What Is Good Credit? Knowing the answer is crucial for financial health. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we break down credit scores, explain what impacts them, and offer insights on building and maintaining a positive credit history. A better credit rating can unlock favorable interest rates and financial opportunities, ensuring a brighter future. Let’s explore the world of creditworthiness and financial responsibility together.
1. Understanding Good Credit
What constitutes good credit? It’s a question many people ask as they navigate the world of finance. Generally, a credit score ranging from the mid-600s to the high 600s and above is considered good. Scores in the high 700s or 800s are deemed excellent. Credit scores typically range from 300 to 850. A substantial portion of consumers achieve these levels of creditworthiness. In fact, a significant percentage have FICO Scores that fall within the 600 to 750 range, with an even larger percentage exceeding that. The average FICO Score in the U.S. was 715 in 2023.
Lenders assess various criteria when deciding whom to lend to and at what interest rates. However, maintaining a higher credit score can significantly improve your chances of qualifying for credit cards or loans with lower interest rates and more favorable terms. Two primary types of credit scores are used: FICO Scores and VantageScore credit scores. While their ranges may differ slightly, they share similar scoring factors.
2. FICO Score: Defining “Good”
2.1 The Good FICO Score Range
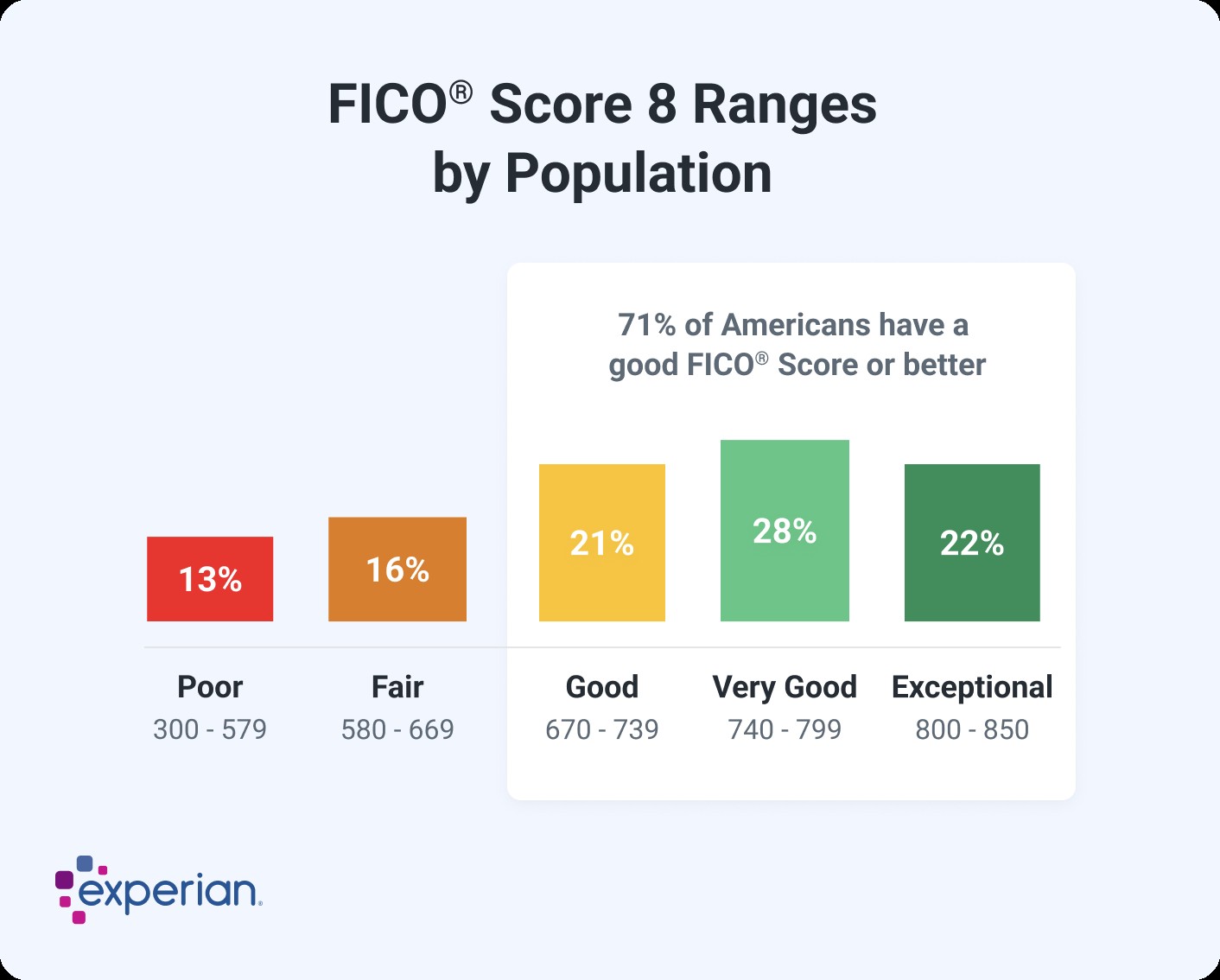
When evaluating credit scores, the base FICO Scores range from 300 to 850. A credit score between 670 and 739 is considered within the good range.
FICO develops various types of consumer credit scores tailored for different industries. These include “base” FICO Scores used by lenders across multiple sectors and industry-specific credit scores designed for credit card issuers and auto lenders. It’s important to note that FICO’s industry-specific credit scores have a different range, spanning from 250 to 900. Despite the variations in ranges, the middle categories remain consistent, with a “good” industry-specific FICO Score still falling between 670 and 739. Scores exceeding this range are classified as very good or exceptional.
2.2 The Importance of Understanding FICO Scores
Understanding what constitutes a good FICO score is essential for managing your financial health. A good score can open doors to better interest rates on loans and credit cards, potentially saving you thousands of dollars over time. Regularly checking your FICO score and understanding the factors that influence it can help you maintain or improve your creditworthiness.
3. VantageScore: Defining “Good”
3.1 The Good VantageScore Range
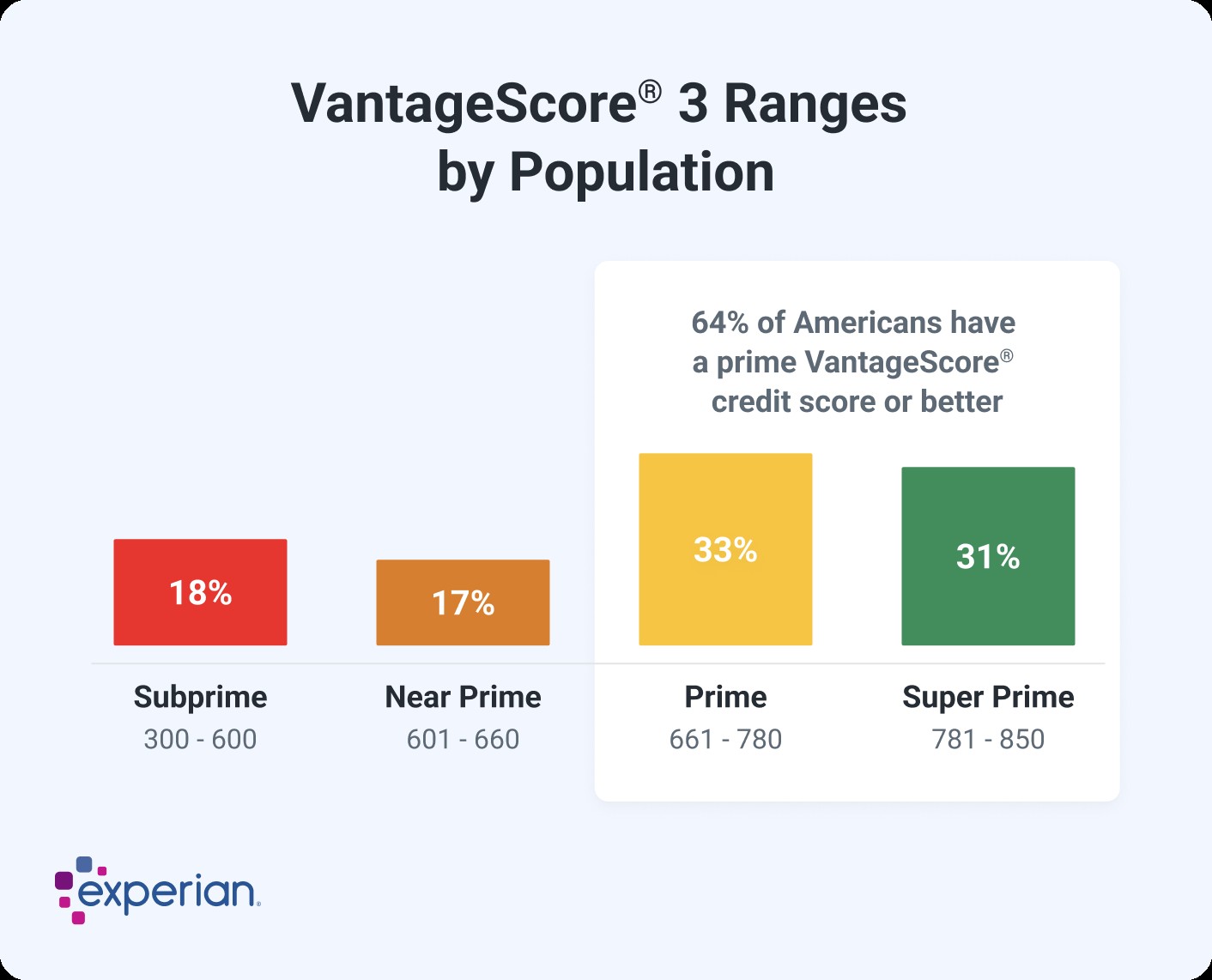
The latest VantageScore 3.0 and 4.0 credit scores also use a range of 300 to 850, aligning with the base FICO Scores. According to VantageScore, a good score falls between 661 and 780.
VantageScore does not offer industry-specific credit scores, but it has introduced updated models over the years. The initial two VantageScore credit scores operated on a range of 501 to 990. However, these scores are not commonly used by lenders.
3.2 How VantageScore Differs from FICO
While both FICO and VantageScore are widely used, they have some key differences. VantageScore tends to be more lenient for individuals with limited credit history, while FICO is often preferred by mortgage lenders. Understanding these differences can help you better interpret your credit scores and make informed financial decisions.
4. Factors Affecting Your Credit Scores
4.1 Common Factors Influencing Credit Scores
Several common factors can impact all your credit scores, regardless of whether they are FICO or VantageScore. These factors generally fall into the following categories:
- Payment History: Your track record of making payments on time.
- Amounts Owed: The total amount of debt you owe and your credit utilization ratio.
- Length of Credit History: The age of your credit accounts.
- Credit Mix: The variety of credit accounts you have.
- New Credit: Recent credit applications and new accounts opened.
4.2 FICO Score Factors
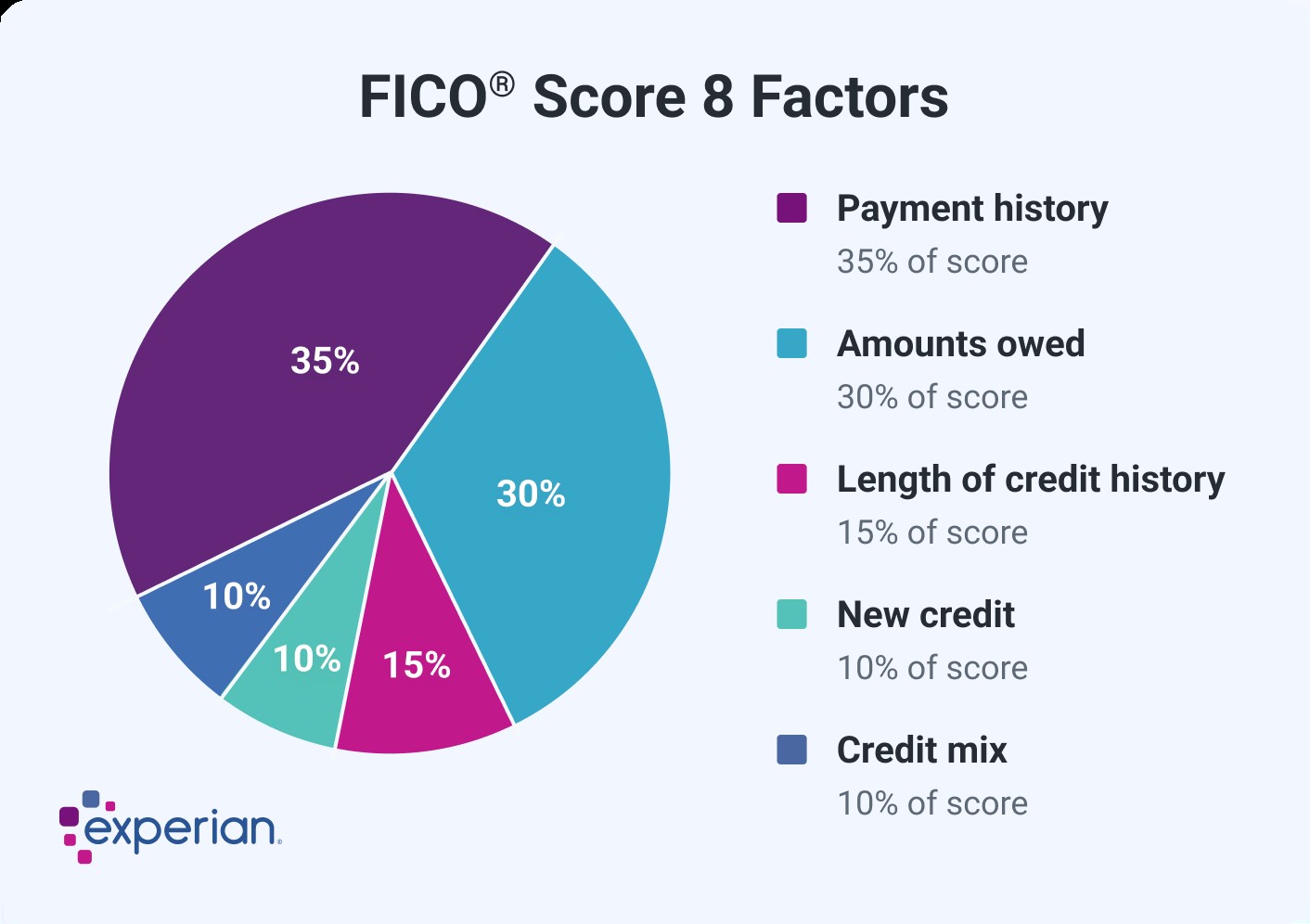
FICO uses percentages to represent the relative importance of each category. However, the specific percentage breakdown used to determine your credit score will depend on your unique credit report. FICO considers scoring factors in the following order of importance:
- Payment History (35%): The most significant factor.
- Amounts Owed (30%): Your debt levels and credit utilization.
- Length of Credit History (15%): How long you’ve had credit accounts.
- Credit Mix (10%): The variety of your credit accounts.
- New Credit (10%): Recent credit activity.
4.3 VantageScore Credit Score Factors
VantageScore lists the factors by how influential they generally are in determining a credit score. This also depends on your individual credit report. VantageScore considers factors in the following order:
| VantageScore Credit Scoring Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Payment history | Extremely influential |
| Total credit usage | Highly influential |
| Credit mix and experience | Highly influential |
| New accounts opened | Moderately influential |
| Balances and available credit | Less influential |

4.4 Information Not Considered in Credit Scores
It’s important to note that FICO and VantageScore do not consider certain information when calculating credit scores. This includes factors such as your race, religion, national origin, gender, marital status, and employment history. Additionally, information like your income, savings, and investment accounts are not directly factored into your credit scores.
