Convenience sampling is a non-probability sampling technique where researchers select participants based on their accessibility and readiness to participate. Want free answers to your questions? This method, also known as availability sampling, offers a quick and cost-effective way to gather initial data and insights. Discover the advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications of this sampling approach and explore how it can be used effectively. Learn more about research methodologies and data collection techniques at WHAT.EDU.VN.
1. What Is Convenience Sampling?
Convenience sampling is a type of non-probability sampling where researchers gather data from participants who are easily accessible and readily available. This method involves selecting individuals who are conveniently located or easily contacted, without using random selection or other rigorous sampling techniques. Convenience sampling is often used when time and resources are limited, or when the primary goal is to obtain preliminary insights rather than to generalize findings to a larger population. This sampling method is also referred to as availability sampling or grab sampling.
Key Characteristics of Convenience Sampling:
- Accessibility: Participants are chosen based on their easy availability.
- Non-Random: Selection is not based on random chance or probability.
- Cost-Effective: It is typically less expensive than other sampling methods.
- Time-Efficient: Data can be collected quickly due to ease of access.
- Preliminary Insights: Useful for exploratory research and pilot studies.
Convenience sampling can be particularly useful in situations where researchers need to gather data quickly or when exploring a new topic. However, it is important to recognize its limitations, including potential biases and limited generalizability. For example, a researcher might stand outside a store and ask shoppers to participate in a survey. While this can provide quick feedback, the sample may not be representative of the broader population of consumers.
2. How Does Convenience Sampling Work?
Convenience sampling is a straightforward process that involves several key steps. The goal is to efficiently collect data from readily available participants. Here’s a detailed look at how it works:
-
Define Research Objectives:
- Clearly outline the goals of your research.
- Determine what specific information you need to gather.
- For instance, if you’re a coffee shop owner, your objective might be to understand customer preferences for new beverage options.
-
Identify Target Population:
- Determine the group of individuals who can provide relevant data.
- Consider the characteristics of this population that are important to your research.
- Using the coffee shop example, your target population would be your regular customers.
-
Choose a Convenient Location or Method:
- Select a location or method where you can easily access potential participants.
- This could be a physical location (e.g., a shopping mall, a company cafeteria) or an online platform (e.g., a social media group, an online forum).
- For the coffee shop, the most convenient location is likely your coffee shop itself.
-
Recruit Participants:
- Approach individuals who are available and willing to participate.
- Explain the purpose of your research and what their participation will involve.
- Ensure participants understand that their involvement is voluntary.
- In the coffee shop, you might ask customers waiting in line if they’d be willing to answer a few questions about their drink preferences.
-
Collect Data:
- Use surveys, interviews, or observations to gather the required data.
- Ensure that the data collection method aligns with your research objectives.
- Maintain consistency in your approach to ensure reliable data.
- Provide a structured questionnaire to gather standardized feedback on new beverage options.
-
Analyze Data:
- Examine the collected data to identify patterns, trends, and insights.
- Use descriptive statistics to summarize the data and draw conclusions.
- Interpret the findings in the context of your research objectives.
- Analyze the survey responses to determine which new beverage options are most popular among your customers.
Example Scenario:
Let’s consider a marketing student conducting a survey on consumer preferences for sustainable products. The student stands outside a grocery store and asks shoppers exiting the store if they would be willing to answer a short questionnaire about their purchasing habits related to eco-friendly products. The student records the responses and uses the data to draw preliminary conclusions about consumer interest in sustainability.
This method allows the student to collect data quickly and efficiently. However, it is important to acknowledge that the sample is limited to shoppers at that particular store and may not be representative of the broader population of consumers.
3. Advantages of Convenience Sampling
Convenience sampling offers several benefits that make it a popular choice for researchers in certain situations. Here are some key advantages:
-
Ease of Implementation:
- Convenience sampling is one of the easiest sampling methods to implement.
- Researchers can quickly gather data without needing extensive planning or resources.
- This makes it ideal for pilot studies or exploratory research where the goal is to get a quick overview.
-
Cost-Effectiveness:
- It is a low-cost method, as it requires minimal investment in time and resources.
- There are no expenses associated with recruiting a representative sample or traveling to different locations.
- This makes it a practical option for researchers with limited budgets.
-
Speed and Efficiency:
- Data can be collected rapidly, allowing researchers to meet tight deadlines.
