Every business, regardless of its size or industry, needs a way to measure success. This is where Key Performance Indicators, or KPIs, come into play. KPIs are quantifiable metrics used to evaluate the success of an organization, department, team, or individual in reaching their objectives and goals. They provide a focused way to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. Think of them as signposts that guide businesses towards their desired outcomes.
KPIs are not just about measuring activities; they are about measuring outcomes that are directly linked to strategic goals. A good KPI is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By focusing on these key indicators, businesses can gain a clearer picture of their performance and ensure they are on the right track to success.
Let’s explore some examples of KPIs across different departments to understand how they are applied in practice.
Key Performance Indicators by Department
Different departments within a company have unique objectives and, therefore, different KPIs that are relevant to their operations and contributions to the overall business goals. Here are some key examples categorized by department:
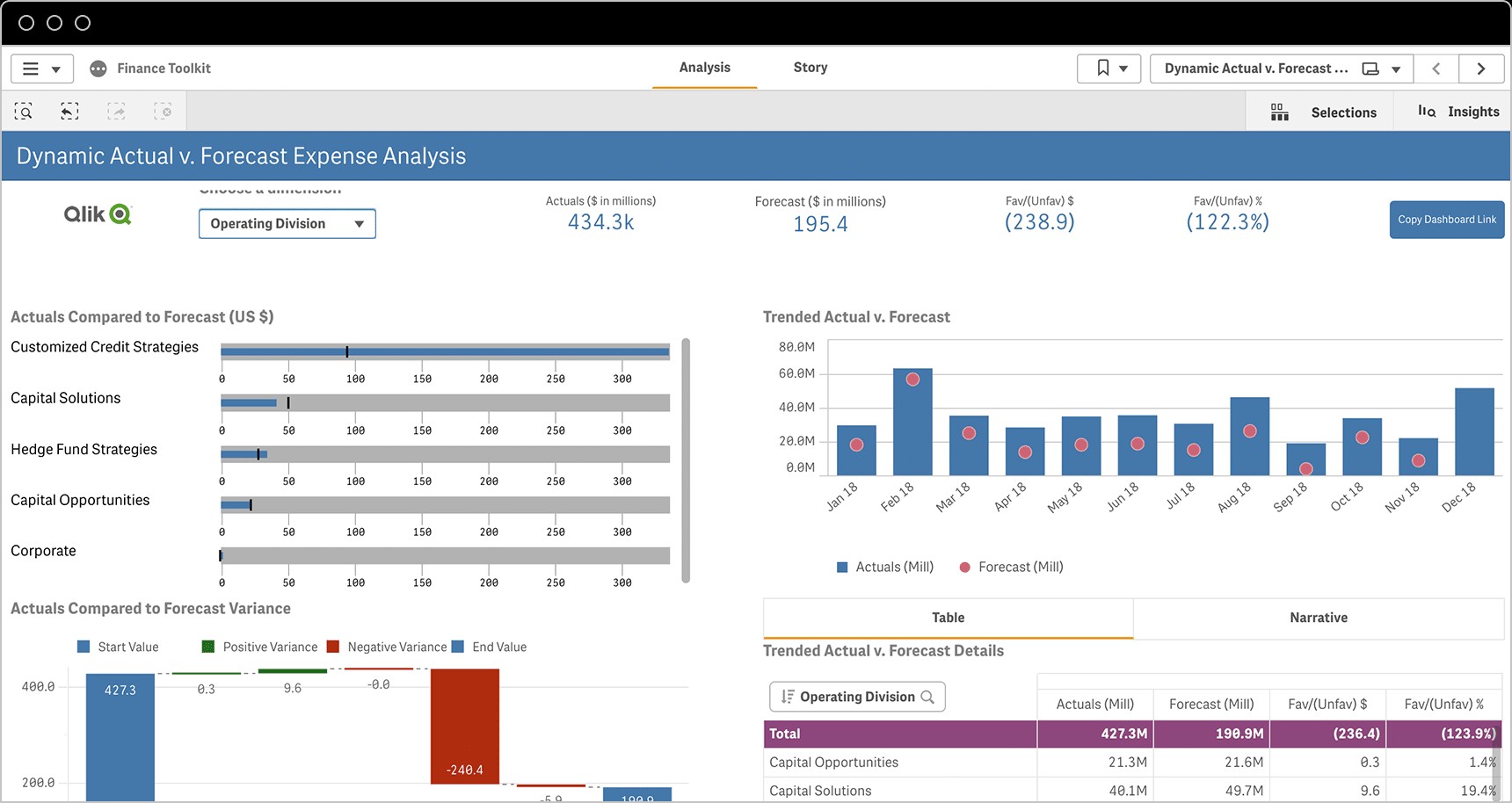
Finance KPIs: Monitoring Financial Health
For the finance department, KPIs are crucial for maintaining the financial health and stability of the organization. These metrics help in tracking profitability, managing expenses, and ensuring efficient use of capital. Finance KPIs provide insights into the company’s financial performance and guide strategic financial decisions.
- Gross Profit Margin (and %)
- Operating Profit Margin (and %)
- Net Profit Margin (and %)
- Operating Expense Ratio
- Working Capital Ratio
Alt text: Actual versus Forecast Expense Dashboard example illustrating financial KPI tracking.
Sales KPIs: Driving Revenue and Growth
Sales KPIs are essential for tracking the effectiveness of sales strategies and the performance of sales teams. These indicators focus on lead generation, opportunity conversion, sales volume, and revenue generation. Monitoring sales KPIs helps to ensure that sales targets are met and that the business is growing its revenue streams.
- New Inbound Leads
- New Qualified Opportunities
- Total Pipeline Value
- Sales Volume by Location
- Average Order Value
Alt text: Executive sales dashboard showcasing KPIs for revenue, opportunity status, and quota performance trends.
Marketing KPIs: Measuring Campaign Effectiveness
Marketing KPIs are vital for assessing the success of marketing campaigns and strategies. They help marketers understand what’s working, what’s not, and how to optimize their efforts for better results. These KPIs often focus on lead generation, conversion rates, return on investment, and brand awareness.
- Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs)
- Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs)
- Conversion Rates (For Specific Goals)
- Social Program ROI (By Platform)
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
Alt text: Marketing inbound leads dashboard integrating multi-platform data to analyze campaign leads and goal attainment.
IT KPIs: Ensuring Operational Efficiency
IT KPIs are used to monitor the performance and efficiency of IT operations. They help IT departments ensure smooth operations, minimize downtime, and manage costs effectively. These KPIs can range from system uptime and support ticket resolution times to security-related metrics and cost management.
- Total Support Tickets
- Open Support Tickets
- Ticket Resolution Time
- Security Related Downtime
- IT Costs vs Revenue
- Reopened Tickets
Alt text: IT Management Overview dashboard example displaying cost metrics for customer service, development, and budget analysis.
Customer Service KPIs: Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
Customer service KPIs are centered around measuring and improving the customer experience. They help customer service teams track their responsiveness, efficiency, and impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty. These KPIs are crucial for ensuring that customers are satisfied and that the customer service function is contributing positively to the business.
- First Contact Resolution Rate
- Average Response Time
- Most Active Support Agents
- Cost Per Conversation
- Customer Effort Score
Alt text: Executive dashboard example for CIO or CTO, illustrating budget and forecasting improvements for IT lifecycle cost management.
In conclusion, KPIs are indispensable tools for businesses to define, track, and achieve their strategic objectives. By selecting and monitoring the right KPIs for each department and for the organization as a whole, companies can gain valuable insights into their performance, make informed decisions, and drive continuous improvement and success. Understanding “What Is A Kpi” and how to effectively use them is a foundational step for any organization aiming for growth and efficiency.