What Is A Pos System? It’s the technology that empowers businesses to process transactions and manage sales efficiently. At what.edu.vn, we aim to demystify this essential tool, exploring its functionalities, advantages, and impact on modern commerce. Discover how a point of sale system can streamline your business operations, enhance customer experience, and boost profitability. If you are curious to learn more about retail management, point of sale software, and payment processing, then read on.
1. Understanding the Fundamentals of a POS System
A Point of Sale (POS) system is a critical component of any business that sells products or services. It’s more than just a cash register; it’s a comprehensive solution that integrates hardware and software to streamline transactions and manage various aspects of your business. To fully understand what a POS system is, let’s break down its core elements and functionalities.
1.1. What is a POS System?
A POS system is essentially the point at which a customer makes a payment for goods or services at your business. It encompasses all the hardware and software necessary to complete a transaction, from scanning items to processing payments and generating receipts. Modern POS systems have evolved from simple cash registers to sophisticated platforms that offer a wide range of features.
1.2. Core Components of a POS System
A typical POS system includes several key components:
- Hardware: This includes physical devices such as:
- Touchscreen Monitor: Allows for easy navigation and transaction input.
- Barcode Scanner: Quickly scans product barcodes to retrieve pricing and inventory information.
- Credit Card Reader: Processes credit and debit card payments securely.
- Cash Drawer: Stores cash and provides a secure place for transactions.
- Receipt Printer: Generates printed receipts for customers.
- Software: This is the operating system of the POS system and includes functionalities such as:
- Sales Processing: Manages sales transactions, including discounts, taxes, and refunds.
- Inventory Management: Tracks product inventory levels and alerts you when stock is low.
- Customer Management: Stores customer data for loyalty programs and personalized service.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides insights into sales trends, popular items, and overall business performance.
- Employee Management: Tracks employee hours, sales performance, and access permissions.
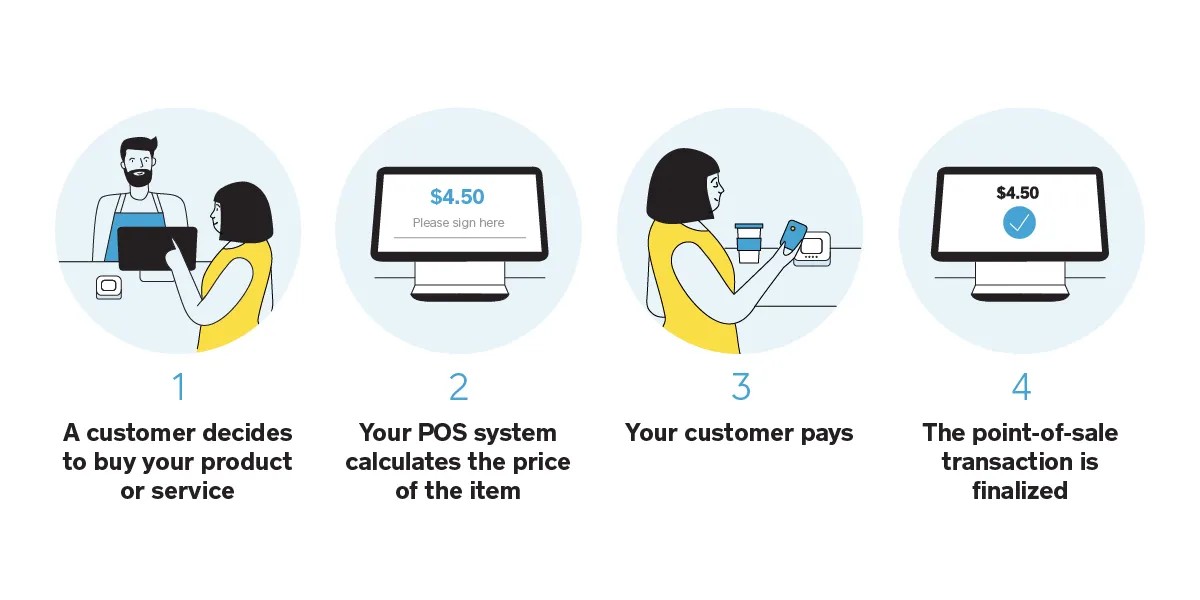
1.3. How Does a POS System Work?
The basic process of using a POS system involves several steps:
- Item Selection: The cashier scans the barcode of the item or manually enters it into the system.
- Price Calculation: The POS system calculates the total price, including any applicable taxes or discounts.
- Payment Processing: The customer pays using cash, credit card, mobile payment, or other accepted methods.
- Transaction Completion: The POS system records the transaction, updates inventory, and generates a receipt.
- Reporting: The system generates detailed reports on sales, inventory, and other key metrics.
1.4. Evolution of POS Systems
POS systems have come a long way from traditional cash registers. Early cash registers were simple mechanical devices that only recorded transactions. Over time, they evolved to include electronic components and basic inventory tracking. Today’s POS systems are sophisticated, cloud-based platforms that integrate with other business systems like accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and CRM tools. This evolution has made it easier for businesses to manage their operations and make informed decisions.
1.5. Why is a POS System Important?
A POS system is essential for several reasons:
- Efficiency: It streamlines the checkout process, reducing transaction times and improving customer satisfaction.
- Accuracy: It minimizes errors in pricing and inventory management.
- Insight: It provides valuable data and analytics to help you make informed business decisions.
- Integration: It integrates with other business systems to provide a holistic view of your operations.
- Customer Service: It enables personalized service and loyalty programs to improve customer retention.
1.6. Key Features to Look for in a POS System
When selecting a POS system, consider the following features:
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive interface makes it easy for employees to learn and use the system.
- Customization: The ability to customize the system to meet your specific business needs.
- Scalability: The system should be able to grow with your business.
- Security: Secure payment processing and data protection are essential.
- Reliability: A reliable system ensures minimal downtime and uninterrupted operations.
- Integration Capabilities: Compatibility with other business systems.
- Mobile Access: Access your system from anywhere using a mobile device.
By understanding the fundamentals of a POS system, you can appreciate its role in modern business and make informed decisions about selecting the right solution for your needs.
2. Benefits of Implementing a POS System
Implementing a Point of Sale (POS) system can significantly transform your business operations, providing numerous advantages that extend beyond just processing transactions. Here are some key benefits of integrating a POS system into your business:
2.1. Enhanced Efficiency
- Faster Transactions: POS systems expedite the checkout process by quickly scanning items, calculating totals, and processing payments, reducing wait times for customers.
- Automated Processes: Automates tasks such as inventory updates, sales tracking, and report generation, freeing up staff to focus on customer service and other important activities.
- Reduced Errors: Minimizes manual entry errors, ensuring accurate pricing, discounts, and tax calculations.
2.2. Improved Inventory Management
- Real-Time Tracking: Provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing you to monitor stock levels and identify fast-moving and slow-moving items.
- Automated Alerts: Sets up automated alerts to notify you when stock levels are low, preventing stockouts and ensuring you always have enough product on hand.
- Efficient Stock Control: Optimizes inventory control by tracking product movement, reducing waste, and improving order accuracy.
2.3. Better Customer Service
- Personalized Service: Stores customer data, enabling you to personalize interactions and offer tailored recommendations.
- Loyalty Programs: Integrates with loyalty programs to reward repeat customers and encourage customer retention.
- Faster Checkout: Speeds up the checkout process, improving customer satisfaction and reducing lines.
2.4. Accurate Reporting and Analytics
- Detailed Sales Reports: Generates detailed sales reports, providing insights into sales trends, peak hours, and popular products.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Enables data-driven decision-making by providing accurate and timely information about your business performance.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances forecasting accuracy by analyzing sales data to predict future demand and optimize inventory levels.
