Flu B: Understand the virus, its effects, and how to protect yourself. Find quick and reliable answers about Influenza B at WHAT.EDU.VN. This guide provides clarity on flu prevention, symptom relief, and differences between flu and common colds. Learn effective flu management and stay informed with our comprehensive coverage of seasonal illnesses and respiratory infections.
Table of Contents
1. What Is Influenza B?
2. Flu B vs. Common Cold: Key Differences
3. Symptoms of Influenza B
4. How to Prevent Influenza B
5. Transmission of Influenza B
6. Treatment Options for Influenza B
7. How Contagious Is Influenza B?
8. Influenza B: Viral or Bacterial?
9. How Influenza B Affects the Body
10. Avoiding the Spread of Flu
11. When to Seek Medical Advice for the Flu
12. Why Annual Flu Vaccines Are Necessary
13. Recovering from the Flu: Tips and Guidelines
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Flu B
1. What Is Influenza B?
Influenza, widely known as the flu, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. Severity can range from mild to severe, sometimes leading to serious complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, or worsening of chronic conditions like asthma or heart disease. In rare cases, it may result in life-threatening complications like encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), respiratory failure requiring assisted ventilation, and, occasionally, death. Influenza B is one specific type of influenza virus. For more comprehensive health information and answers to your questions, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
2. Flu B vs. Common Cold: Key Differences
Both the flu and the common cold are contagious respiratory illnesses, but different viruses cause them. The flu is caused exclusively by influenza viruses, while the common cold can be triggered by a variety of viruses, including rhinoviruses, parainfluenza, and seasonal coronaviruses. Understanding these differences is essential for proper treatment and prevention.
| Feature | Flu (Influenza) | Common Cold |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Influenza viruses (A, B, C, D) | Various viruses (rhinoviruses, etc.) |
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual |
| Fever | High (100-104°F), lasting 3-4 days | Rare or low-grade |
| Headache | Common, often severe | Uncommon |
| Aches/Pains | Common, often severe | Mild |
| Fatigue | Common, can last for weeks | Mild |
| Stuffy Nose | Sometimes | Common |
| Sneezing | Sometimes | Common |
| Sore Throat | Sometimes | Common |
| Cough | Common, can be severe | Mild to moderate |
| Complications | Pneumonia, bronchitis, hospitalization, death | Sinus infection, ear infection |
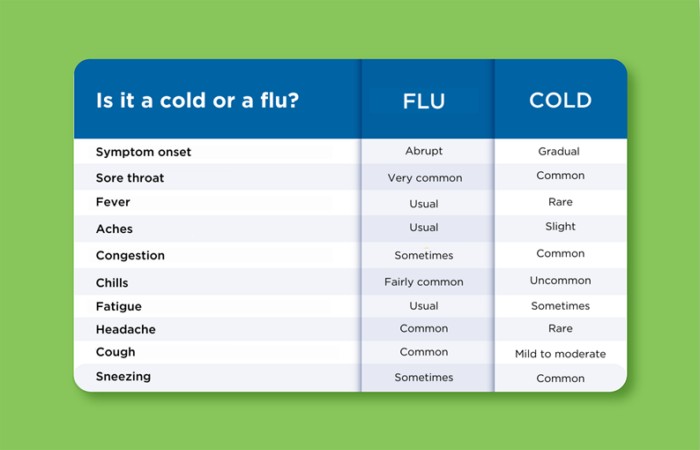 What is influenza b? Differences between the flu and the cold
What is influenza b? Differences between the flu and the cold
Understanding the distinctions between the flu and the common cold is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate care, enhancing your health and promoting effective illness management.
3. Symptoms of Influenza B
Symptoms of Influenza B can include:
- Fever
- Body aches
- Chills
- Headache
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Gastrointestinal issues in a few cases like nausea and diarrhea
- Often, muscle pain can be severe and may require hospitalization
It’s important to note that the severity and presentation of symptoms can vary from person to person. If you have concerns about your health, visit WHAT.EDU.VN for reliable and quick answers.
4. How to Prevent Influenza B
Preventing and managing influenza B can be supported through vaccination, good hygiene practices, and antiviral medications. It’s important for everyone in your family to get their flu shot every year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that everyone aged 6 months and older receive their annual flu vaccination by late October, ideally before the start of flu season.
However, if you haven’t received your flu shot yet, it’s not too late The vaccine is still highly recommended for anyone who hasn’t been vaccinated. Not only does it help protect you from the flu, but it significantly lowers the risk of severe complications, such as hospitalizations or even death.
The flu shot does not cause the flu and helps keep kids and parents from getting sick. Babies younger than 6 months can’t get the vaccine. But if their parents, other caregivers, and older kids in the household get it, that can help protect the baby.
| Prevention Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Flu Vaccination | Getting a flu shot every year | Reduces the risk of getting the flu, lowers the chance of severe complications (hospitalization, death), protects vulnerable populations |
| Good Hygiene Practices | Regular hand washing, covering coughs and sneezes, avoiding touching face | Prevents the spread of the virus, reduces personal risk of infection |
| Antiviral Medications | Using antiviral drugs when diagnosed with the flu, especially for high-risk individuals | Can shorten the duration of symptoms and reduce their severity, helps prevent complications |
5. Transmission of Influenza B
Influenza spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or even talks. It is common for people to cover their mouths when they cough, but they should then wash their hands as our hands are a common way to contaminate surfaces or to pass the virus to others through a friendly handshake. Simple actions can significantly reduce the spread of influenza.
6. Treatment Options for Influenza B
Treatment for Influenza B mainly focuses on easing symptoms while the body fights off the virus. Antiviral medications can help shorten the duration and reduce the severity of symptoms. Antiviral medication should be strongly considered when influenza (A or B) is diagnosed or when someone is seeking medical attention for influenza-like illness (ILI). This is of greater importance in children and other people with underlying diseases or who require treatments that weaken the immune system or with chronic respiratory illness like asthma.
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic Relief | Rest, hydration, over-the-counter pain relievers (acetaminophen) | Alleviates symptoms like fever, headache, and body aches, supports the body’s natural healing process |
| Antiviral Medications | Medications like oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) | Can shorten the duration of the illness, reduce the severity of symptoms, prevent complications (especially in high-risk individuals) |
| Supportive Care | Monitoring symptoms, avoiding close contact with others, practicing good hygiene | Prevents the spread of the virus to others, ensures timely medical intervention if complications arise |
7. How Contagious Is Influenza B?
Influenza B is highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. People with the flu can be contagious about one day before symptoms start and up to five to seven days after they begin to feel sick. However, young children may remain contagious for a longer period than adults. Individuals with weakened immune systems can be contagious for several weeks.
8. Influenza B: Viral or Bacterial?
Influenza B is a highly contagious viral infection that spreads through the air. Understanding this distinction is critical because viral infections do not respond to antibiotics, which are designed to treat bacterial infections. Accurate knowledge helps in applying the correct treatment strategies.
9. How Influenza B Affects the Body
Influenza B mainly targets the respiratory system, causing discomfort throughout the body. The virus primarily infects the nose, throat, and sometimes the lungs, leading to symptoms like cough, congestion, and a sore throat. Although less common in adults, children may also experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, alongside the typical respiratory symptoms. Severe muscle pain is common in patients with influenza B.
10. Avoiding the Spread of Flu
- Avoid close contact with others until you have been fever-free for at least 24 hours without using fever-reducing medications.
- Be sure to clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces like doorknobs, countertops, and light switches.
- Cover your nose and mouth when sneezing and wash your hands with soap and water or use hand sanitizer regularly.
These steps are essential in preventing the spread of influenza within communities.
11. When to Seek Medical Advice for the Flu
Consider seeking medical attention if you have ILI, as antiviral medication may be helpful. You should seek medical attention if your symptoms persist for more than 5 days or if you’re feeling worse or not improving after 2 – 3 days. If you develop a new fever, chest pain, or difficulty breathing within 1 – 3 weeks after influenza or ILI, you should seek medical attention since serious bacterial infections often follow uncomplicated influenza.
| Symptom or Condition | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Persistent ILI | Seek medical attention, as antiviral medication may be helpful |
| Symptoms lasting more than 5 days | Consult a healthcare provider |
| Worsening condition after initial improvement | Seek immediate medical attention |
| New fever, chest pain, or difficulty breathing | Seek immediate medical attention, as these may indicate serious complications or secondary bacterial infections |
12. Why Annual Flu Vaccines Are Necessary
Even if you received the flu vaccine last year, it may not offer enough protection this year due to changes in the flu viruses. That’s why the flu vaccine is updated annually to include the most current strains of the virus. Sometimes, the same strains from one year are included in the next, but it’s still important to get the flu vaccine each year. Over time, the body’s immunity against the influenza virus weakens, so regular vaccination is essential. Getting the flu vaccine not only protects you but also helps safeguard those around you. It reduces your chances of getting the flu and, as a result, lowers the likelihood of spreading it to others.
13. Recovering from the Flu: Tips and Guidelines
To aid your recovery, make sure you get plenty of rest, stay hydrated, and take over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen to help manage symptoms. Do not use medications like ibuprofen unless instructed by a health care provider. Do not take aspirin when you have influenza or ILI, particularly if you have influenza B.
| Recovery Tip | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Rest | Get plenty of sleep and avoid strenuous activities | Allows the body to focus on healing and recovery |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of fluids like water, herbal tea, and broth | Helps prevent dehydration, thins mucus, and supports overall bodily functions |
| Symptom Management | Use over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen for fever and pain relief (avoid aspirin and ibuprofen) | Reduces discomfort, helps manage symptoms, and improves overall quality of life during recovery |
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Flu B
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What exactly is influenza B? | Influenza B is a type of flu virus that causes respiratory illness, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. |
| How does flu B differ from flu A? | Flu A and B are both influenza viruses, but they belong to different categories. Flu A is known for causing pandemics, while flu B generally leads to regional or local outbreaks. |
| Who is most at risk from flu B? | High-risk groups include young children, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic health conditions. |
| Can you get flu B more than once? | Yes, you can get flu B multiple times because the virus can mutate, and immunity from one infection may not protect against new strains. |
| How effective is the flu vaccine against flu B? | The flu vaccine is designed to protect against both flu A and B strains. Its effectiveness varies each year depending on how well the vaccine matches the circulating strains, but it generally reduces the risk of infection. |
| How long does flu B typically last? | Flu B typically lasts for about 1 to 2 weeks. |
| Are there any long-term effects of flu B? | While most people recover fully, complications like pneumonia can lead to long-term effects, especially in high-risk individuals. |
| How can I tell if I have flu B or COVID-19? | Symptoms can overlap, so it’s best to get tested to confirm the diagnosis. Common symptoms of both include fever, cough, and fatigue. |
| Is there a specific test for flu B? | Yes, diagnostic tests like rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs) and PCR tests can identify influenza B. |
| Can natural remedies help with flu B? | Natural remedies like rest, hydration, and honey can help alleviate symptoms, but they are not a substitute for medical treatment or antiviral medications if prescribed by a doctor. |
Do you have more questions about flu B or other health concerns? Don’t hesitate to ask your questions for free on WHAT.EDU.VN! Our community of experts is ready to provide you with quick, accurate, and reliable answers. We understand the challenges of finding trustworthy information, especially when you need it fast. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re committed to offering a platform where you can easily seek advice and gain knowledge without any cost.
We know that you might be unsure where to turn for answers, and the thought of expensive consultations can be daunting. That’s why we’ve created WHAT.EDU.VN: to bridge that gap and offer a seamless way to get your questions answered by knowledgeable individuals. Our service is designed to be user-friendly, ensuring that everyone, regardless of their technical expertise, can easily navigate and benefit from our platform.
Ready to experience the convenience and reliability of free expert advice? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question! Let us help you find the answers you need, quickly and easily.
Contact Us:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn