What Is A Hologram? Holograms are three-dimensional images formed by the interference of light beams from a laser or other coherent light source. If you are seeking a deeper understanding of optical holography and its applications, WHAT.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive and accessible resource to address your inquiries. Delve into the world of 3D imaging, holographic technology, and optical illusions!
1. Understanding the Basics: What is a Hologram?
A hologram is a unique type of photograph that records the light scattered from an object and then reconstructs it to appear three-dimensional. Unlike a traditional photograph, which captures only the intensity of light, a hologram also records the phase, allowing for a complete recreation of the original light field. This creates the illusion of depth and allows viewers to see the object from different angles, as if it were truly present.
1.1 The Science Behind Holograms
Creating a hologram involves a process called holography, which uses laser light to record the interference pattern created when two beams of light meet. One beam, called the object beam, is directed at the object being recorded. The light reflected from the object then interferes with a second beam, called the reference beam, which is directed straight onto the recording medium. The resulting interference pattern is what gets recorded on the holographic plate.
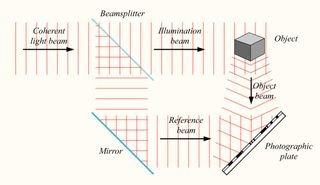 Diagram illustrating how a hologram is created using laser beams, an object, and a recording medium
Diagram illustrating how a hologram is created using laser beams, an object, and a recording medium
Alt text: Hologram creation process with laser beams and recording medium.
1.2 Key Components for Creating a Hologram
To create a hologram, you need several key components:
- Object: The subject you want to record.
- Laser Beam: A coherent light source to illuminate the object and create the reference beam.
- Mirrors: To split and redirect the laser beam.
- Recording Medium: A material sensitive to light that can record the interference pattern, such as holographic film or photopolymer.
- Clear Environment: A stable environment free from vibrations and air currents.
1.3 How Holograms Differ From Regular Photographs
| Feature | Hologram | Regular Photograph |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensionality | Three-dimensional | Two-dimensional |
| Light Recorded | Intensity and phase | Intensity only |
| Viewing Angle | Can be viewed from different angles, revealing different perspectives | Viewed from a fixed angle |
| Recording Process | Interference pattern of two laser beams | Direct capture of light reflected from the object using a lens |
| Information Storage | Stores a complete record of the light field | Stores a flat representation of the object’s appearance |
2. A Brief History of Holography
The concept of holography was first developed in 1947 by Hungarian-British physicist Dennis Gabor, who later won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1971 for his invention. However, it wasn’t until the 1960s, with the invention of the laser, that holography became practical.
2.1 Early Developments in Holography
- 1947: Dennis Gabor invents holography.
- 1960s: Development of lasers makes holography practical. Yuri Denisyuk and Emmett Leith independently develop techniques for recording 3D objects using lasers.
- 1962: The first laser transmission hologram was created by Emmett Leith and Juris Upatnieks at the University of Michigan.
2.2 Advancements in Materials and Techniques
Over the years, significant advancements have been made in both the materials used for recording holograms and the techniques employed. Early holograms used silver halide photographic emulsions, but these had limitations in terms of clarity and brightness. New materials, such as photopolymers, have been developed that offer higher resolution and greater efficiency.
2.3 Notable Milestones in Holographic Technology
- Rainbow Holograms: Developed by Stephen Benton in 1968, these holograms can be viewed with white light, making them more accessible and practical for everyday applications like security features on credit cards.
- Computer-Generated Holograms (CGH): These holograms are created using computer algorithms and can represent virtual objects or data, opening up new possibilities for scientific visualization and data storage.
- Holographic Interferometry: A technique that uses holograms to detect minute changes or deformations in objects, with applications in engineering and materials science.
3. Types of Holograms: A Comprehensive Overview
Holograms come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the different types can help you appreciate the versatility of this technology.
3.1 Transmission Holograms
Transmission holograms are created by shining a laser beam through the hologram to reconstruct the image. The viewer looks through the hologram to see the three-dimensional image. These types of holograms are often used in scientific and industrial applications.
- Viewing Method: Laser beam shone through the hologram.
- Image Appearance: Three-dimensional image seen by looking through the hologram.
- Common Uses: Scientific research, industrial inspection.
3.2 Reflection Holograms
Reflection holograms, also known as Denisyuk holograms, are viewed by shining white light onto the surface of the hologram. The light is reflected off the holographic structure, recreating the three-dimensional image. These holograms are commonly found on credit cards, driver’s licenses, and other security applications.
- Viewing Method: White light shone onto the surface.
- Image Appearance: Three-dimensional image reflected off the surface.
- Common Uses: Security features, decorative items.
3.3 Rainbow Holograms
Rainbow holograms are a type of transmission hologram that can be viewed with white light. They are designed to produce a bright, multi-colored image when illuminated. These holograms are widely used for security purposes and in novelty items.
- Viewing Method: White light illumination.
