Gastro, also known as gastroenteritis, is a widespread ailment affecting the digestive system, causing discomfort and disruption. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we aim to provide clear, accessible information to help you understand, manage, and prevent gastro. Explore causes, symptoms, and treatments to regain control of your digestive health with practical advice and reliable resources on digestive health.
1. Defining Gastroenteritis: What Is Gastro?
Gastroenteritis, commonly known as “gastro,” is an inflammation of the digestive tract, specifically the stomach and intestines. This condition leads to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms affecting people of all ages. It’s typically caused by a viral or bacterial infection, leading to irritation and impaired function of the digestive system. Understanding the fundamentals of gastroenteritis is the first step toward effective management and prevention.
1.1. Understanding the Digestive System’s Role
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. It includes organs such as the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. When gastro strikes, it disrupts this process, leading to symptoms like vomiting and diarrhea. Knowing how these organs function can help you appreciate the impact of gastro on your overall health.
1.2. Gastro vs. Food Poisoning: Is There a Difference?
While the terms “gastro” and “food poisoning” are often used interchangeably, there are distinctions. Food poisoning is a type of gastroenteritis caused specifically by consuming contaminated food containing bacteria, viruses, or toxins. Gastro, on the other hand, can result from various sources, including person-to-person transmission of viruses. Recognizing the cause can help guide appropriate treatment and prevention strategies.
1.3. Common Misconceptions About Gastroenteritis
Many misconceptions surround gastroenteritis. Some people believe it’s always caused by food poisoning, while others think it’s simply a severe stomach ache. Understanding the true nature of gastro, its causes, and its symptoms can help you take appropriate action and seek timely medical advice when needed.
2. Identifying the Culprits: What Causes Gastro?
Gastroenteritis can be triggered by a variety of factors, including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and even certain medications. Understanding the specific cause of your gastro is essential for effective treatment and preventing future occurrences. Let’s explore the most common causes and how they lead to gastro.
2.1. Viral Gastroenteritis: The Most Common Cause
Viruses are the most frequent culprits behind gastroenteritis. Common viral offenders include norovirus and rotavirus. These viruses are highly contagious and spread through contaminated food, water, or surfaces, as well as close contact with infected individuals. Knowing how these viruses spread can help you take preventive measures to protect yourself and your family.
2.2. Bacterial Gastroenteritis: When Bacteria Attack
Bacteria can also cause gastroenteritis, often through contaminated food or water. Common bacterial culprits include Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter. These bacteria can trigger inflammation and infection in the digestive tract, leading to symptoms like diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Practicing proper food handling and hygiene can minimize your risk of bacterial gastro.
2.3. Parasitic Gastroenteritis: Less Common but Still a Threat
Parasites are less common causes of gastroenteritis but can still pose a threat, especially in areas with poor sanitation or contaminated water sources. Giardia and Cryptosporidium are examples of parasites that can cause gastro. These parasites can lead to prolonged diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms. Awareness of parasitic risks and proper sanitation practices can help prevent infection.
2.4. Other Potential Causes of Gastroenteritis
While viruses, bacteria, and parasites are the primary causes of gastroenteritis, other factors can also contribute. Certain medications, food sensitivities, and underlying medical conditions can sometimes trigger gastro-like symptoms. Recognizing these potential causes can help you identify triggers and manage your symptoms effectively.
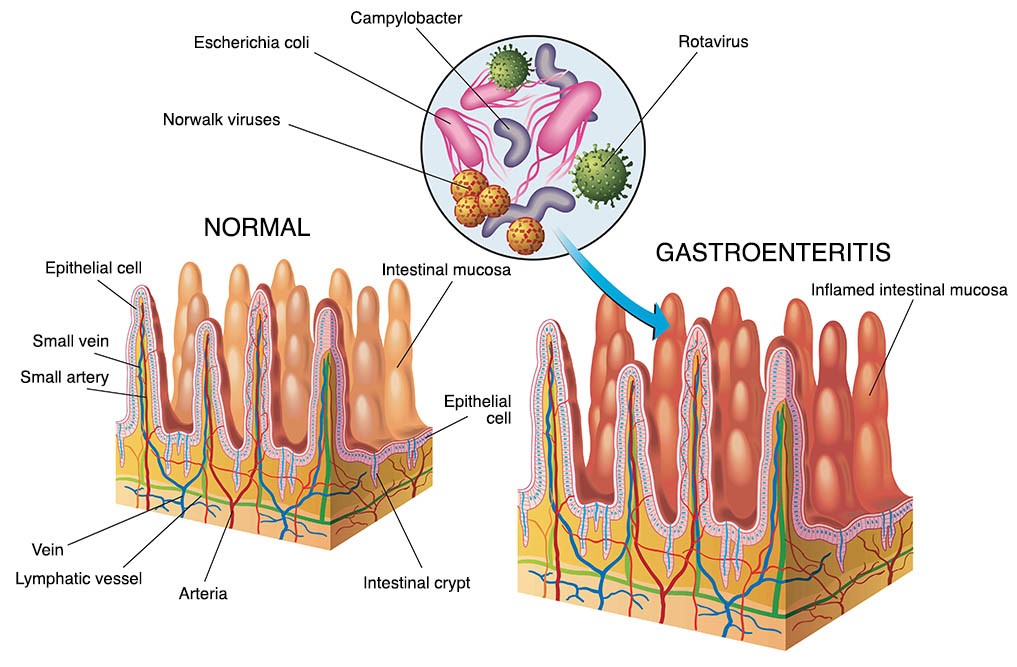 Gastroenteritis inflames the lining of the stomach and intestines
Gastroenteritis inflames the lining of the stomach and intestines
3. Spotting the Signs: What Are the Symptoms of Gastro?
Gastroenteritis presents with a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity depending on the cause and individual factors. Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for prompt treatment and preventing complications. Let’s explore the most common symptoms of gastro.
3.1. Nausea and Vomiting: The Body’s Defense Mechanism
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of gastroenteritis as the body attempts to rid itself of harmful substances. These symptoms can be distressing and lead to dehydration if not managed properly. Staying hydrated and avoiding trigger foods can help alleviate nausea and vomiting.
3.2. Diarrhea: The Intestinal Uprising
Diarrhea is another hallmark symptom of gastroenteritis, characterized by frequent, loose, or watery stools. Diarrhea occurs when the digestive tract becomes inflamed and unable to absorb fluids properly. Staying hydrated is essential to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
3.3. Abdominal Pain and Cramping: The Gut’s Distress Signals
Abdominal pain and cramping are common complaints among individuals with gastroenteritis. These symptoms result from inflammation and irritation of the digestive tract. Gentle heat, rest, and avoiding trigger foods can help relieve abdominal discomfort.
3.4. Other Common Symptoms of Gastroenteritis
In addition to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, gastroenteritis can also cause other symptoms, such as:
- Fever: Elevated body temperature as the body fights infection.
- Headache: Pain or discomfort in the head.
- Muscle Aches: Generalized pain or soreness in the muscles.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or lacking energy.
Recognizing these symptoms can help you differentiate gastro from other illnesses and seek appropriate medical care.
4. Diagnosing Gastroenteritis: When to See a Doctor
In many cases, gastroenteritis resolves on its own with supportive care at home. However, certain situations warrant medical attention to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. Knowing when to see a doctor is crucial for protecting your health.
4.1. When to Seek Medical Attention for Adults
Adults should seek medical attention for gastroenteritis if they experience any of the following:
- Severe Dehydration: Signs include decreased urination, dizziness, and extreme thirst.
- High Fever: A temperature of 103°F (39.4°C) or higher.
- Bloody Stools: Presence of blood in the stool.
- Persistent Vomiting: Inability to keep down fluids.
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Intense or worsening abdominal pain.
These symptoms may indicate a more serious infection or complication that requires medical intervention.
4.2. When to Seek Medical Attention for Children
Children are more vulnerable to complications from gastroenteritis, so it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly if they experience any of the following:
- Signs of Dehydration: Dry mouth, sunken eyes, and decreased urination.
- High Fever: A temperature of 102°F (38.9°C) or higher.
- Bloody Diarrhea: Presence of blood in the stool.
- Persistent Vomiting: Inability to keep down fluids.
- Lethargy: Unusual drowsiness or lack of energy.
Prompt medical evaluation can help prevent dehydration and other serious complications in children.
4.3. Diagnostic Tests for Gastroenteritis
In some cases, doctors may order diagnostic tests to determine the cause of gastroenteritis and guide treatment. Common tests include:
- Stool Culture: Identifies bacteria, viruses, or parasites in the stool sample.
- Blood Tests: Evaluates electrolyte levels and assesses hydration status.
- Physical Examination: Assessing symptoms and overall health.
These tests can help doctors tailor treatment to the specific cause of gastroenteritis.
5. Treatment Strategies: How to Manage Gastroenteritis
Most cases of gastroenteritis can be effectively managed at home with supportive care and attention to hydration and diet. Treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms, preventing dehydration, and allowing the digestive system to recover.
5.1. Hydration: The Cornerstone of Treatment
Staying hydrated is essential for managing gastroenteritis, as vomiting and diarrhea can lead to significant fluid loss. Drink plenty of clear fluids, such as water, oral rehydration solutions (ORS), or diluted juices. Avoid sugary drinks, as they can worsen diarrhea.
5.2. Dietary Adjustments: Eating for Recovery
During gastroenteritis, it’s essential to make dietary adjustments to ease the burden on the digestive system. Stick to bland, easy-to-digest foods, such as:
- Bananas: Gentle on the stomach and provide potassium.
- Rice: Easy to digest and helps absorb fluids.
- Applesauce: Provides fiber and nutrients.
- Toast: Plain toast can help settle the stomach.
Avoid fatty, spicy, or overly processed foods, as they can worsen symptoms.
5.3. Medications: When Are They Necessary?
In most cases, medications are not necessary for treating gastroenteritis, as it typically resolves on its own. However, certain situations may warrant medication, such as:
- Anti-diarrheal Medications: May be used to reduce diarrhea symptoms in adults, but should be used with caution and under medical supervision.
- Anti-emetic Medications: Can help relieve nausea and vomiting.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed for bacterial gastroenteritis, but not effective against viral infections.
Always consult a healthcare professional before taking any medications for gastroenteritis.
5.4. Probiotics: Restoring Gut Health
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore balance to the gut microbiome after gastroenteritis. Probiotics may help reduce the duration and severity of symptoms, especially diarrhea. You can find probiotics in yogurt, fermented foods, or dietary supplements.
6. Prevention is Key: How to Avoid Gastroenteritis
Preventing gastroenteritis involves practicing good hygiene, food safety, and vaccination when available. Taking proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk of contracting and spreading gastro.
6.1. Hand Hygiene: The First Line of Defense
Washing your hands frequently with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of gastroenteritis. Wash your hands thoroughly after using the bathroom, before preparing food, and after contact with sick individuals.
6.2. Food Safety: Preventing Contamination
Practicing proper food safety is essential for preventing foodborne gastroenteritis. Follow these guidelines:
- Wash: Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating.
- Cook: Cook foods to the recommended internal temperature.
- Separate: Prevent cross-contamination by keeping raw and cooked foods separate.
- Chill: Refrigerate perishable foods promptly.
6.3. Vaccination: Protecting Against Rotavirus
Rotavirus is a common cause of gastroenteritis in infants and young children. Vaccination against rotavirus is highly effective in preventing severe illness. Consult with your pediatrician about vaccinating your child against rotavirus.
6.4. Other Preventive Measures
In addition to hand hygiene, food safety, and vaccination, other preventive measures include:
- Avoid Close Contact: Limit contact with individuals who are sick.
- Clean and Disinfect: Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces, especially in bathrooms and kitchens.
- Safe Water: Drink safe, clean water, especially when traveling.
7. Special Considerations: Gastroenteritis in Specific Populations
Gastroenteritis can present unique challenges for certain populations, such as infants, children, pregnant women, and older adults. Understanding these special considerations is essential for providing appropriate care and support.
7.1. Gastroenteritis in Infants and Children
Infants and children are more vulnerable to complications from gastroenteritis, particularly dehydration. Ensure they receive plenty of fluids, such as breast milk, formula, or oral rehydration solutions. Monitor for signs of dehydration and seek medical attention promptly if needed.
7.2. Gastroenteritis During Pregnancy
Gastroenteritis during pregnancy can be concerning due to the potential impact on both the mother and the developing fetus. Pregnant women should stay well-hydrated and seek medical attention if they experience severe symptoms. Avoid certain medications that may be harmful during pregnancy.
7.3. Gastroenteritis in Older Adults
Older adults are at higher risk of complications from gastroenteritis, such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. They may also have underlying medical conditions that can be exacerbated by gastro. Ensure older adults receive adequate hydration and medical care as needed.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gastroenteritis
Here are some frequently asked questions about gastroenteritis to address common concerns and provide further clarification.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How long does gastroenteritis typically last? | Most cases of gastroenteritis resolve within a few days to a week. |
| Is gastroenteritis contagious? | Yes, gastroenteritis is highly contagious, especially viral forms. |
| Can I prevent gastroenteritis? | Practicing good hygiene, food safety, and vaccination can help prevent gastroenteritis. |
| When should I see a doctor for gastroenteritis? | Seek medical attention if you experience severe dehydration, high fever, bloody stools, persistent vomiting, or severe abdominal pain. |
| What should I eat during gastroenteritis? | Stick to bland, easy-to-digest foods like bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast. |
| How can I stay hydrated during gastroenteritis? | Drink plenty of clear fluids, such as water, oral rehydration solutions (ORS), or diluted juices. |
| Are there any medications I should avoid? | Avoid sugary drinks, as they can worsen diarrhea. Consult a healthcare professional before taking any medications. |
| Is it safe to breastfeed during gastroenteritis? | Yes, it is safe and encouraged to continue breastfeeding during gastroenteritis. |
| Can probiotics help with gastroenteritis? | Probiotics may help restore balance to the gut microbiome and reduce the duration and severity of symptoms. |
| How can I prevent spreading gastroenteritis to others? | Wash your hands frequently, avoid close contact with sick individuals, and clean and disinfect surfaces regularly. |
| What are the most common causes of gastroenteritis? | Viruses (such as norovirus and rotavirus) are the most common causes, followed by bacteria (such as Salmonella and E. coli) and parasites (such as Giardia). |
| Can stress cause gastroenteritis? | While stress doesn’t directly cause infectious gastroenteritis, it can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Additionally, stress can worsen symptoms of existing digestive issues. |
| Is there a vaccine for gastroenteritis? | Yes, there is a vaccine for rotavirus, which is a common cause of gastroenteritis in infants and young children. The rotavirus vaccine is typically given in a series of doses during infancy. |
| What is the difference between gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? | Gastroenteritis is an acute infection of the digestive system, usually caused by a virus, bacteria, or parasite, resulting in temporary inflammation and symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. IBS is a chronic functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or both) without evidence of infection or inflammation. |
| Can I get gastroenteritis from contaminated surfaces? | Yes, you can get gastroenteritis from contaminated surfaces if you touch them and then touch your mouth, nose, or eyes without washing your hands. Viruses and bacteria can survive on surfaces for hours or even days. |
9. Navigating the Digital Landscape: Online Resources for Gastroenteritis
In today’s digital age, a wealth of online resources is available to help you learn more about gastroenteritis and access support. However, it’s essential to evaluate the credibility and reliability of these resources to ensure you’re receiving accurate information.
9.1. Reliable Websites and Online Resources
When searching for information about gastroenteritis online, look for reputable sources, such as:
- Medical Organizations: Websites of medical organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Government Health Agencies: Websites of government health agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
- Academic Institutions: Websites of universities and research institutions.
- Healthcare Providers: Websites of hospitals and clinics.
These sources provide evidence-based information and expert guidance on gastroenteritis.
9.2. Evaluating the Credibility of Online Information
When evaluating online information about gastroenteritis, consider the following:
- Source: Is the source reputable and trustworthy?
- Author: Is the author qualified to provide medical advice?
- Evidence: Is the information supported by scientific evidence?
- Date: Is the information up-to-date?
- Bias: Is the information free from bias or commercial influence?
Be cautious of websites that promote unproven remedies or make exaggerated claims.
9.3. Online Support Communities and Forums
Online support communities and forums can provide valuable peer support and emotional encouragement for individuals dealing with gastroenteritis. However, it’s essential to exercise caution and discretion when participating in these communities.
- Protect Your Privacy: Avoid sharing personal information or medical details online.
- Seek Professional Advice: Don’t rely solely on advice from other members; consult with a healthcare professional for medical guidance.
- Be Respectful: Treat other members with respect and empathy.
Online support communities can be a helpful resource, but they should not replace professional medical care.
10. WHAT.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Health Education
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing accessible, accurate, and trustworthy health information to empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Whether you have questions about gastroenteritis or any other health topic, we’re here to help.
10.1. Free Question-Answering Services
Do you have questions about gastroenteritis or any other health concern? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN and ask your questions for free. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing clear, concise, and evidence-based answers to help you understand your health and make informed decisions.
10.2. Expert-Reviewed Content
All of our content is meticulously reviewed by healthcare professionals to ensure accuracy and reliability. You can trust that the information you find on WHAT.EDU.VN is up-to-date and evidence-based.
10.3. Easy Access to Information
Our website is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to everyone. Whether you’re using a computer, tablet, or smartphone, you can easily find the information you need to take control of your health.
Don’t let gastroenteritis disrupt your life. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get the answers you need to stay healthy and informed.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Are you struggling to find quick, reliable answers to your health questions? Do you feel lost in the sea of medical information online? You’re not alone. Many people face challenges in finding trustworthy and easy-to-understand health advice. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand these challenges, and we’re here to provide you with a solution. We offer a free platform where you can ask any health-related question and receive prompt, accurate answers from our team of experts. Don’t let uncertainty and confusion hold you back. Visit what.edu.vn today and experience the convenience and peace of mind that comes with having access to reliable health information. Let us help you navigate the complexities of health and wellness.