2.5. Streamlined Employee Management
- Time Tracking: Tracks employee hours and attendance, simplifying payroll processing and reducing time theft.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitors employee sales performance, identifying top performers and areas for improvement.
- Access Control: Restricts access to sensitive data and functions based on employee roles and responsibilities.
2.6. Cost Savings
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automates tasks and improves efficiency, reducing the need for manual labor and lowering labor costs.
- Optimized Inventory: Prevents overstocking and stockouts, minimizing waste and maximizing sales.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduces errors and discrepancies, preventing financial losses and improving profitability.
2.7. Integration with Other Business Systems
- Accounting Software: Integrates with accounting software such as QuickBooks or Xero, streamlining financial management and improving accuracy.
- E-commerce Platforms: Connects with e-commerce platforms such as Shopify or WooCommerce, providing a unified view of sales and inventory across all channels.
- CRM Systems: Integrates with CRM systems to enhance customer relationship management and personalize marketing efforts.
2.8. Enhanced Security
- Secure Payment Processing: Protects customer payment data with secure encryption and tokenization, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches.
- Compliance: Ensures compliance with industry standards such as PCI DSS, minimizing the risk of fines and penalties.
- Audit Trails: Provides audit trails of all transactions and activities, improving accountability and reducing the risk of theft or fraud.
2.9. Scalability
- Grows with Your Business: Adapts to the changing needs of your business as it grows, providing the flexibility to add new features, users, and locations.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Offers cloud-based solutions that can be accessed from anywhere, providing scalability and flexibility.
2.10. Improved Decision Making
- Real-Time Data: Provides real-time data and insights, enabling you to make informed decisions quickly and effectively.
- Strategic Planning: Supports strategic planning by providing a clear understanding of your business performance and identifying opportunities for growth.
By implementing a POS system, your business can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, customer service, and profitability. The benefits of a POS system are numerous and can provide a competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced business environment.
3. Key Features of a Modern POS System
Modern Point of Sale (POS) systems are packed with features designed to streamline business operations, enhance customer experience, and provide valuable insights. Here are some key features that define a modern POS system:
3.1. Payment Processing
- Multiple Payment Options: Accepts a wide range of payment methods, including cash, credit cards, debit cards, mobile payments (Apple Pay, Google Pay), and contactless payments.
- Secure Transactions: Ensures secure payment processing with encryption and tokenization, protecting customer data and reducing the risk of fraud.
- EMV Compliance: Supports EMV chip card transactions, ensuring compliance with industry standards and reducing liability for fraudulent transactions.
- Online Payment Integration: Integrates with online payment gateways for seamless online and in-store payment processing.
3.2. Inventory Management
- Real-Time Tracking: Provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing you to monitor stock levels and identify fast-moving and slow-moving items.
- Automated Alerts: Sets up automated alerts to notify you when stock levels are low, preventing stockouts and ensuring you always have enough product on hand.
- Stock Control: Optimizes inventory control by tracking product movement, reducing waste, and improving order accuracy.
- Barcode Scanning: Supports barcode scanning for quick and accurate inventory tracking and sales processing.
3.3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Customer Profiles: Creates detailed customer profiles with purchase history, contact information, and preferences.
- Loyalty Programs: Integrates with loyalty programs to reward repeat customers and encourage customer retention.
- Personalized Marketing: Enables personalized marketing campaigns based on customer data and purchase history.
- Feedback Collection: Collects customer feedback through surveys and reviews, providing valuable insights for improving customer service.
3.4. Reporting and Analytics
- Sales Reports: Generates detailed sales reports, providing insights into sales trends, peak hours, and popular products.
- Inventory Reports: Provides detailed inventory reports, including stock levels, product performance, and reorder recommendations.
- Financial Reports: Generates financial reports, including profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Customizable Dashboards: Offers customizable dashboards with key performance indicators (KPIs) for monitoring business performance.
3.5. Employee Management
- Time Tracking: Tracks employee hours and attendance, simplifying payroll processing and reducing time theft.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitors employee sales performance, identifying top performers and areas for improvement.
- Access Control: Restricts access to sensitive data and functions based on employee roles and responsibilities.
- Commission Tracking: Tracks employee commissions and bonuses, ensuring accurate and timely compensation.
3.6. E-commerce Integration
- Online Store Synchronization: Synchronizes inventory and sales data between your online store and POS system, providing a unified view of your business.
- Omnichannel Sales: Supports omnichannel sales by allowing customers to purchase products online and pick them up in-store (BOPIS) or return them in-store.
- Centralized Management: Provides centralized management of your online and offline sales channels, simplifying operations and improving efficiency.
3.7. Mobile POS (mPOS)
- Portable Devices: Enables sales processing on portable devices such as tablets and smartphones, allowing you to conduct business anywhere.
- Mobile Payments: Accepts mobile payments and credit card payments on the go, providing flexibility and convenience.
- Real-Time Data: Provides real-time access to sales and inventory data, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information.
3.8. Cloud-Based Technology
- Remote Access: Allows you to access your POS system from anywhere with an internet connection, providing flexibility and convenience.
- Automatic Updates: Provides automatic software updates, ensuring you always have the latest features and security enhancements.
- Data Backup: Automatically backs up your data to the cloud, protecting against data loss and ensuring business continuity.
3.9. Hardware Compatibility
- Wide Range of Devices: Compatible with a wide range of hardware devices, including barcode scanners, receipt printers, cash drawers, and credit card readers.
- Easy Integration: Provides easy integration with existing hardware, minimizing the cost and disruption of upgrading your POS system.
3.10. Customer Loyalty Programs
- Points-Based Systems: Rewards customers with points for every purchase, encouraging repeat business and increasing customer loyalty.
- Tiered Programs: Offers tiered loyalty programs with increasing benefits for higher-spending customers, incentivizing customers to spend more.
- Personalized Rewards: Provides personalized rewards and offers based on customer data and purchase history, enhancing customer engagement.
By leveraging these key features, a modern POS system can transform your business operations, improve customer satisfaction, and drive profitability.
4. Types of POS Systems Available
The market offers a variety of Point of Sale (POS) systems, each designed to cater to different business needs and sizes. Understanding the different types of POS systems available can help you choose the one that best fits your specific requirements. Here’s an overview of the main types of POS systems:
4.1. Traditional POS Systems
- Description: Traditional POS systems are typically hardware-based and consist of a cash register, barcode scanner, receipt printer, and credit card reader. These systems are often installed on-site and require local servers to store data.
- Pros:
- Reliability: Less dependent on internet connectivity, making them reliable for businesses with unstable internet access.
- Customization: Offers extensive customization options to meet specific business needs.
- Security: Data is stored locally, providing more control over data security.
- Cons:
- High Upfront Costs: Requires significant upfront investment in hardware and software.
- Limited Scalability: Difficult to scale as your business grows, requiring additional hardware and software upgrades.
- Maintenance: Requires ongoing maintenance and IT support.
4.2. Cloud-Based POS Systems
- Description: Cloud-based POS systems store data on remote servers and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. These systems typically run on tablets or mobile devices and offer a range of features such as inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and reporting.
- Pros:
- Low Upfront Costs: Requires minimal upfront investment, as you typically pay a monthly subscription fee.
- Scalability: Easy to scale as your business grows, allowing you to add new users, locations, and features as needed.
- Remote Access: Access your POS system from anywhere with an internet connection, providing flexibility and convenience.
- Automatic Updates: Automatic software updates, ensuring you always have the latest features and security enhancements.
- Cons:
- Internet Dependency: Requires a stable internet connection to function properly.
- Security Concerns: Data is stored on remote servers, which may raise security concerns for some businesses.
- Limited Customization: May offer limited customization options compared to traditional POS systems.
4.3. Mobile POS (mPOS) Systems
- Description: Mobile POS systems are designed for businesses that need to process transactions on the go. These systems typically consist of a mobile device (such as a smartphone or tablet) and a card reader that connects via Bluetooth or a headphone jack.
- Pros:
- Portability: Highly portable, allowing you to process transactions anywhere.
- Low Cost: Affordable, with minimal upfront costs and low monthly fees.
- Easy to Use: Simple and intuitive, making them easy to learn and use.
- Cons:
- Limited Functionality: May offer limited functionality compared to traditional or cloud-based POS systems.
- Security Concerns: Security can be a concern, especially when processing transactions on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Battery Life: Battery life can be a limitation, especially for businesses that process a high volume of transactions.
4.4. Self-Service Kiosks
- Description: Self-service kiosks allow customers to place orders and make payments without the assistance of a cashier. These kiosks are typically used in fast-food restaurants, coffee shops, and retail stores.
- Pros:
- Reduced Labor Costs: Reduces the need for cashiers, lowering labor costs.
- Improved Efficiency: Speeds up the ordering and payment process, reducing wait times for customers.
- Increased Sales: Can increase sales by encouraging customers to add more items to their orders.
- Cons:
- High Upfront Costs: Requires significant upfront investment in hardware and software.
- Maintenance: Requires ongoing maintenance and IT support.
- Customer Adoption: May face resistance from customers who prefer to interact with a cashier.
4.5. Open-Source POS Systems
- Description: Open-source POS systems are software programs that are available for free and can be customized by developers to meet specific business needs.
- Pros:
- Customization: Offers extensive customization options, allowing you to tailor the system to your exact requirements.
- Low Cost: Free to use, with no licensing fees.
- Community Support: Benefits from a large community of developers who contribute to the project and provide support.
- Cons:
- Technical Expertise: Requires technical expertise to install, configure, and maintain.
- Security Risks: May be vulnerable to security risks if not properly configured and maintained.
- Limited Support: Limited support from the developers, requiring you to rely on community forums and online resources for assistance.
4.6. Choosing the Right POS System
When choosing a POS system, consider the following factors:
- Business Size: Small businesses may benefit from a cloud-based or mobile POS system, while larger businesses may require a traditional or enterprise POS system.
- Budget: Determine your budget and choose a system that fits your financial constraints.
- Features: Identify the features that are most important to your business, such as inventory management, CRM, and reporting.
- Scalability: Choose a system that can scale as your business grows.
- Support: Ensure the system offers reliable customer support and training.
By understanding the different types of POS systems available, you can make an informed decision and choose the one that best meets your business needs.
5. How to Choose the Right POS System for Your Business
Selecting the right Point of Sale (POS) system for your business is a critical decision that can significantly impact your operations, efficiency, and profitability. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the selection process:
5.1. Assess Your Business Needs
- Identify Your Requirements: Start by identifying your specific business needs and requirements. Consider factors such as the size of your business, the type of products or services you sell, and your target market.
- Evaluate Current Processes: Evaluate your current business processes and identify areas where a POS system can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer service.
- Future Growth: Consider your future growth plans and choose a POS system that can scale as your business expands.
5.2. Define Your Budget
- Determine Your Budget: Determine your budget for a POS system, taking into account upfront costs, ongoing fees, and maintenance expenses.
- Compare Pricing Models: Compare different pricing models, such as monthly subscription fees, transaction fees, and one-time licensing fees.
- Consider ROI: Consider the return on investment (ROI) of a POS system by evaluating the potential benefits, such as increased sales, reduced costs, and improved efficiency.
5.3. Evaluate Key Features
- Payment Processing: Ensure the POS system supports a wide range of payment methods, including cash, credit cards, debit cards, mobile payments, and contactless payments.
- Inventory Management: Look for robust inventory management features, such as real-time tracking, automated alerts, and stock control.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Consider CRM features, such as customer profiles, loyalty programs, and personalized marketing.
- Reporting and Analytics: Evaluate the reporting and analytics capabilities of the POS system, ensuring it provides detailed sales reports, inventory reports, and financial reports.
- Employee Management: Look for employee management features, such as time tracking, performance monitoring, and access control.
- E-commerce Integration: If you have an online store, ensure the POS system integrates seamlessly with your e-commerce platform.
- Mobile POS (mPOS): Consider a mobile POS system if you need to process transactions on the go.
5.4. Research and Compare POS Systems
- Online Research: Conduct online research to identify potential POS systems that meet your needs.
- Read Reviews: Read online reviews and testimonials from other businesses to get an unbiased opinion of the POS system.
- Compare Systems: Compare different POS systems based on features, pricing, and customer reviews.
5.5. Request Demos and Trials
- Request Demos: Request demos from POS system providers to see the system in action and evaluate its functionality.
- Free Trials: Take advantage of free trials to test the POS system in your business environment.
- Ask Questions: Ask questions to the POS system provider about features, pricing, and support.
5.6. Consider Hardware Requirements
- Hardware Compatibility: Ensure the POS system is compatible with your existing hardware, such as barcode scanners, receipt printers, and credit card readers.
- Hardware Costs: Consider the costs of purchasing new hardware, if necessary.
- Hardware Maintenance: Evaluate the maintenance requirements of the hardware and factor in the costs of repairs and replacements.
5.7. Evaluate Customer Support and Training
- Customer Support: Ensure the POS system provider offers reliable customer support, including phone support, email support, and online resources.
- Training: Evaluate the training options available, such as on-site training, online training, and user manuals.
- Response Time: Consider the response time of the customer support team and ensure they can provide timely assistance.
5.8. Check Security and Compliance
- Security Measures: Ensure the POS system implements robust security measures to protect customer data and prevent fraud.
- Compliance: Verify that the POS system complies with industry standards, such as PCI DSS.
- Data Encryption: Ensure the POS system encrypts sensitive data, such as credit card numbers and customer information.
5.9. Review Contracts and Agreements
- Read the Fine Print: Carefully read the contracts and agreements before signing up for a POS system.
- Understand the Terms: Understand the terms and conditions, including pricing, payment terms, and cancellation policies.
- Seek Legal Advice: Seek legal advice if you have any concerns or questions about the contracts and agreements.
5.10. Make a Decision
- Weigh the Pros and Cons: Weigh the pros and cons of each POS system and choose the one that best meets your business needs and budget.
- Consider Long-Term Value: Consider the long-term value of the POS system, including its scalability, reliability, and customer support.
- Implement and Train: Implement the POS system and provide training to your employees to ensure they can use it effectively.
By following these steps, you can make an informed decision and choose the right POS system for your business.
6. POS System Hardware and Software Components
A Point of Sale (POS) system is comprised of both hardware and software components that work together to facilitate sales transactions and manage various aspects of your business. Understanding these components is essential for choosing and maintaining an effective POS system. Here’s an overview of the key hardware and software elements:
6.1. POS Hardware Components
- Touchscreen Monitor:
- Function: Displays the POS software interface, allowing users to navigate and input transaction details.
- Features: Touchscreen capability for easy interaction, high resolution for clear display, and durable construction for long-term use.
- Barcode Scanner:
- Function: Scans product barcodes to quickly retrieve pricing and inventory information.
- Types: Handheld scanners, countertop scanners, and presentation scanners.
- Features: Fast scanning speed, accurate barcode recognition, and compatibility with various barcode formats.
- Credit Card Reader:
- Function: Processes credit and debit card payments securely.
- Types: Magstripe readers, EMV chip card readers, and contactless (NFC) readers.
- Features: Secure encryption, EMV compliance, and compatibility with mobile payment systems.
- Cash Drawer:
- Function: Stores cash and provides a secure place for transactions.
- Features: Multiple compartments for different denominations of currency, secure locking mechanism, and automatic opening upon transaction completion.
- Receipt Printer:
- Function: Generates printed receipts for customers.
- Types: Thermal printers and impact printers.
- Features: Fast printing speed, high-quality printing, and compatibility with various receipt paper sizes.
- PIN Pad:
- Function: Allows customers to enter their PIN for debit card transactions.
- Features: Secure PIN entry, tamper-resistant design, and compliance with security standards.
- Scales:
- Function: Weighs products for accurate pricing in businesses that sell items by weight (e.g., grocery stores, delis).
- Features: Accurate weighing, digital display, and integration with the POS system.
- Mobile Devices (Tablets, Smartphones):
- Function: Used as portable POS terminals for processing transactions on the go.
- Features: Touchscreen display, wireless connectivity, and compatibility with mobile payment systems.
6.2. POS Software Components
- Sales Processing:
- Function: Manages sales transactions, including discounts, taxes, and refunds.
- Features: Easy-to-use interface, support for multiple payment methods, and customizable tax rates.
- Inventory Management:
- Function: Tracks product inventory levels and alerts you when stock is low.
- Features: Real-time tracking, automated alerts, and stock control.
- Customer Management:
- Function: Stores customer data for loyalty programs and personalized service.
- Features: Customer profiles, purchase history, and loyalty program integration.
- Reporting and Analytics:
- Function: Provides insights into sales trends, popular items, and overall business performance.
- Features: Detailed sales reports, inventory reports, and financial reports.
- Employee Management:
- Function: Tracks employee hours, sales performance, and access permissions.
- Features: Time tracking, performance monitoring, and access control.
- Menu Management (for Restaurants):
- Function: Allows you to create and manage your menu, including adding new items, updating prices, and modifying descriptions.
- Features: Customizable menu layout, support for modifiers and add-ons, and integration with kitchen display systems (KDS).
- Table Management (for Restaurants):
- Function: Manages table layouts and seating arrangements.
- Features: Drag-and-drop table arrangement, real-time table status, and reservation management.
- Kitchen Display System (KDS) (for Restaurants):
- Function: Displays orders to kitchen staff in real-time, improving order accuracy and efficiency.
- Features: Customizable display, order prioritization, and integration with the POS system.
- E-commerce Integration:
- Function: Connects your POS system with your online store, allowing you to manage sales and inventory across all channels.
- Features: Online store synchronization, omnichannel sales, and centralized management.
- Accounting Integration:
- Function: Integrates with accounting software such as QuickBooks or Xero, streamlining financial management and improving accuracy.
- Features: Automatic data synchronization, financial reporting, and tax management.
6.3. Choosing the Right Hardware and Software
When choosing POS hardware and software, consider the following factors:
- Business Needs: Identify your specific business needs and choose components that meet those requirements.
- Budget: Determine your budget and select hardware and software that fits your financial constraints.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the hardware and software are compatible with each other.
- Scalability: Choose components that can scale as your business grows.
- Support: Ensure the vendor offers reliable customer support and training.
By understanding the hardware and software components of a POS system, you can make informed decisions and choose the right solution for your business.
7. POS Systems for Different Industries
Point of Sale (POS) systems are versatile tools that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries. The right POS system can streamline operations, enhance customer service, and provide valuable insights for businesses of all types. Here’s an overview of POS systems designed for different industries:
7.1. Retail POS Systems
- Key Features:
- Inventory Management: Real-time tracking, automated alerts, and stock control.
- Barcode Scanning: Quick and accurate product scanning.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Loyalty programs, customer profiles, and personalized marketing.
- Reporting and Analytics: Sales reports, inventory reports, and customer behavior analysis.
- Specific Needs:
- Apparel Stores: Size and color matrix, style tracking, and seasonal inventory management.
- Grocery Stores: Integration with scales, produce lookup, and frequent price updates.
- Electronics Stores: Serial number tracking, warranty management, and product bundling.
7.2. Restaurant POS Systems
- Key Features:
- Menu Management: Easy menu creation and updates.
- Table Management: Table layout and seating arrangements.
- Order Management: Efficient order taking and routing to the kitchen.
- Kitchen Display System (KDS): Real-time order display in the kitchen.
- Payment Processing: Split bills, tips, and multiple payment options.
- Specific Needs:
- Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs): Fast order processing, drive-thru support, and self-service kiosks.
- Full-Service Restaurants: Table reservations, server management, and detailed order customization.
- Bars and Nightclubs: Drink recipes, age verification, and tab management.
7.3. Salon and Spa POS Systems
- Key Features:
- Appointment Scheduling: Online booking, calendar integration, and appointment reminders.
- Customer Management: Client profiles, service history, and preferences.
- Service Tracking: Service packages, memberships, and gift cards.
- Inventory Management: Product sales and professional use tracking.
- Employee Management: Commission tracking and performance monitoring.
- Specific Needs:
- Hair Salons: Haircut history, color formulas, and product recommendations.
- Spas: Treatment scheduling, room management, and package deals.
- Nail Salons: Polish inventory, nail art designs, and appointment reminders.
7.4. Healthcare POS Systems
- Key Features:
- Patient Management: Patient records, insurance information, and appointment history.
- Billing and Invoicing: Automated billing, insurance claims, and payment processing.
- Inventory Management: Medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and equipment tracking.
- Compliance: HIPAA compliance and data security measures.
- Specific Needs:
- Medical Clinics: Appointment scheduling, patient check-in, and electronic health records (EHR) integration.
- Dental Offices: Treatment planning, dental charting, and insurance claims processing.
- Pharmacies: Prescription management, drug interactions, and patient counseling.
7.5. Hospitality POS Systems
- Key Features:
- Property Management System (PMS) Integration: Room booking, check-in/check-out, and guest services.
- Point of Sale (POS): Restaurant, bar, and gift shop sales.
- Event Management: Catering, banquet, and conference room booking.
- Reporting and Analytics: Occupancy rates, revenue analysis, and guest satisfaction.
- Specific Needs:
- Hotels: Room service orders, mini-bar sales, and concierge services.
- Resorts: Spa treatments, golf bookings, and recreational activities.
- Event Venues: Ticket sales, concessions, and vendor management.
7.6. Choosing the Right POS System for Your Industry
When selecting a POS system for your industry, consider the following factors:
- Industry-Specific Features: Ensure the POS system includes features that are tailored to your industry’s specific needs.
- Integration: Look for a POS system that integrates with other business systems, such as accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and CRM tools.
- Scalability: Choose a POS system that can scale as your business grows.
- Support: Ensure the vendor offers reliable customer support and training.
By understanding the specific needs of your industry and choosing a POS system that meets those requirements, you can streamline operations, enhance customer service, and improve profitability.
8. Future Trends in POS Systems
The Point of Sale (POS) system landscape is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Staying informed about future trends in POS systems can help businesses prepare for the future and maintain a competitive edge. Here’s a look at some key trends shaping the future of POS systems:
8.1. Mobile POS (mPOS) Dominance
- Trend: Mobile POS systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their portability, flexibility, and low cost.
- Impact: Businesses are adopting mPOS systems to process transactions anywhere, enhance customer service, and reduce costs.
- Examples:
- Pop-up shops: Using tablets or smartphones to process sales at temporary locations.
- Food trucks: Taking orders and payments on the go.
- Field service: Processing invoices and payments at customer sites.
- Considerations:
- Security: Ensuring secure payment processing on mobile devices.
- Integration: Seamless integration with other business systems.
- Battery life: Reliable power for uninterrupted operation.
8.2. Cloud-Based POS Adoption
- Trend: Cloud-based POS systems are gaining traction due to their scalability, accessibility, and automatic updates.
- Impact: Businesses are migrating to cloud-based POS