5. Good Credit for Buying a Home
5.1 Credit Score Requirements for Mortgages
To increase your chances of approval and secure a lower-rate mortgage, it’s advisable to aim for a credit score in the good range or higher. A FICO Score of at least 670 is generally recommended. The minimum credit score needed to buy a house can vary, typically ranging from around 500 to 700. This depends on the type of mortgage loan you’re applying for and the lender’s requirements. Many lenders require a minimum credit score of 620 for a conventional mortgage. Other types of mortgages have different credit score requirements:
| Minimum Credit Score for Government-Backed Mortgages |
|---|
| FHA home loans |
| USDA loans |
| VA loans |
5.2 The Impact of Credit Score on Mortgage Terms
Your credit score plays a crucial role in determining the interest rate and payment terms of a mortgage loan. Lenders base the interest they charge on how risky they perceive you as a borrower. While it may be possible to get a mortgage with bad credit, it’s generally better to improve your score before applying for a mortgage. A higher credit score can result in significant savings over the life of the loan.
6. Good Credit for Buying a Car
6.1 Credit Score Requirements for Auto Loans
While there isn’t a specific minimum credit score required to buy a car, a VantageScore credit score of 661 or higher is generally considered good. Qualifying for better auto loan terms typically becomes easier as your score increases.
Auto lenders view low credit scores as a sign of risk. An applicant with poor or fair credit will likely pay more in interest and might receive a lower loan limit. If you don’t have a good score, it’s advisable to improve your credit before buying a car.
6.2 The Impact of Credit Score on Auto Loan Terms
The interest rate you receive on an auto loan is directly tied to your credit score. A good credit score can save you hundreds or even thousands of dollars over the life of the loan. Conversely, a low credit score can result in higher interest rates and less favorable terms.
7. Why Different Credit Scores Exist
7.1 The Credit Scoring Landscape
Many different credit scores exist because credit scoring companies continually update and sell their scores to lenders. Lenders use credit scores to make lending and account management decisions, such as whom to approve and whether to change your credit limit. For the most part, lenders can choose which model they want to use.
FICO and VantageScore create and sell different credit scoring models. Both companies periodically release new versions of their credit scores, similar to how a software company might offer a new operating system.
7.2 VantageScore’s Different Credit Scores
VantageScore creates a generic tri-bureau scoring model, meaning the score is designed for any type of lender. The same model can evaluate your credit reports from the three major consumer credit bureaus (Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax).
VantageScore launched its first model, the VantageScore 1.0, in 2006. In 2017, it released VantageScore 4.0, which was the first generic credit score to use trended data.
VantageScore announced its VantageScore 4plus™ model in May 2024. This model allows creditors to ask consumers if they would like to link a bank account and share their banking data.
| VS 3.0 | VS 4.0 | VS 4plus |
|---|---|---|
| Only considers data from a credit report | Only considers data from a credit report | Only considers data from a credit report |
| Considers trended data | Considers trended data | |
| Can consider additional data |
7.3 FICO’s Different Credit Scores
In 1989, FICO became the first company to create credit scoring models based on consumer credit reports. Although recent FICO Score versions share a common name, such as FICO Score 8, FICO creates different versions of the models for each credit bureau.
There are three general types of consumer FICO Scores:
- Base FICO Scores: These scores are created for any type of lender and range from 300 to 850.
- Industry-specific FICO Scores: FICO creates auto scores and bankcard scores specifically for auto lenders and card issuers.
- FICO Scores that use alternative data: FICO has models that can incorporate alternative credit data, such as the UltraFICO and FICO XD scores.
