What Is Confidence Level? This question delves into a crucial statistical concept. It helps gauge the reliability of estimates. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we unravel this topic, providing clarity on its applications and benefits. Explore confidence intervals, statistical significance, and hypothesis testing.
1. Defining Confidence Level: An In-Depth Look
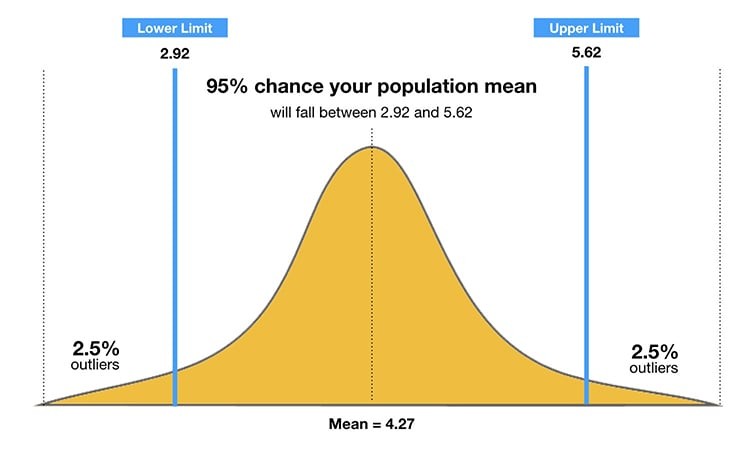
Confidence level is a cornerstone of statistical inference. It quantifies the degree of certainty. This applies to a sample accurately representing a population parameter. It’s often expressed as a percentage. Common values include 90%, 95%, and 99%.
Higher confidence levels mean a greater probability. The true population parameter lies within the calculated confidence interval. It’s a critical tool. Analysts assess the reliability of their findings.
1.1. Key Components of Confidence Level
Understanding confidence level requires grasping its core components.
-
Confidence Interval: A range of values. It estimates an unknown population parameter. It is calculated from sample data.
-
Significance Level (Alpha): The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. This when it’s actually true. It is calculated as 1 – confidence level.
-
Margin of Error: The amount of error tolerated. It depends on the desired confidence level. Sample size also plays a role.
-
Sample Size: The number of observations in a sample. A larger sample size generally leads to more precise estimates. Thus, it increases confidence.
1.2. The Significance of Confidence Level in Research
Confidence level plays a vital role in research. It helps researchers draw meaningful conclusions. This from sample data. It ensures the findings are reliable. This is crucial for informing decisions. This includes policy-making. It also includes business strategy.
Without a clear understanding of confidence level, researchers risk misinterpreting data. They may make incorrect generalizations. This can lead to flawed outcomes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dotdash_Final_Confidence_Intervals_June_2020-01-4e18069e7a0249b5a6589d17642d251b.jpg)
2. Understanding Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals provide a range of values. These are likely to contain the true population parameter. They’re calculated based on sample data. This helps to quantify the uncertainty. It is associated with estimates.
2.1. The Relationship Between Confidence Level and Confidence Interval
The confidence level directly influences the width of the confidence interval. Higher confidence levels result in wider intervals. This means greater certainty. The true parameter lies within the range. However, it comes at the cost of precision.
Conversely, lower confidence levels produce narrower intervals. This means more precision. However, there’s a higher chance. The interval may not contain the true parameter.
2.2. Factors Affecting the Width of Confidence Intervals
Several factors can affect the width of confidence intervals:
-
Sample Size: Larger sample sizes typically lead to narrower intervals.
-
Variability: Higher variability in the population results in wider intervals.
-
Confidence Level: Higher confidence levels result in wider intervals.
2.3. Interpreting Confidence Intervals Correctly
It’s crucial to interpret confidence intervals accurately. A common misconception is. That the interval represents the range. Most of the data falls within. Instead, it indicates a level of confidence. The true population parameter lies within.
For example, a 95% confidence interval suggests. 95% of intervals. Calculated from repeated samples. Would contain the true population parameter.
3. Practical Applications of Confidence Level
Confidence level finds applications. A wide range of fields. From healthcare to finance. It’s a valuable tool. Analysts assess the reliability of their findings.
