What Is A Past Participle? It’s a verb form that plays a vital role in English grammar, crucial for forming perfect tenses and passive voice. WHAT.EDU.VN provides clear explanations and examples to master this essential concept, ensuring you understand its diverse functions and applications, including participial adjectives and perfect tenses. Unlock the secrets of verb forms and enhance your grammar proficiency with WHAT.EDU.VN today.
1. Understanding the Basics: What Is a Past Participle?
The past participle is a specific form of a verb that indicates completed action. It is one of the principal parts of a verb, alongside the base form, past simple, and present participle. Understanding past participles is essential for mastering various verb tenses and grammatical structures in English.
1.1. Definition and Explanation
A past participle typically denotes an action that has been completed or finished. In regular verbs, the past participle is formed by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the base form of the verb. For example, the past participle of “walk” is “walked,” and the past participle of “bake” is “baked.” However, many verbs in English are irregular and have unique past participle forms that must be memorized.
1.2. Regular vs. Irregular Verbs
The formation of the past participle differs between regular and irregular verbs.
1.2.1. Regular Verbs
Regular verbs follow a predictable pattern:
- Add “-ed” to the base form (e.g., walk becomes walked).
- If the verb ends in “e,” add “-d” (e.g., bake becomes baked).
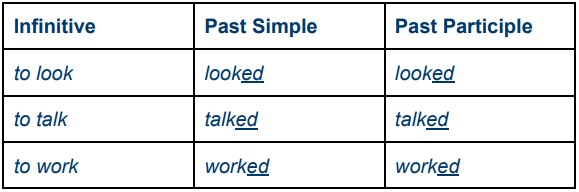 Regular verb past participle formation: Walk becomes Walked
Regular verb past participle formation: Walk becomes Walked
1.2.2. Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs have unique past participle forms that do not follow a standard pattern. These forms must be memorized.
Examples include:
- go – went – gone
- eat – ate – eaten
- see – saw – seen
- take – took – taken
1.3. Common Examples of Past Participles
Here are some common examples to illustrate the usage of past participles:
- Regular Verbs:
- Played: The children have played in the park.
- Watched: She had watched the movie before.
- Cleaned: They have cleaned the house.
- Irregular Verbs:
- Eaten: He has eaten all the cookies.
- Driven: She had driven to the city.
- Written: They have written a letter.
1.4. How to Identify Past Participles in Sentences
Identifying past participles in sentences involves recognizing the form of the verb and its function. Past participles are often used with auxiliary verbs such as “have,” “has,” and “had” to form perfect tenses, or with forms of “be” in the passive voice.
Examples:
- “I have finished my homework.” (finished is the past participle used with “have” in the present perfect tense.)
- “The cake was baked by Mary.” (baked is the past participle used with “was” in the passive voice.)
2. Usage in Perfect Tenses
Past participles are integral to forming perfect tenses, which indicate actions completed at a specific time or before another action. The perfect tenses include the present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect.
2.1. Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense combines the auxiliary verb “have” or “has” with the past participle. It indicates an action that started in the past and continues to have relevance in the present.
Structure: have/has + past participle
Examples:
- “I have seen that movie.”
- “She has traveled to Europe.”
- “They have lived here for ten years.”
2.2. Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense combines the auxiliary verb “had” with the past participle. It indicates an action completed before another action in the past.
Structure: had + past participle
Examples:
- “I had finished my work before they arrived.”
- “She had eaten dinner when I called.”
- “They had left before the storm began.”
2.3. Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense combines the auxiliary verbs “will have” with the past participle. It indicates an action that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
Structure: will have + past participle
Examples:
- “I will have finished the report by tomorrow.”
- “She will have graduated by next year.”
- “They will have moved to their new house by then.”
2.4. Examples of Perfect Tenses in Context
To further illustrate the usage of past participles in perfect tenses, consider the following examples:
- “By the time you arrive, I will have cooked dinner.” (Future Perfect)
- “He has studied English for five years.” (Present Perfect)
- “We had visited Paris before we went to Rome.” (Past Perfect)
3. Use in Passive Voice
The passive voice is another significant application of past participles. It is used to indicate that the subject of the sentence is receiving the action rather than performing it.
3.1. Forming the Passive Voice
The passive voice is formed using a form of the verb “be” (is, are, was, were, been, being) combined with the past participle of the main verb.
