In the realm of data analysis, the question “What Is An Anomaly?” is fundamental. Anomalies, often called outliers, are data points that deviate significantly from the norm. Understanding anomalies is crucial in various fields, from cybersecurity to eDiscovery. Let’s explore this concept in detail.
In simple terms, an anomaly is something that is “different, abnormal, peculiar, or not easily classified.” It is “inconsistent with or deviating from what is usual, normal, or expected.” Think of anomalies as the opposite of the ordinary, a departure from the routine, a break from business as usual. They represent an abnormality.
Data scientists have extensively researched anomalies and their detection methods. In a 2007 article in Computer Networks, researchers defined anomaly detection systems as those that “compare activities against a ‘normal’ baseline.” Similarly, a 2013 Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research paper described anomaly detection as “identifying unlikely and rare events.”
Anomalies in eDiscovery
Within the context of eDiscovery, anomalies play a vital role. A 2016 McGuireWoods E-Discovery Update pointed out that hit reports “sometimes identify anomalies that can be researched further by looking at sample documents.” John Davis, senior counsel at Crowell & Moring, stated in a 2019 article:
“AI systems can also search for anomalies—”irregular occurrences or omissions, things that are or are not there, contrary to expectations,” says Davis. “People are now more guarded about how they communicate in emails. They may avoid emailing about a sensitive subject or use a different terminology or channel. These analytics help you look for out-of-character communications, code language, or patterns that point toward underlying meaning. For example, if someone who is usually chatty in texts suddenly sends one saying, ‘Just call me on my cell,’ the system can flag that.” It can also find suspicious gaps in communication frequency that can raise red flags for further inquiry or signal failures of production or destruction of evidence.”
Sarah Moran of Lighthouse noted in an earlier post this year:
“[If] a litigation involves an employee accused of stealing company information, advanced AI technology can analyze all the employee’s communications and digital activities and identify any anomalies, such as an activity that occurred during abnormal work hours or communications with other employees with whom they normally would not have reason to interact.”
The Significance of Anomalies
Anomalies are essential because they provide attorneys and investigators with critical information for determining what truly happened and why.
One expert witness, an econometrician, explained that anomalies, or outliers, can reveal inconsistencies in someone’s account of events compared to the available facts. These stories might involve descriptions of what happened, explanations of how something occurred, or indications of why someone acted in a certain way.
The process involves creating a map, either from the available data or from a constructed narrative. This map is then tested against the opposing information source, identifying discrepancies – the anomalies.
For example, an elaborate, manual process was used to map out the other side’s story in a two-dimensional graph, resembling a bell curve. Spikes along the curve, particularly at the edges, represented outliers or data points that did not align with the curve. By examining these spikes, specific data points could be investigated to determine the root cause of the anomaly.
This process allowed for the construction of a different narrative of the case, where the story and the facts were in closer agreement. Modern technology now automates this process, making anomaly detection more efficient.
Identifying Anomalies
Anomalies can be found in various types of data and are identified through mechanisms like anomaly detection algorithms. eDiscovery platforms and AI can help identify unusual behavior based on criteria such as:
- Data Range
- Sender or receiver of a communication
- Concepts expressed in a document or communication
- Tone used by an author
- Named entities discussed
- Domains used
- Frequency of occurrences of specific information within a designated timeframe
Working with Anomalies: Examples
Platforms like Reveal offer tools to process data and identify anomalous information, using natural language processing, unsupervised and supervised machine learning, and other advanced techniques to develop baselines of behavior and action. This allows users to identify deviations from these baselines.
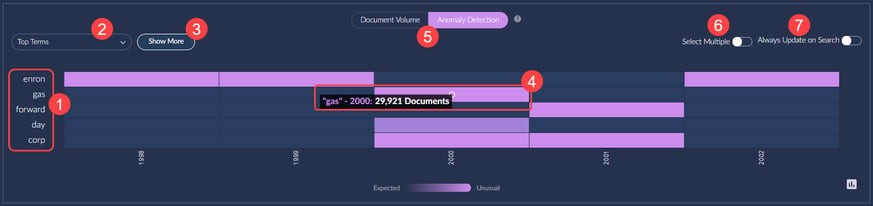
Brainspace Anomaly Detection Heatmap
Brainspace includes an Analytics Dashboard with a timeline chart, top terms, and a graph displaying the volume of original, near-duplicate, and exact-duplicate documents. Another key element is the Anomaly Detection Heatmap.
Anomaly detection heatmap showing the frequency of terms from a dataset over time, with brighter colors indicating higher-than-average usage.
The Anomaly Detection Heatmap displays the frequency of terms from your dataset over time. It uses a standard score to determine when a term’s frequency is higher than average. Brighter colors indicate higher-than-average usage. Key elements of the heatmap include:
- Displaying the top five terms from a search by default.
- Options to select “Top Terms” to create and manage custom term lists.
- Ability to display up to ten terms in the Heatmap.
- Viewing a term’s frequency for a node (e.g., an email address, domain).
- Switching between the “Anomaly Detection” view and the “Document Volume” view.
- Selecting “Select Multiple” to add multiple terms to a search.
- Enabling “Always Update on Search” to automatically update the Heatmap after a search.
Reveal AI Baseball Cards
Reveal’s baseball card displays profiles of entities. Selecting an entity, such as “Vince J Kaminski,” displays their baseball card with an activity page.
Entity profile displayed as a baseball card, providing a quick overview of an individual’s activities and communications.
This page shows various types of anomalous information:
- Topics of Interest: Top seven hotly debated topics (high negative sentiment) and topics discussed at unusual hours.
- Related People: Top five close confidants, top four tenuous communications (high pressure), and top four external communications.
- Other information: email addresses, pseudonyms, business cards, concepts, communicators, and similar communicators.
An activity page showing various types of anomalous information, including topics of interest, related people, and communication patterns.
Reveal AI Cards
Reveal AI Cards highlight anomalous patterns found in a user’s data. These cards are packed with outlier information, allowing users to focus on key anomalies.
Reveal AI Cards showcasing anomalous patterns in user data, with uniqueness scores indicating the level of deviation from the norm.
Each card is given a uniqueness score, with cards sorted from most unique to least. Blue cards represent very high uniqueness, green cards indicate moderate uniqueness, and yellow cards show common uniqueness. These cards can highlight communications outside regular business hours, unusually large numbers of communications, and expressions of sentiment.
Harnessing the Power of Anomalies
Identifying anomalous information early in a case allows you to build a picture of what seems to have happened, who was involved, what they talked about, when, and how. With the right data, you can even begin to understand the motivations behind these events.
By continuously returning to anomalous data, you can refine the case narrative and better position yourself for a satisfactory conclusion. Anomalies provide crucial insights that can make all the difference in understanding complex situations. They can reveal hidden patterns, uncover suspicious activities, and ultimately, help you arrive at the truth.