Calcium carbonate is a vital compound with diverse applications. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of calcium carbonate, exploring its characteristics, uses, and significance in various industries. Discover the power of this ubiquitous substance and uncover its many benefits, including its role as a dietary supplement and acid neutralizer. Curious? Let’s delve into the world of limestone, chalk, and marble.
1. Defining Calcium Carbonate: A Chemical Overview
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a chemical compound comprised of one calcium atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms. It’s the primary component of numerous natural materials, including limestone, marble, chalk, eggshells, and coral. This compound exists as either a white powder or colorless crystal, possessing a molecular weight of approximately 100.1 grams per mole. When heated, calcium carbonate decomposes into carbon dioxide and calcium oxide (quicklime). It is an essential building block in both natural and industrial processes.
2. Natural Forms of Calcium Carbonate: Polymorphism in Nature
Calcium carbonate naturally occurs in three primary mineral forms: calcite, aragonite, and vaterite.
- Calcite: The most prevalent form, recognized for its well-developed and diverse crystal structures. It constitutes a significant portion of limestones and is a key ingredient in marls, travertines, calcite veins, cave formations, many marbles, carbonatites, and some ore-bearing veins. Calcite is the stable form of calcium carbonate under most temperature and pressure conditions.
Alt text: Close-up of a vibrant orange calcite mineral specimen showcasing its natural crystalline structure.
-
Aragonite: This orthorhombic form of calcium carbonate is frequently deposited in nature. However, it is metastable at room temperature and pressure, readily converting to calcite.
-
Vaterite: A rare hexagonal form of calcium carbonate that transforms into calcite, aragonite, or both.
3. Limestone: The Foundation of Calcium Carbonate Applications
Limestone, primarily composed of calcium carbonate, has been used since ancient times. It is burned to produce quicklime (CaO), which is then slaked to create hydrated lime [Ca(OH)2]. This hydrated lime is mixed with sand to create mortar. Limestone is a vital component in the manufacture of portland cement. Furthermore, it functions as a flux in metallurgical processes like smelting iron ores. Crushed limestone has extensive applications in riprap, aggregate for concrete and asphalt mixtures, agricultural lime, and as an inert component in medicines.
Alt text: A vast limestone quarry showcasing the scale of limestone extraction for various industrial applications.
4. Marble: Beauty and Utility in Calcium Carbonate
Marble, another form of calcium carbonate, is prized for statuary, carvings, and as a popular facing stone when polished into slabs. In the marketplace, the term marble is applied more broadly to any coarse-grained carbonate rock that can be polished, regardless of its metamorphic origin. Crystalline diagenetic limestones are among the most widely used commercial marbles. Travertine and onyx marble (banded calcite) are also popular for interior facing stones.
Alt text: The pristine white marble portal of the Taj Mahal, featuring intricate Arabic inscriptions and precious stone inlays.
5. Industrial Uses of Calcium Carbonate: Versatility in Manufacturing
Calcium carbonate, whether obtained from natural sources or produced synthetically, serves as a filler in a diverse range of products. These include paper, ceramics, glass, plastics, and paint. Synthetic calcium carbonate, often called “precipitated” calcium carbonate, is used when high purity is essential. This is common in medicine (antacids and calcium supplements), food (baking powder), and laboratory applications.
6. Calcium Carbonate in Medicine: Health and Wellness Applications
In the medical field, calcium carbonate is a crucial ingredient in antacids. It effectively neutralizes stomach acid, providing relief from heartburn and indigestion. Additionally, it serves as a dietary supplement, delivering a concentrated dose of calcium necessary for bone health and various physiological functions.
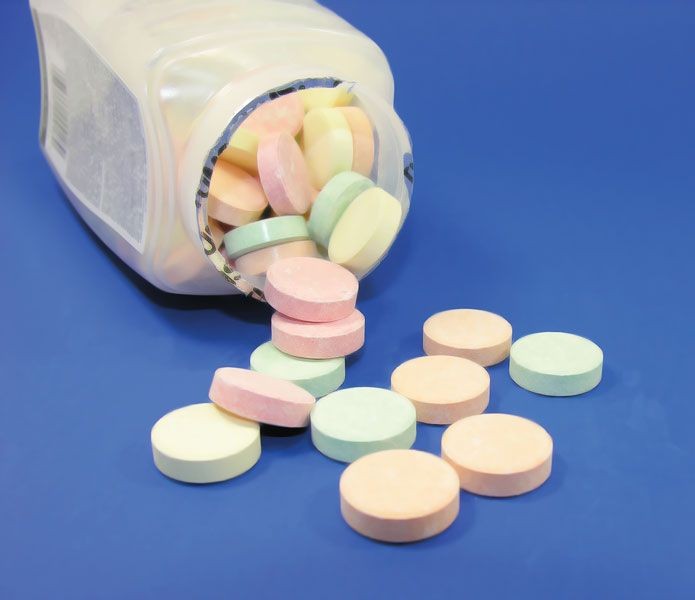 Tums Antacid
Tums Antacid
Alt text: Close-up of Tums antacid tablets, highlighting calcium carbonate as the active ingredient for neutralizing stomach acid.
7. Food Industry Applications: Enhancing Food Products
Calcium carbonate plays a significant role in the food industry. It is a common component in baking powder, aiding in the leavening process. It’s also used as a food additive, providing essential calcium fortification to various products.
8. Environmental Impact: Calcium Carbonate and Sustainability
The extraction and processing of calcium carbonate can have environmental impacts. Sustainable practices in quarrying and manufacturing are essential to minimize these effects. Calcium carbonate also plays a role in carbon sequestration, capturing and storing carbon dioxide to mitigate climate change.
9. The Chemistry of Calcium Carbonate: Reactions and Properties
Calcium carbonate undergoes several important chemical reactions. Its decomposition upon heating releases carbon dioxide, a critical process in various industrial applications. The reaction with acids results in the release of carbon dioxide and the formation of calcium salts.
10. Calcium Carbonate in Construction: A Cornerstone Material
In construction, calcium carbonate in the form of limestone and marble is fundamental. Limestone is used in cement production, while marble serves as a decorative and structural material. The durability and aesthetic appeal of these materials make them indispensable in building and infrastructure projects.
11. Calcium Carbonate in Agriculture: Improving Soil Health
Agricultural lime, composed primarily of calcium carbonate, is used to neutralize acidic soils. This improves soil health, enhancing nutrient availability for plants. The application of calcium carbonate in agriculture leads to increased crop yields and overall soil fertility.
12. Global Production and Distribution: Where Does Calcium Carbonate Come From?
Calcium carbonate is produced globally, with major sources in regions rich in limestone and marble deposits. The distribution network ensures that this essential compound is available worldwide for various industrial, medical, and agricultural applications.
13. Synthetic Calcium Carbonate: Production Methods and Advantages
Synthetic calcium carbonate, or precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), is produced through chemical processes that allow for greater control over particle size and purity. This makes it ideal for applications requiring high-quality material.
14. Calcium Carbonate in Paper Manufacturing: Enhancing Paper Quality
In the paper industry, calcium carbonate is used as a filler to improve brightness, opacity, and printability. It reduces the amount of wood pulp needed, contributing to resource conservation.
15. Calcium Carbonate in Plastics: Improving Material Properties
Calcium carbonate is incorporated into plastics to enhance their properties, such as impact resistance, stiffness, and dimensional stability. It also reduces the cost of plastic production.
16. Calcium Carbonate in Paints and Coatings: Enhancing Performance
In paints and coatings, calcium carbonate acts as an extender and filler, improving opacity, texture, and durability. It also contributes to the overall performance and aesthetic appeal of the final product.
17. The Role of Calcium Carbonate in Water Treatment: Ensuring Water Quality
Calcium carbonate is used in water treatment to adjust pH levels and remove impurities. It helps in the coagulation and sedimentation processes, ensuring the production of clean and safe drinking water.
18. Calcium Carbonate in Adhesives and Sealants: Enhancing Bonding
Calcium carbonate is added to adhesives and sealants to improve their strength, durability, and bonding properties. It enhances the overall performance and longevity of these products.
19. Calcium Carbonate in Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: Gentle and Effective
In cosmetics and personal care products, calcium carbonate serves as a gentle abrasive and opacifier. It is used in toothpaste, powders, and creams to enhance their texture and effectiveness.
20. The Future of Calcium Carbonate: Innovations and Research
Ongoing research is exploring new applications of calcium carbonate, including its use in advanced materials, environmental remediation, and energy storage. These innovations promise to expand the role of calcium carbonate in addressing global challenges.
21. Calcium Carbonate and Coral Reefs: A Vital Connection
Coral reefs are primarily composed of calcium carbonate secreted by coral polyps. These structures provide habitat for diverse marine life and protect coastlines from erosion. Understanding the role of calcium carbonate in coral reef formation is crucial for conservation efforts.
Alt text: A vibrant and thriving coral reef ecosystem off the coast of Okinawa, Japan, showcasing the biodiversity supported by calcium carbonate structures.
22. Calcium Carbonate and Shell Formation: Nature’s Armor
Many marine organisms, such as shellfish, use calcium carbonate to build their shells. These shells provide protection from predators and environmental stressors. The study of shell formation offers insights into biomineralization processes.
