Augmented Reality (AR) is a revolutionary technology, seamlessly blending digital information with our real-world environment, and WHAT.EDU.VN is here to illuminate its wonders. Explore how AR enhances our perception, from gaming to education, offering a richer, more interactive experience. Discover the power of AR and explore virtual enhancements and augmented experiences today.
1. Understanding the Core of Augmented Reality
1.1. Defining Augmented Reality: What Is It Really?
Augmented Reality, or AR, is the technology that superimposes a computer-generated image on a user’s view of the real world, thus providing a composite view. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which creates a completely simulated environment, AR enhances the existing reality. This means you can still see the world around you, but with digital elements added to it. Think of it as a digital layer on top of your physical surroundings.
1.2. How Augmented Reality Works: The Technical Aspects
AR works by using various technologies, including:
- Cameras and Sensors: These capture the surrounding environment.
- Software: This analyzes the visual data to identify objects and surfaces.
- Projection: This projects digital information onto the real-world view.
- Display: This presents the augmented view to the user, often through a smartphone, tablet, or headset.
The process typically involves:
- Detection: The device’s camera detects the real-world environment.
- Recognition: The AR software recognizes objects, surfaces, and markers in the environment.
- Augmentation: Digital content, such as images, videos, or 3D models, is overlaid onto the real-world view.
- Display: The augmented view is displayed on the device, allowing the user to interact with both the physical and digital elements.
1.3. Key Components of an Augmented Reality System
An AR system typically consists of the following key components:
- Input Devices: These include cameras, sensors, and GPS to capture real-world information.
- Processing Unit: This is where the AR software runs, analyzing the data and generating the augmented view.
- Display Unit: This presents the augmented view to the user, such as a smartphone screen, tablet, or AR headset.
- Tracking System: This tracks the user’s movements and orientation to ensure the digital content is accurately aligned with the real world.
- Software and Algorithms: These are the brains of the AR system, responsible for object recognition, image tracking, and content rendering.
Understanding these components helps appreciate the complexity and sophistication of AR technology. WHAT.EDU.VN is committed to providing clear, accessible explanations of these concepts to make AR understandable for everyone.
2. Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality: Understanding the Differences
2.1. Augmented Reality (AR): Enhancing Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real world by overlaying digital information onto it. With AR, users can still see their physical surroundings but with added virtual elements.
2.2. Virtual Reality (VR): Creating New Realities
Virtual Reality (VR), on the other hand, creates a completely simulated environment. VR users are fully immersed in a digital world, often through a headset, blocking out the real world entirely.
2.3. Key Differences Summarized
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Enhances the real world with digital overlays | Creates a completely simulated environment |
| Immersion | Partially immersive; users remain aware of their surroundings | Fully immersive; users are isolated from the real world |
| Devices | Smartphones, tablets, AR glasses | VR headsets, controllers |
| Use Cases | Navigation, retail, gaming, education | Gaming, training simulations, virtual tourism |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher due to specialized equipment |
| Accessibility | More accessible due to widespread use of smartphones | Less accessible due to the need for dedicated VR equipment |
| Interaction | Interacts with both real and virtual elements | Primarily interacts with virtual elements within the VR environment |
2.4. Mixed Reality (MR): Blurring the Lines
Mixed Reality (MR) combines elements of both AR and VR, allowing digital and real-world objects to coexist and interact in real-time. MR applications often involve advanced sensors and spatial computing to create seamless interactions between the physical and digital worlds.
2.5. Real-World Examples
- AR: Pokemon Go, Snapchat filters, IKEA Place app
- VR: Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, PlayStation VR
- MR: Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap
Understanding the differences between AR, VR, and MR is crucial for appreciating the unique applications and potential of each technology. WHAT.EDU.VN aims to clarify these concepts, making them accessible to everyone, regardless of their technical background.
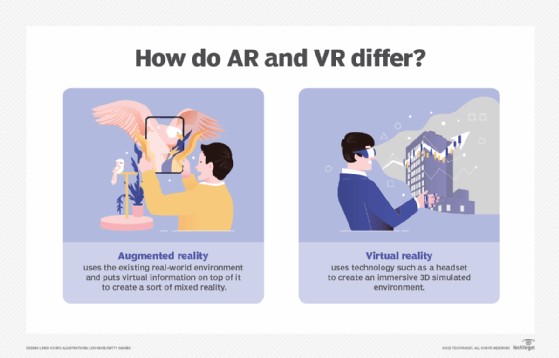 A comparison of augmented reality vs virtual reality
A comparison of augmented reality vs virtual reality
3. Applications of Augmented Reality Across Industries
3.1. Augmented Reality in Retail: Enhancing the Shopping Experience
AR is revolutionizing the retail industry by enhancing the shopping experience for customers. Retailers are using AR to allow customers to virtually try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, and explore product features in an interactive way.
Examples include:
- Virtual Try-On: Customers can use AR apps to virtually try on clothes, accessories, and makeup before making a purchase.
- Furniture Visualization: AR apps allow customers to see how furniture will look in their homes by overlaying 3D models onto their real-world environment.
- Interactive Product Exploration: AR can be used to provide customers with interactive product demonstrations and information, enhancing their understanding and engagement.
3.2. Augmented Reality in Education: Interactive Learning
AR is transforming education by creating interactive and engaging learning experiences for students of all ages. AR apps can bring textbooks to life, allow students to explore historical sites virtually, and provide hands-on learning experiences in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields.
Examples include:
- Interactive Textbooks: AR can be used to overlay 3D models, animations, and interactive elements onto textbook pages, making learning more engaging and memorable.
- Virtual Field Trips: AR apps allow students to take virtual field trips to historical sites, museums, and landmarks around the world, without leaving the classroom.
- STEM Education: AR can provide hands-on learning experiences in STEM fields, allowing students to conduct virtual experiments, build virtual models, and explore complex concepts in an interactive way.
3.3. Augmented Reality in Healthcare: Improving Patient Care
AR is improving patient care by providing healthcare professionals with real-time information, enhancing training and education, and enabling remote assistance. AR applications in healthcare include:
- Real-Time Information: AR can provide surgeons with real-time information during surgery, such as patient vitals, medical imaging, and surgical plans.
- Training and Education: AR can enhance medical training by allowing students to practice surgical procedures on virtual patients, reducing the risk of errors and improving their skills.
- Remote Assistance: AR can enable remote experts to provide guidance and assistance to healthcare professionals in remote locations, improving access to specialized care.
3.4. Augmented Reality in Gaming and Entertainment
AR is transforming the gaming and entertainment industries by creating immersive and interactive experiences for users. AR games overlay virtual elements onto the real world, allowing players to interact with their surroundings in new and exciting ways.
Examples include:
- Pokemon Go: A popular AR game that allows players to catch virtual Pokemon characters in the real world.
- AR Filters: Social media apps like Snapchat and Instagram use AR filters to overlay fun and creative effects onto users’ faces and surroundings.
- Interactive Storytelling: AR can be used to create interactive storytelling experiences, allowing users to explore virtual worlds and interact with characters in a more immersive way.
3.5. Augmented Reality in Manufacturing and Engineering
AR is streamlining manufacturing and engineering processes by providing workers with real-time information, enhancing training and collaboration, and improving efficiency.
Examples include:
- Real-Time Information: AR can provide workers with real-time information about equipment status, maintenance schedules, and assembly instructions, reducing errors and improving productivity.
- Training and Collaboration: AR can enhance training and collaboration by allowing workers to practice complex tasks on virtual equipment, reducing the risk of errors and improving their skills.
- Remote Assistance: AR can enable remote experts to provide guidance and assistance to workers in the field, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
AR’s versatility makes it a valuable tool in numerous sectors. WHAT.EDU.VN is dedicated to showcasing these applications, providing insights into how AR is shaping our world and improving our lives.
4. Benefits of Using Augmented Reality
4.1. Enhanced User Experience
Augmented Reality enhances user experience by blending digital content with the real world, making interactions more intuitive and engaging. This technology provides immersive experiences that capture attention and offer unique ways to interact with information.
4.2. Improved Efficiency
AR improves efficiency in various sectors by providing real-time data and guidance. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, or education, AR tools offer immediate access to critical information, streamlining workflows and reducing errors.
4.3. Increased Engagement
AR increases engagement by creating interactive and immersive experiences. This technology captivates users, making learning, shopping, and entertainment more captivating and memorable.
4.4. Enhanced Training
AR enhances training programs by offering realistic simulations and interactive learning environments. Trainees can practice complex tasks and procedures in a safe, controlled setting, improving their skills and confidence.
4.5. Cost Reduction
AR can lead to cost reduction in several ways, such as reducing the need for physical prototypes, improving training efficiency, and minimizing errors in manufacturing and healthcare.
4.6. Better Decision-Making
AR facilitates better decision-making by providing real-time data visualization and contextual information. Users can make more informed choices with access to relevant data overlaid onto their physical environment.
4.7. Accessibility
AR is becoming more accessible due to the widespread adoption of smartphones and the development of user-friendly AR applications. This technology is now available to a broad audience, enhancing various aspects of daily life.
These benefits highlight the transformative potential of AR across different sectors. WHAT.EDU.VN aims to bring these advantages to light, helping users understand how AR can improve their lives and work.
5. Challenges and Limitations of Augmented Reality
5.1. Technical Limitations
5.1.1. Processing Power
AR applications often require significant processing power to render digital content in real-time. This can be a limitation, especially for mobile devices with limited processing capabilities.
5.1.2. Battery Life
AR applications can drain battery life quickly due to the intensive processing and sensor usage. This can be a significant limitation for mobile AR experiences.
5.1.3. Tracking Accuracy
Accurate tracking is essential for AR applications to properly align digital content with the real world. However, tracking accuracy can be affected by factors such as lighting conditions, occlusions, and device limitations.
5.2. User Experience Challenges
5.2.1. Usability Issues
AR interfaces can be complex and challenging to use, especially for users who are not familiar with the technology. This can lead to frustration and abandonment.
5.2.2. Comfort and Ergonomics
AR headsets and glasses can be uncomfortable to wear for extended periods, especially if they are heavy or poorly designed. This can limit the usability of AR devices for certain applications.
5.2.3. Social Acceptance
Some users may feel self-conscious or uncomfortable using AR devices in public, which can limit the adoption of AR technology in social settings.
5.3. Content Creation Challenges
5.3.1. High Development Costs
Creating high-quality AR content can be expensive and time-consuming. This can be a barrier to entry for small businesses and individual developers.
5.3.2. Lack of Standardization
The lack of standardization in AR development tools and platforms can make it difficult to create content that is compatible with multiple devices and operating systems.
5.3.3. Content Relevance and Quality
Ensuring that AR content is relevant, engaging, and high-quality can be a challenge. Poorly designed or irrelevant content can detract from the user experience and limit the effectiveness of AR applications.
5.4. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
5.4.1. Data Privacy
AR applications often collect data about the user’s environment, location, and activities. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, especially if the data is not properly protected.
5.4.2. Social Impact
The use of AR technology can have unintended social consequences, such as increased social isolation, addiction, and the spread of misinformation.
5.4.3. Accessibility
Ensuring that AR technology is accessible to users with disabilities can be a challenge. AR interfaces may not be compatible with assistive technologies, which can limit the usability of AR applications for users with visual or motor impairments.
Addressing these challenges and limitations is essential for the continued growth and adoption of AR technology. WHAT.EDU.VN is committed to exploring these issues and providing insights into how they can be overcome.
6. The Future of Augmented Reality
6.1. Technological Advancements
6.1.1. Improved Hardware
The future of AR will see more powerful and energy-efficient processors, better displays, and more accurate sensors, leading to improved AR experiences.
6.1.2. Enhanced Software
Advancements in software algorithms, machine learning, and computer vision will enable more realistic and interactive AR content.
6.1.3. 5G and Cloud Computing
The rollout of 5G networks and the increasing availability of cloud computing resources will enable more seamless and immersive AR experiences, with lower latency and higher bandwidth.
6.2. Industry Trends
6.2.1. Increased Adoption
AR adoption will continue to grow across various industries, including retail, education, healthcare, manufacturing, and entertainment.
6.2.2. New Use Cases
AR will be used in new and innovative ways, such as remote collaboration, virtual tourism, and personalized advertising.
6.2.3. Integration with Other Technologies
AR will be increasingly integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and blockchain, to create more powerful and versatile solutions.
6.3. Social Impact
6.3.1. Enhanced Communication
AR will enhance communication and collaboration by enabling more immersive and interactive experiences.
6.3.2. Improved Education
AR will transform education by providing students with more engaging and personalized learning experiences.
6.3.3. Enhanced Accessibility
AR will improve accessibility for users with disabilities by providing assistive technologies and enhancing their ability to interact with the world around them.
6.4. Potential Challenges
6.4.1. Privacy Concerns
As AR technology becomes more pervasive, privacy concerns will need to be addressed to ensure that user data is protected and used responsibly.
6.4.2. Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations, such as the potential for bias and discrimination, will need to be addressed to ensure that AR technology is used in a fair and equitable manner.
6.4.3. Social Acceptance
Social acceptance of AR technology will depend on addressing concerns about usability, comfort, and social impact.
The future of AR is bright, with the potential to transform the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. WHAT.EDU.VN is dedicated to exploring these possibilities and providing insights into the future of AR.
7. Getting Started with Augmented Reality
7.1. Hardware and Software Requirements
7.1.1. Smartphones and Tablets
Most modern smartphones and tablets are equipped with the necessary hardware and software to run AR applications.
7.1.2. AR Headsets and Glasses
Specialized AR headsets and glasses, such as Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap, offer more immersive AR experiences.
7.1.3. Development Tools
AR development tools, such as ARKit and ARCore, provide developers with the necessary tools to create AR applications.
7.2. Popular AR Platforms and Frameworks
7.2.1. ARKit
ARKit is Apple’s AR development platform for iOS devices.
7.2.2. ARCore
ARCore is Google’s AR development platform for Android devices.
7.2.3. Unity
Unity is a popular game engine that supports AR development.
7.2.4. Vuforia
Vuforia is a software development kit (SDK) for creating AR applications.
7.3. Learning Resources
7.3.1. Online Courses
Online courses, such as those offered by Coursera and Udemy, provide comprehensive training in AR development.
7.3.2. Tutorials
Online tutorials and documentation provide step-by-step instructions on how to create AR applications.
7.3.3. Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums, such as Stack Overflow and Reddit, provide a platform for developers to ask questions, share knowledge, and collaborate on projects.
7.4. Example Projects
7.4.1. Simple AR App
Create a simple AR app that overlays a 3D model onto a real-world surface.
7.4.2. Interactive AR Game
Develop an interactive AR game that allows users to interact with virtual objects in the real world.
7.4.3. AR Shopping App
Build an AR shopping app that allows users to visualize products in their homes before making a purchase.
Getting started with AR is easier than ever, thanks to the availability of powerful development tools, learning resources, and example projects. WHAT.EDU.VN is committed to providing users with the information and resources they need to get started with AR development.
8. Augmented Reality: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Augmented Reality (AR)? | Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real world by overlaying digital information, such as images, videos, and 3D models, onto the user’s view. |
| How does AR differ from Virtual Reality (VR)? | AR enhances the real world, while VR creates a completely simulated environment. AR users can still see their surroundings, while VR users are fully immersed in a digital world. |
| What are the key components of an AR system? | Key components include input devices (cameras, sensors), processing unit, display unit, tracking system, and AR software. |
| What industries use AR? | AR is used in retail, education, healthcare, gaming, manufacturing, and more. |
| What are the benefits of using AR? | Benefits include enhanced user experience, improved efficiency, increased engagement, enhanced training, and cost reduction. |
| What are the challenges of AR? | Challenges include technical limitations (processing power, battery life), usability issues, content creation costs, and ethical concerns (data privacy). |
| What is the future of AR? | The future of AR includes improved hardware and software, increased adoption, new use cases, and integration with other technologies like AI and 5G. |
| What hardware is needed for AR? | Modern smartphones and tablets, as well as specialized AR headsets like Microsoft HoloLens, can be used for AR experiences. |
| How can I get started with AR development? | Start by exploring AR development platforms like ARKit (iOS) and ARCore (Android), and utilize online courses, tutorials, and developer communities. |
| What ethical considerations are associated with AR? | Ethical considerations include data privacy, potential for bias, and ensuring accessibility for users with disabilities. |
| Are there any health concerns with using AR devices? | Prolonged use of AR devices may cause eye strain or discomfort. Taking breaks and adjusting settings can help mitigate these issues. |
| Can AR be used for remote collaboration? | Yes, AR can enable remote collaboration by allowing users to share and interact with virtual objects in a real-world environment. |
| Is AR technology expensive? | The cost of AR technology varies depending on the application and hardware requirements. While some AR solutions are affordable, others may require significant investment. |
| How secure is AR technology? | Security is a concern with AR, as AR applications often collect sensitive data. Ensuring robust security measures is crucial to protect user privacy and prevent unauthorized access. |
| What impact does AR have on the economy? | AR has the potential to create new jobs, drive economic growth, and transform industries. As AR technology becomes more widespread, its impact on the economy is expected to increase significantly. |
9. Need Answers? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
Finding answers to your questions shouldn’t be a struggle. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of quickly accessing reliable information. That’s why we offer a platform where you can ask any question and receive answers for free!
Are you tired of sifting through endless search results? Do you need expert advice without the hefty consultation fees? WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. Our community of knowledgeable users is ready to provide you with the answers you need, quickly and accurately.
Here’s how WHAT.EDU.VN solves your challenges:
- Free Access: Ask any question without worrying about subscription fees or hidden costs.
- Quick Responses: Get answers fast from our community of experts.
- Reliable Information: Benefit from the knowledge of experienced users and professionals.
- Easy to Use Platform: Our user-friendly interface makes it simple to ask questions and receive answers.
- Diverse Topics: Whether it’s academic, professional, or personal, no question is off-limits.
Ready to get started?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question. Our community is eager to assist you.
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Join what.edu.vn now and experience the convenience of having your questions answered for free!