What Is Ct scan? A CT scan, also known as computed tomography scan, is a powerful diagnostic imaging technique that utilizes X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we aim to provide you with clear and comprehensive answers to your medical questions, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health. This article will explore the various applications of CT scans, their benefits, and potential risks, offering a comprehensive guide to understanding computed tomography and radiology.
1. Understanding the Basics: What Is CT Scan?
Computed tomography (CT), sometimes called computed axial tomography (CAT) scanning, is a noninvasive diagnostic imaging procedure that uses special X-ray equipment to obtain cross-sectional pictures of the body. A CT scanner uses a thin X-ray beam that rotates around the body. With WHAT.EDU.VN, get the information you need to understand complex medical procedures without the jargon.
1.1 How Does a CT Scan Work?
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that slides through a donut-shaped machine. As the machine rotates, it emits X-rays that pass through the body. Detectors measure the amount of radiation that passes through, and a computer uses this information to create detailed images. CT scans are more detailed than regular X-rays and can show soft tissues, blood vessels, and bones in various parts of the body.
1.2 What Are the Different Types of CT Scans?
There are several types of CT scans, each designed for specific purposes. These include:
- Conventional CT Scan: This is the standard type of CT scan, providing detailed images of the body.
- CT Angiography (CTA): This type uses contrast dye to visualize blood vessels, helping to detect aneurysms, blockages, and other vascular conditions.
- Cardiac CT Scan: Specifically designed to image the heart and coronary arteries, this scan can detect coronary artery disease.
- Dual-Energy CT Scan: This technique uses two different X-ray energy levels to enhance the contrast between different tissues, improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Perfusion CT Scan: Measures blood flow in the brain to assess brain perfusion and evaluate for stroke.
2. Why Is a CT Scan Performed?
CT scans are performed for a variety of reasons, ranging from diagnosing medical conditions to guiding treatment plans. They are invaluable tools in modern medicine, aiding in the detection and management of numerous health issues.
2.1 Diagnosing Medical Conditions
CT scans can help diagnose a wide range of conditions, including:
- Infections: CT scans can detect abscesses, pneumonia, and other infections in the body.
- Injuries: They are used to assess bone fractures, internal bleeding, and other injuries, particularly in trauma cases.
- Cancer: CT scans can identify tumors, determine their size and location, and help stage cancer.
- Cardiovascular Disease: They can detect blockages in blood vessels and assess the health of the heart.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: CT scans can identify bone abnormalities, joint problems, and other musculoskeletal conditions.
- Neurological Disorders: Detects stroke, brain tumors, or bleeding in the brain
2.2 Guiding Medical Procedures
CT scans are often used to guide medical procedures, such as:
- Biopsies: CT scans can help guide needles to specific areas for tissue sampling.
- Radiation Therapy: They are used to plan and target radiation treatment for cancer.
- Surgery: CT scans provide detailed images that help surgeons plan and perform complex procedures.
- Drainage Procedures: Used to guide the placement of drainage tubes to remove fluid collections within the body.
2.3 Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
CT scans are also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for various conditions. For example, they can help assess whether a tumor is shrinking in response to chemotherapy or whether an infection is resolving with antibiotics.
3. Benefits of CT Scans
CT scans offer numerous benefits over other imaging techniques, making them a preferred choice for many diagnostic and treatment applications.
3.1 High-Quality Imaging
CT scans provide detailed, high-resolution images of the body’s internal structures. This allows doctors to visualize even small abnormalities that might be missed by other imaging methods.
3.2 Speed and Efficiency
CT scans are relatively quick and efficient, often taking only a few minutes to complete. This is particularly important in emergency situations where rapid diagnosis is critical.
3.3 Noninvasive Procedure
CT scans are noninvasive, meaning they do not require any incisions or surgical procedures. This reduces the risk of complications and allows patients to return to their normal activities shortly after the scan.
3.4 Wide Range of Applications
CT scans can be used to image virtually any part of the body, making them a versatile tool for diagnosing and managing a wide range of conditions.
3.5 Accurate Diagnosis
The detailed images produced by CT scans enable accurate diagnoses, which can lead to more effective treatment plans and better patient outcomes.
4. Risks Associated with CT Scans
While CT scans are generally safe, there are some risks associated with the procedure. It’s important to be aware of these risks and discuss them with your doctor before undergoing a CT scan. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide balanced information, so you can weigh the benefits against the risks.
4.1 Radiation Exposure
CT scans use X-rays, which involve exposure to ionizing radiation. While the radiation dose from a single CT scan is generally low, repeated exposure can increase the risk of cancer over time.
4.2 Allergic Reactions to Contrast Dye
Some CT scans require the use of contrast dye to enhance the images. Some people may be allergic to this dye, leading to reactions ranging from mild itching to severe anaphylaxis.
4.3 Kidney Damage
In rare cases, contrast dye can cause kidney damage, particularly in people with pre-existing kidney problems.
4.4 Pregnancy Considerations
Radiation exposure from CT scans can be harmful to a developing fetus. Pregnant women should inform their doctors before undergoing a CT scan, and alternative imaging methods may be recommended.
4.5 Claustrophobia
The CT scanner is a confined space, which can trigger claustrophobia in some individuals. Doctors can often provide medication or other strategies to help patients manage their anxiety.
**5. Preparing for a CT Scan
Proper preparation is essential for ensuring the accuracy and safety of a CT scan. Here are some steps to follow before your appointment.
5.1 Discussing Medical History
Inform your doctor about any medical conditions you have, including allergies, kidney problems, or diabetes. Also, tell them about any medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
5.2 Fasting Instructions
Depending on the type of CT scan, you may need to fast for several hours before the procedure. Your doctor will provide specific instructions regarding fasting.
5.3 Hydration
Staying well-hydrated can help protect your kidneys, especially if you are receiving contrast dye. Drink plenty of water in the days leading up to your CT scan.
5.4 Clothing and Jewelry
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing to your appointment. You will likely be asked to remove any jewelry, eyeglasses, or other metal objects that could interfere with the images.
5.5 Pregnancy Notification
If you are pregnant or think you might be, inform your doctor immediately. Alternative imaging methods may be recommended to avoid radiation exposure to the fetus.
6. What to Expect During a CT Scan
Knowing what to expect during a CT scan can help ease anxiety and ensure a smooth procedure.
6.1 Arrival and Preparation
Upon arrival at the imaging center, you will be asked to fill out paperwork and change into a hospital gown. A technician will explain the procedure and answer any questions you may have.
6.2 Positioning
You will lie on a table that slides into the CT scanner. The technician will position you to ensure the correct area of your body is being imaged.
6.3 Contrast Administration
If your CT scan requires contrast dye, it will be administered intravenously (through a vein in your arm). You may feel a warm sensation or a metallic taste in your mouth during the injection.
6.4 Scanning Process
As the scanner rotates around you, you will need to remain as still as possible to avoid blurring the images. The technician may ask you to hold your breath for short periods.
6.5 Duration
The entire CT scan typically takes only a few minutes, although the exact duration can vary depending on the area being imaged and the complexity of the case.
7. Understanding CT Scan Results
After your CT scan, a radiologist will analyze the images and prepare a report for your doctor. Understanding your CT scan results can help you better understand your health condition.
7.1 Radiologist’s Report
The radiologist’s report will describe the findings of the CT scan, including any abnormalities or areas of concern. It will also provide an interpretation of the results and recommendations for further evaluation or treatment.
7.2 Discussing Results with Your Doctor
Your doctor will review the radiologist’s report with you and explain the findings in detail. They will discuss the implications of the results and develop a plan for managing your condition.
7.3 Follow-Up Testing
Depending on the CT scan results, your doctor may recommend additional testing, such as further imaging studies, blood tests, or biopsies.
7.4 Treatment Options
If the CT scan reveals a medical condition, your doctor will discuss the available treatment options. These may include medication, surgery, radiation therapy, or other interventions.
8. Innovations in CT Scan Technology
CT scan technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations aimed at improving image quality, reducing radiation exposure, and enhancing diagnostic capabilities.
8.1 Iterative Reconstruction
Iterative reconstruction is an advanced technique that reduces radiation dose while maintaining image quality. It uses sophisticated algorithms to reconstruct images from less data, resulting in lower radiation exposure for patients.
8.2 Dual-Energy CT
Dual-energy CT uses two different X-ray energy levels to enhance the contrast between different tissues. This can improve the detection of subtle abnormalities and provide more detailed information about tissue composition.
8.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to develop new tools for analyzing CT scan images. AI algorithms can help radiologists detect subtle abnormalities, improve diagnostic accuracy, and streamline the workflow.
8.4 Photon-Counting CT
Photon-counting CT is an emerging technology that directly detects individual X-ray photons, providing higher resolution images and reducing radiation dose.
9. CT Scans in Emergency Medicine
CT scans play a crucial role in emergency medicine, providing rapid and accurate diagnoses that can save lives.
9.1 Stroke Diagnosis
CT scans are used to quickly diagnose strokes by identifying bleeding in the brain or blockages in blood vessels. This allows doctors to administer timely treatment, such as clot-busting drugs or endovascular therapy.
9.2 Trauma Assessment
In trauma cases, CT scans can quickly assess the extent of injuries, including bone fractures, internal bleeding, and organ damage. This helps doctors prioritize treatment and improve patient outcomes.
9.3 Abdominal Pain
CT scans can help diagnose the cause of severe abdominal pain, such as appendicitis, kidney stones, or bowel obstruction. This allows for prompt treatment and prevents complications.
9.4 Pulmonary Embolism
CT angiography (CTA) is used to diagnose pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition in which blood clots travel to the lungs.
10. CT Scans in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
CT scans are an essential tool in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment of cancer.
10.1 Tumor Detection
CT scans can detect tumors in various parts of the body, including the lungs, liver, pancreas, and kidneys. They can also help determine the size, shape, and location of tumors.
10.2 Cancer Staging
CT scans are used to stage cancer, which involves determining the extent of the disease and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. This information is crucial for developing a treatment plan.
10.3 Treatment Planning
CT scans are used to plan radiation therapy for cancer. They help doctors target the radiation beam to the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
10.4 Monitoring Treatment Response
CT scans are used to monitor the response of tumors to treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This helps doctors determine whether the treatment is effective and make adjustments as needed.
11. CT Scans vs. Other Imaging Techniques
CT scans are just one of many imaging techniques available to doctors. Here’s a comparison of CT scans with other common imaging methods.
11.1 CT Scan vs. X-Ray
X-rays are simpler and less expensive than CT scans, but they provide less detailed images. CT scans can show soft tissues and blood vessels that are not visible on X-rays.
11.2 CT Scan vs. MRI
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) provides highly detailed images of soft tissues, but it takes longer than a CT scan and may not be suitable for people with certain metal implants. CT scans are better for imaging bones and detecting fractures.
11.3 CT Scan vs. Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images and is often used for imaging pregnant women and children. CT scans provide more detailed images and are better for imaging bones and internal organs.
11.4 CT Scan vs. PET Scan
PET (positron emission tomography) scans use radioactive tracers to detect metabolic activity in the body, which can help identify cancer and other diseases. CT scans provide more detailed anatomical images.
12. The Future of CT Scanning
The field of CT scanning is continuously evolving, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving image quality, reducing radiation dose, and enhancing diagnostic capabilities.
12.1 Improved Image Resolution
Researchers are working on new technologies to improve the resolution of CT images, allowing doctors to visualize even smaller structures and abnormalities.
12.2 Reduced Radiation Dose
Efforts are being made to reduce the radiation dose associated with CT scans, including the development of new scanning protocols and image reconstruction techniques.
12.3 Advanced Applications
New applications for CT scanning are being explored, such as using CT to guide minimally invasive procedures and to monitor the effectiveness of new therapies.
12.4 Integration with AI
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into CT scanning is expected to revolutionize the field, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses, as well as personalized treatment planning.
13. Addressing Common Concerns About CT Scans
Many people have concerns about CT scans, particularly regarding radiation exposure and the use of contrast dye. Here are some answers to common questions.
13.1 Is a CT Scan Safe?
CT scans are generally safe when performed appropriately. The radiation dose from a single CT scan is relatively low, and the benefits of accurate diagnosis often outweigh the risks.
13.2 How Much Radiation Is Involved in a CT Scan?
The amount of radiation from a CT scan varies depending on the area being imaged and the scanning protocol. Your doctor will use the lowest possible radiation dose to obtain the necessary images.
13.3 What Are the Side Effects of Contrast Dye?
Most people tolerate contrast dye well, but some may experience mild side effects, such as a warm sensation or a metallic taste in the mouth. Allergic reactions are rare but can be serious.
