optimizes valve timing to improve engine performance and fuel economy across a wide range of RPMs.
- Cylinder Deactivation (MDS): MDS deactivates certain cylinders under light load conditions to improve fuel economy.
- Direct Injection: Direct injection precisely meters fuel directly into the combustion chamber, improving combustion efficiency and reducing emissions.
- Forced Induction: Superchargers and turbochargers are used to force more air into the engine, significantly increasing power output.
- Advanced Engine Management Systems: Modern engine management systems precisely control fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other parameters to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
10. The Future of Hemi Engines
The future of Hemi engines is evolving with the automotive industry’s shift towards electrification and more efficient combustion technologies.
- Hybridization: Hemi engines may be paired with electric motors in hybrid powertrains to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions.
- Alternative Fuels: Research is ongoing to adapt Hemi engines to run on alternative fuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel.
- Advanced Combustion Technologies: Future Hemi engines may incorporate advanced combustion technologies, such as gasoline direct injection (GDI) and advanced ignition systems, to further improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Downsizing and Turbocharging: Smaller displacement Hemi engines with turbocharging may become more common, offering a balance of power and efficiency.
11. Maintaining and Caring for a Hemi Engine
Proper maintenance is essential to keep a Hemi engine running smoothly and reliably.
- Regular Oil Changes: Use high-quality synthetic oil and change it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace the air filter regularly to ensure proper airflow into the engine.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replace the spark plugs according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to maintain optimal ignition performance.
- Coolant Flushes: Flush the cooling system periodically to prevent corrosion and maintain optimal cooling performance.
- Regular Inspections: Have the engine inspected regularly by a qualified mechanic to identify and address any potential issues.
12. Common Problems with Hemi Engines
While Hemi engines are generally reliable, they can experience certain common problems.
- Hemi Tick: A ticking noise that can be caused by various factors, including exhaust manifold leaks, lifter issues, or valve train wear.
- Exhaust Manifold Bolts: Exhaust manifold bolts can break or loosen over time, leading to exhaust leaks.
- Oil Consumption: Some Hemi engines may experience excessive oil consumption, which can be caused by worn piston rings or valve seals.
- Camshaft and Lifter Wear: Camshaft and lifter wear can occur, especially in engines that are not properly maintained or are subjected to excessive stress.
- Sensor Failures: Various sensors, such as oxygen sensors and crankshaft position sensors, can fail over time, leading to engine performance issues.
13. Performance Upgrades for Hemi Engines
Many performance upgrades are available for Hemi engines, allowing enthusiasts to further enhance their power and performance.
- Cold Air Intake: A cold air intake can improve airflow into the engine, increasing horsepower and torque.
- Performance Exhaust System: A performance exhaust system can reduce backpressure, allowing the engine to breathe more freely and increasing power.
- Performance Tuner: A performance tuner can remap the engine’s computer to optimize fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other parameters for increased power.
- Supercharger or Turbocharger: Adding a supercharger or turbocharger can significantly increase the engine’s power output.
- Camshaft Upgrade: Upgrading the camshaft can improve valve lift and duration, further enhancing the engine’s performance.
14. Hemi Engine Swaps: A Popular Modification
Swapping a Hemi engine into another vehicle is a popular modification among automotive enthusiasts.
- Classic Cars: Hemi engine swaps are often performed on classic cars to add modern power and performance.
- Trucks and SUVs: Swapping a Hemi engine into a truck or SUV can significantly increase its towing and hauling capabilities.
- Custom Builds: Hemi engines are often used in custom car builds, providing a powerful and reliable engine option.
- Considerations: When performing a Hemi engine swap, it’s important to consider factors such as engine mounts, wiring, cooling, and exhaust systems.
15. Famous Vehicles with Hemi Engines
Several famous vehicles have been powered by Hemi engines, cementing their place in automotive history.
- 1966-1971 Plymouth Barracuda: The Hemi-powered Barracuda was a dominant force in drag racing and a sought-after muscle car.
- 1968-1970 Dodge Charger: The Hemi-powered Charger is an iconic muscle car known for its power and performance.