7.4 Lender Choice in Credit Scores
Lenders can choose which of your credit reports to request and which score, or scores, to receive. You often won’t know which report or score the lender will use. Lenders might change their preferences or test different approaches.
Most FICO and VantageScore credit scores rely on the same underlying information from one of your credit reports. They also all aim to make the same prediction: the likelihood that a person will become 90 days past due on a bill within the next 24 months.
8. The Importance of a Good Credit Score
8.1 Benefits of Having Good Credit
Having good credit can make achieving your financial goals easier. It could be the difference between qualifying or being denied for an important loan, such as a home mortgage or car loan. It can also directly impact how much you’ll have to pay in interest or fees if you’re approved.
For example, the difference between taking out a 30-year, fixed-rate $350,000 mortgage with a 620 FICO Score and a 700 FICO Score could be significant. A better score would save you money in interest payments over the lifetime of the loan.
8.2 Non-Lending Decisions Influenced by Credit Scores
Credit scores can also impact non-lending decisions, such as whether a landlord will agree to rent you an apartment. Some employers may review your credit reports before making a hiring or promotion decision. In most states, insurance companies may use credit-based insurance scores to help determine your premiums for auto, home, and life insurance.
| FICO® Score | Interest Rate, 30-Year Fixed-Rate Mortgage | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 620 | 7.71% | $2,806.11 | $549,199 |
| 700 | 7.13% | $2,667.53 | $499,310 |
| 840 | 6.69% | $2,564.49 | $462,214 |
8.3 Real-World Impact of Credit Scores
The real-world impact of credit scores extends beyond just loans and credit cards. Your creditworthiness can affect your ability to secure housing, employment, and even insurance coverage. Maintaining a good credit score is an investment in your overall financial well-being.
9. How to Improve Your Credit Scores
9.1 Steps to Enhance Creditworthiness
To improve your credit scores, focus on the underlying factors that affect your scores. The basic steps you need to take are fairly straightforward:
- Pay Bills on Time: Make all payments on or before the due date.
- Lower Credit Utilization: Keep your credit card balances low.