- The ease of access to participants means that data collection can be completed in a short period.
- This is particularly useful when timely insights are needed for decision-making.
-
Preliminary Insights:
- It is useful for generating initial hypotheses and gaining a preliminary understanding of a topic.
- The data collected can provide valuable insights that inform further research efforts.
- This can help researchers refine their research questions and methodologies.
-
Accessibility of Participants:
- Participants are readily available, making it easy to reach the desired sample.
- Researchers can choose locations or methods that maximize their access to potential respondents.
- This is particularly beneficial when studying niche populations or specific demographic groups.
-
Flexibility:
- The method allows for flexibility in data collection, as researchers can adapt their approach based on the situation.
- Researchers can modify their questions or sampling strategy as they gather data.
- This adaptability can lead to richer and more nuanced insights.
Illustrative Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Simple to set up and execute without specialized skills or resources. |
| Cost-Effective | Minimal costs involved, making it ideal for projects with limited budgets. |
| Time-Efficient | Quick data collection, useful for projects with tight deadlines. |
| Initial Insights | Provides preliminary data that can inform further research. |
| Accessible Samples | Easy to reach participants, simplifying the data collection process. |
| Adaptable | Flexible approach allows adjustments during data collection. |
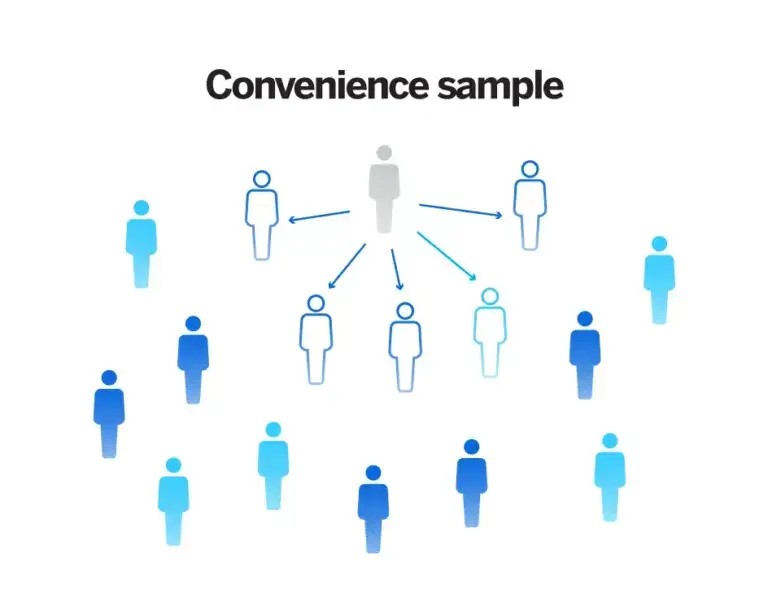

Example Scenario:
A small business owner wants to gather quick feedback on a new product idea. They set up a table at a local farmer’s market and ask passersby to fill out a short survey. This allows them to collect initial data rapidly and at minimal cost, providing valuable insights into potential customer interest.
4. Disadvantages of Convenience Sampling
While convenience sampling offers several advantages, it also has significant drawbacks that researchers need to be aware of. Here are some key disadvantages:
-
Sampling Bias:
- Convenience samples are highly susceptible to sampling bias.
- The sample may not be representative of the broader population, leading to skewed results.
- This bias can arise because participants are selected based on their availability rather than random selection.
-
Selection Bias:
- Researchers may unintentionally select participants who share similar characteristics or opinions.
- This can lead to an overrepresentation of certain subgroups within the sample.
- Selection bias can compromise the validity and generalizability of the findings.
-
Limited Generalizability:
- The findings from convenience samples cannot be easily generalized to the larger population.
- The sample may not accurately reflect the diversity and complexity of the population.
- This limits the ability to draw broad conclusions or make predictions based on the data.
-
Low External Validity:
- External validity refers to the extent to which the results of a study can be applied to other settings or populations.
- Convenience samples often have low external validity due to their non-representative nature.
- This makes it difficult to replicate the findings or apply them to real-world situations.
-
Positivity Bias:
- Participants who are easily accessible may be more likely to provide positive feedback or responses.
- This can result in an overestimation of positive attitudes or behaviors within the population.
- Positivity bias can distort the accuracy of the research findings.
-
Demographic Representation Issues:
- Convenience samples may not adequately represent various demographic subgroups within the population.
- This can lead to an underrepresentation or overrepresentation of certain groups, such as age, gender, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status.
- This skewed representation can limit the applicability of the research findings to diverse populations.
Illustrative Table:
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Sampling Bias | The sample may not accurately represent the broader population. |
| Selection Bias | Researchers may unintentionally choose participants with similar traits. |
| Limited Scope | Findings may not be generalizable to other settings or populations. |
| Low Validity | Results may not hold true in real-world scenarios due to lack of representativeness. |
| Positivity Bias | Participants may be inclined to provide overly positive feedback. |
| Skewed Demographics | The sample may not reflect the demographic diversity of the population. |
Example Scenario:
A researcher conducts a survey on customer satisfaction by interviewing shoppers at a high-end boutique. The resulting data may be skewed towards individuals with higher incomes and a preference for luxury goods, thus failing to represent the broader consumer population.
5. Why Is Convenience Sampling Important for Businesses?
Despite its limitations, convenience sampling can be a valuable tool for businesses in certain contexts. Here’s why it matters:
-
Quick Market Insights:
- Businesses can use convenience sampling to quickly gather feedback on new product ideas, marketing campaigns, or customer service initiatives.
- This allows them to make timely decisions and adjustments based on preliminary data.
- For example, a restaurant might survey customers dining in to get immediate feedback on a new menu item.
-
Cost-Effective Research:
- Convenience sampling is a cost-effective way for businesses to conduct research without investing significant resources.
- This is particularly beneficial for small businesses or startups with limited budgets.
- A small retail store can easily survey customers at the point of sale to gather insights on shopping preferences.
-
Initial Testing:
- It can be used for initial testing of hypotheses or concepts before committing to more extensive research.
- This allows businesses to validate their assumptions and identify potential issues early on.
- A software company might conduct a usability test with employees to identify potential problems with a new software interface.
-
Feedback on Specific Issues:
- Businesses can target specific groups of customers or stakeholders to gather feedback on particular issues.
- This allows them to address concerns or improve specific aspects of their products or services.
- A hotel might survey guests staying on a particular floor to gather feedback on recent renovations.
-
Identifying Problems:
- Convenience sampling can help businesses identify potential problems or areas for improvement.
- By gathering feedback from readily available sources, businesses can uncover issues that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- A car dealership might survey customers waiting for their cars to be serviced to identify areas for improving the customer experience.
-
Enhancing Customer Engagement:
- Engaging with customers through convenience sampling can enhance their sense of value and loyalty.
- Customers appreciate being asked for their opinions and feel more connected to the business.
- A coffee shop might offer a small discount to customers who participate in a short survey, increasing engagement and loyalty.
Real-World Example:
Consider a local bookstore that wants to evaluate the appeal of a new author. They survey customers browsing the new releases section to gauge their interest. The bookstore can quickly determine whether to feature the author more prominently or adjust their marketing strategy based on this immediate feedback.
6. Three Business Use Case Examples of Convenience Sampling
To illustrate the practical applications of convenience sampling in business, here are three specific use case examples:
-
Assessing Public Reaction to a Brand Event (e.g., Launch of a New Gaming Product)
- Scenario: A gaming company launches a new video game and wants to gauge public reaction immediately after the launch.
- Convenience Sampling Method: Researchers stand outside a gaming store or monitor online gaming forums, asking gamers about their initial impressions of the new game.
- Data Collection: The researchers ask questions such as: “Have you purchased the game?”, “What do you like or dislike about the game?”, and “How do you rate the game’s graphics, storyline, and gameplay?”
- Outcome: The company quickly gathers feedback on the game’s strengths and weaknesses, which can inform immediate marketing adjustments and future game development decisions.
-
Gathering Employee Feedback on Company Improvements (e.g., Revamping the Company Dining Room)
- Scenario: A company wants to improve its dining room to enhance employee satisfaction and productivity.
- Convenience Sampling Method: Researchers survey employees who use the dining room during lunchtime. They may also send out an online survey via the company newsletter.
- Data Collection: The survey includes questions about the current dining room’s atmosphere, food quality, seating arrangements, and suggestions for improvement.
- Outcome: The company gains direct insights from employees about their dining preferences, enabling them to make informed decisions about the dining room’s renovation, ultimately improving employee morale.
-
Determining the Viability of Full-Scale Research through a Pilot Study
- Scenario: A business is considering investing in a full-scale market research project but wants to test the waters first.
- Convenience Sampling Method: The business conducts a pilot study using a convenience sample to gather preliminary data and insights.
- Data Collection: Researchers approach readily available participants (e.g., customers, employees, online forum members) with a brief survey or interview to gauge their interest in the research topic.
- Outcome: If the pilot study yields promising results and indicates potential value in the full-scale research, the business is more likely to allocate resources to the larger project. This approach helps businesses make data-driven decisions about whether to proceed with more extensive research efforts.
Snapshot Summary:
| Use Case | Method | Data Collection | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Reaction to Gaming Product Launch | Researchers at gaming stores or online forums | Questions about game purchase, likes, dislikes, and ratings of specific features. | Immediate feedback for marketing adjustments and future game development. |
| Employee Feedback on Dining Room Revamp | Surveying employees who use the dining room | Questions about atmosphere, food quality, seating, and suggestions for improvement. | Informed decisions about renovation to improve employee morale. |
| Viability Assessment of Full-Scale Research (Pilot Study) | Approaching available participants (customers, employees, forum members) | Brief survey or interview to gauge interest in the research topic. | Data-driven decision on whether to invest in full-scale research. |
7. How to Use Convenience Sampling Without Skewing Data Collection
While convenience sampling is prone to bias, there are strategies to minimize skewing and improve the quality of the data collected:
-
Diversify the Sample:
- Collect data from a variety of locations and at different times to capture a more diverse range of participants.
- Avoid relying on a single source, which can lead to overrepresentation of certain groups.
- For example, survey customers at different store locations or during different times of the day.
-
Use Larger Sample Sizes:
- Increase the number of participants to reduce the impact of individual biases on the overall results.
- A larger sample is more likely to reflect the diversity of the population, even if it is not perfectly representative.
- Aim for a sample size that is large enough to provide meaningful insights.
-
Be Transparent About Limitations:
- Acknowledge the limitations of convenience sampling when reporting the results.
- Clearly state that the findings may not be generalizable to the broader population.
- Transparency helps readers interpret the results with caution and avoid drawing unwarranted conclusions.
-
Combine with Other Methods:
- Supplement convenience sampling with other sampling methods to improve the representativeness of the sample.
- For example, use stratified sampling to ensure that key demographic groups are adequately represented.
- Combining methods can help mitigate the biases associated with convenience sampling.
-
Weight the Data:
- Use statistical weighting techniques to adjust the data and account for known biases.
- Weighting can help correct for underrepresentation or overrepresentation of certain groups.
- Consult with a statistician to determine the appropriate weighting strategy.
-
Control for Confounding Variables:
- Identify and control for potential confounding variables that could influence the results.
- Use statistical techniques to adjust for the effects of these variables.
- Controlling for confounding variables can improve the accuracy and validity of the findings.
Practical Table:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample Diversification | Gather data from multiple locations and times. |
| Increased Sample Size | Collect data from a larger number of participants. |
| Transparency | Clearly state the limitations of convenience sampling in the results. |
| Method Combination | Supplement with stratified sampling or other methods. |
| Data Weighting | Use statistical techniques to adjust for known biases. |
| Confounding Variable Control | Identify and control for variables that could influence the results. |
Real-World Example:
A researcher wants to study the opinions of college students on a new campus policy. Instead of only surveying students in the library, they also survey students in the cafeteria, student union, and dormitories to capture a more diverse range of perspectives.
8. How to Analyze Convenience Sampling Data
Analyzing data collected through convenience sampling requires careful consideration of the method’s limitations. Here’s how to approach the analysis:
-
Descriptive Statistics:
- Use descriptive statistics to summarize the data, including measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of dispersion (standard deviation, range).
- Descriptive statistics can provide a basic overview of the sample characteristics and patterns.
- For example, calculate the average age, gender distribution, and frequency of responses to survey questions.
-
Comparative Analysis:
- Compare the characteristics of the convenience sample to known characteristics of the broader population.
- Identify any significant differences between the sample and the population.
- This comparison can help assess the extent to which the sample is representative.
-
Trend Analysis:
- Look for trends and patterns within the data, even if the sample is not representative.
- Identify common themes, recurring responses, and significant relationships between variables.
- Trend analysis can provide valuable insights, even if the findings cannot be generalized to the population.
-
Qualitative Analysis:
- Analyze qualitative data (e.g., open-ended survey responses, interview transcripts) to gain a deeper understanding of the participants’ perspectives.
- Use techniques such as thematic analysis or content analysis to identify key themes and patterns.
- Qualitative analysis can provide rich insights that complement the quantitative data.
-
Subgroup Analysis:
- Divide the sample into subgroups based on relevant characteristics (e.g., age, gender, income) and compare the responses of these subgroups.
- Subgroup analysis can reveal differences in attitudes, opinions, or behaviors among different segments of the sample.
- This can provide valuable insights for targeted marketing or intervention strategies.
-
Limitations Acknowledgment:
- When presenting the results, clearly acknowledge the limitations of convenience sampling.
- Emphasize that the findings may not be generalizable to the broader population.
- Encourage caution in interpreting the results and avoid drawing unwarranted conclusions.
Summary Presentation:
| Analysis Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Descriptive Stats | Summarize sample characteristics using mean, median, standard deviation, etc. |
| Comparative Analysis | Compare sample traits with known population traits. |
| Trend Analysis | Identify recurring patterns and relationships in the data. |
| Qualitative Analysis | Analyze open-ended responses to understand participant perspectives. |
| Subgroup Analysis | Compare responses among subgroups based on demographics. |
| Limitation | Acknowledge that findings are not generalizable to the broader population. |
Real-World Example:
A convenience sample of customers at a coffee shop reveals that most prefer iced coffee over hot coffee during the summer months. While this finding may not represent all coffee drinkers, it provides valuable insights for the coffee shop to adjust its seasonal menu and marketing efforts.
9. How Qualtrics Software Enhances and Simplifies Convenience Sampling
Qualtrics software offers a range of features that can enhance and simplify the process of convenience sampling, making it more efficient and effective.
-
Survey Creation:
- Qualtrics provides a user-friendly interface for creating surveys quickly and easily.
- Researchers can use pre-built templates or customize their own surveys with a variety of question types.
- The drag-and-drop functionality simplifies the survey design process, saving time and effort.
-
Mobile-Friendly Surveys:
- Qualtrics surveys are mobile-friendly, allowing participants to complete them on their smartphones or tablets.
- This increases accessibility and response rates, as participants can respond to the survey at their convenience.
- Mobile optimization ensures a seamless experience for participants, regardless of their device.
-
Real-Time Data Collection:
- Qualtrics allows researchers to collect data in real-time, as participants complete the survey.
- This provides immediate access to the data, enabling researchers to monitor response rates and identify any issues.
- Real-time data collection facilitates timely analysis and decision-making.
-
Automated Analysis:
- Qualtrics offers automated analysis tools that simplify the process of analyzing survey data.
- Researchers can generate reports and visualizations with just a few clicks.
- The software automatically calculates descriptive statistics, performs trend analysis, and identifies significant relationships between variables.
-
Panel Management:
- Qualtrics provides panel management tools that facilitate the recruitment and management of participants.
- Researchers can create and manage their own panels or use Qualtrics’ pre-built panels.
- Panel management simplifies the process of finding and engaging with potential participants.
-
Integration with Other Tools:
- Qualtrics integrates with other tools and platforms, such as CRM systems and social media channels.
- This allows researchers to seamlessly integrate survey data with other data sources, providing a more comprehensive view of the customer experience.
- Integration enhances the value and impact of the research findings.
Quick Guide Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| User-Friendly Surveys | Quick and easy survey creation with drag-and-drop functionality. |
| Mobile-Friendly | Increased accessibility and higher response rates through mobile optimization. |
| Real-Time Data | Immediate access to data for monitoring and timely analysis. |
| Automated Analysis | Simplified analysis with automated reports and visualizations. |
| Panel Management | Easy recruitment and management of participants. |
| Tool Integration | Seamless integration with other tools for a comprehensive data view. |
Illustrative Use:
A marketing team uses Qualtrics to create a quick survey to gather feedback on a new advertising campaign. They distribute the survey via social media and email, collecting real-time data and using the automated analysis tools to identify the campaign’s strengths and weaknesses.
Are you looking for a convenient way to get answers to your questions? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask questions and receive free answers from our community of experts. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or just curious, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help you find the information you need quickly and easily.
For assistance with your research needs, contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890 or visit our website at what.edu.vn.