Blender is a free and open-source 3D creation suite. It supports the entirety of the 3D pipeline—modeling, rigging, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing and motion tracking, even video editing and game creation. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we aim to provide clear and concise answers to your questions, and understanding Blender is a great place to start your 3D journey. Delve into the world of 3D design, animation software, and digital art with our comprehensive guide.
1. Understanding the Basics: What Is Blender?
Blender is more than just a software; it’s a gateway to endless creative possibilities. It’s a professional-grade, free and open-source 3D creation suite used by artists, designers, and hobbyists around the globe. Whether you’re interested in creating stunning visual effects, designing intricate 3D models, or animating captivating stories, Blender provides the tools and flexibility you need.
1.1 The Core Definition of Blender
At its core, Blender is a 3D computer graphics software toolset used for creating animated films, visual effects, art, 3D printed models, motion graphics, interactive 3D applications, virtual reality, and computer games. Blender’s features include 3D modeling, UV unwrapping, texturing, raster graphics editing, rigging and skinning, fluid and smoke simulation, particle simulation, soft body simulation, sculpting, animating, match moving, rendering, motion graphics, video editing, and compositing.
1.2 The Open Source Advantage
Blender distinguishes itself through its open-source nature. This means the software is free to use, distribute, and modify. The source code is publicly available, allowing users to customize the software to fit their specific needs. This collaborative environment fosters innovation and ensures Blender remains at the forefront of 3D technology. The open-source model also means that a global community of developers and artists contribute to Blender’s development, ensuring continuous improvement and support.
1.3 Who Uses Blender?
Blender’s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of users. From independent artists and small studios to large production houses, Blender is used across various industries:
- Film and Television: Creating visual effects and animated content.
- Game Development: Designing 3D models and environments for video games.
- Architecture: Visualizing architectural designs and creating 3D renderings.
- Product Design: Prototyping and showcasing product designs.
- Education: Teaching 3D modeling, animation, and visual effects.
- Hobbyists: Personal projects, 3D printing, and digital art.
No matter your background or skill level, Blender offers a powerful and accessible platform for bringing your creative visions to life.
2. Key Features of Blender: A Deep Dive
Blender’s extensive feature set can seem daunting at first, but understanding its core capabilities is crucial for harnessing its full potential. Let’s explore some of Blender’s key features:
2.1 Modeling: Shaping Your Imagination
Modeling is the foundation of any 3D project, and Blender offers a robust set of tools for creating and manipulating 3D shapes.
- Mesh Modeling: Constructing 3D models using vertices, edges, and faces. Blender supports various mesh editing tools, including extrusion, beveling, and loop cutting, allowing for precise control over your model’s geometry.
- Curve Modeling: Creating smooth, flowing shapes using Bézier curves. This is ideal for creating organic forms, logos, and intricate designs.
- Sculpting: Similar to digital clay, sculpting allows you to shape and refine your models with brushes, adding details and textures. Blender’s sculpting tools are powerful enough to create highly detailed characters and environments.
- Modifiers: Non-destructive operations that can be applied to your models to add complexity and detail. Modifiers can be used for tasks such as subdivision, mirroring, and arraying objects.
2.2 Rigging and Animation: Bringing Your Creations to Life
Rigging and animation are the processes of creating a digital skeleton for your 3D models and then defining how they move.
- Armatures: Digital skeletons that control the movement of your 3D models. Blender’s armature system is highly flexible, allowing for complex character rigs and mechanical animations.
- Constraints: Defining relationships between different objects and bones in your scene. Constraints can be used to create realistic movements and interactions.
- Keyframe Animation: Setting poses at specific points in time and letting Blender interpolate the movement between them. This is the most common method of animation in Blender.
- Drivers: Linking object properties to other objects or bones, allowing for automated animations and complex control systems.
- Shape Keys: Morphing between different shapes of a model. This is often used for facial expressions and subtle deformations.
2.3 Rendering: Turning Your Scene into a Picture
Rendering is the process of generating a 2D image from your 3D scene. Blender offers two powerful rendering engines:
- Cycles: A physically based path tracer that simulates the way light interacts with objects in the real world. Cycles is known for its realistic results, but it can be slower than other rendering engines.
- Eevee: A real-time rendering engine that provides fast and interactive previews of your scene. Eevee is ideal for game development, architectural visualization, and quick renders.
Both Cycles and Eevee support a wide range of materials, textures, and lighting options, allowing you to create visually stunning images.
2.4 Visual Effects (VFX): Adding the Magic
Blender is a capable tool for creating visual effects, offering features such as:
- Motion Tracking: Analyzing footage to extract camera and object movements, allowing you to integrate 3D elements into real-world scenes.
- Compositing: Combining multiple images and videos to create a final shot. Blender’s compositor allows you to add effects, color correct, and refine your images.
- Particle Systems: Simulating large numbers of small objects, such as smoke, fire, and water. Blender’s particle systems are highly versatile and can be used to create a wide range of effects.
- Fluid Simulation: Simulating the behavior of liquids and gases. Blender’s fluid simulator can be used to create realistic water, lava, and smoke effects.
2.5 Video Editing: The Final Polish
Blender includes a fully-featured video editor that allows you to assemble and edit your footage, add effects, and create a final video.
- Non-Linear Editing: Arranging and editing video clips on a timeline.
- Color Correction: Adjusting the colors and tones of your video.
- Video Effects: Adding visual effects to your video, such as transitions, fades, and color grading.
- Audio Editing: Mixing and editing audio tracks.
2.6 Grease Pencil: 2D Animation in 3D
Grease Pencil is a unique feature that allows you to draw and animate in 2D directly within the 3D viewport. This opens up new possibilities for creating traditional animation, storyboarding, and adding hand-drawn elements to your 3D scenes.
3. Why Choose Blender? Advantages and Benefits
With so many 3D software options available, why choose Blender? Here are some compelling reasons:
3.1 Cost: Free and Open Source
The most obvious advantage of Blender is that it’s free. You can download and use Blender without paying any licensing fees. This makes it an ideal choice for students, hobbyists, and small studios with limited budgets. The open-source nature also means you have the freedom to modify and customize the software to fit your specific needs.
3.2 Cross-Platform Compatibility
Blender is compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems, allowing you to work on your projects regardless of your preferred platform.
3.3 A Thriving Community
Blender has a large and active community of users who are passionate about the software. This community provides a wealth of resources, including tutorials, forums, and add-ons. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, you can find help and support from the Blender community.
3.4 Constant Updates and Improvements
Blender is constantly being updated with new features and improvements. The Blender Foundation, along with the community, actively develops the software, ensuring it remains at the forefront of 3D technology. New versions of Blender are released regularly, providing users with access to the latest tools and features.
3.5 Versatility and Flexibility
Blender is a versatile tool that can be used for a wide range of projects. Whether you’re creating animated films, visual effects, game assets, or architectural visualizations, Blender has the tools you need. Its flexible nature allows you to customize the software to fit your specific workflow.
4. Getting Started with Blender: A Beginner’s Guide
Ready to dive into the world of Blender? Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
4.1 Downloading and Installing Blender
- Go to the Blender website (https://www.blender.org/download).
- Download the appropriate version of Blender for your operating system.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
4.2 Navigating the Interface
Blender’s interface can seem overwhelming at first, but understanding the basic layout is essential for getting started.
- 3D Viewport: The main area where you view and interact with your 3D scene.
- Outliner: A hierarchical list of all the objects in your scene.
- Properties Editor: A panel where you can adjust the properties of selected objects.
- Timeline: A panel for controlling animation playback.
- Toolbar: A set of tools for modeling, sculpting, and other tasks.
4.3 Basic Operations
- Selecting Objects: Right-click on an object to select it.
- Moving Objects: Press
Gto grab an object and move it with your mouse. - Rotating Objects: Press
Rto rotate an object with your mouse. - Scaling Objects: Press
Sto scale an object with your mouse. - Adding Objects: Press
Shift + Ato add a new object to your scene.
4.4 Recommended Learning Resources
- Blender’s Official Documentation: A comprehensive guide to all of Blender’s features.
- Blender Guru: A popular YouTube channel with tutorials for beginners and advanced users.
- CG Cookie: A subscription-based website with in-depth Blender courses.
- WHAT.EDU.VN: Ask any question and receive free answers from our community of experts.
5. Blender in Various Industries: Real-World Applications
Blender’s versatility has led to its adoption in various industries. Let’s explore some real-world examples:
5.1 Film and Animation
Blender has been used to create numerous independent films, short films, and animated series. Its capabilities in modeling, animation, rendering, and compositing make it a powerful tool for filmmakers.
- Next Gen: An animated feature film created entirely in Blender.
- Spring: An open-source animated short film created by the Blender Foundation.
5.2 Game Development
Blender is used to create 3D models, textures, and animations for video games. Its integration with game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine makes it a popular choice for indie game developers.
5.3 Architecture and Design
Architects and designers use Blender to create visualizations of their projects. Blender’s modeling and rendering capabilities allow them to create realistic and compelling presentations.
5.4 Product Visualization
Blender is used to create photorealistic renderings of products for marketing and advertising purposes. Its ability to simulate materials and lighting accurately makes it an ideal tool for showcasing products.
6. Frequently Asked Questions About Blender (FAQ)
To further clarify your understanding of Blender, here are some frequently asked questions:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is Blender really free? | Yes, Blender is completely free to download, use, and distribute. It is licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL). |
| What are the system requirements for Blender? | Blender’s system requirements vary depending on the complexity of your projects. However, a good starting point is a 64-bit dual-core CPU, 8 GB of RAM, and a graphics card with 2 GB of VRAM. |
| Is Blender hard to learn? | Blender has a steep learning curve, but with dedication and the right resources, it is possible to master. Many tutorials and online courses are available to help you learn Blender. |
| Can Blender be used for commercial projects? | Yes, Blender can be used for commercial projects. The GPL license allows you to use Blender for any purpose, including creating and selling your work. |
| What file formats does Blender support? | Blender supports a wide range of file formats, including OBJ, FBX, STL, and more. This allows you to import and export models from other 3D software. |
| Does Blender have plugins? | Yes, Blender has a vast library of plugins (also known as add-ons) that extend its functionality. These add-ons can be used for tasks such as modeling, animation, rendering, and more. |
| What is the difference between Cycles and Eevee? | Cycles is a physically based path tracer that produces realistic results, while Eevee is a real-time rendering engine that provides fast and interactive previews. Cycles is better for high-quality renders, while Eevee is better for game development and quick previews. |
| Is Blender used in the industry? | Yes, Blender is used in various industries, including film, animation, game development, architecture, and product design. Many companies and studios use Blender as part of their workflow. |
| Can I customize Blender’s interface? | Yes, Blender’s interface is highly customizable. You can rearrange panels, create custom shortcuts, and install themes to personalize your workspace. |
| Where can I find help with Blender? | You can find help with Blender from the Blender community, the Blender Foundation, and online resources such as tutorials and forums. At WHAT.EDU.VN, you can ask any question and receive free answers from our community of experts. |
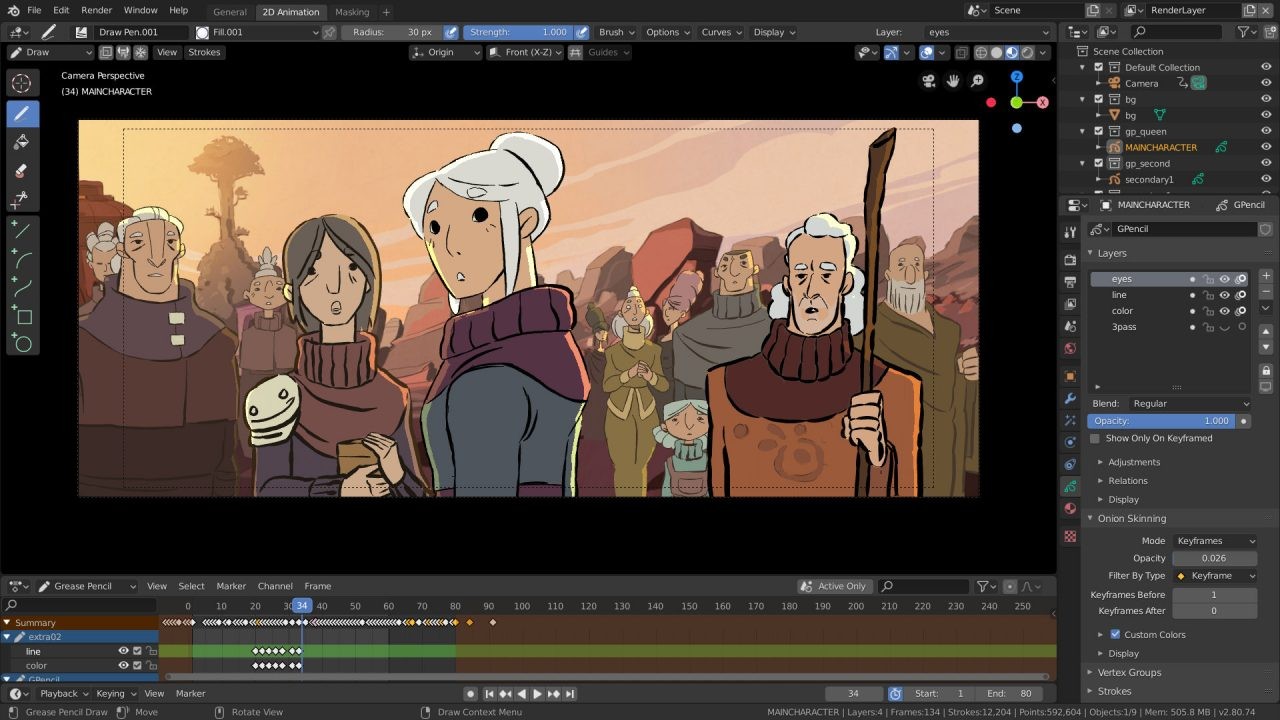

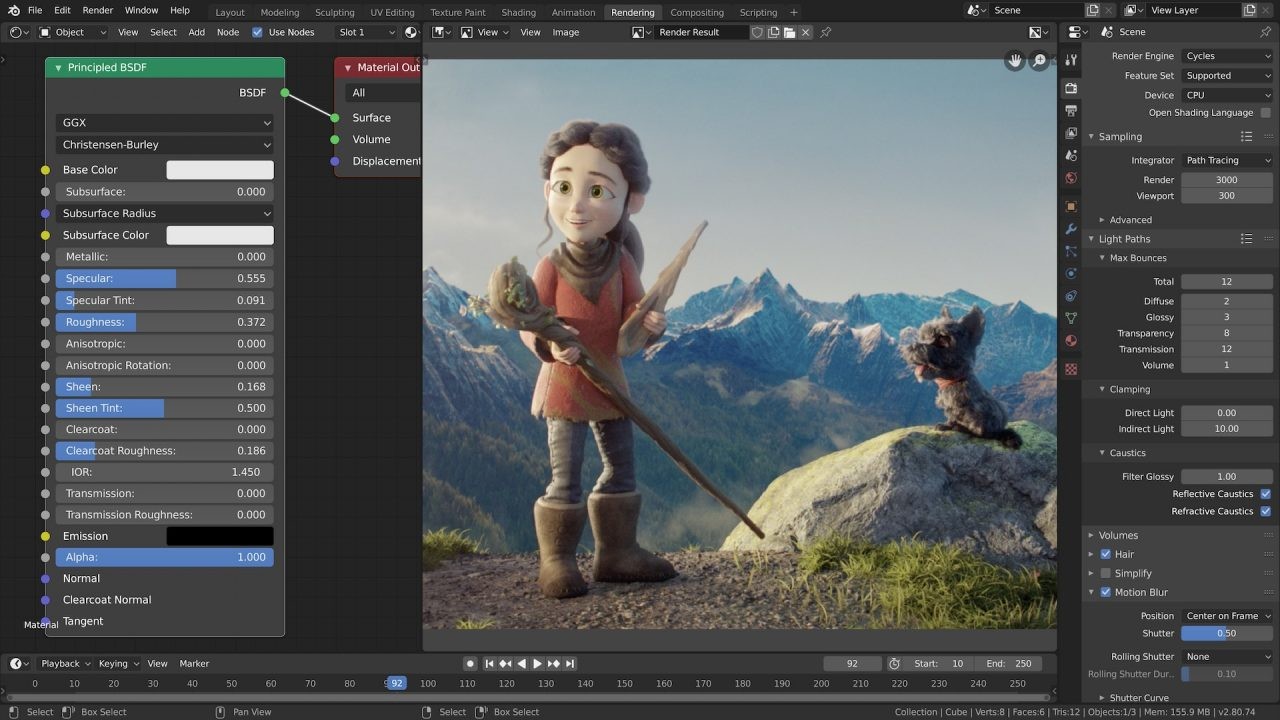
7. Advanced Techniques and Tips for Blender Users
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore some advanced techniques to take your Blender skills to the next level:
7.1 Mastering Modifiers
Modifiers are non-destructive operations that can be applied to your models to add complexity and detail. Experiment with different modifiers and learn how to combine them to create intricate effects.
7.2 Creating Custom Materials
Understanding how to create custom materials is essential for achieving realistic renders. Learn how to use Blender’s shader editor to create complex materials with textures, nodes, and custom properties.
7.3 Rigging Complex Characters
Rigging is a crucial skill for animators. Learn how to create complex character rigs with custom bone shapes, constraints, and drivers.
7.4 Using Python Scripting
Blender has a powerful Python API that allows you to automate tasks, create custom tools, and extend the software’s functionality. Learning Python scripting can significantly improve your workflow.
7.5 Optimizing Your Workflow
Optimize your workflow by using shortcuts, customizing your interface, and organizing your scene. A streamlined workflow can save you time and improve your productivity.
8. The Future of Blender: What to Expect
Blender is continuously evolving, with new features and improvements being added regularly. Here are some trends and developments to watch out for:
8.1 Real-Time Rendering Advancements
Real-time rendering is becoming increasingly important for game development, architectural visualization, and virtual reality. Expect to see further advancements in Blender’s Eevee engine, making it even more powerful and versatile.
8.2 Improved Sculpting Tools
Sculpting is a popular method for creating detailed 3D models. Expect to see improvements in Blender’s sculpting tools, making them more intuitive and efficient.
8.3 Enhanced Animation Capabilities
Animation is a key area of focus for Blender development. Expect to see new features and improvements in Blender’s animation tools, making it easier to create complex and realistic animations.
8.4 Artificial Intelligence Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming various industries, and 3D creation is no exception. Expect to see AI-powered tools integrated into Blender, such as automated modeling, rigging, and animation.
8.5 Cloud-Based Workflows
Cloud-based workflows are becoming increasingly popular for collaboration and remote work. Expect to see Blender integrated with cloud platforms, allowing users to work on projects together from anywhere in the world.
9. Blender’s Impact on the 3D Industry
Blender’s rise in popularity has had a significant impact on the 3D industry. Its accessibility, versatility, and open-source nature have democratized 3D creation, making it accessible to a wider audience.
9.1 Empowering Independent Creators
Blender has empowered independent artists, filmmakers, and game developers to create high-quality content without the need for expensive software.
9.2 Driving Innovation
Blender’s open-source nature has fostered innovation, with developers and artists constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
9.3 Challenging the Status Quo
Blender’s success has challenged the dominance of proprietary 3D software, forcing companies to innovate and offer more competitive pricing.
9.4 Fostering Collaboration
Blender’s community-driven development model has fostered collaboration among artists and developers, leading to a more vibrant and inclusive 3D industry.
10. Ask Your Questions on WHAT.EDU.VN
Still have questions about Blender? Don’t hesitate to ask them on WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with free and accurate answers. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, we’re here to help you on your 3D journey.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding quick and reliable answers to your questions. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive free answers from knowledgeable individuals. We believe that everyone should have access to information and support, regardless of their background or skill level.
Here’s how WHAT.EDU.VN can help you with Blender:
- Ask any question: No matter how simple or complex your question is, our community is ready to provide you with an answer.
- Get free answers: Our service is completely free. You don’t have to worry about subscription fees or hidden charges.
- Connect with experts: Our community includes experienced Blender users who are passionate about sharing their knowledge.
- Get fast responses: We strive to provide you with answers as quickly as possible.
- Access a wealth of information: Our platform contains a vast library of questions and answers related to Blender and other topics.
Don’t struggle with your Blender questions alone. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get the answers you need!
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Let WHAT.EDU.VN be your go-to resource for all your Blender questions and beyond. We’re here to empower you with knowledge and help you succeed in your creative endeavors.
Take the first step towards mastering Blender by asking your questions on what.edu.vn today!