- Image Appearance: Bright, multi-colored three-dimensional image.
- Common Uses: Security features, novelty items, packaging.
3.4 Computer-Generated Holograms (CGH)
Computer-generated holograms are created using computer algorithms to simulate the interference pattern that would be produced by an object. These holograms can represent virtual objects or data and can be used in a variety of applications, including scientific visualization and data storage.
- Creation Method: Computer algorithms.
- Image Representation: Virtual objects or data.
- Common Uses: Scientific visualization, data storage, optical elements.
3.5 Embossed Holograms
Embossed holograms are created by pressing a holographic pattern onto a thin film of plastic. These holograms are inexpensive to produce and are widely used for security features on credit cards and other products.
- Creation Method: Pressing a holographic pattern onto plastic.
- Production Cost: Inexpensive.
- Common Uses: Security features, packaging.
4. Applications of Holograms: Where Are They Used?
Holograms have a wide range of applications across various industries, from security and entertainment to science and medicine. Their unique ability to create three-dimensional images makes them invaluable in many fields.
4.1 Security Applications
Holograms are widely used for security purposes to prevent counterfeiting and fraud. They are found on credit cards, driver’s licenses, currency, and other valuable documents. The complex interference patterns in holograms are difficult to replicate, making them an effective security feature.
- Credit Cards: Holographic images provide a visual authentication feature.
- Driver’s Licenses: Help prevent forgery and identity theft.
- Currency: Enhance security and reduce the risk of counterfeiting.
- Product Packaging: Protect against product piracy and ensure authenticity.
4.2 Entertainment and Art
Holograms have made a significant impact on the entertainment industry, creating captivating visual experiences in movies, concerts, and exhibitions. They can bring virtual characters to life and create stunning visual effects.
- Movies: Used for special effects and creating realistic three-dimensional scenes.
- Concerts: Enable virtual performances of deceased artists or create immersive stage experiences.
- Exhibitions: Display historical artifacts or artistic creations in a unique and engaging way.
- Theme Parks: Enhance attractions with holographic projections and interactive displays.
4.3 Scientific and Industrial Applications
In science and industry, holograms are used for a variety of purposes, including data storage, microscopy, and non-destructive testing. Their ability to record and reconstruct detailed three-dimensional information makes them valuable tools for research and development.
- Data Storage: Holographic data storage offers high-density storage capabilities.
- Microscopy: Holographic microscopy provides three-dimensional imaging of microscopic samples.
- Non-Destructive Testing: Holographic interferometry detects flaws and deformations in materials without damaging them.
- Optical Elements: Computer-generated holograms are used to create custom optical elements for various applications.
4.4 Medical Imaging
Holographic imaging techniques are being developed for medical applications, such as three-dimensional X-ray imaging and holographic microscopy. These techniques can provide detailed views of the human body and enable more accurate diagnoses.
- Three-Dimensional X-Ray Imaging: Provides detailed anatomical views.
- Holographic Microscopy: Enables high-resolution imaging of cells and tissues.
- Surgical Planning: Aids in visualizing complex anatomical structures for surgical procedures.
- Medical Education: Offers interactive three-dimensional models for training purposes.
4.5 Display Technology
Holographic display technology is emerging as a promising alternative to traditional displays. Holographic displays can create true three-dimensional images without the need for special glasses or headsets.
- Heads-Up Displays (HUDs): Project information onto windshields or visors for pilots and drivers.
- 3D Televisions and Monitors: Provide immersive viewing experiences without glasses.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Displays: Overlay virtual information onto the real world.
- Mobile Devices: Enable glasses-free 3D viewing on smartphones and tablets.
5. The Future of Holograms: What’s Next?
The field of holography is constantly evolving, with new technologies and applications emerging all the time. Researchers are working to improve the resolution, brightness, and interactivity of holograms, paving the way for exciting new possibilities.
5.1 Advancements in Holographic Displays
One of the most promising areas of development is in holographic displays. Researchers are working on creating displays that can project realistic three-dimensional images that can be viewed from any angle without the need for special glasses. These displays could revolutionize the way we interact with computers and other devices.
- Increased Resolution: Improving the clarity and detail of holographic images.
- Larger Viewing Angles: Allowing more people to view the hologram simultaneously.
- Interactive Holograms: Enabling users to interact with holographic images in real-time.
- Real-Time Holography: Creating dynamic holograms that can change and respond to user input.
5.2 Holographic Memory and Data Storage
Holographic memory is another area of active research. Holograms can store vast amounts of data in a three-dimensional space, offering the potential for much higher storage densities than traditional storage media.
- High-Density Storage: Storing terabytes of data in a small volume.
- Fast Data Access: Retrieving data quickly and efficiently.
- Long-Term Archiving: Preserving data for extended periods.
- Secure Data Storage: Protecting data from unauthorized access.
5.3 Holographic Telepresence
Holographic telepresence aims to create a realistic, three-dimensional representation of a person in a remote location. This technology could revolutionize communication and collaboration, allowing people to interact as if they were in the same room.