13.4 Can I Have a CT Scan If I Am Pregnant?
Radiation exposure from CT scans can be harmful to a developing fetus. If you are pregnant, your doctor may recommend alternative imaging methods, such as MRI or ultrasound.
13.5 How Do I Prepare for a CT Scan?
Your doctor will provide specific instructions on how to prepare for your CT scan. This may include fasting, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding certain medications.
14. Real-World Examples of CT Scan Applications
CT scans are used in a wide range of medical scenarios. Here are some real-world examples of how CT scans can help diagnose and manage various conditions.
14.1 Case Study: Diagnosing Appendicitis
A young adult presents to the emergency room with severe abdominal pain. A CT scan reveals an inflamed appendix, leading to a diagnosis of appendicitis. Prompt surgical removal of the appendix prevents complications.
14.2 Case Study: Detecting Lung Cancer
A smoker undergoes a routine CT scan of the chest. The scan reveals a small nodule in the lung. Further testing confirms a diagnosis of lung cancer, which is treated with surgery and chemotherapy.
14.3 Case Study: Assessing Traumatic Brain Injury
A person involved in a car accident undergoes a CT scan of the head. The scan reveals a brain hemorrhage, allowing doctors to provide immediate treatment to reduce brain swelling and prevent further damage.
14.4 Case Study: Identifying Kidney Stones
A patient experiences severe flank pain. A CT scan reveals a kidney stone blocking the ureter. Treatment options include pain medication, increased fluid intake, or surgical removal of the stone.
15. The Role of CT Scans in Research
CT scans are also used in medical research to study various diseases and conditions, develop new treatments, and improve patient outcomes.
15.1 Clinical Trials
CT scans are used in clinical trials to assess the effectiveness of new drugs and therapies. They can help researchers measure the size of tumors, evaluate the response to treatment, and monitor the progression of disease.
15.2 Anatomical Studies
CT scans are used to study the anatomy of the human body, providing detailed images of internal organs, bones, and blood vessels.
15.3 Disease Modeling
CT scans are used to create computer models of diseases, which can help researchers understand how diseases progress and develop new strategies for prevention and treatment.
15.4 Imaging Biomarkers
Researchers are exploring the use of CT scans to identify imaging biomarkers, which are measurable characteristics that can be used to predict the risk of disease, monitor the response to treatment, and personalize patient care.
16. Understanding CT Scan Costs and Insurance Coverage
The cost of a CT scan can vary depending on several factors, including the location of the imaging center, the type of scan, and whether contrast dye is used.
16.1 Factors Affecting Cost
The cost of a CT scan can be affected by the following factors:
- Location: Imaging centers in urban areas may charge more than those in rural areas.
- Type of Scan: Complex CT scans that require contrast dye or specialized imaging techniques may cost more.
- Insurance Coverage: The amount of your insurance coverage will affect your out-of-pocket costs.
16.2 Insurance Coverage
Most health insurance plans cover CT scans when they are medically necessary. However, you may need to meet certain requirements, such as obtaining pre-authorization or paying a deductible or co-pay.
16.3 Negotiating Costs
If you do not have insurance or your insurance does not cover the full cost of the CT scan, you may be able to negotiate a lower price with the imaging center. Some centers offer discounts for cash payments or for patients who are willing to pay upfront.
16.4 Financial Assistance Programs
Some hospitals and imaging centers offer financial assistance programs to help patients who cannot afford the cost of a CT scan. These programs may provide free or reduced-cost imaging services.
17. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle After a CT Scan
After undergoing a CT scan, it’s important to maintain a healthy lifestyle to protect your overall health and well-being.
17.1 Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water to help flush any contrast dye from your system and support kidney function.
17.2 Follow Medical Advice
Follow your doctor’s advice regarding any follow-up testing, treatment, or lifestyle changes.
17.3 Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eat a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
17.4 Exercise Regularly
Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and improve your overall health.
17.5 Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Avoid smoking and limit your alcohol consumption to reduce your risk of various health problems.
18. Debunking Myths About CT Scans
There are many myths and misconceptions about CT scans. Here are some common myths debunked.
18.1 Myth: CT Scans Are Always Dangerous
While CT scans do involve radiation exposure, the risk is generally low, and the benefits of accurate diagnosis often outweigh the risks.
18.2 Myth: Everyone Is Allergic to Contrast Dye
Allergic reactions to contrast dye are rare. Most people tolerate contrast dye well, and serious reactions are uncommon.
18.3 Myth: CT Scans Always Find Something Wrong
CT scans are used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, but they do not always find something wrong. In some cases, the scan may reveal that there is no problem.
18.4 Myth: You Can’t Have a CT Scan If You Have Metal Implants
While certain metal implants can interfere with CT scan images, many people with metal implants can safely undergo a CT scan. Your doctor will determine whether a CT scan is appropriate for you based on your individual circumstances.
18.5 Myth: CT Scans Are Only for Serious Conditions
CT scans are used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, from minor injuries to serious illnesses. They are a versatile tool that can help doctors assess your health and develop a treatment plan.
19. Resources for Learning More About CT Scans
If you want to learn more about CT scans, here are some resources to explore.
19.1 Medical Websites
Reputable medical websites, such as the Mayo Clinic, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the American College of Radiology (ACR), offer detailed information about CT scans and other imaging techniques.
19.2 Medical Journals
Medical journals, such as the New England Journal of Medicine, The Lancet, and Radiology, publish research articles and reviews on CT scanning and other medical topics.
19.3 Books
There are many books available that provide detailed information about CT scanning and medical imaging.
19.4 Healthcare Professionals
Your doctor, radiologist, and other healthcare professionals can provide valuable information about CT scans and answer any questions you may have.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About CT Scans
Here are some frequently asked questions about CT scans, along with detailed answers.
20.1 What Is the Purpose of a CT Scan?
A CT scan is used to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures, which can help diagnose a wide range of medical conditions.
20.2 How Long Does a CT Scan Take?
A CT scan typically takes only a few minutes, although the exact duration can vary depending on the area being imaged and the complexity of the case.
20.3 Is Contrast Dye Necessary for All CT Scans?
No, contrast dye is not necessary for all CT scans. It is used to enhance the images and make certain structures, such as blood vessels, more visible.
20.4 What Should I Wear for a CT Scan?
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing to your appointment. You will likely be asked to remove any jewelry, eyeglasses, or other metal objects that could interfere with the images.
20.5 Can I Eat Before a CT Scan?
Depending on the type of CT scan, you may need to fast for several hours before the procedure. Your doctor will provide specific instructions regarding fasting.
20.6 What Happens After a CT Scan?
After a CT scan, a radiologist will analyze the images and prepare a report for your doctor. Your doctor will review the report with you and explain the findings in detail.
20.7 How Accurate Are CT Scans?
CT scans are highly accurate and can provide detailed images of the body’s internal structures, allowing for accurate diagnoses.
20.8 What Are the Alternatives to a CT Scan?
Alternatives to a CT scan include X-ray, MRI, ultrasound, and PET scan. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate imaging method for your individual circumstances.
20.9 How Can I Reduce My Risk from CT Scan Radiation?
You can reduce your risk from CT scan radiation by discussing the need for the scan with your doctor, choosing a facility with advanced imaging technology, and following your doctor’s instructions regarding preparation and follow-up care.
20.10 Where Can I Get a CT Scan?
CT scans are available at hospitals, imaging centers, and some doctors’ offices. Your doctor can refer you to a qualified imaging facility.
CT scans are invaluable tools in modern medicine, providing detailed images that help diagnose and manage a wide range of conditions. While there are some risks associated with CT scans, the benefits often outweigh the risks, especially when the scan is performed appropriately and the results are used to guide effective treatment.
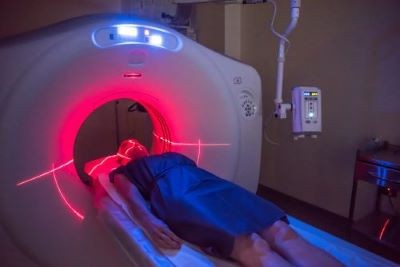 CT scan displaying internal organs
CT scan displaying internal organs
Alt text: Detailed CT scan displaying internal organs, aiding in medical diagnostics.
Remember, understanding your health is the first step towards taking control of it. If you have more questions or need further clarification, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at WHAT.EDU.VN. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of medical information and get the answers you need. Have questions? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN and ask away! Our team of experts is ready to provide you with free, reliable answers to all your queries. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890. Website: what.edu.vn.
