What Is A Phone Extension? It’s a question many businesses ask as they grow. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide simple answers and solutions for all your business communication needs. Phone extensions streamline communication, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. Discover the benefits of implementing extensions, virtual phone systems, and more. Explore ways to optimize your phone system with us and start asking questions today.
Table of Contents:
- Understanding Phone Extensions
-
- What is a Phone Extension?
-
- How Do Phone Extensions Work?
-
- Business vs. Home Telephone Extension Numbers
-
- Differences Between Phone Extensions and Virtual Phone Numbers
-
- Setting Up Phone Extensions with WHAT.EDU.VN
-
- How to Set Up Phone Extensions
-
- User Roles and Permissions
-
- Emergency Services and VoIP
-
- How to Set Up Ring Groups
-
- Ring Groups Options
-
- Benefits and Advantages
-
- Benefits of Virtual Extensions
-
- How to Call an Extension Number
-
- Internal vs. External Calls
-
- Routing Calls to Extensions
-
- Calling Algorithms
-
- Use Cases and Practical Applications
-
- Individuals
-
- Teams
-
- Departments
-
- Conclusion
-
- The Power of Phone Extensions
-
- FAQ Section
-
- General Questions
-
- Technical Questions
-
- Setup Questions
-
- Troubleshooting Questions
-
1. Understanding Phone Extensions
1.1. What is a Phone Extension?
A phone extension is a numerical add-on to your primary business phone number, enabling direct routing to specific employees, teams, or departments within your organization. It acts as a sub-address within your phone system, streamlining communication and enhancing efficiency. Phone extensions eliminate the need for a central operator to manually direct calls, saving time and resources. This functionality is especially crucial for larger organizations where numerous employees and departments require individual contact points.
For instance, if your main business number is (206) 555-1212, individual extensions could be assigned as follows:
- Sales Department: (206) 555-1212 ext. 101
- Customer Support: (206) 555-1212 ext. 102
- Accounting: (206) 555-1212 ext. 103
This setup allows callers to reach the appropriate department directly by dialing the main number followed by the specific extension.
Phone extensions in MightyCall
1.2. How Do Phone Extensions Work?
Phone extensions operate by integrating with your phone system to create a hierarchical structure within your communication network. When a caller dials your main business number, they are presented with options to either dial an extension directly or navigate through an automated menu (auto-attendant) to reach the intended recipient.
The process typically unfolds as follows:
- Incoming Call: A caller dials your main business phone number.
- Automated Greeting: An auto-attendant answers the call and provides instructions, such as “Press 1 for Sales, 2 for Support, or dial the extension number.”
- Extension Input: The caller either selects a menu option or directly enters the extension number of the person or department they wish to reach.
- Call Routing: The phone system routes the call to the designated extension, connecting the caller with the appropriate party.
- Call Connection: The recipient answers the call, and communication begins.
This system ensures calls are efficiently directed to the right person or department, enhancing customer service and internal communication.
1.3. Business vs. Home Telephone Extension Numbers
While both business and home telephone extension numbers serve the purpose of extending communication options, their implementation and functionality differ significantly.