- Real-Time Communication: Transmitting holographic images in real-time.
- Three-Dimensional Representation: Creating a realistic representation of a person’s appearance and movements.
- Interactive Communication: Enabling users to interact with the holographic image.
- Remote Collaboration: Facilitating remote meetings and collaborations.
5.4 Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the exciting potential of holography, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. These include improving the brightness and resolution of holographic images, reducing the cost of holographic displays, and developing new materials and techniques for creating holograms.
- Improving Brightness and Resolution: Enhancing the visual quality of holograms.
- Reducing Costs: Making holographic technology more accessible.
- Developing New Materials: Creating more efficient and versatile holographic materials.
- Overcoming Technical Challenges: Addressing issues related to coherence, stability, and environmental factors.
6. Common Misconceptions About Holograms
There are many misconceptions about what holograms are and how they work. It’s important to understand the difference between true holograms and other types of three-dimensional displays.
6.1 Holograms vs. 3D Projections
One common misconception is that any three-dimensional image is a hologram. In reality, many so-called “holograms” are actually 3D projections created using techniques like Pepper’s ghost or volumetric displays. These projections may look three-dimensional, but they don’t have the same properties as true holograms.
- True Holograms: Record and reconstruct the entire light field, allowing viewers to see the object from different angles.
- 3D Projections: Create the illusion of depth using tricks of perspective or by projecting images onto a surface.
6.2 Holograms in Popular Culture
Movies like “Star Wars” and “Iron Man” have popularized the idea of holograms as interactive, real-time displays. While holographic technology is advancing rapidly, we are not yet at the point where we can create the kinds of holograms seen in these movies.
- Movie Holograms: Often depict advanced holographic displays with features that are not yet possible.
- Current Technology: Holograms are typically static or require specialized equipment to view.
6.3 Understanding the Limitations of Current Technology
It’s important to have realistic expectations about what holograms can do. Current holographic technology has limitations in terms of brightness, resolution, and interactivity. However, researchers are constantly working to overcome these limitations and develop new and improved holographic techniques.
- Brightness: Holograms can be dim and difficult to see in bright light.
- Resolution: The resolution of holographic images is often lower than that of traditional displays.
- Interactivity: Most holograms are static and cannot be interacted with in real-time.
7. Frequently Asked Questions About Holograms
Here are some frequently asked questions about holograms:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between a hologram and a photograph? | A hologram records both the intensity and phase of light, creating a three-dimensional image, while a photograph records only the intensity, resulting in a two-dimensional image. |
| How are holograms created? | Holograms are created by recording the interference pattern of two laser beams: one directed at the object and one used as a reference. |
| What are the different types of holograms? | There are several types of holograms, including transmission holograms, reflection holograms, rainbow holograms, computer-generated holograms, and embossed holograms. |
| What are holograms used for? | Holograms are used in a variety of applications, including security, entertainment, scientific research, medical imaging, and display technology. |
| Can holograms be viewed with white light? | Some types of holograms, such as rainbow holograms and reflection holograms, can be viewed with white light. |
| Are holograms the same as 3D projections? | No, holograms are different from 3D projections. Holograms record and reconstruct the entire light field, allowing viewers to see the object from different angles, while 3D projections create the illusion of depth using tricks of perspective. |
| What is holographic memory? | Holographic memory is a type of data storage that uses holograms to store data in a three-dimensional space, offering the potential for high storage densities. |
| What is holographic telepresence? | Holographic telepresence is a technology that aims to create a realistic, three-dimensional representation of a person in a remote location, allowing for more immersive and interactive communication. |
| What are the challenges of holographic technology? | Challenges include improving the brightness and resolution of holographic images, reducing the cost of holographic displays, and developing new materials and techniques for creating holograms. |
| Where can I learn more about holograms? | You can learn more about holograms through books, articles, online resources, and educational websites like WHAT.EDU.VN. |
8. Explore the World of Holograms with WHAT.EDU.VN
Do you still have questions about holograms or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a platform where you can freely ask any question and receive answers from knowledgeable individuals. Whether you’re curious about the science behind holograms, their applications, or the latest advancements in the field, we’re here to help.
Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Questioning: Ask any question without any cost.
- Fast and Accurate Answers: Receive quick and reliable responses from experts.
- Easy-to-Understand Information: Get explanations that are clear and accessible to everyone.
- Community Support: Connect with others to exchange knowledge and ideas.
- Convenient and Accessible: Get answers anytime, anywhere.
Don’t let your curiosity wait. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and start exploring the world of knowledge!
Contact Information:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Take the Next Step: Ask Your Question Now!
Ready to dive deeper into the world of holograms and beyond? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question. Our community of experts is eager to provide you with the answers you need. Start your journey of discovery now!
By visiting what.edu.vn, you open the door to a world of knowledge and endless possibilities. Ask your question today and let us help you explore the fascinating world of holograms!