Structure: be + past participle
Examples:
- Active: “The dog chased the cat.”
- Passive: “The cat was chased by the dog.”
- Active: “She writes the letters.”
- Passive: “The letters are written by her.”
3.2. Examples of Passive Voice Sentences
Consider these additional examples to understand how past participles are used in passive voice sentences:
- “The car was repaired by the mechanic.”
- “The book was written by a famous author.”
- “The house is being painted by the workers.”
- “Mistakes were made.”
3.3. Why Use the Passive Voice?
The passive voice is often used when the actor is unknown, unimportant, or when the focus is on the action itself.
- Unknown actor: “The window was broken.” (We don’t know who broke it.)
- Unimportant actor: “The law was passed by the parliament.” (The focus is on the law, not the parliament.)
- Focus on the action: “The experiment was conducted carefully.” (The emphasis is on the careful conduct of the experiment.)
4. Past Participles as Adjectives
Past participles can also function as adjectives, modifying nouns and providing descriptive information. These are often referred to as participial adjectives.
4.1. What Are Participial Adjectives?
Participial adjectives are past participles that describe nouns. They can appear before the noun they modify or after a linking verb.
Examples:
- “The broken window needs to be repaired.” (broken describes the window)
- “She felt defeated after the loss.” (defeated describes how she felt)
- “The written agreement was carefully reviewed.” (written describes the agreement)
4.2. Examples of Past Participle Adjectives in Sentences
Here are more examples illustrating the use of past participle adjectives:
- “The frozen lake sparkled in the sunlight.”
- “He is a retired teacher.”
- “The lost dog was found.”
- “She wore a knitted sweater.”
4.3. Distinguishing Between Past Participles and Adjectives
It’s important to distinguish between past participles used in verb tenses and those used as adjectives. As adjectives, they directly modify nouns, whereas, in verb tenses, they form part of the verb phrase.
- Verb Tense: “The letter was written yesterday.”
- Adjective: “The written letter was clear and concise.”
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding past participles can be challenging, and several common mistakes can occur. Awareness of these pitfalls can help improve accuracy.
5.1. Confusing Past Simple and Past Participle
One common mistake is confusing the past simple and past participle forms, especially with irregular verbs.
Examples:
- Incorrect: “I have went to the store.” (Should be “I have gone to the store.”)
- Incorrect: “She seen the movie yesterday.” (Should be “She saw the movie yesterday.”)
5.2. Incorrect Usage with Auxiliary Verbs
Using the wrong auxiliary verb with the past participle is another frequent error.
Examples:
- Incorrect: “He is ate the cake.” (Should be “He has eaten the cake.”)
- Incorrect: “They had saw the concert.” (Should be “They had seen the concert.”)
5.3. Misusing Regular and Irregular Verb Forms
Applying regular verb endings to irregular verbs or vice versa is a common mistake.
Examples:
- Incorrect: “I goed to the party.” (Should be “I went to the party.”)
- Incorrect: “She has breaked the vase.” (Should be “She has broken the vase.”)
5.4. Tips to Avoid These Mistakes
- Memorize irregular verb forms: Create flashcards or use online resources to learn irregular verbs.
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice helps reinforce correct usage.
- Review grammar rules: Regularly review grammar rules and examples.
- Seek feedback: Ask for feedback from teachers, peers, or online grammar tools.
6. Practice Exercises and Quizzes
To solidify your understanding of past participles, engaging in practice exercises and quizzes is essential.
6.1. Identifying Past Participles in Sentences
Identify the past participle in each of the following sentences:
- The book was written by a famous author.
- She has traveled to many countries.
- The door was closed tightly.
- He had finished his work before the deadline.
- The cake was baked by my mother.
Answers:
- written
- traveled
- closed
- finished
- baked
6.2. Using Past Participles in Perfect Tenses
Fill in the blank with the correct form of the verb in the present perfect, past perfect, or future perfect tense:
- I ______ (see) that movie before.
- She ______ (finish) her work by tomorrow.
- They ______ (eat) dinner when I arrived.
- We ______ (live) here for ten years.
- He ______ (travel) to Europe before he turned 30.
Answers:
- have seen
- will have finished
- had eaten
- have lived
- had traveled
6.3. Forming Passive Voice Sentences
Rewrite the following active sentences in the passive voice:
- The chef cooked the meal.
- The students wrote the essays.
- The mechanic repaired the car.
- The author wrote the book.
- The teacher graded the papers.
Answers:
- The meal was cooked by the chef.
- The essays were written by the students.
- The car was repaired by the mechanic.
- The book was written by the author.
- The papers were graded by the teacher.
6.4. Using Past Participles as Adjectives
Use the past participle form of the verb in parentheses as an adjective in the following sentences:
- The ______ (break) window needs to be fixed.
- She wore a ______ (knit) sweater.
- The ______ (lose) dog was found.
- He is a ______ (retire) teacher.
- The ______ (write) letter was clear and concise.
Answers:
- broken
- knitted
- lost
- retired
- written
7. Advanced Uses and Nuances
Beyond the basic applications, past participles have more advanced uses that can enhance writing and communication skills.
7.1. Participial Phrases
Participial phrases are groups of words that begin with a past participle and modify a noun or pronoun. They add detail and context to sentences.
7.1.1. Definition and Examples
A participial phrase includes the past participle along with its modifiers and complements. It functions as an adjective, providing additional information about the noun or pronoun it modifies.
Examples:
- Exhausted from the race, the runner collapsed on the ground.
- Driven by ambition, she worked tirelessly to achieve her goals.
- Illuminated by the moonlight, the castle looked magical.
7.1.2. Placement and Punctuation
The placement of the participial phrase is crucial for clarity. It should be placed as close as possible to the noun or pronoun it modifies. Use a comma to set off the participial phrase if it introduces the sentence or if it is nonrestrictive (provides additional, nonessential information).
Examples:
- Having finished the report, he went home. (Introductory phrase)
- The book, written by a famous author, became a bestseller. (Nonrestrictive phrase)
7.2. Reduced Relative Clauses
Reduced relative clauses are another advanced use of past participles. They involve shortening relative clauses (which use words like “who,” “which,” or “that”) by omitting the relative pronoun and the auxiliary verb.
7.2.1. Definition and Examples
A reduced relative clause uses the past participle to convey the same information as a full relative clause but in a more concise manner.
Examples:
- Full: “The book that was written by a famous author became a bestseller.”
- Reduced: “The book written by a famous author became a bestseller.”
- Full: “The car that was repaired by the mechanic is now running smoothly.”
- Reduced: “The car repaired by the mechanic is now running smoothly.”
7.2.2. How to Form Reduced Relative Clauses
To form a reduced relative clause, follow these steps:
- Start with a relative clause.
- Remove the relative pronoun (who, which, that).
- Remove the auxiliary verb (is, are, was, were, has, have, had).
- Leave the past participle.
7.3. Common Idioms and Expressions
Past participles are also found in many common idioms and expressions in English. Understanding these expressions can enhance language proficiency.
7.3.1. Examples of Idiomatic Usage
Here are some examples of common idioms and expressions that use past participles:
- A done deal: An agreement that is finalized and cannot be changed.
- Gone with the wind: Disappeared or vanished.
- Lost in translation: Meaning is lost or altered during interpretation.
- Spoken for: Already claimed or taken.
- Well-written: Of high quality in writing style.
7.3.2. How to Learn and Use Idioms Effectively
To learn and use idioms effectively:
- Study idioms in context: Understand how idioms are used in sentences and conversations.
- Use flashcards: Create flashcards to memorize idioms and their meanings.
- Practice using idioms: Incorporate idioms into your writing and speaking.
- Seek feedback: Ask for feedback from native speakers or language partners.
8. Resources for Further Learning
To continue improving your understanding and use of past participles, consider the following resources:
8.1. Online Grammar Websites
Numerous websites offer comprehensive grammar lessons, exercises, and quizzes.
8.1.1. Recommended Websites
- Grammarly: Provides grammar checking tools and explanations.
- Khan Academy: Offers free grammar lessons and exercises.
- EnglishClub: Features grammar guides, quizzes, and forums.
- Perfect English Grammar: Provides clear explanations and practice activities.
8.2. Grammar Textbooks
Grammar textbooks provide structured lessons and exercises for learning grammar rules.
8.2.1. Popular Grammar Books
- English Grammar in Use by Raymond Murphy
- The Elements of Style by William Strunk Jr. and E.B. White
- Understanding and Using English Grammar by Betty Schrampfer Azar
8.3. Language Learning Apps
Language learning apps offer interactive lessons and practice activities to improve grammar skills.
8.3.1. Top Language Learning Apps
- Duolingo: Provides gamified grammar lessons.
- Babbel: Offers structured language courses with grammar explanations.
- Memrise: Uses flashcards and mnemonics to help memorize grammar rules.
8.4. English Language Courses
Enrolling in an English language course can provide structured learning and personalized feedback from instructors.
8.4.1. Types of Courses Available
- Online courses: Convenient and flexible learning options.
- In-person courses: Traditional classroom-based learning.
- Private tutoring: Personalized instruction tailored to individual needs.
9. Real-World Applications
Understanding and correctly using past participles is essential for effective communication in various real-world contexts.
9.1. Academic Writing
In academic writing, precise grammar is crucial for conveying complex ideas clearly and accurately. Past participles are used in perfect tenses, passive voice, and participial phrases to enhance the sophistication and clarity of writing.
Examples:
- “The data collected from the experiment has been analyzed thoroughly.”
- “The research, conducted over several years, has revealed significant findings.”
9.2. Professional Communication
In professional settings, clear and concise communication is essential for success. Correctly using past participles in emails, reports, and presentations helps convey professionalism and competence.
Examples:
- “The report prepared by the team has been submitted for review.”
- “We have completed the project and are ready to present the results.”
9.3. Everyday Conversations
In everyday conversations, using past participles correctly can improve the clarity and effectiveness of communication. While minor errors may not always impede understanding, accurate grammar enhances the overall impression and credibility.
Examples:
- “I have seen that movie before.”
- “She has traveled to many places.”
9.4. Creative Writing
In creative writing, past participles can be used to add depth and nuance to descriptions and narratives. Participial phrases and adjectives can create vivid imagery and convey emotions effectively.
Examples:
- “The forest, shrouded in mist, felt mysterious and enchanting.”
- “He stood there, lost in thought, contemplating the meaning of life.”
10. FAQs About Past Participles
10.1. What is the main function of a past participle?
The main function of a past participle is to form perfect tenses and the passive voice. It can also be used as an adjective to describe nouns.
10.2. How do I identify a past participle in a sentence?
A past participle is usually identified by its form (typically ending in -ed for regular verbs) and its use with auxiliary verbs like “have,” “has,” “had,” “is,” “are,” “was,” or “were.”
10.3. What are the differences between regular and irregular past participles?
Regular past participles are formed by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the base form of the verb. Irregular past participles have unique forms that must be memorized.
10.4. Can a past participle be used as an adjective?
Yes, a past participle can be used as an adjective to describe nouns. These are known as participial adjectives.
10.5. How do I avoid common mistakes when using past participles?
To avoid common mistakes, memorize irregular verb forms, practice regularly, review grammar rules, and seek feedback from teachers or peers.
10.6. What is a participial phrase?
A participial phrase is a group of words that begins with a past participle and modifies a noun or pronoun, adding detail and context to the sentence.
10.7. How are past participles used in reduced relative clauses?
In reduced relative clauses, the relative pronoun and auxiliary verb are omitted, leaving only the past participle to convey the same information more concisely.
10.8. Where can I find resources to practice using past participles?
You can find resources on online grammar websites, in grammar textbooks, through language learning apps, and in English language courses.
10.9. Why is it important to learn past participles?
Learning past participles is important for mastering English grammar, improving communication skills, and enhancing clarity and accuracy in writing and speaking.
10.10. How can I improve my use of past participles in everyday language?
Practice using past participles in your daily conversations, review grammar rules regularly, and seek feedback from native speakers or language partners.
Still have questions about past participles? Unsure how to use them correctly in your writing or speech? Don’t worry. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we offer a free question-and-answer service to help you with all your grammar needs. Whether you’re struggling with perfect tenses, passive voice, or participial adjectives, our experts are here to provide clear, concise explanations and examples. Simply visit our website, ask your question, and receive a personalized response.
Our services are designed to make learning easy and accessible for everyone, regardless of their background or skill level. We understand that grammar can be confusing, which is why we strive to provide simple, straightforward answers that you can understand and apply immediately.
So why wait? Take advantage of our free service today and start mastering past participles with confidence. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN now and ask your question. Let us help you unlock the secrets of English grammar and achieve your language learning goals. We are located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Start learning today at what.edu.vn.
