Gaza, a strip of land with a complex history, is a focal point of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and has been a region of significant geopolitical importance. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide access to a wealth of knowledge and free resources to help you understand such intricate topics. Learn about the Gaza Strip, its people, and the challenges it faces today through our comprehensive guides and expert analyses as well as regional insights.
1. Gaza: A Concise Overview
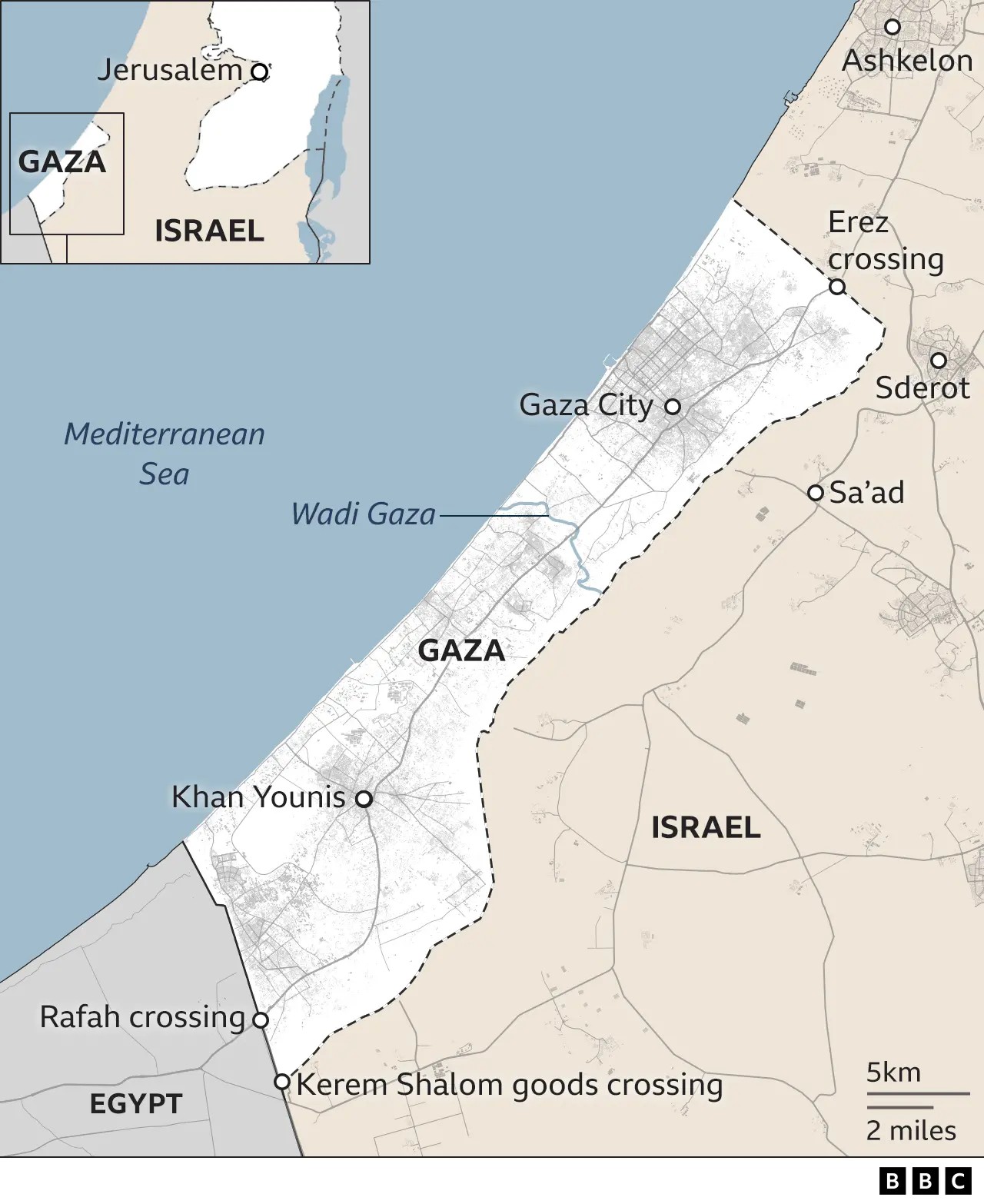
The Gaza Strip is a self-governing Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It borders Egypt on the southwest and Israel on the east and north. It’s one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
1.1. Geography and Demographics
Gaza is a small territory, only about 41 kilometers (25 miles) long and 10 kilometers (6 miles) wide. Despite its small size, it is home to approximately 2.3 million Palestinians. This makes it one of the most densely populated areas globally.
1.2. Key Cities and Infrastructure
The major cities in Gaza include Gaza City, which serves as the largest urban center, and Khan Younis, a significant city in the southern part of the strip. The infrastructure in Gaza has been severely impacted by repeated conflicts and a prolonged blockade. Essential services like water, electricity, and healthcare face persistent challenges.
2. Historical Background of Gaza
Understanding Gaza requires delving into its rich yet turbulent history. From ancient times to modern conflicts, Gaza has been at the crossroads of civilizations and conflicts.
2.1. Ancient History
Gaza has a history dating back thousands of years, serving as an important port and trading center for various empires. It was a part of the Philistine Pentapolis, mentioned in the Bible, and later came under the rule of the Romans, Byzantines, and Arabs.
2.2. Ottoman and British Control
During the Ottoman Empire, Gaza was part of the larger region of Palestine. After World War I, the British took control of Palestine, including Gaza, under a League of Nations mandate. This period saw increasing tensions between Jewish and Arab populations in the region.
2.3. The 1948 Arab-Israeli War and its Aftermath
The 1948 Arab-Israeli War, also known as the War of Independence in Israel, drastically altered Gaza’s status. Following the war, Gaza came under Egyptian control. The war also led to a significant influx of Palestinian refugees into Gaza, exacerbating the region’s demographic challenges.
3. The Six-Day War and Israeli Occupation
The Six-Day War in 1967 was another pivotal moment in Gaza’s history. The war resulted in Israel’s occupation of Gaza, along with the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Sinai Peninsula.
3.1. Impact of the War on Gaza
The Israeli occupation had profound effects on Gaza. It led to increased restrictions on movement, economic activities, and daily life for Palestinians. The occupation also spurred the growth of Palestinian resistance movements.
3.2. Israeli Settlements in Gaza
During the occupation, Israel established settlements in Gaza. These settlements became a point of contention and a source of conflict between Israelis and Palestinians.
4. The First Intifada and Oslo Accords
The First Intifada, or Palestinian uprising, began in 1987 and marked a new phase in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The Oslo Accords in the 1990s aimed to establish a framework for peace and Palestinian self-governance.
4.1. The First Intifada
The First Intifada was largely a grassroots movement characterized by protests, strikes, and civil disobedience. It highlighted the growing frustration and resistance among Palestinians living under occupation.
4.2. The Oslo Accords and the Palestinian Authority
The Oslo Accords led to the establishment of the Palestinian Authority (PA), which was granted limited self-governance in parts of the West Bank and Gaza. However, the peace process stalled, and many issues remained unresolved.
5. Israeli Withdrawal from Gaza
In 2005, Israel unilaterally withdrew its troops and settlers from Gaza. This was a significant event, but it did not end the conflict or the Israeli control over Gaza’s borders, airspace, and shoreline.
5.1. The Disengagement Plan
The disengagement plan involved the removal of all Israeli settlements and military presence from Gaza. While hailed by some as a step towards peace, others viewed it as a strategic move by Israel to consolidate its control over other territories.
5.2. Continued Control of Borders and Airspace
Despite the withdrawal, Israel maintained control over Gaza’s borders, airspace, and shoreline. This has had a significant impact on the movement of people and goods, contributing to the ongoing humanitarian crisis.
6. Hamas Takes Control
In 2006, Hamas won the Palestinian elections. The following year, after a brief but intense conflict with Fatah, Hamas took control of Gaza.
6.1. 2006 Elections and Hamas Victory
Hamas’ victory in the 2006 elections was a turning point. It reflected growing dissatisfaction with the PA and a desire for more decisive action against the Israeli occupation.
6.2. The 2007 Conflict with Fatah
The conflict between Hamas and Fatah in 2007 resulted in Hamas seizing control of Gaza. This led to a split in Palestinian governance, with Hamas ruling Gaza and the PA governing parts of the West Bank.
7. The Blockade of Gaza
Following Hamas’ takeover, Israel and Egypt imposed a blockade on Gaza, severely restricting the movement of people and goods. This blockade has had a devastating impact on Gaza’s economy and humanitarian situation.
7.1. Imposition of the Blockade
The blockade was imposed in response to Hamas’ control of Gaza and the ongoing security concerns of Israel. However, it has been widely criticized for its collective punishment of the civilian population.
7.2. Impact on the Economy and Humanitarian Situation
The blockade has crippled Gaza’s economy, leading to high unemployment rates, poverty, and food insecurity. Essential supplies like medicine, building materials, and fuel are often in short supply.
8. Major Conflicts: 2008-09, 2012, 2014, and 2021
Since Hamas took control, Gaza has been the site of several major conflicts between Hamas and Israel. These conflicts have resulted in significant loss of life and widespread destruction.
8.1. Operation Cast Lead (2008-09)
Operation Cast Lead was a large-scale military offensive launched by Israel in response to rocket fire from Gaza. The operation resulted in the deaths of hundreds of Palestinians and significant damage to infrastructure.
8.2. Operation Pillar of Defense (2012)
Operation Pillar of Defense was another Israeli military operation aimed at stopping rocket fire from Gaza. The conflict lasted for eight days and resulted in casualties on both sides.
8.3. Operation Protective Edge (2014)
Operation Protective Edge was the longest and deadliest of the conflicts. It resulted in the deaths of thousands of Palestinians and significant destruction in Gaza.
8.4. The May 2021 Conflict
The May 2021 conflict was triggered by tensions in Jerusalem and resulted in another round of intense fighting between Hamas and Israel. The conflict lasted for 11 days and caused significant damage in Gaza.
9. The October 7, 2023 Attack and Subsequent War
On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched a surprise attack on Israel, resulting in the deaths of approximately 1,200 Israelis and the capture of over 250 hostages. This attack triggered a massive Israeli military offensive in Gaza.
9.1. Hamas Attack on Israel
The attack by Hamas on October 7 was unprecedented in its scale and audacity. It caught Israel by surprise and led to a swift and forceful response.
9.2. Israeli Military Offensive in Gaza
The Israeli military offensive in Gaza has resulted in the deaths of tens of thousands of Palestinians, the majority of them women and children, according to the Hamas-run health ministry. The offensive has also caused widespread destruction and displacement.
10. Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza
The ongoing conflict and blockade have created a severe humanitarian crisis in Gaza. The population faces shortages of essential supplies, limited access to healthcare, and widespread psychological trauma.
10.1. Shortages of Essential Supplies
Gaza suffers from chronic shortages of essential supplies, including medicine, food, water, and electricity. The blockade restricts the flow of these goods, exacerbating the crisis.
10.2. Limited Access to Healthcare
The healthcare system in Gaza is on the brink of collapse. Hospitals lack essential equipment and supplies, and many healthcare workers have been displaced or killed.
10.3. Psychological Trauma
The repeated conflicts and ongoing crisis have taken a heavy toll on the mental health of Gaza’s population. Many people suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health issues.
11. International Response and Efforts for Peace
The international community has been actively involved in efforts to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and address the humanitarian crisis in Gaza. However, a lasting solution remains elusive.
11.1. UN Resolutions and Involvement
The United Nations has passed numerous resolutions calling for a peaceful resolution to the conflict and an end to the blockade of Gaza. UN agencies also provide humanitarian assistance to the population.
11.2. Peace Initiatives and Negotiations
Various peace initiatives have been proposed over the years, but none have led to a lasting settlement. Negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians have repeatedly stalled due to unresolved issues such as borders, settlements, and the status of Jerusalem.
12. The Future of Gaza
The future of Gaza remains uncertain. The ongoing conflict, blockade, and humanitarian crisis pose significant challenges to the region and its people.
12.1. Potential Scenarios
Several potential scenarios could play out in Gaza. These include a continuation of the status quo, a renewed peace process, or further escalation of the conflict.
12.2. Challenges and Opportunities
Gaza faces numerous challenges, including the need to rebuild its infrastructure, revive its economy, and address the psychological trauma of its population. However, there are also opportunities for positive change, such as increased international support and a renewed commitment to peace.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Gaza
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the Gaza Strip? | The Gaza Strip is a self-governing Palestinian territory located on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It borders Egypt and Israel and is one of the most densely populated areas in the world. |
| Why is Gaza important? | Gaza is strategically important due to its location and its role in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It is a focal point of regional tensions and humanitarian concerns. |
| Who controls Gaza? | Hamas, a Palestinian Sunni-Islamist fundamentalist organization, has controlled the Gaza Strip since 2007. |
| What is the blockade of Gaza? | The blockade of Gaza is a land, air, and sea blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt after Hamas took control in 2007. It restricts the movement of people and goods, leading to a severe humanitarian crisis. |
| What are the main challenges in Gaza? | The main challenges include poverty, unemployment, shortages of essential supplies, limited access to healthcare, and the ongoing impact of repeated conflicts. |
| What is the role of the UN in Gaza? | The UN provides humanitarian assistance, monitors human rights, and works towards a peaceful resolution to the conflict. UN agencies like UNRWA support Palestinian refugees in Gaza. |
| What is the two-state solution? | The two-state solution proposes an independent Palestinian state in the West Bank and Gaza, with East Jerusalem as its capital, existing alongside Israel. This is a widely supported but currently stalled approach to resolving the conflict. |
| How does the conflict affect civilians? | The conflict has a devastating impact on civilians, leading to loss of life, displacement, psychological trauma, and a deterioration of living conditions. |
| What are the prospects for peace? | The prospects for peace remain uncertain due to unresolved issues and a lack of trust between the parties. However, international efforts continue to seek a lasting solution. |
| How can I help the people of Gaza? | You can help by supporting humanitarian organizations that provide assistance to Gaza, advocating for a peaceful resolution to the conflict, and raising awareness about the situation. |
| What are the long-term impacts of the conflict on Gaza’s infrastructure? | The repetitive conflicts have left Gaza’s infrastructure in ruins, which has disrupted access to basic necessities like healthcare and education. The restoration process is difficult and can take years due to the ongoing geopolitical environment. |
| What is the role of external actors in the Gaza conflict? | External parties, such as regional forces and international organizations, have a crucial impact on the conflict’s path. Mediation attempts, diplomatic involvement, and the provision of humanitarian aid are all examples of how outside actors have shaped Gaza’s situation. |

14. Useful Resources and Further Reading
To deepen your understanding of Gaza, here are some useful resources:
- United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA): Provides assistance and protection to Palestinian refugees.
- Human Rights Watch: Reports on human rights issues in Gaza and the region.
- B’Tselem: An Israeli human rights organization documenting human rights violations in the Occupied Territories.
15. Understanding the Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Gaza Strip | A self-governing Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. |
| Hamas | A Palestinian Sunni-Islamist fundamentalist organization that has controlled the Gaza Strip since 2007. |
| Blockade | A land, air, and sea blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt on the Gaza Strip since 2007. |
| Occupied Territories | Refers to the Palestinian territories occupied by Israel since the 1967 Six-Day War, including the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem. |
| UNRWA | United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East, providing assistance and protection to Palestinian refugees. |
| Intifada | Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupation. The First Intifada began in 1987, and the Second Intifada (also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada) began in 2000. |
| Two-State Solution | A proposed resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict that envisions an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, based on the pre-1967 borders. |
| Settlements | Israeli communities built on occupied Palestinian territories, considered illegal under international law. |
| Nakba | Arabic term meaning “catastrophe,” referring to the displacement and dispossession of Palestinians during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. |
| Ceasefire | A temporary cessation of hostilities, often brokered by external parties, aimed at halting violence and providing an opportunity for negotiations. |
| Humanitarian Aid | Assistance provided to alleviate suffering and meet basic needs during crises, including food, water, medicine, shelter, and other essential supplies. |
| Diplomatic Efforts | Negotiations and discussions between parties involved in the conflict, often facilitated by international mediators, aimed at finding a peaceful resolution. |
| Security Concerns | Issues related to the safety and protection of civilians, military personnel, and infrastructure, often cited as justification for military actions and security measures. |
16. Navigating the Socio-Political Landscape of Gaza
16.1. The Role of Political Parties
Gaza’s socio-political landscape is dominated by political parties that represent different ideological viewpoints and interests.
16.1.1. Hamas
Hamas is a Palestinian Sunni-Islamist fundamentalist organization that has governed the Gaza Strip since winning the 2006 Palestinian elections. As the de facto governing authority, Hamas oversees various aspects of governance, including security, social services, and infrastructure development.
16.1.2. Fatah
Fatah is a Palestinian political party and the largest faction within the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). While Fatah does not directly govern Gaza, it maintains a presence and influence in the region, particularly among segments of the population that align with its secular nationalist ideology.
16.2. Social Dynamics and Cultural Identity
Social dynamics and cultural identity in Gaza are deeply intertwined with the region’s history, politics, and socio-economic conditions.
16.2.1. Resilience and Resistance
Despite facing numerous challenges, including conflict, blockade, and socio-economic hardship, the people of Gaza have demonstrated remarkable resilience and resistance. Cultural expressions, such as art, music, and literature, often serve as a means of asserting Palestinian identity and challenging occupation.
16.2.2. Community Solidarity
Community solidarity plays a crucial role in Gaza’s social fabric, with families, neighbors, and local organizations providing support and assistance to those in need. This sense of collective responsibility is particularly evident during times of crisis, when communities come together to cope with adversity and rebuild their lives.
16.3. Challenges to Governance and Stability
Governance and stability in Gaza are undermined by a range of challenges, including political divisions, security threats, and socio-economic disparities.
16.3.1. Internal Political Divisions
The ongoing divide between Hamas and Fatah has hindered efforts to promote reconciliation, unity, and effective governance in the Palestinian territories. Resolving these internal political divisions is essential for addressing the broader challenges facing Gaza and advancing the Palestinian national cause.
16.3.2. Security Threats
Security threats, including militant activities, cross-border violence, and the presence of armed groups, pose a constant challenge to governance and stability in Gaza. Efforts to address these threats must prioritize the protection of civilians, adherence to international law, and the pursuit of peaceful solutions to conflict.
17. The Role of Media and Information
17.1. Media Landscape
The media landscape in Gaza is diverse but constrained by political and security realities. Several local news outlets, including television channels, radio stations, and online platforms, operate in the region, providing news and information to the public.
17.1.1. Local News Outlets
Local news outlets in Gaza play a crucial role in reporting on events, amplifying voices, and documenting the realities of life in the region. However, they often face challenges related to censorship, intimidation, and access restrictions, which can impact their ability to operate freely and independently.
17.1.2. International Media Coverage
International media coverage of Gaza tends to focus on moments of conflict, political developments, and humanitarian crises, often overlooking the everyday experiences and perspectives of ordinary people. While international media attention can raise awareness and mobilize support, it is essential to ensure that coverage is accurate, balanced, and contextualized.
17.2. Access to Information
Access to information in Gaza is affected by various factors, including physical infrastructure, connectivity, and political restrictions. While many people have access to internet and mobile devices, internet access is limited by infrastructure challenges and political restrictions.
17.2.1. Digital Divide
The digital divide between Gaza and the rest of the world poses a significant challenge to accessing information, education, and opportunities. Addressing this divide requires investing in digital infrastructure, promoting digital literacy, and ensuring equitable access to technology and resources.
17.2.2. Censorship and Surveillance
Censorship and surveillance are concerns in Gaza, where authorities monitor and regulate media content and online activities. These practices can stifle freedom of expression, limit access to diverse perspectives, and undermine democratic participation.
18. Testimonials and Personal Stories
18.1. Voices from Gaza
To truly understand the situation in Gaza, it’s essential to listen to the voices of those who live there. Here are a few testimonials and personal stories that shed light on the realities of life in Gaza:
18.1.1. Aisha, a Teacher
“Teaching in Gaza is both a privilege and a challenge. Despite the difficulties we face, I am committed to providing my students with the best education possible. I want them to have hope for the future and believe in their ability to make a difference.”
18.1.2. Ahmed, a Doctor
“Working as a doctor in Gaza is incredibly demanding. We are constantly dealing with shortages of medicine and equipment, and the trauma of repeated conflicts. But we are dedicated to saving lives and providing care to those who need it most.”
18.2. Sharing Experiences
Sharing these experiences helps to humanize the conflict and remind us of the real people behind the headlines. It’s important to amplify these voices and ensure that their stories are heard.
18.2.1. Community Initiatives
Many community initiatives aim to support and empower people in Gaza. These initiatives provide education, healthcare, job training, and other essential services. By supporting these initiatives, we can help to create a more resilient and sustainable future for Gaza.
18.2.2. Advocacy Efforts
Advocacy efforts play a crucial role in raising awareness about the situation in Gaza and calling for policy changes. These efforts include grassroots activism, lobbying, and international campaigns. By supporting these efforts, we can help to ensure that the voices of people in Gaza are heard by decision-makers around the world.
19. How WHAT.EDU.VN Can Help You Understand
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing accurate, accessible, and comprehensive information on complex topics like the situation in Gaza. We offer a range of resources, including articles, guides, and expert analyses, to help you understand the history, politics, and humanitarian issues at stake.
19.1. Free Question and Answer Platform
Our free question and answer platform allows you to ask any question and receive answers from knowledgeable experts and community members. This is a valuable tool for deepening your understanding of Gaza and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
19.2. Expert Analysis
We work with experts in the field to provide insightful analysis and commentary on the situation in Gaza. Our experts offer diverse perspectives and help to contextualize the events on the ground.
20. Call to Action
Do you have questions about Gaza or any other topic? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question for free. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with the answers you need.
20.1. Ask Your Questions
Whether you’re a student, a researcher, or simply someone who wants to learn more, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. Don’t hesitate to ask your questions and explore our wealth of resources.
20.2. Contact Information
For further information, please contact us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
At what.edu.vn, we believe that access to information is essential for creating a more informed and engaged world. Join us in our mission to provide free, reliable, and comprehensive knowledge to everyone.