- Chrysler 300: The modern Chrysler 300 offers a Hemi engine option, providing a blend of luxury and performance.
- Dodge Challenger: The Dodge Challenger is available with a range of Hemi engines, including the supercharged Hellcat versions.
- Ram Trucks: Ram trucks offer Hemi engine options, providing powerful and reliable performance for towing and hauling.
16. Hemi Engine Myths and Misconceptions
Several myths and misconceptions surround Hemi engines.
- Myth: All Chrysler engines are Hemis.
- Fact: Not all Chrysler engines are Hemis; the Hemi is a specific engine design with hemispherical combustion chambers.
- Myth: Hemis are only good for racing.
- Fact: While Hemis have a successful racing history, they are also used in passenger cars, trucks, and SUVs.
- Myth: Hemis are unreliable.
- Fact: Hemis are generally reliable engines when properly maintained.
- Myth: Hemis are fuel-efficient.
- Fact: Hemis are not typically known for their fuel efficiency, but modern versions with advanced technologies offer improved MPG.
- Myth: Hemis are outdated technology.
- Fact: While the Hemi design has been around for decades, modern versions incorporate advanced technologies to improve performance and efficiency.
17. Hemi Engine Terminology
Understanding common Hemi engine terminology can help you better understand their workings and performance characteristics.
- Cubic Inch (CID): A measure of the engine’s displacement, which is the total volume of air and fuel that the engine can draw in during one complete cycle.
- Horsepower (HP): A measure of the engine’s power output.
- Torque (lb-ft): A measure of the engine’s twisting force.
- Compression Ratio: The ratio of the volume of the cylinder when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke to the volume when the piston is at the top of its stroke.
- Valve Lift: The distance that the valve opens.
- Valve Duration: The length of time that the valve remains open.
- RPM (Revolutions Per Minute): A measure of how fast the engine’s crankshaft is rotating.
18. The Role of Valve Train in a Hemi Engine
The valve train is a critical component of the Hemi engine, responsible for controlling the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves.
- Components: The valve train includes the camshaft, lifters, pushrods, rocker arms, and valves.
- Camshaft: The camshaft is a rotating shaft with lobes that actuate the lifters.
- Lifters: Lifters are located between the camshaft and pushrods, and they transmit the motion of the camshaft lobes to the pushrods.
- Pushrods: Pushrods transmit the motion of the lifters to the rocker arms.
- Rocker Arms: Rocker arms pivot to open and close the valves.
- Valve Timing: The valve train controls the timing of the valve openings and closings, which is critical for engine performance.
19. Why is the Hemi Engine Popular in Motorsports?
The Hemi engine has a long and successful history in motorsports due to its high power output and durability.
- NASCAR: Hemi engines were a dominant force in NASCAR throughout the 1960s and 1970s.
- Drag Racing: Hemi engines are a popular choice for drag racing due to their ability to produce massive amounts of power.
- Engine Design Advantages: The Hemi’s design advantages, such as improved airflow and efficient combustion, make it well-suited for racing applications.
- Aftermarket Support: A wide range of aftermarket parts and upgrades are available for Hemi engines, making them a popular choice for racers.
- Durability: Hemi engines are known for their durability, which is essential in the demanding environment of motorsports.
20. How to Identify a Hemi Engine
Identifying a Hemi engine can be done through several key characteristics.
- Hemispherical Heads: The most obvious characteristic of a Hemi engine is its hemispherical heads.
- Valve Arrangement: The valves are arranged on opposite sides of the combustion chamber.
- Spark Plug Location: The spark plug is located at the top center of the hemisphere.
- Engine Markings: Hemi engines typically have specific markings or designations on the engine block and heads.
- Vehicle Application: Certain vehicles are known to have Hemi engine options, such as the Chrysler 300, Dodge Charger, and Ram trucks.
21. Understanding Hemi Engine Displacement
Displacement is a critical factor in determining an engine’s power output.
- Definition: Engine displacement refers to the total volume of air and fuel that an engine can draw in during one complete cycle, typically measured in cubic inches (CID) or liters (L).
- Impact on Power: Generally, larger displacement engines produce more power than smaller displacement engines, assuming similar designs and technologies.
- Hemi Engine Examples: Hemi engines have been produced in various displacements, including 331 CID, 354 CID, 392 CID, 426 CID, 5.7L, 6.1L, 6.4L, and 6.2L.
- Relationship to Performance: Higher displacement Hemi engines often offer more torque at lower RPMs, while smaller displacement engines may offer better fuel efficiency.
22. The Impact of Cylinder Head Design on Hemi Performance
The cylinder head design is crucial to the Hemi engine’s performance.
- Hemispherical Shape: The hemispherical shape of the combustion chamber allows for larger valves and improved airflow.
- Valve Angle: The angle of the valves in relation to the cylinder bore affects the engine’s breathing characteristics.
- Port Design: The design of the intake and exhaust ports influences the flow of air and exhaust gases.
- Material: The material used to construct the cylinder head affects its ability to dissipate heat and withstand high pressures.
- Cooling: Efficient cooling of the cylinder head is essential to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance.
23. How Does Forced Induction Enhance Hemi Engine Performance?
Forced induction, such as supercharging and turbocharging, can significantly enhance Hemi engine performance.
- Supercharging: A supercharger is a mechanical device that is driven by the engine’s crankshaft and forces more air into the cylinders.
- Turbocharging: A turbocharger uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which then forces more air into the cylinders.
- Increased Power: Forced induction increases the amount of air and fuel that can be burned in the cylinders, resulting in significantly higher power output.
- Boost Pressure: The amount of pressure that the forced induction system generates is known as boost pressure.
- Intercooling: An intercooler is often used to cool the air that is compressed by the supercharger or turbocharger, further increasing its density and power potential.
24. Understanding the Hemi Engine’s Ignition System
The ignition system is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders.
- Components: The ignition system includes the spark plugs, ignition coil, distributor (in older engines), and ignition control module.
- Spark Plugs: Spark plugs create an electrical spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture.
- Ignition Coil: The ignition coil generates the high voltage required to create the spark.
- Distributor: The distributor (in older engines) distributes the high voltage to the spark plugs in the correct firing order.
- Ignition Control Module: The ignition control module controls the timing of the spark.
- Modern Systems: Modern Hemi engines use coil-on-plug ignition systems, which eliminate the distributor and provide a more precise and reliable spark.
25. The Role of Fuel Injection in Modern Hemi Engines
Fuel injection plays a critical role in the performance and efficiency of modern Hemi engines.
- Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI): EFI systems use electronic sensors and a computer to precisely control the amount of fuel that is injected into the cylinders.
- Multi-Port Fuel Injection (MPFI): MPFI systems inject fuel into each intake port, providing a more even distribution of fuel to the cylinders.
- Direct Injection (DI): DI systems inject fuel directly into the combustion chamber, allowing for more precise control of fuel delivery and improved combustion efficiency.
- Fuel Injectors: Fuel injectors are responsible for delivering fuel into the cylinders.
- Fuel Pump: The fuel pump provides the necessary fuel pressure to the fuel injectors.
26. How Does the Hemi Engine’s Cooling System Work?
The cooling system is essential to prevent the Hemi engine from overheating.
- Components: The cooling system includes the radiator, water pump, thermostat, coolant hoses, and coolant.
- Radiator: The radiator dissipates heat from the coolant.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates the coolant through the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the temperature of the coolant.
- Coolant Hoses: Coolant hoses connect the various components of the cooling system.
- Coolant: Coolant is a mixture of water and antifreeze that helps to dissipate heat and prevent corrosion.
27. Understanding the Hemi Engine’s Lubrication System
The lubrication system is responsible for lubricating the engine’s moving parts, reducing friction and wear.
- Components: The lubrication system includes the oil pump, oil filter, oil pan, and oil passages.
- Oil Pump: The oil pump circulates oil through the engine.
- Oil Filter: The oil filter removes contaminants from the oil.
- Oil Pan: The oil pan stores the oil.
- Oil Passages: Oil passages distribute oil to the engine’s moving parts.
- Oil Viscosity: The viscosity of the oil is a measure of its resistance to flow.
28. The Future of Hemi Engines in Electric Vehicles
As the automotive industry shifts towards electric vehicles, the future of Hemi engines is uncertain.
- Hybridization: Hemi engines may be paired with electric motors in hybrid powertrains to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions.
- Synthetic Fuels: The use of synthetic fuels could allow Hemi engines to continue to be used in a more environmentally friendly way.
- Performance Applications: Hemi engines may continue to be used in performance applications, such as racing and high-performance vehicles.
- Legacy: The Hemi engine will likely remain a significant part of automotive history, even as electric vehicles become more prevalent.
- Innovation: There may be new innovations in Hemi engine technology that could allow them to remain relevant in the future.
29. Hemi Engine Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Proper diagnosis is essential for maintaining and repairing Hemi engines.
- OBD-II Scanners: OBD-II scanners can be used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the engine’s computer.
- Multimeters: Multimeters can be used to test the voltage, resistance, and current of various electrical components.
- Compression Testers: Compression testers can be used to measure the compression in each cylinder.
- Leak-Down Testers: Leak-down testers can be used to identify leaks in the cylinders.
- Scan Tools: Advanced scan tools can be used to access more detailed engine data and perform diagnostic tests.
30. Hemi Engine Restoration Tips for Classic Car Enthusiasts
Restoring a classic car with a Hemi engine can be a rewarding but challenging project.
- Research: Research the specific Hemi engine that you are restoring to ensure that you have the correct parts and information.
- Documentation: Document the restoration process with photos and notes.
- Parts Sourcing: Source high-quality parts from reputable suppliers.
- Cleaning: Thoroughly clean all of the engine components.
- Machining: Have the engine block and heads machined as needed.
- Assembly: Carefully assemble the engine, following the manufacturer’s specifications.
31. How to Choose the Right Hemi Engine for Your Project
Choosing the right Hemi engine for your project depends on several factors.
- Budget: Determine your budget for the engine and any necessary modifications.
- Application: Consider the intended use of the engine, such as street driving, racing, or towing.
- Power Goals: Determine your power goals for the engine.
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure that the engine is compatible with your vehicle.
- Availability: Check the availability of the engine and any necessary parts.
32. The Environmental Impact of Hemi Engines
The environmental impact of Hemi engines is a growing concern.
- Emissions: Hemi engines can produce significant emissions, including carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons.
- Fuel Consumption: Hemi engines can have high fuel consumption, especially in older models.
- Modern Technologies: Modern Hemi engines incorporate technologies such as variable valve timing and cylinder deactivation to reduce emissions and improve fuel economy.
- Alternative Fuels: The use of alternative fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel can reduce the environmental impact of Hemi engines.
- Electric Hybrids: Pairing Hemi engines with electric motors in hybrid powertrains can significantly reduce emissions and improve fuel economy.
33. Hemi Engine Aftermarket: Performance Parts and Accessories
The Hemi engine aftermarket offers a wide range of performance parts and accessories.
- Intake Manifolds: Aftermarket intake manifolds can improve airflow into the engine.
- Exhaust Systems: Aftermarket exhaust systems can reduce backpressure and increase power.
- Camshafts: Aftermarket camshafts can improve valve lift and duration.
- Cylinder Heads: Aftermarket cylinder heads can improve airflow and combustion efficiency.
- Superchargers and Turbochargers: Aftermarket superchargers and turbochargers can significantly increase power output.
34. The Resale Value of Vehicles with Hemi Engines
Vehicles with Hemi engines often have strong resale value.
- Demand: There is strong demand for vehicles with Hemi engines, especially among enthusiasts.
- Performance: The Hemi engine’s reputation for performance helps to maintain the vehicle’s value.
- Condition: The condition of the vehicle and the engine is a major factor in determining its resale value.
- Mileage: Lower mileage vehicles typically have higher resale values.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance and service records can help to increase the vehicle’s resale value.
35. Hemi Engine Security: Preventing Theft and Vandalism
Protecting a Hemi engine from theft and vandalism is essential.
- Alarm Systems: Install an alarm system to deter theft.
- GPS Tracking: Use a GPS tracking device to locate the vehicle if it is stolen.
- Engine Immobilizers: Install an engine immobilizer to prevent the engine from being started without the correct key.
- Garage Parking: Park the vehicle in a garage or secure location whenever possible.
- Security Cameras: Install security cameras to monitor the vehicle.
36. Hemi Engine Communities and Online Resources
Numerous online communities and resources are available for Hemi engine enthusiasts.
- Forums: Online forums provide a place for enthusiasts to share information, ask questions, and connect with other Hemi owners.
- Websites: Websites dedicated to Hemi engines offer technical information, articles, and product reviews.
- Social Media: Social media groups and pages provide a platform for enthusiasts to share photos, videos, and information about their Hemi engines.
- Clubs: Car clubs often have members who are Hemi engine enthusiasts.
- Events: Car shows and racing events provide opportunities to see Hemi engines in action and connect with other enthusiasts.
37. Famous People Who Love Hemi Engines
Many famous people are known to be fans of Hemi engines.
- Jay Leno: Jay Leno is a well-known car enthusiast who owns several vehicles with Hemi engines.
- Tim Allen: Tim Allen is a car enthusiast who has customized several vehicles with Hemi engines.
- Richard Petty: Richard Petty is a NASCAR legend who drove Hemi-powered cars during his racing career.
- Don Garlits: Don Garlits is a drag racing legend who is known for his Hemi-powered dragsters.
- Chip Foose: Chip Foose is a car designer and builder who has worked on several projects involving Hemi engines.
38. Frequently Asked Questions About Hemi Engines
Here are some frequently asked questions about Hemi engines:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What does “Hemi” stand for? | “Hemi” stands for hemispherical, referring to the shape of the combustion chamber. |
| What are the advantages of a Hemi engine? | Improved airflow, efficient combustion, high compression ratio, reduced heat loss, and greater valve size. |
| What are the disadvantages of a Hemi engine? | Complex design, larger size, two-valve configuration, combustion chamber shape, and weight. |
| What are some common problems with Hemi engines? | Hemi tick, exhaust manifold bolts, oil consumption, camshaft and lifter wear, and sensor failures. |
| Can I upgrade my Hemi engine for more power? | Yes, many performance upgrades are available, including cold air intakes, performance exhaust systems, performance tuners, superchargers, and camshaft upgrades. |
| Are Hemi engines reliable? | Hemi engines are generally reliable when properly maintained. |
| What vehicles come with Hemi engines? | Chrysler 300, Dodge Charger, Dodge Challenger, and Ram trucks. |
| How can I identify a Hemi engine? | Look for hemispherical heads, valve arrangement, spark plug location, engine markings, and vehicle application. |
| Are Hemi engines fuel-efficient? | Modern Hemi engines with advanced technologies offer improved fuel economy, but they are not typically known for being the most fuel-efficient engines. |
| What is the future of Hemi engines? | Hybridization, alternative fuels, advanced combustion technologies, downsizing, and turbocharging. |
Do you have more questions about Hemi engines or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN! Our team of experts is here to provide you with quick, accurate, and free answers to all your queries.
Need Answers? Ask Away at WHAT.EDU.VN
Are you tired of searching endlessly for reliable answers? Do you have questions that need immediate solutions? Look no further! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding accurate information quickly and easily. That’s why we’ve created a platform dedicated to providing you with free, expert answers to all your questions.
Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Answers: Get expert answers without spending a dime.
- Fast Responses: Receive prompt and accurate information.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is designed for simplicity and convenience.
- Community Support: Connect with knowledgeable individuals and share insights.
- Expert Advice: Benefit from the expertise of experienced professionals.
Get in Touch
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the ease of finding the information you need!
Whether you’re a student, professional, or simply curious, what.edu.vn is your go-to resource for free and reliable answers. Join our community and start asking questions today!