- Review Credit Reports: Check for errors and dispute them.
- Avoid Opening Too Many New Accounts: Limit new credit applications.
9.2 Additional Factors to Consider
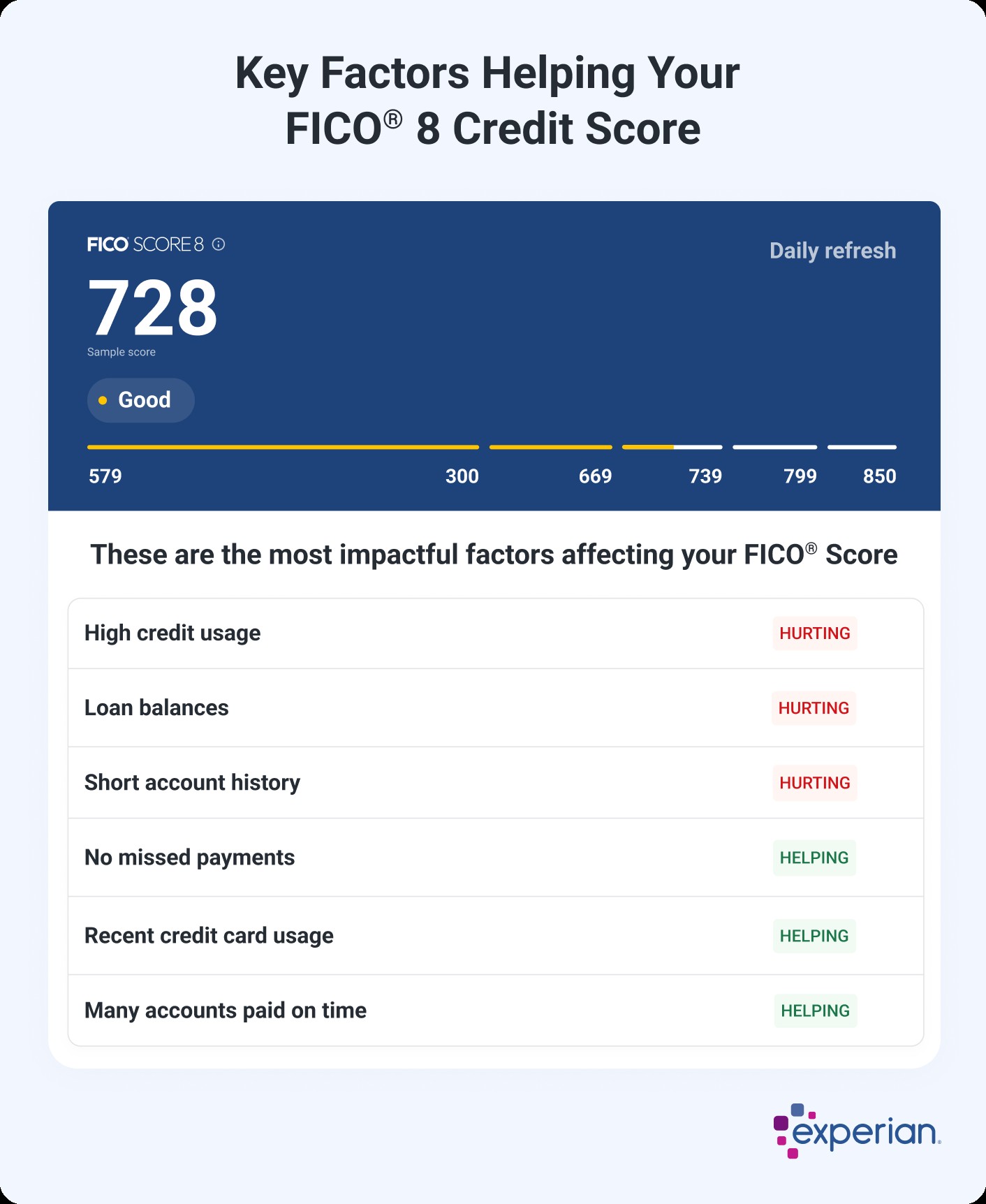
Increasing the average age of your accounts could help your scores. Checking your credit scores might also give you insight into what you can do to improve them. For example, when you check your FICO Score 8 from Experian for free, you can get an overview of how lenders see you based on your credit.
9.3 Understanding Your Credit Profile
You’ll also get an overview of your score profile, with an explanation of what’s helping and hurting your score the most. This personalized feedback can help you target specific areas for improvement.
10. What to Do If You Don’t Have a Credit Score
10.1 Establishing a Credit History
Credit scoring models can’t score credit reports that don’t have enough information. For FICO Scores, you need:
- An account that’s at least six months old
- An account that has been active in the past six months
VantageScore can score your credit report if it has at least one active account, even if the account is only a month old.
10.2 Steps to Build Credit
If you aren’t scoreable, you can:
- Become an authorized user on someone else’s credit card.
- Apply for a secured credit card.
- Take out a credit-builder loan.
- Use a service like Experian Boost to add utility and telecom payments to your credit report.
10.3 Alternative Credit Data
Exploring alternative credit data can be a valuable option if you have limited or no traditional credit history. By leveraging sources like utility bills and rent payments, you can demonstrate your creditworthiness and gradually build a positive credit profile.
11. Why Your Credit Score Changed
11.1 Factors Influencing Credit Score Fluctuations
Your credit score can change for many reasons, and it’s not uncommon for scores to move up or down throughout the month as new information gets added to your credit reports.
-
Credit scores might increase if:
- Negative items fall off your credit report.
- You lower your credit utilization rate.
- You pay off or settle collection accounts.
- You add new on-time payments to your credit report.
-
Credit scores might decrease if:
- A credit card or loan payment becomes 30 days past due.
- Your credit utilization rate increases.
- You apply for or open a new credit account.
- You file for bankruptcy.
11.2 Unexpected Impacts on Credit Scores
Some actions might have an unexpected impact on your credit scores. Paying off a loan, for example, could lead to a score drop even though it’s a positive action. Additionally, credit scoring models use complicated calculations to determine a score.
11.3 Understanding Score Variations
Understanding why your credit score changed requires careful analysis of your credit report and the factors that influence your score. By identifying the specific reasons behind score fluctuations, you can take targeted actions to improve or maintain your creditworthiness.
12. Monitoring Your Credit Report and Score
12.1 The Importance of Regular Monitoring
Checking your credit score right before you apply for a new loan or credit card can help you understand your chances of getting approved and qualifying for favorable terms. Regularly checking it further ahead of time gives you the chance to improve your scores.
12.2 Free Credit Monitoring Services
You can check and monitor your FICO Score and credit report for free from Experian with daily updates and real-time alerts for suspicious changes in your report. A free account also offers free credit-building features, like Experian Boost, and insights into your credit history and score.
12.3 Proactive Credit Management
Proactive credit management involves regularly monitoring your credit report and score, identifying areas for improvement, and taking consistent action to build and maintain good credit. By staying informed and engaged, you can take control of your financial health and achieve your goals.
13. FAQs About Good Credit
13.1 Common Questions About Credit Scores
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between a FICO score and a VantageScore? | FICO scores are the most widely used type of credit score, while VantageScores are a newer model that is gaining popularity. FICO scores place more emphasis on payment history and amounts owed, while VantageScores give more weight to credit mix and credit utilization. |
| How often should I check my credit score? | It is recommended to check your credit score at least once a year, or more frequently if you are planning to apply for a loan or credit card. |
| What is a good credit utilization ratio? | A good credit utilization ratio is generally considered to be below 30%. This means that you should aim to keep your credit card balances below 30% of your credit limit. |
| How long does it take to build good credit? | Building good credit takes time and consistency. It can take several months to a year or more to establish a good credit history, depending on your starting point and the actions you take to improve your credit. |
| Can I get a loan with bad credit? | It is possible to get a loan with bad credit, but you will likely pay a higher interest rate and have less favorable terms. It is generally recommended to improve your credit score before applying for a loan, if possible. |
| What is the impact of closing a credit card account? | Closing a credit card account can have a negative impact on your credit score, especially if it is an older account or has a high credit limit. Closing an account can reduce your overall available credit and increase your credit utilization ratio. |
| How do I dispute errors on my credit report? | To dispute errors on your credit report, you will need to contact the credit bureau that issued the report and provide documentation to support your claim. The credit bureau is required to investigate the dispute and correct any errors within 30 days. |
| What are the benefits of having good credit? | Having good credit can save you money on loans and credit cards, make it easier to rent an apartment or buy a home, and even improve your chances of getting a job. Good credit can also provide access to better insurance rates and other financial benefits. |
| How does bankruptcy affect my credit score? | Bankruptcy can have a significant negative impact on your credit score and can remain on your credit report for up to 10 years. It is important to consider the long-term consequences of bankruptcy before making a decision. |
| What is the difference between a secured and unsecured credit card? | A secured credit card requires you to make a cash deposit as collateral, while an unsecured credit card does not. Secured credit cards are often used by people with limited or no credit history to build credit, while unsecured credit cards are typically offered to people with good credit. |
13.2 Expert Insights on Credit Management
Obtaining expert insights on credit management can provide valuable guidance and strategies for building and maintaining good credit. Financial advisors, credit counselors, and other professionals can offer personalized advice tailored to your unique circumstances.
14. Call to Action
Navigating the complexities of credit scores doesn’t have to be daunting. WHAT.EDU.VN is here to simplify the process and provide you with the knowledge you need to achieve your financial goals.
Do you have questions about your credit score or how to improve it?
Don’t hesitate to reach out to us at WHAT.EDU.VN for free, expert advice. Our team is dedicated to providing clear, concise answers to all your credit-related inquiries.
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question!
Let us help you unlock the doors to better financial opportunities.
Contact Information:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn
