What Is Afd In Germany? The Alternative for Germany (AfD) is a political party that has gained prominence in recent years, understanding its role and influence is crucial. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we aim to provide clarity and answers to your questions, offering insights into the German political landscape and providing LSI keywords and semantic keywords.
1. Understanding AfD: Alternative for Germany
The Alternative for Germany (AfD) is a German political party founded in April 2013. Initially, it focused primarily on opposition to the Eurozone and the European Union’s policies. However, its platform has evolved to encompass a broader range of issues, including immigration, national identity, and security. Over the years, the AfD has experienced significant growth and has become a notable force in German politics, sparking considerable debate and discussion about its impact on the country’s political landscape.
1.1. Historical Context
The AfD emerged during a period of economic uncertainty in Europe, marked by the Eurozone crisis. Its initial appeal was rooted in skepticism toward the euro and the European Union’s handling of financial issues. As the political climate shifted, the AfD adapted its platform to address concerns about immigration and cultural identity, attracting a diverse base of supporters.
1.2. Core Ideologies
The AfD’s core ideologies can be summarized as follows:
- Euroskepticism: The party advocates for reforming or even dissolving the Eurozone, arguing that the common currency has negatively impacted Germany’s economic sovereignty.
- Immigration Control: A central theme in the AfD’s platform is stricter immigration policies. The party has called for limiting the number of refugees and asylum seekers entering Germany and has expressed concerns about the integration of immigrants into German society.
- National Identity: The AfD emphasizes the importance of preserving German culture and identity. It opposes what it views as the erosion of traditional values and seeks to promote a sense of national pride.
- Law and Order: The party advocates for stronger law enforcement and stricter penalties for crimes. It often highlights issues related to crime and security to bolster its support.
1.3. Key Figures and Leadership
Throughout its existence, the AfD has been led by several prominent figures who have shaped its direction and messaging. These leaders have played a crucial role in articulating the party’s positions and mobilizing its supporters. Some notable individuals include:
- Frauke Petry: One of the early leaders of the AfD, Petry played a significant role in the party’s initial success. However, she later left the party due to internal conflicts.
- Jörg Meuthen: Meuthen served as one of the party’s co-leaders for several years. He represented a more moderate faction within the AfD.
- Alice Weidel and Tino Chrupalla: Currently, Alice Weidel and Tino Chrupalla serve as the AfD’s leaders. They represent different wings of the party and have been instrumental in shaping its current political agenda.
1.4. Electoral Successes and Representation
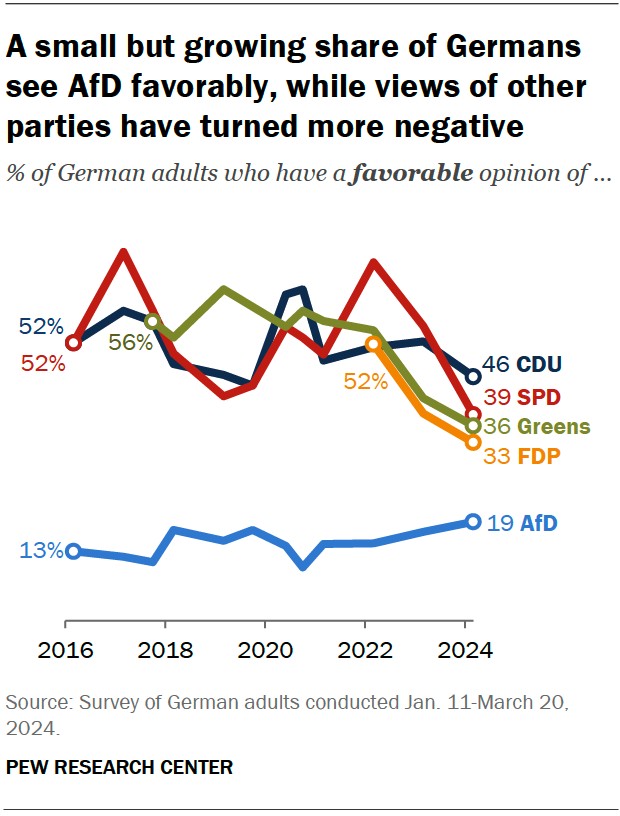
The AfD has achieved significant electoral successes since its formation. It first gained representation in the European Parliament in 2014 and subsequently entered several state parliaments. In 2017, the AfD made history by becoming the first far-right party to enter the German Bundestag (federal parliament) in over half a century. This milestone marked a turning point in German politics, as the AfD became the largest opposition party.
Alternative Text: Trend showing increase in Germans that view AfD favorably
2. AfD’s Impact on German Politics
The AfD’s rise has had a profound impact on German politics, influencing the dynamics of the political landscape and prompting significant discussions about the country’s future.
2.1. Shifting the Political Discourse
One of the most notable effects of the AfD’s emergence has been its role in shifting the political discourse in Germany. The party’s focus on issues such as immigration, national identity, and security has compelled other political parties to address these topics more directly. This has led to a broader debate about the direction of German society and the challenges it faces.
2.2. Polarization of Society
The AfD’s presence in German politics has contributed to the polarization of society. Its often controversial statements and positions have sparked strong reactions from both supporters and opponents. This polarization has made it more challenging to find common ground on various issues and has deepened divisions within the country.
2.3. Influence on Government Policy
While the AfD has primarily been an opposition party, it has still managed to exert influence on government policy. The ruling parties have, at times, adopted stricter stances on immigration and security in response to the AfD’s popularity. This demonstrates the party’s ability to shape the political agenda, even from outside the government.
2.4. Challenges to Traditional Parties
The AfD’s rise has posed challenges to traditional political parties in Germany, particularly the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the Social Democratic Party (SPD). These parties have had to adapt their strategies to compete with the AfD and to address the concerns of voters who might be drawn to the party’s message.
3. The AfD’s Supporters: Who Are They?
Understanding the AfD’s supporters is crucial to comprehending its appeal and the factors that drive its popularity.
3.1. Demographic Profile
The AfD’s support base is diverse and includes individuals from various demographic groups. However, some patterns have emerged:
- Gender: Men are more likely to support the AfD than women. This gender gap is a notable characteristic of the party’s support base.
- Education: Individuals with lower levels of education are more inclined to support the AfD compared to those with higher education levels.
- Region: The AfD tends to be stronger in certain regions of Germany, particularly in the eastern states. These regions often have distinct socio-economic characteristics that contribute to the party’s appeal.
3.2. Motivations and Concerns
The AfD’s supporters are motivated by a range of concerns and beliefs, including:
- Economic Anxiety: Some supporters feel left behind by economic changes and globalization. They may believe that the AfD offers solutions to their economic challenges.
- Cultural Identity: Concerns about the preservation of German culture and identity are significant motivators for AfD supporters. They may feel that traditional values are being eroded.
- Immigration Concerns: Opposition to immigration and concerns about its impact on German society are central to the AfD’s appeal. Supporters may believe that stricter immigration policies are necessary.
- Distrust of Mainstream Parties: A sense of disillusionment with mainstream political parties is common among AfD supporters. They may believe that the established parties are not addressing their concerns effectively.
3.3. Misconceptions and Stereotypes
It’s essential to avoid misconceptions and stereotypes when discussing the AfD’s supporters. While some may hold extreme views, many are ordinary citizens with legitimate concerns about the direction of their country. Understanding their motivations and grievances is crucial for fostering constructive dialogue.
4. Controversies and Criticisms
The AfD has faced numerous controversies and criticisms due to its rhetoric and policies.
4.1. Allegations of Racism and Xenophobia
One of the most frequent criticisms leveled against the AfD is that it promotes racism and xenophobia. Opponents point to statements made by party members that are perceived as discriminatory toward immigrants and minorities.
4.2. Extremist Elements Within the Party
There have been concerns about extremist elements within the AfD. Some individuals associated with the party have been linked to far-right groups and have expressed views that are considered anti-constitutional.
4.3. Monitoring by Intelligence Agencies
Due to concerns about extremism, some branches of the AfD have been placed under surveillance by German intelligence agencies. This monitoring reflects the government’s concerns about the party’s potential threat to democracy.
4.4. Responses from Other Political Parties
Other political parties in Germany have responded to the AfD in various ways. Some have sought to directly confront the party’s positions, while others have attempted to address the concerns of voters who might be drawn to the AfD.
5. The AfD and the Future of Germany
The AfD’s role in the future of Germany remains a subject of considerable debate and uncertainty.
5.1. Potential Scenarios
Several potential scenarios could unfold:
- Continued Growth: The AfD could continue to grow in popularity, potentially becoming a dominant force in German politics.
- Decline: The party’s support could decline due to internal divisions, controversies, or shifts in public opinion.
- Coalition Possibilities: The AfD’s potential to form coalitions with other parties remains a contentious issue. Many parties have ruled out cooperation with the AfD due to its extremist tendencies.
5.2. Impact on German Identity
The AfD’s emphasis on national identity has sparked discussions about what it means to be German in the 21st century. The party’s vision of German identity is often seen as exclusionary and at odds with the country’s diverse and multicultural society.
5.3. European Implications
The AfD’s rise has implications for the European Union as well. Its Eurosceptic stance and its criticism of EU policies could contribute to further divisions within the bloc.
5.4. The Role of Civil Society
Civil society organizations, including advocacy groups, think tanks, and grassroots movements, play a crucial role in countering the AfD’s influence. These organizations work to promote tolerance, combat hate speech, and defend democratic values.
6. AfD’s Position on Key Issues
To fully understand the AfD’s political stance, it is essential to examine its positions on key issues.
6.1. Immigration and Asylum
The AfD advocates for strict limitations on immigration and asylum. It calls for the closure of Germany’s borders and the deportation of individuals who have been denied asylum. The party argues that immigration poses a threat to German culture and security.
6.2. Economy and Social Welfare
On economic issues, the AfD generally supports free-market principles and deregulation. However, it also advocates for protectionist measures to safeguard German industries. The party’s stance on social welfare is somewhat mixed, with some factions calling for cuts in social spending and others emphasizing the need to protect the social safety net.
6.3. Foreign Policy and Defense
In foreign policy, the AfD is critical of Germany’s involvement in international organizations such as the European Union and NATO. It favors closer ties with Russia and advocates for a more assertive German foreign policy. On defense, the party calls for increased military spending and a stronger German army.
6.4. Environment and Energy
The AfD is skeptical of climate change and opposes policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. It supports the continued use of fossil fuels and criticizes Germany’s transition to renewable energy sources.
Alternative Text: Graph showing increase in popularity of AfD
7. Comparing AfD to Other Political Parties
To gain a clearer perspective on the AfD, it is helpful to compare it to other political parties in Germany.
7.1. Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
The CDU is a center-right party that has traditionally been one of the dominant forces in German politics. While the CDU shares some conservative positions with the AfD, it is generally more moderate and pro-European.
7.2. Social Democratic Party (SPD)
The SPD is a center-left party that advocates for social justice and equality. It differs significantly from the AfD on issues such as immigration, social welfare, and European integration.
7.3. Green Party
The Green Party focuses on environmental protection and sustainability. It has a fundamentally different approach to issues such as climate change and energy policy compared to the AfD.
7.4. Free Democratic Party (FDP)
The FDP is a liberal party that emphasizes individual freedom and free-market principles. While the FDP shares some economic views with the AfD, it is generally more open to immigration and international cooperation.
8. The Role of Media in Shaping Perceptions of AfD
The media plays a crucial role in shaping public perceptions of the AfD.
8.1. Media Coverage
The AfD receives extensive media coverage in Germany, both positive and negative. The tone of coverage often depends on the media outlet’s political orientation.
8.2. Bias and Objectivity
Concerns have been raised about bias in media coverage of the AfD. Some critics argue that the media is unfairly critical of the party, while others contend that the media has a responsibility to scrutinize its positions and rhetoric.
8.3. Social Media’s Impact
Social media platforms have become important channels for the AfD to communicate with its supporters. However, they have also been used to spread misinformation and propaganda.
9. AfD’s Relationship with Foreign Governments and Organizations
The AfD’s relationship with foreign governments and organizations has been a subject of scrutiny.
9.1. Ties to Russia
The AfD has been criticized for its close ties to Russia. Some party members have expressed support for President Vladimir Putin and have called for closer cooperation with Russia.
9.2. International Alliances
The AfD has formed alliances with other far-right parties in Europe and beyond. These alliances reflect a shared ideology and a desire to coordinate political strategies.
9.3. Foreign Funding
Concerns have been raised about the possibility of foreign funding for the AfD. Investigations have been launched to determine whether the party has received financial support from foreign governments or organizations.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About AfD
Here are some frequently asked questions about the AfD:
10.1. What is the AfD’s stance on immigration?
The AfD advocates for strict limitations on immigration and asylum. It calls for the closure of Germany’s borders and the deportation of individuals who have been denied asylum.
10.2. How does the AfD compare to other political parties in Germany?
The AfD differs significantly from mainstream parties such as the CDU, SPD, and Green Party on issues such as immigration, social welfare, and European integration.
10.3. What are the main criticisms of the AfD?
The AfD has been criticized for promoting racism and xenophobia, as well as for its ties to extremist elements and foreign governments.
10.4. Who are the AfD’s main supporters?
The AfD’s supporters come from diverse demographic groups, but they tend to be more likely to be men, individuals with lower levels of education, and residents of eastern Germany.
10.5. What is the AfD’s impact on German politics?
The AfD has shifted the political discourse in Germany, contributed to the polarization of society, and posed challenges to traditional political parties.
11. Countering Misinformation and Propaganda
Combating misinformation and propaganda is crucial in the context of the AfD.
11.1. Fact-Checking Initiatives
Fact-checking organizations play a vital role in debunking false claims and exposing disinformation related to the AfD.
11.2. Media Literacy Education
Promoting media literacy is essential to help citizens critically evaluate information and resist propaganda.
11.3. Community Engagement
Community engagement and dialogue can help counter the spread of misinformation and promote understanding.
12. The Importance of Informed Dialogue
Engaging in informed dialogue about the AfD is essential for a healthy democracy.
12.1. Respectful Communication
It is important to engage in respectful communication, even when discussing controversial topics.
12.2. Understanding Different Perspectives
Seeking to understand different perspectives can help bridge divides and foster constructive dialogue.
12.3. Promoting Tolerance
Promoting tolerance and respect for diversity is crucial for countering the AfD’s divisive rhetoric.
Alternative Text: Graph showing favorable and unfavorable views of NATO members
13. The AfD’s Influence on Younger Generations
The AfD’s influence on younger generations is a growing concern.
13.1. Online Radicalization
Online platforms have become breeding grounds for radicalization among young people.
13.2. Educational Initiatives
Educational initiatives can help young people develop critical thinking skills and resist extremist ideologies.
13.3. Role Models and Mentors
Positive role models and mentors can play a crucial role in guiding young people away from extremism.
14. The Future of German Democracy
The future of German democracy depends on addressing the challenges posed by the AfD.
14.1. Strengthening Democratic Institutions
Strengthening democratic institutions and promoting civic engagement are essential for safeguarding democracy.
14.2. Addressing Social and Economic Inequalities
Addressing social and economic inequalities can help reduce the appeal of extremist ideologies.
14.3. Promoting Inclusive Policies
Promoting inclusive policies that benefit all members of society is crucial for building a more cohesive and resilient nation.
15. The AfD and the European Parliament
The AfD’s presence in the European Parliament has implications for the EU.
15.1. Eurosceptic Agenda
The AfD uses its platform in the European Parliament to promote its Eurosceptic agenda.
15.2. Alliances with Other Far-Right Parties
The AfD has formed alliances with other far-right parties in the European Parliament to advance its goals.
15.3. Impact on EU Policy
The AfD’s presence in the European Parliament can influence EU policy, particularly on issues such as immigration and border control.
16. The AfD’s Stance on LGBTQ+ Rights
The AfD’s stance on LGBTQ+ rights has been a subject of controversy.
16.1. Opposition to Same-Sex Marriage
The AfD opposes same-sex marriage and has called for the protection of traditional family values.
16.2. Concerns About Discrimination
LGBTQ+ rights advocates have expressed concerns about discrimination and hate speech targeting LGBTQ+ individuals.
16.3. Legal Protections
Legal protections for LGBTQ+ individuals in Germany have been a topic of debate in the context of the AfD’s rise.
17. The AfD and Religious Minorities
The AfD’s relationship with religious minorities has been fraught with tension.
17.1. Anti-Muslim Rhetoric
The AfD has been criticized for its anti-Muslim rhetoric and its efforts to restrict the construction of mosques.
17.2. Protecting Religious Freedom
Protecting religious freedom for all religious minorities is a key challenge in the face of the AfD’s divisive rhetoric.
17.3. Interfaith Dialogue
Interfaith dialogue can help promote understanding and cooperation between different religious communities.
18. The AfD’s Economic Policies in Detail
A deeper dive into the AfD’s economic policies reveals a complex mix of ideas.
18.1. Tax Cuts
The AfD generally favors tax cuts for businesses and individuals, arguing that this will stimulate economic growth.
18.2. Deregulation
The party also supports deregulation to reduce the burden on businesses and promote investment.
18.3. Trade Protectionism
However, the AfD also advocates for trade protectionism to safeguard German industries from foreign competition.
19. The AfD and the German Welfare State
The AfD’s vision for the German welfare state is a contentious issue.
19.1. Reforming Social Security
The party calls for reforming the social security system to make it more sustainable.
19.2. Reducing Unemployment Benefits
Some factions within the AfD have advocated for reducing unemployment benefits to encourage people to find work.
19.3. Protecting Pensions
However, the AfD also emphasizes the need to protect pensions for retirees.
20. The AfD’s Impact on Germany’s International Relations
The AfD’s foreign policy positions have implications for Germany’s international relations.
20.1. Relations with the United States
The AfD is critical of Germany’s close relationship with the United States and has called for a more independent foreign policy.
20.2. Relations with Russia
As mentioned earlier, the AfD favors closer ties with Russia and has called for an end to sanctions.
20.3. Relations with the European Union
The AfD’s Eurosceptic stance has strained Germany’s relations with the European Union.
We hope this comprehensive overview has provided you with a better understanding of the AfD in Germany. Remember, at WHAT.EDU.VN, we are here to answer your questions and provide clarity on complex issues. If you have any further inquiries, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. Our address is 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890 or visit our website at WHAT.EDU.VN for more information and free consultation. Don’t hesitate, ask your questions on what.edu.vn today and get free answers.