23. The Significance of Calcium Carbonate in Cave Formations: Natural Wonders
Cave formations, such as stalactites and stalagmites, are created by the precipitation of calcium carbonate from water dripping through limestone bedrock. These formations are stunning examples of natural mineral deposition.
24. Calcium Carbonate in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Versatile Excipient
In the pharmaceutical industry, calcium carbonate is used as an excipient, a substance that aids in the formulation and delivery of drugs. It provides bulk, improves flowability, and enhances the stability of pharmaceutical products.
25. Calcium Carbonate in the Ceramic Industry: Enhancing Ceramic Properties
Calcium carbonate is added to ceramic compositions to improve their firing properties, strength, and whiteness. It plays a vital role in the production of tiles, pottery, and other ceramic products.
26. Calcium Carbonate in Drilling Muds: Facilitating Oil and Gas Extraction
In the oil and gas industry, calcium carbonate is used as a weighting agent in drilling muds. These muds help to control pressure, stabilize the wellbore, and carry cuttings to the surface.
27. Calcium Carbonate and Paper Recycling: Sustainable Practices
Calcium carbonate-containing paper can be recycled, reducing the need for virgin wood pulp. Recycling processes can recover and reuse calcium carbonate, contributing to sustainable paper production.
28. The Role of Calcium Carbonate in Carbon Capture and Storage: Mitigating Climate Change
Calcium carbonate can be used in carbon capture and storage technologies. It can react with carbon dioxide to form stable carbonates, preventing the release of this greenhouse gas into the atmosphere.
29. Calcium Carbonate in the Glass Industry: Enhancing Glass Properties
In the glass industry, calcium carbonate is a key ingredient that enhances the chemical durability and processability of glass. It also contributes to the overall strength and clarity of glass products.
30. Addressing Common Misconceptions about Calcium Carbonate: Clearing Up Confusion
There are several common misconceptions about calcium carbonate. Some believe it is only used in antacids, while others are unaware of its diverse industrial applications. By providing accurate information, we can dispel these myths and promote a better understanding of this valuable compound.
31. The Environmental Impact of Calcium Carbonate Mining: Balancing Needs and Conservation
Calcium carbonate mining can have environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and air emissions. Sustainable mining practices, such as land reclamation and dust control, are essential to mitigate these effects.
32. Differentiating Between Calcium Carbonate and Other Calcium Compounds: Understanding the Nuances
While calcium carbonate is a common calcium compound, it is distinct from other forms like calcium chloride and calcium sulfate. Each compound has unique properties and applications, and understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for a given task.
33. The Economic Significance of Calcium Carbonate: A Global Commodity
Calcium carbonate is a significant global commodity, with a wide range of industries relying on its availability and affordability. Its economic impact extends from mining and manufacturing to healthcare and agriculture.
34. Calcium Carbonate and Pet Cemeteries: A Unique Use
While not a widespread application, calcium carbonate is sometimes used in pet cemeteries as a component of burial materials. This unique application highlights the versatility of the compound.
35. The Purity Standards of Calcium Carbonate: Ensuring Quality and Safety
The purity of calcium carbonate is critical in many applications, particularly in medicine and food. Strict quality control measures ensure that calcium carbonate meets the required standards for safety and effectiveness.
36. The Impact of Particle Size on Calcium Carbonate Applications: Tailoring Properties
The particle size of calcium carbonate can significantly impact its performance in various applications. Fine particles are preferred for fillers in paper and plastics, while coarser particles are used in construction materials.
37. The Role of Calcium Carbonate in Historic Preservation: Protecting Cultural Heritage
Calcium carbonate is used in the preservation of historic buildings and monuments. It can be applied as a protective coating to prevent weathering and erosion of stone surfaces.
38. Calcium Carbonate in the Production of Table Salt: Ensuring Quality
Calcium carbonate is sometimes added to table salt to improve its flowability and prevent caking. This ensures that the salt remains easy to pour and use.
39. Calcium Carbonate as a Food Preservative: Extending Shelf Life
Calcium carbonate can act as a food preservative by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms and maintaining the pH level. This helps to extend the shelf life of various food products.
40. Calcium Carbonate and Bone Health: Essential for Life
Calcium carbonate is a crucial source of calcium, essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Adequate calcium intake throughout life helps to prevent osteoporosis and other bone-related disorders.
Navigating the world of calcium carbonate can be complex, but you don’t have to do it alone. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding reliable information and getting quick answers can be challenging. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive free, accurate, and easy-to-understand responses.
Whether you’re a student tackling a tough assignment, a professional seeking expert advice, or simply curious about the world around you, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. Don’t spend hours searching for answers – let our community of knowledgeable experts provide you with the insights you need, fast.
Ready to experience the convenience and expertise of WHAT.EDU.VN? Ask your question today and discover a world of knowledge at your fingertips!
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn