The W-9 form, officially known as Request for Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and Certification, is a crucial Internal Revenue Service (IRS) document for anyone working as a freelancer, independent contractor, or consultant in the United States. Essentially, it’s how you provide your essential tax information to those who pay you, ensuring accurate tax reporting to the IRS.
At its core, the W-9 form serves to collect your correct Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN). This TIN is then used by the entity or individual paying you (the “requester”) to accurately report your earnings to the IRS. This reporting is done via information returns, such as Form 1099-NEC for non-employee compensation. Without a correctly filled out W-9, businesses can’t properly report payments made to you, potentially leading to tax complications for both parties.
Purpose of Form W-9: Why is it Required?
The primary purpose of the W-9 form is to facilitate accurate information reporting to the IRS. When a business pays an individual or another entity for services, in many cases, they are required to report these payments to the IRS. This is where the W-9 comes in. By collecting your TIN, the requester can accurately fill out information returns, detailing how much they paid you throughout the tax year. This system allows the IRS to track income and ensure that everyone is paying their fair share of taxes.
Think of it as a verification tool. The W-9 form ensures that the payer has the correct information to report your income under your correct tax identification number. This helps prevent mismatches and errors that could arise if businesses were to guess or use outdated information.
Who Needs to Fill Out a W-9 Form?
Generally, you’ll need to fill out a W-9 form if you are a U.S. person (including a resident alien), and you are working as:
- An Independent Contractor or Freelancer: This is the most common scenario. If you provide services to businesses as a non-employee, you’ll likely be asked to complete a W-9. This includes consultants, gig workers, and anyone who is paid for services but not considered an employee.
- A Sole Proprietor: If you operate your business as a sole proprietorship, even if it’s under your own name, you will use Form W-9 to provide your TIN.
- Partnerships, LLCs, and Corporations: Businesses structured as partnerships, limited liability companies (LLCs), or corporations will also use Form W-9 to provide their TIN when they are being paid for services.
- Anyone Receiving Reportable Income: Beyond service-based income, you might also need to fill out a W-9 if you receive other types of reportable income, such as royalties or rent.
Essentially, if a business is paying you and needs to report that payment to the IRS, they will likely request a W-9 form from you.
Key Information Required on Form W-9
The W-9 form is relatively straightforward to complete. It asks for essential information to correctly identify you or your business for tax purposes. Here are the key sections:
-
Name: For individuals, this is your legal name as shown on your Social Security card. For businesses, it’s the legal name of the entity.
-
Business Name/Disregarded Entity Name (if applicable): If you operate a business under a name different from your personal name (doing business as or DBA), you’ll enter that here. This also applies to disregarded entities.
-
Federal Tax Classification: This section asks you to classify yourself for tax purposes. You’ll check the appropriate box, whether you are an individual/sole proprietor, C-corporation, S-corporation, partnership, trust/estate, or LLC. For LLCs, you must further indicate your tax classification (partnership, corporation, or disregarded entity).
-
Exemptions (if applicable): Certain payees are exempt from backup withholding. If you are exempt, you would indicate the exemption code here. This is less common for typical independent contractors.
-
Address: Your current address. Importantly, a change of address alone does not require a new W-9 form.
-
Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): This is the most critical part. Your TIN can be one of the following:
- Social Security Number (SSN): For individuals and sole proprietors.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): For corporations, partnerships, LLCs (sometimes), and other entities.
- Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN): For resident and nonresident aliens who don’t qualify for an SSN but are required to have a TIN.
- Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN): For individuals in the process of adopting a child.
-
Signature: You must sign and date the W-9 form to certify that the information you’ve provided is correct.
How Often Do You Need to Provide a W-9 Form?
Generally, you only need to provide a W-9 form once to a requester, and it remains valid indefinitely as long as your information is accurate. You only need to submit a new W-9 if there are changes to your information that would make the original form inaccurate. Examples of changes that require a new W-9 include:
- Name Change: If you legally change your name.
- Change in Business Structure or Entity Type: If your business changes its legal structure (e.g., from sole proprietorship to LLC).
A change of address alone does not necessitate a new W-9 form.
Signature Requirements and Digital Signatures
The W-9 form must be signed by a U.S. person, which includes U.S. citizens and U.S. resident aliens. The person signing should have the authority to do so on behalf of the entity if signing for a business.
In today’s digital age, electronic signatures are often accepted. According to the IRS, digital signatures from platforms like Adobe Acrobat or DocuSign are generally acceptable, provided they include a validation envelope that ensures the document’s authenticity and security. However, simple typed signatures are not considered valid digital signatures.
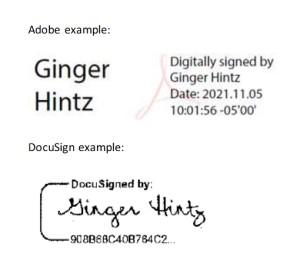 Examples of a validated e-signature with a validation envelope (date and time details) done in Adobe Acrobat and DocuSign
Examples of a validated e-signature with a validation envelope (date and time details) done in Adobe Acrobat and DocuSign
Special Case: W-9 Forms for Minors
When dealing with payments to minors, the W-9 form should be completed using the minor’s name and TIN (usually their Social Security Number), as the income legally belongs to the minor. While a minor can sign the W-9, it’s also acceptable for a legal guardian (parent or court-appointed guardian) to sign on their behalf. It’s important to note that the W-9 is not a contract, so legal restrictions on minors signing contracts do not apply here.
Getting the Correct W-9 Form and Instructions
It’s always best to use the most current version of the W-9 form directly from the IRS website (IRS Forms web page). Using outdated forms can cause delays in payment processing as the requester will need to ask you for a current form. The IRS website also provides detailed instructions for completing the form, which can be very helpful if you have any questions.
In conclusion, understanding the W-9 form is essential for anyone working in the U.S. as an independent contractor or freelancer. It’s a simple yet vital document that ensures accurate tax reporting and helps you and the businesses you work with stay compliant with IRS regulations. By understanding its purpose and how to fill it out correctly, you can navigate the tax aspects of your work with confidence.