| Feature | Business Phone Extensions | Home Telephone Extensions |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Facilitate internal and external communication within an organization, routing calls to specific employees or departments. | Provide convenience within a residential setting, allowing multiple phones to share a single phone line. |
| Technology | Often utilizes VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) or PBX (Private Branch Exchange) systems, enabling advanced features such as call routing, auto-attendants, and voicemail. | Typically relies on traditional analog phone lines, offering basic call-sharing functionality. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, allowing businesses to add or remove extensions as needed to accommodate growth or changes in organizational structure. | Limited scalability, as the number of extensions is constrained by the capacity of the analog phone line. |
| Simultaneous Calls | Supports multiple simultaneous calls, as each extension operates independently. | Only one call can be active at a time, as all extensions share the same phone line. |
| Features | Advanced features such as call forwarding, call recording, conference calling, and integration with CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems are common. | Limited features, typically restricted to basic call-sharing and intercom functionality. |
| Cost | May involve ongoing costs for VoIP service, PBX system maintenance, and feature upgrades. | Generally lower initial cost, but limited functionality and scalability may lead to higher long-term costs as communication needs evolve. |
| Example | A customer calls a business and uses an extension to reach the sales department directly, bypassing the need to speak with a receptionist. | A family uses extensions to answer calls from different rooms in their house, all sharing the same phone line. |
| User Cases | Large corporations, small businesses, call centers, remote teams. | Residential homes, small apartments. |
| Typical Setup | VoIP Phone System, PBX (Private Branch Exchange), Cloud-based solutions. | Multi-line phone systems, wired phone extensions. |
| Management | Centralized management interface for easy configuration and monitoring. | Manual configuration, often requiring physical rewiring. |
| Security | Advanced security features such as encryption and access controls. | Limited security features. |
| Integration | Seamless integration with other business tools and systems. | Limited integration capabilities. |
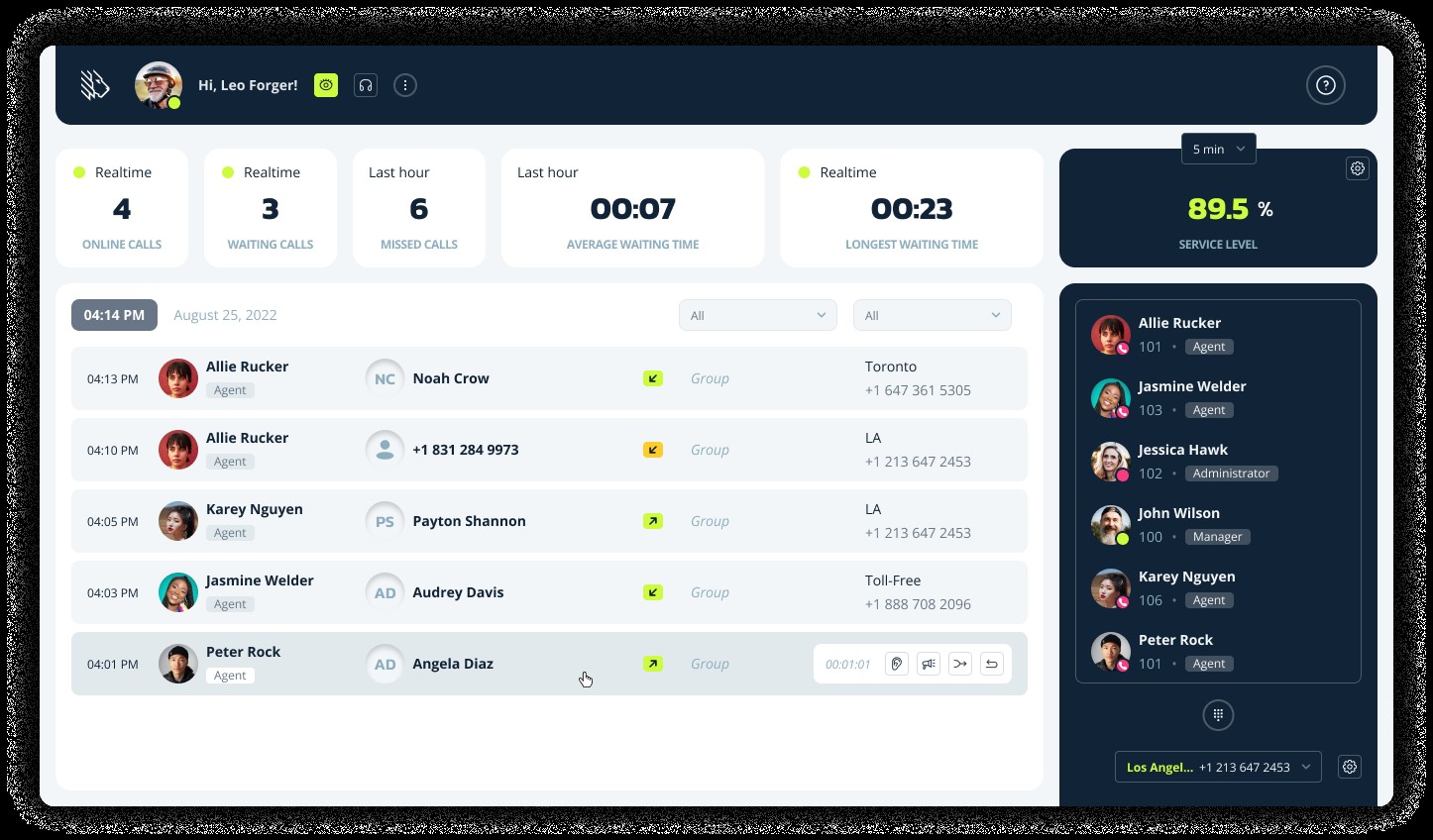

1.4. Differences Between Phone Extensions and Virtual Phone Numbers
Phone extensions and virtual phone numbers are both valuable tools for enhancing communication, but they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways.
| Feature | Phone Extensions | Virtual Phone Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Numerical add-ons to your primary business phone number, routing calls to specific employees or departments within your organization. | Phone numbers that are not tied to a specific physical location or device, forwarding calls to a designated phone number or device. |
| Functionality | Operate as sub-addresses within your phone system, streamlining internal and external communication by directing calls to the appropriate recipient. | Act as a proxy phone number, allowing you to receive calls from anywhere in the world without disclosing your actual phone number. |
| Purpose | Improve internal communication efficiency, enhance customer service, and create a more organized phone system. | Establish a local presence in different geographic areas, protect your privacy, and manage multiple phone lines from a single device. |
| Location | Tied to your main business phone number and physical location. | Not tied to any physical location, offering flexibility and mobility. |
| Cost | Typically included as part of your phone system plan, with no additional charges for adding or managing extensions. | Incur monthly fees for each virtual phone number, depending on the provider and features included. |
| Setup | Configured within your phone system’s settings, usually requiring minimal technical expertise. | Obtained from a virtual phone number provider, requiring you to set up call forwarding and other features through their online portal. |
| Use Cases | Directing calls to specific employees or departments, creating a professional phone system, and improving internal communication efficiency. | Establishing a local presence in different markets, protecting your personal phone number, and managing multiple phone lines for different purposes (e.g., business, personal, marketing campaigns). |
| Advanced Features | Advanced features often depend on the phone system, but typically do not include features such as call recording, voicemail transcription, or detailed analytics. | Often come with advanced features such as call recording, voicemail transcription, call screening, and detailed analytics. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, allowing businesses to add or remove extensions as needed to accommodate growth or changes in organizational structure. | Scalable, but each additional number incurs additional costs. |
| Integration | Integrates with your existing phone system, providing seamless communication within your organization. | Can be integrated with various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers, providing flexibility and mobility. |
| User Cases | Internal team collaboration, routing calls to specific departments, customer service. | Remote teams, international businesses, marketing campaigns. |
| Example | A customer calls a business and uses an extension to reach the customer support team directly. | A business uses a virtual phone number with a local area code to attract customers in a new market. |
| Typical Setup | Part of a traditional or VoIP phone system. | Cloud-based virtual phone system or app. |
| Number Format | Follows the format of the main business number, with additional digits for the extension (e.g., 206-555-1212 ext. 101). | Can have different area codes, appearing as a local or toll-free number (e.g., 206-555-3434 or 800-555-6767). |
| Call Handling | Routes calls based on the dialed extension. | Routes calls based on preset configurations, such as call forwarding or routing to different devices. |
2. Setting Up Phone Extensions with WHAT.EDU.VN
2.1. How to Set Up Phone Extensions
Setting up phone extensions involves several steps that vary based on your phone system. Here’s a general guide:
- Choose a Phone System: Select a suitable phone system. Options include traditional PBX systems, VoIP services, or cloud-based solutions.
- Account Creation: Sign up for an account with your chosen provider.
- Access Settings: Log into your account and navigate to the settings or administration panel.
- Add Users: Add each employee or department as a user in the system. Provide names, email addresses, and other relevant details.
- Assign Extensions: Assign a unique extension number to each user. This number will be used to route calls directly to that user.
- Configure Routing Rules: Set up call routing rules to define how calls are directed to each extension. Options include direct dialing, auto-attendant menus, and ring groups.
- Test Extensions: Test each extension to ensure calls are routed correctly. Call the main number and dial the extension to verify functionality.
- Train Employees: Train employees on how to use the new phone system and extensions. Provide instructions on transferring calls, checking voicemail, and other features.
2.2. User Roles and Permissions
Phone systems often include various user roles, each with different levels of access and permissions. Common roles include:
- Administrator: Full access to all system settings and features. Can manage users, extensions, routing rules, and other configurations.
- Manager: Limited access to system settings. Can manage users within their department, monitor call activity, and generate reports.
- Agent/User: Basic access to system features. Can make and receive calls, check voicemail, and access their call history.
Assigning appropriate roles ensures that each user has the necessary access to perform their job duties while maintaining system security and stability.
2.3. Emergency Services and VoIP
When using VoIP phone systems, it’s crucial to understand how emergency services (such as 911) are handled. VoIP systems may handle emergency calls differently than traditional phone lines.
- Address Information: Ensure your service provider has your accurate physical address. This information is used to route emergency calls to the appropriate local responders.
- Power Outages: VoIP systems rely on electricity. During a power outage, your phone service may be unavailable. Have a backup communication method in place, such as a mobile phone.
- 911 Dialing: Understand how to dial 911 using your VoIP system. Some systems may require dialing a prefix or following specific instructions.
Familiarize yourself with your provider’s emergency calling procedures and ensure all employees are aware of the process and limitations.
2.4. How to Set Up Ring Groups
Ring groups are a feature that allows incoming calls to ring multiple phones simultaneously or sequentially, ensuring that calls are answered promptly. To set up ring groups, follow these steps:
- Access Settings: Log into your phone system’s settings or administration panel.
- Create Ring Group: Create a new ring group and assign a name and extension number to it.
- Add Members: Add users to the ring group. These users will receive calls when the ring group’s extension is dialed.
- Configure Ring Strategy: Choose a ring strategy, such as simultaneous ringing (all phones ring at once) or sequential ringing (phones ring in a specific order).
- Set Call Forwarding: Configure call forwarding rules to determine what happens if no one answers the call. Options include forwarding to voicemail, another extension, or an external number.
- Test Ring Group: Test the ring group to ensure calls are routed correctly and that all members receive the calls.
2.5. Ring Groups Options
Ring groups offer several configuration options, including:
- Simultaneous Ringing: All phones in the ring group ring at the same time until someone answers the call.
- Sequential Ringing: Phones ring in a specific order until someone answers the call.
- Round Robin: Calls are distributed evenly among the members of the ring group.
- Call Forwarding: Calls are forwarded to another destination if no one answers within a specified time.
Choosing the right ring strategy and configuration options depends on your specific needs and call volume.
Ring groups in MightyCall
3. Benefits and Advantages
3.1. Benefits of Virtual Extensions
Virtual extensions offer numerous benefits, including:
- Cost Savings: Reduce phone costs by sharing a single phone line among multiple users.
- Improved Communication: Streamline communication by routing calls directly to the appropriate person or department.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Ensure calls are answered promptly and efficiently, improving customer satisfaction.
- Increased Productivity: Save time and improve productivity by eliminating the need for a central operator to manually direct calls.
- Flexibility: Easily add or remove extensions as needed to accommodate growth or changes in organizational structure.
- Professional Image: Project a professional image by providing customers with a direct line to specific employees or departments.
- Remote Work Support: Enable remote employees to stay connected and communicate effectively, regardless of their location.
3.2. How to Call an Extension Number
Calling an extension number typically involves dialing the main business number followed by the extension number. For example, if the main number is (206) 555-1212 and the extension is 101, you would dial (206) 555-1212 and then enter 101.
Some phone systems may require dialing a prefix or following specific instructions to reach the extension. Check with your service provider for details.
3.3. Internal vs. External Calls
Internal calls are calls made within the organization, while external calls are calls made to or from outside the organization.
- Internal Calls: Typically require dialing only the extension number or a short code.
- External Calls: Require dialing the full phone number, including the area code and exchange.
Some phone systems may offer different dialing patterns for internal and external calls to simplify the process.
3.4. Routing Calls to Extensions
Calls can be routed to extensions in several ways, including:
- Direct Dialing: Callers dial the extension number directly to reach the intended recipient.
- Auto-Attendant: Callers navigate through an automated menu to reach the appropriate extension.
- Ring Groups: Calls ring multiple phones simultaneously or sequentially until someone answers.
- Call Forwarding: Calls are forwarded to another extension or external number based on predefined rules.
3.5. Calling Algorithms
Calling algorithms determine how calls are distributed within a ring group or among available agents. Common algorithms include:
- Simultaneous: All members receive calls at the same time, irrespective of their present task.
- Sequential: The call goes from one member to another in sequence, based on pre-defined criteria.
- Round-robin: The call goes in a circular path from one member to another until it is answered. If all members are busy during the first cycle, the call repeats the cycle.
The choice of algorithm depends on the specific needs of the team and the desired call distribution pattern.
4. Use Cases and Practical Applications
4.1. Individuals
- Personalized Call Routing: Individuals can set up extensions to route calls to different devices based on the time of day or their availability.
- Voicemail Management: Extensions can be configured with personalized voicemail greetings and settings.
- Call Screening: Individuals can use extensions to screen incoming calls and prioritize important ones.
4.2. Teams
- Efficient Call Distribution: Teams can use ring groups and calling algorithms to distribute calls evenly among members, ensuring prompt responses.
- Collaboration: Extensions can be used to facilitate internal communication and collaboration among team members.
- Remote Work: Extensions can enable remote team members to stay connected and communicate effectively.
4.3. Departments
- Organized Call Handling: Departments can use extensions to create a structured phone system that directs calls to the appropriate personnel.
- Specialized Support: Different departments can have dedicated extensions for specific types of inquiries or support requests.
- Customer Service: Extensions can be used to provide customers with a direct line to the appropriate department for assistance.
5. Conclusion
5.1. The Power of Phone Extensions
Phone extensions are a powerful tool for enhancing communication, improving efficiency, and providing better customer service. By implementing phone extensions, businesses can streamline call handling, reduce costs, and project a professional image. Whether you’re a small business or a large corporation, phone extensions can help you stay connected and communicate effectively.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of effective communication. Our platform offers comprehensive solutions for all your communication needs. If you have any questions or need assistance with setting up your phone system, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Contact Information:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Do you have questions about phone extensions or any other topic? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and receive free answers from our community of experts. Experience the convenience and efficiency of our platform today. We offer a free consultation to address any questions about phone extensions or other topics.
Don’t struggle with unanswered questions. Join WHAT.EDU.VN and get the answers you need quickly and easily. Ask your question today and experience the difference.
6. FAQ Section
6.1. General Questions
Q1: What is a phone extension and how does it work?
A phone extension is a short numerical add-on to your main business phone number that directs calls to specific employees or departments. It works by routing incoming calls to the designated extension when callers dial the main number followed by the extension code. According to the FCC, phone systems and extensions are essential for efficient business communications.
Q2: Why do businesses use phone extensions?
Businesses use phone extensions to streamline communication, improve customer service, enhance internal coordination, and create a more organized phone system. They also help reduce costs by allowing multiple employees to share the same phone line. According to Forbes, effective communication systems boost productivity and customer satisfaction.
Q3: What are the benefits of using virtual phone extensions?
Virtual phone extensions offer benefits such as cost savings, improved communication efficiency, enhanced customer service, increased productivity, flexibility, and a professional image. They also support remote work and enable easy scalability. According to a study by Grand View Research, the global VoIP market is expected to grow, driven by these advantages.
Q4: Can I use phone extensions with a mobile phone?
Yes, you can use phone extensions with a mobile phone through VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) services. VoIP apps allow you to make and receive calls using your extension number on your smartphone. According to TechRadar, many VoIP apps offer seamless integration with mobile devices.
6.2. Technical Questions
Q5: How many digits can a phone extension have?
A phone extension can have various lengths, typically ranging from two to five digits. The length depends on the phone system’s configuration and the number of extensions needed. According to Cisco, the length of the extension should be determined based on the size and complexity of the organization.
Q6: What is the difference between a phone extension and a virtual phone number?
A phone extension is an add-on to your main business number for internal call routing, while a virtual phone number is a separate phone number that forwards calls to a designated phone or device. Extensions are for internal organization, whereas virtual numbers are for creating a local presence or protecting privacy. According to RingCentral, understanding the distinction between these tools is crucial for optimizing communication strategies.
Q7: How do I set up call forwarding on a phone extension?
Call forwarding can be set up through your phone system’s settings. Log into your account, navigate to the extension settings, and configure the call forwarding rules to direct calls to another extension or external number when the extension is busy or unanswered. According to Avaya, call forwarding is a standard feature in most business phone systems.
Q8: What is a PBX system, and how does it relate to phone extensions?
A PBX (Private Branch Exchange) system is a private telephone network used within a company. It manages internal and external calls and enables features like phone extensions, call routing, and voicemail. PBX systems are the backbone of business communication and facilitate the use of extensions. According to Mitel, PBX systems provide essential communication infrastructure for businesses of all sizes.
6.3. Setup Questions
Q9: How do I choose the right phone system for setting up extensions?
Choosing the right phone system depends on your business needs, size, and budget. Consider factors such as the number of users, call volume, required features, and integration with other business tools. Options include traditional PBX systems, VoIP services, and cloud-based solutions. According to Nextiva, assessing your business requirements is the first step in selecting the appropriate phone system.
Q10: What equipment do I need to set up phone extensions?
The equipment needed depends on the type of phone system. For a traditional PBX system, you’ll need phones, a PBX unit, and wiring. For a VoIP system, you’ll need IP phones or softphones, a reliable internet connection, and a VoIP service provider. According to 8×8, having the right equipment is essential for a smooth and efficient phone system setup.
Q11: How do I assign extensions to different employees?
Extensions can be assigned through your phone system’s administration panel. Log into your account, add each employee as a user, and assign a unique extension number to each. Ensure that the extension numbers are easy to remember and consistent with your company’s naming conventions. According to Vonage, a well-organized extension assignment strategy enhances internal communication.
6.4. Troubleshooting Questions
Q12: What should I do if my phone extension is not working?
If your phone extension is not working, check the following:
- Ensure the phone is properly connected and powered on.
- Verify that the extension number is correctly configured in the phone system.
- Check for any network connectivity issues if using a VoIP system.
- Contact your phone system administrator or service provider for assistance.
According to Dialpad, systematic troubleshooting is key to resolving phone extension issues quickly.
Q13: How do I resolve call quality issues on my phone extension?
Call quality issues can be caused by several factors, including:
- Poor internet connection (for VoIP systems).
- Network congestion.
- Hardware problems.
- Incorrect audio settings.
Try troubleshooting your network connection, adjusting audio settings, and using a headset to improve call quality. According to Fuze, optimizing your network is crucial for maintaining clear and consistent call quality.
Q14: How do I prevent unauthorized access to my phone extensions?
To prevent unauthorized access, implement the following security measures:
- Use strong passwords for all user accounts.
- Enable call recording to monitor phone activity.
- Implement call restrictions to limit outgoing calls to certain numbers or regions.
- Regularly review and update your phone system’s security settings.
According to Verizon, proactive security measures are essential for protecting your phone system from unauthorized access and fraud.
Remember, what.edu.vn is here to provide you with quick and accurate answers to all your questions. If you need further assistance or have more questions, visit our website and ask away.