The global landscape of business is rapidly changing, with international commerce becoming increasingly streamlined. This evolution is fueled by a growing desire for collaboration, facilitated by advancements in financial technology. The SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) network plays a crucial role in this interconnected world, providing a secure and efficient means for cross-border payments and fostering a robust intermediary network among banks.
In 2021, the SWIFT network facilitated an impressive average of 42 million messages daily, sent by over 11,000 member institutions worldwide. This figure represents an 11.4% increase compared to 2020, demonstrating the network’s continued growth and importance in the global financial ecosystem. For businesses aiming to simplify international transactions, enhance overseas commerce, and ensure payment security, the SWIFT network offers a powerful solution.
Understanding SWIFT Codes
A SWIFT code is a standardized format used for international money transfers between banks and financial institutions. It acts as a unique identifier, specifying the bank, branch, and country where an account is registered. Through BIC (Bank Identifier Codes), SWIFT codes effectively communicate the “who, what, and where” of international transactions.
SWIFT, the organization, owns and manages the BIC system, enabling rapid bank identification and payment processing. The SWIFT network also played a key role in standardizing the formats for International Bank Account Numbers (IBANs).
The SWIFT network relies on BIC codes to facilitate secure payments, including international bank wires, money transfers, and SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) payments. Additionally, the network functions as a secure messaging system between financial institutions.
It’s important to note that when a business utilizes the SWIFT network, they are not directly sending funds. Instead, the transaction is processed as a “payment order” exchanged between two banks.
SWIFT codes are also known by several other names, including:
- SWIFT ID
- BIC code
- ISO9362
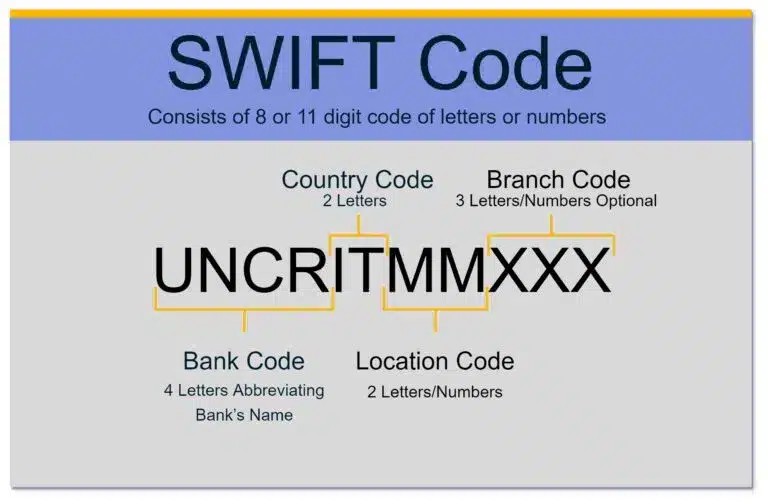
Decoding the SWIFT Code Format
A SWIFT code consists of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters, arranged in a standardized format:
- Bank Code (4 letters): Represents an abbreviation of the bank’s name.
- Country Code (2 letters): Denotes the country where the bank is located.
- Location Code (2 letters or numbers): Identifies the bank’s head office.
- Branch Code (3 letters or numbers): Specifies a particular branch of the bank.
The branch code functions similarly to a routing number in the US. In some cases, the branch code may be represented as “XXX,” indicating that the transfer should be directed to the bank’s main office.
The International Standard for SWIFT/BIC codes is ISO 9362. This standard governs the structure of a SWIFT code, including the use of letters, numbers, and the overall length of the code.
Example of a SWIFT Code: UniCredit Banca, Milan
Consider the example of UniCredit Banca, an Italian bank located in Milan. Its SWIFT code is:
UNCRITMM (XXX)
- UNCR: Bank code for UniCredit.
- IT: Country code for Italy.
- MM: Location code for Milan.
In this case, the absence of a specific branch code indicates that the transfer will be routed to the main UniCredit Banca office in Milan.
When Do You Need a SWIFT Code?
A SWIFT code is generally required when sending or receiving funds internationally between banks, especially for wire transfers or SEPA payments.
Initially designed to facilitate communication regarding treasury and correspondent transactions, the SWIFT network’s messaging format proved highly scalable. Today, SWIFT provides services to a wide range of entities, including:
- Banks
- Corporations
- Foreign exchange institutions
- Clearing systems
- Asset management companies
- Money brokers
- Non-bank financial institutions
- Treasury market participants
- Depositories
- And more
How SWIFT Codes Facilitate International Payments
The SWIFT network was established to enable efficient and secure communication between banks, primarily for processing international payments. It acts as a messenger, transmitting payment instructions from the sending bank (the payor) to the receiving bank (the beneficiary).
When financial institutions utilize a SWIFT code, they are essentially specifying the destination for international funds. This includes identifying the recipient’s bank, the sender’s bank, and the final location of the funds.
In addition to the sending and receiving banks, a SWIFT payment may involve an intermediary bank. This is often necessary due to varying banking regulations in different countries. The intermediary bank facilitates the transaction between the two primary banks.
To ensure seamless SWIFT transactions, banks often establish accounts with each other, known as Nostro and Vostro accounts.
Nostro and Vostro Accounts: A Mirror Image
Nostro and Vostro accounts are mirrored ledgers that enable banks to track withdrawals and deposits in international transactions.
- Nostro: Derived from the Latin word for “ours,” a Nostro account refers to an account that a bank holds in a foreign country with another bank.
- Vostro: Meaning “yours” in Latin, a Vostro account is used by a bank to refer to accounts that other banks hold with them.
When banks maintain Nostro and Vostro accounts with each other, SWIFT transfers can be processed directly and efficiently. However, if such a relationship does not exist, the SWIFT network relies on an intermediary bank to facilitate the transaction.
The SWIFT transaction can proceed once a correspondent bank (a bank with relationships with both the sending and receiving banks) is identified. However, the involvement of multiple banks in these international transactions can lead to increased fees, longer processing times, and potentially higher risks.
Finding and Verifying a SWIFT Code
Locating a SWIFT code is generally straightforward. Here are some common sources:
- Bank account statements
- Online banking portals
- Bank’s website
- Directly from the bank (phone or in person)
Online SWIFT code search tools can also be used to quickly find a code.
Once you have a SWIFT code, it’s crucial to verify its accuracy. Numerous online SWIFT code checkers are available to validate the code and confirm its legitimacy. Given that international banks typically publish these codes online, verifying a SWIFT code is a quick and simple process.
Frequently Asked Questions About SWIFT Codes
-
Is a SWIFT Code the Same as a BIC?
BIC (Bank Identifier Code) is the umbrella term for a SWIFT code. International bank statements may use either term interchangeably.
-
Does it Cost Money to Use a SWIFT Code?
International money transfers typically involve fees, regardless of the method used. The specific fees depend on factors such as the destination country, the transfer method, and the banks involved. Some banks may waive certain fees for account holders. If an intermediary bank is required, additional charges may apply. Exchange rates should also be considered. SWIFT also offers additional services such as business intelligence tools, professional apps and compliance assistance, which may incur separate costs.
-
What Happens if You Give the Wrong SWIFT Code (BIC)?
In the best-case scenario, the SWIFT network will reject the transaction, and the funds will be returned within one to three weeks. While this can be inconvenient, particularly for small businesses, it is preferable to the funds being misdirected. A minor error, such as an incorrect branch code, may be easily corrected. However, it’s crucial to not rely on the banks to automatically fix such errors. To avoid potential problems, always use a SWIFT checker to verify the accuracy of the receiving bank’s SWIFT code. Double-checking is always recommended.
-
Is a SWIFT Code or BIC Like a Routing Number?
A SWIFT code is similar in concept to a U.S. routing number, which is used for domestic transactions. However, the two differ significantly in terms of structure, subcodes, and function. SWIFT codes are used for international transfers, while routing numbers are used for domestic transfers.
-
Is a SWIFT Code the Same as an IBAN?
The key difference between SWIFT codes and IBANs lies in the information they convey. A SWIFT code identifies a specific bank, while an IBAN identifies an individual account. The SWIFT network is currently the most widely used international payment system, surpassing the IBAN system in terms of transaction volume.
The Future of SWIFT
Despite competition from other real-time messaging services, SWIFT maintains a leading position in capital markets. This is largely due to its ongoing efforts to adapt to evolving fintech processes and changing financial needs.
The network continuously updates its database with new message codes to accommodate a wide range of financial transactions. This adaptability makes SWIFT one of the most valuable and versatile systems for international transfers worldwide.