3.1. Confidence Level in Healthcare
In healthcare, confidence levels are used. To evaluate the effectiveness of treatments. This also includes diagnostic tests. Clinical trials often report results with confidence intervals. These can indicate the range of possible outcomes.
For example, a study assessing a new drug. It may report a 95% confidence interval. The reduction in symptoms. This helps healthcare professionals. They can make informed decisions.
3.2. Confidence Level in Finance
In finance, confidence levels are used. To assess investment risks. This also includes market trends. Financial analysts use confidence intervals. They can estimate the range of potential returns. This can help investors. They can make informed decisions.
A financial model may predict. A 99% confidence interval for a stock’s price. This helps investors understand. The potential upside and downside.
3.3. Confidence Level in Marketing
In marketing, confidence levels are used. To evaluate the effectiveness of campaigns. This also includes consumer surveys. Marketers use confidence intervals. They can estimate the range of consumer opinions. This can help them refine their strategies.
For example, a survey assessing customer satisfaction. It may report a 90% confidence interval. This indicates the proportion of satisfied customers.
4. How to Calculate Confidence Level
Calculating confidence level involves several steps. This includes determining the appropriate statistical formula. This also includes gathering the necessary data.
4.1. Statistical Formulas for Calculating Confidence Level
The formula for calculating a confidence interval depends on several factors. These include the type of data. It also includes the sample size. Commonly used formulas include:
-
For Population Mean (Known Standard Deviation):
Confidence Interval = x̄ ± Z * (σ / √n)
Where:
- x̄ = sample mean
- Z = Z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level
- σ = population standard deviation
- n = sample size
-
For Population Mean (Unknown Standard Deviation):
Confidence Interval = x̄ ± t * (s / √n)
Where:
- x̄ = sample mean
- t = t-score corresponding to the desired confidence level. This also includes degrees of freedom.
- s = sample standard deviation
- n = sample size
-
For Population Proportion:
Confidence Interval = p̂ ± Z * √((p̂(1 – p̂)) / n)
Where:
- p̂ = sample proportion
- Z = Z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level
- n = sample size
4.2. Steps to Calculate Confidence Level
Follow these steps to calculate the confidence interval:
-
Determine the Confidence Level: Choose the desired confidence level. This is commonly 90%, 95%, or 99%.
-
Identify the Sample Statistics: Calculate the sample mean. Determine the sample standard deviation.
-
Determine the Critical Value: Find the appropriate Z-score or t-score. This corresponds to the chosen confidence level. Use a Z-table. You can also use a t-table.
-
Calculate the Margin of Error: Multiply the critical value. It is calculated by the standard error.
-
Calculate the Confidence Interval: Add and subtract the margin of error. It is calculated by the sample mean. This provides the upper and lower bounds.
4.3. Example Calculation
Suppose you want to estimate the average height. Of students in a university. You take a random sample of 50 students. You find the sample mean is 68 inches. The sample standard deviation is 4 inches. You want to calculate a 95% confidence interval.
-
Confidence Level: 95%
-
Sample Statistics:
- Sample Mean (x̄) = 68 inches
- Sample Standard Deviation (s) = 4 inches
- Sample Size (n) = 50
-
Critical Value: For a 95% confidence level. With 49 degrees of freedom (n-1). The t-score is approximately 2.009.
-
Margin of Error: Margin of Error = 2.009 * (4 / √50) ≈ 1.137 inches
-
Confidence Interval:
- Lower Bound = 68 – 1.137 ≈ 66.863 inches
- Upper Bound = 68 + 1.137 ≈ 69.137 inches
Therefore, the 95% confidence interval. For the average height. Of students in the university. It is between 66.863 and 69.137 inches.
5. Factors Influencing Confidence Level Choice
The choice of confidence level depends on the specific context. This includes the consequences of being wrong. Also included is the desired level of certainty.
5.1. Consequences of Being Wrong
If the consequences of being wrong are severe, a higher confidence level is warranted. For example, in medical research, a 99% confidence level might be preferred. This minimizes the risk. False conclusions. This minimizes harm.
5.2. Desired Level of Certainty
The desired level of certainty also plays a role. If high precision is required, a lower confidence level might be acceptable. However, this comes. With an increased risk. The interval may not contain the true parameter.
5.3. Balancing Precision and Certainty
Choosing a confidence level involves balancing precision. The higher the confidence level is, the wider the interval becomes. Conversely, the lower the confidence level is, the narrower the interval becomes.
6. Common Misconceptions About Confidence Level
Several misconceptions surround confidence level. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for proper interpretation.
6.1. Confidence Level as Data Percentage
One common misconception is that the confidence level represents the percentage of data. This falls within the confidence interval. However, the confidence level indicates the proportion of intervals. Calculated from repeated samples. These would contain the true population parameter.
6.2. Certainty of the True Parameter
Another misconception is that a confidence interval guarantees. It contains the true population parameter. A confidence interval provides a range. Within which the true parameter is likely to lie. It does not provide certainty.
6.3. Narrow Intervals as More Accurate
Narrow intervals are not always more accurate. A narrow interval with a low confidence level has a higher chance. Missing the true parameter. The width of the interval. It must be considered. It is done so in conjunction with the confidence level.
7. Confidence Level vs. Significance Level
Confidence level and significance level are related concepts. They are often used together. In hypothesis testing.
7.1. The Relationship Between Confidence Level and Significance Level
The significance level (alpha) is the probability. Rejecting the null hypothesis. This when it’s actually true. The confidence level is the probability. Not rejecting the null hypothesis. This when it’s actually true.
The relationship is:
Significance Level (α) = 1 – Confidence Level
7.2. Using Confidence Level in Hypothesis Testing
In hypothesis testing, the confidence level is used to determine. Critical values. These are used. To assess the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis. If the test statistic falls outside the critical values. The null hypothesis is rejected.
7.3. Example of Hypothesis Testing with Confidence Level
Suppose you want to test the hypothesis. The average height of students in a university. It is 70 inches. You take a sample and calculate a 95% confidence interval. This is for the sample mean. If the confidence interval does not contain 70 inches. You reject the null hypothesis.
8. Advanced Topics in Confidence Level
Several advanced topics build upon the basic understanding of confidence level.
8.1. Bayesian Confidence Intervals
Bayesian confidence intervals. These are known as credible intervals. They incorporate prior beliefs. This is about the population parameter. These beliefs are done into the analysis. This provides a more nuanced estimate.
8.2. Bootstrap Confidence Intervals
Bootstrap confidence intervals. These are based on resampling techniques. These are used to estimate the sampling distribution. The statistic. This can be useful when the data does not meet. Assumptions. These assumptions are done about normality.
8.3. Confidence Bands
Confidence bands provide a range of values. This range is likely. To contain an entire function. This includes a regression line. This is used. To assess the uncertainty. Function estimates.
9. Case Studies: Confidence Level in Action
Examining real-world case studies. This can illustrate the practical applications of confidence level.
9.1. Case Study 1: Pharmaceutical Research
A pharmaceutical company conducts a clinical trial. To test a new drug. The results show a significant reduction. Symptoms. It can be calculated with a 99% confidence interval. This high confidence level. It provides strong evidence. The drug is effective.
9.2. Case Study 2: Political Polling
A political pollster surveys voters. To estimate support. The candidate. They report a 95% confidence interval. The candidate’s approval rating. This helps the campaign. They can understand the range. Possible outcomes.
9.3. Case Study 3: Manufacturing Quality Control
A manufacturing company uses confidence intervals. To monitor the quality of its products. They take samples. They can calculate a 90% confidence interval. This is for the product’s dimensions. This helps them. It ensures compliance. This compliance is according to standards.
10. Addressing Common Concerns and Questions
Addressing common concerns and questions. These can clarify misunderstandings. This provides further insight.
10.1. How Does Sample Size Affect Confidence Level?
Larger sample sizes generally lead to narrower confidence intervals. This provides more precise estimates.
10.2. Can Confidence Level Be 100%?
Achieving a 100% confidence level is often impractical. This requires an infinitely wide interval. It provides no useful information.
10.3. What Are the Limitations of Confidence Intervals?
Confidence intervals are based on assumptions. This includes normality. They may not be accurate if these assumptions are violated.
11. Tools and Resources for Calculating Confidence Level
Several tools and resources are available. These resources can assist. Calculating confidence level.
11.1. Statistical Software Packages
Statistical software packages. These include SPSS, R, and SAS. These can automate the calculation of confidence intervals.
11.2. Online Calculators
Online calculators provide a convenient way. Calculating confidence intervals. Simply enter the sample data.
11.3. Statistical Tables
Statistical tables. These include Z-tables. Also included are t-tables. These are used to find critical values. These can be done for manual calculations.
12. Future Trends in Confidence Level Usage
The use of confidence level is expected. Evolve. It changes. It will be influenced. This will be done by advancements in data science. Also AI.
12.1. Integration with Machine Learning
Confidence intervals are increasingly used. Together with machine learning models. To quantify the uncertainty. Model predictions. This enhances the reliability. These models.
12.2. Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring systems use confidence intervals. To detect anomalies. This includes changes in data patterns. This enables quick responses.
12.3. Enhanced Visualization
Enhanced visualization techniques. These can make confidence intervals more accessible. Easier to interpret. This helps stakeholders. They can understand the uncertainty. Data insights.
13. Getting Started with Confidence Level: A Practical Guide
This practical guide provides steps. You can get started with confidence level.
13.1. Understanding the Basics
Start by understanding the basic concepts. These are confidence level, intervals, and significance.
13.2. Practicing Calculations
Practice calculating confidence intervals. You can use different datasets. This reinforces your understanding.
13.3. Applying in Real-World Scenarios
Apply confidence intervals. To real-world scenarios. These are in your field. This helps you appreciate their practical value.
14. Expert Insights on Confidence Level
Expert insights provide valuable perspectives. This is on the importance of confidence level.
14.1. Expert Quote 1
“Confidence intervals are essential tools. Assessing the reliability. This can be done of statistical estimates. They provide a range of plausible values. The population parameter.” – Dr. Statistician, Professor of Statistics
14.2. Expert Quote 2
“Understanding confidence level is crucial. Making informed decisions. Based on data. It helps us quantify the uncertainty. This associated. This can be done with our estimates.” – Data Analyst, Lead Data Scientist
14.3. Expert Quote 3
“Confidence intervals are vital. Assessing the significance. These statistical findings. They help us distinguish between real effects. Effects caused by chance.” – Research Scientist, Research Director
15. Resources for Further Learning
This section provides resources. You can further your understanding. These resources can be helpful with confidence level.
15.1. Books
- “Statistics” by David Freedman, Robert Pisani, and Roger Purves
- “OpenIntro Statistics” by David Diez, Christopher Barr, and Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel
15.2. Online Courses
- Coursera’s “Statistics with R” Specialization
- edX’s “Introduction to Statistics”
15.3. Websites
- Khan Academy Statistics and Probability
- Stat Trek
16. Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Confidence Level
In conclusion, confidence level is a fundamental concept. This statistical analysis. It helps us quantify the uncertainty. This associated. Our estimates. Understanding confidence level enables us. We can make informed decisions. We can assess the reliability. Our findings.
Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, embracing the power. Confidence level enhances your ability. To interpret data. Draw meaningful conclusions. It also improves decision-making.
FAQ: Your Questions Answered About Confidence Level
Here are some frequently asked questions. This is about confidence level. It answers and provides additional insights.
What Is a Good Confidence Level?
A good confidence level depends on the context. 95% is commonly used. Higher stakes may require 99%. Lower stakes may use 90%.
How Do You Increase Confidence Level?
Increase confidence level by increasing the sample size. This reduces variability.
Can You Have Too Much Confidence?
While higher confidence is generally better, extremely high confidence levels result in wider intervals. This provides less precise estimates.
What Is the Difference Between Confidence Level and Probability?
Confidence level refers to the proportion of intervals that contain the true parameter. Probability refers to the likelihood of an event occurring.
How Does Non-Normality Affect Confidence Intervals?
Non-normality can affect the accuracy of confidence intervals. Techniques. These are bootstrapping. These can be used when data is not normally distributed.
We hope this comprehensive guide. It is about confidence level. It has been informative. Also, that it has been helpful. If you have any questions. Don’t hesitate. Reach out to us.
For any questions or further assistance, contact us at:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Are you struggling to find answers to your questions? Do you need expert advice without the hefty price tag? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a platform. This allows you to ask any question. Receive prompt and accurate responses. Our community of experts is ready to assist you. Join what.edu.vn today. Experience the convenience. Free question-answering services. Let us help you find the answers. You’re looking for.