What is half of 1/4 cup? Understanding fractions and measurements is essential in cooking and baking, but it can be confusing. This guide from WHAT.EDU.VN simplifies the process, providing clear explanations and helpful tips. Master kitchen measurements for perfect recipes with ease, and discover recipe scaling today.
1. Understanding Cup Measurements
Before diving into halving 1/4 cup, let’s establish a clear understanding of cup measurements and their relationship to other common units. A cup is a standard unit of volume, widely used in both cooking and baking for measuring liquid and dry ingredients. However, its precise equivalent in other units may vary slightly depending on the system used (US customary or metric).
1.1. Cup in US Customary Units
In the US customary system, which is commonly used in the United States, a cup is defined as:
- 8 fluid ounces
- 1/2 pint
- 1/4 quart
- 1/16 gallon
It’s important to note that a “fluid ounce” is a unit of volume, not weight. This distinction is crucial when measuring ingredients with different densities.
1.2. Cup in Metric Units
In the metric system, which is used in most other parts of the world, a cup is typically defined as 250 milliliters (mL). This is slightly different from the US customary cup, which is approximately 236.6 mL. While the difference may seem small, it can become significant when scaling recipes or converting measurements.
1.3. Conversion Table
Here’s a quick conversion table for reference:
| Unit | US Customary | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Cup | 8 fluid ounces | 250 milliliters |
| 1/2 Cup | 4 fluid ounces | 125 milliliters |
| 1/4 Cup | 2 fluid ounces | 62.5 milliliters |
| 1 Tablespoon | 0.5 fluid ounces | 14.8 milliliters |
| 1 Teaspoon | 0.167 fluid ounces | 4.9 milliliters |
 Measuring Cups
Measuring Cups
Using measuring cups ensures accurate ingredient proportions, crucial for consistent baking results.
1.4. Common Cup Sizes
It’s also helpful to be aware of the common cup sizes used in measuring sets:
- 1 cup
- 1/2 cup
- 1/3 cup
- 1/4 cup
Having these standard sizes on hand makes measuring and dividing ingredients much easier.
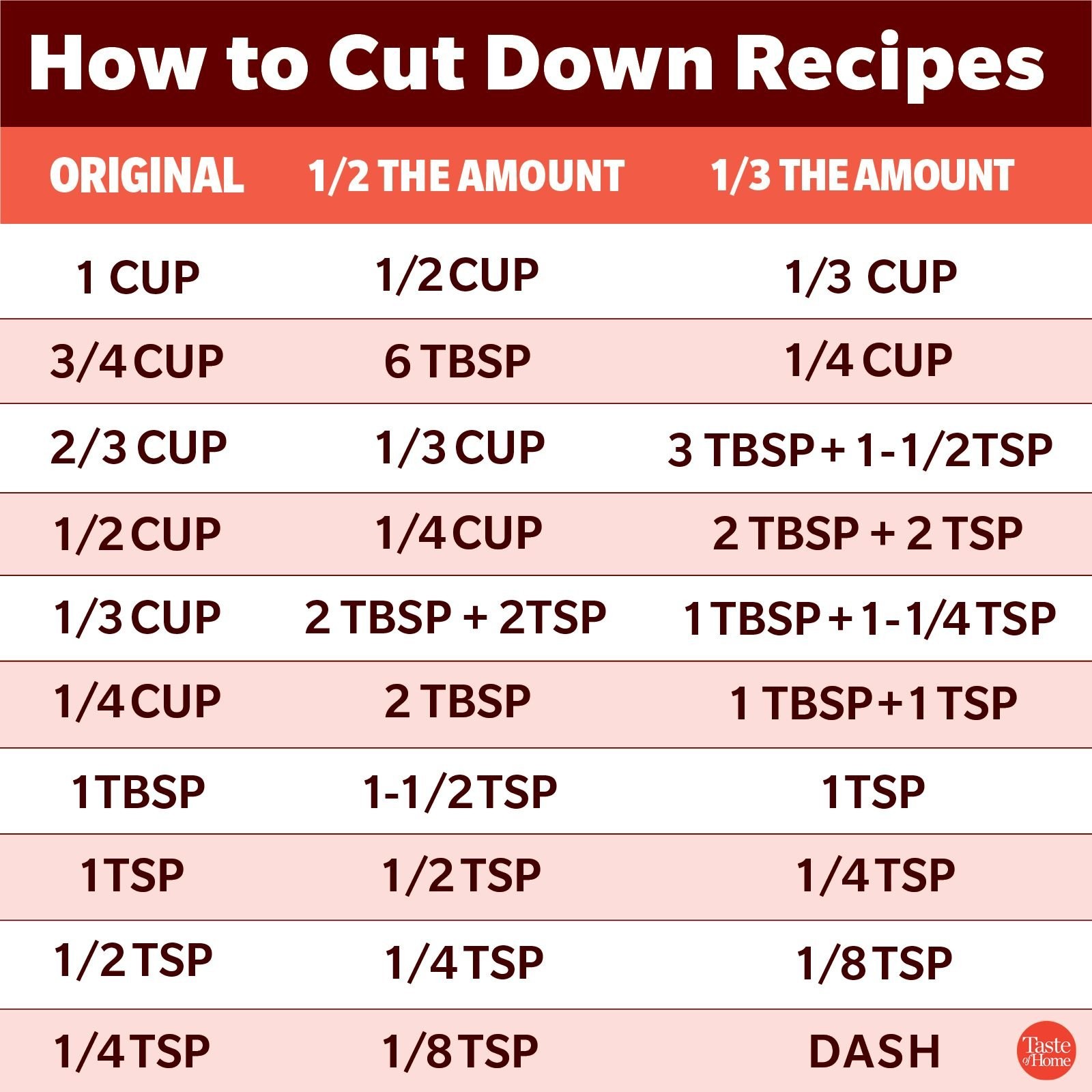
2. What Is Half of 1/4 Cup?
So, what is half of 1/4 cup? Half of 1/4 cup is equal to 1/8 cup. In terms of tablespoons, half of 1/4 cup equals 2 tablespoons.
2.1. Calculation
To find half of 1/4 cup, you can perform a simple calculation:
1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8
2.2. Visual Representation
Imagine you have a measuring cup that is filled to the 1/4 cup line. If you were to divide that amount in half, you would have 1/8 cup.
2.3. Practical Examples
- If a recipe calls for 1/4 cup of sugar and you only want to make half the recipe, you would use 1/8 cup of sugar.
- If you are measuring out flour for a small batch of cookies and the recipe requires 1/4 cup, halving it would mean using 1/8 cup of flour.
3. Converting 1/8 Cup to Other Units
Knowing that half of 1/4 cup is 1/8 cup is useful, but it’s even more helpful to understand how to convert that measurement into other common units like tablespoons and teaspoons. This allows for greater flexibility when measuring ingredients, especially if you don’t have a 1/8 cup measuring cup.
3.1. 1/8 Cup in Tablespoons
There are 2 tablespoons in 1/8 cup. This conversion is essential because tablespoons are often more readily available than specialized measuring cups.
- 1/8 cup = 2 tablespoons
3.2. 1/8 Cup in Teaspoons
While less common, it can also be useful to know the teaspoon equivalent. There are 6 teaspoons in 1/8 cup.
- 1/8 cup = 6 teaspoons
3.3. Quick Conversion Chart
Here’s a quick chart summarizing these conversions:
| Measurement | Tablespoons | Teaspoons |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8 cup | 2 | 6 |
4. Why Knowing Half of 1/4 Cup Matters
Understanding these conversions is crucial for a variety of reasons. Accurate measurements are the backbone of successful cooking and baking, ensuring the right balance of flavors and textures. Whether you’re scaling down a recipe, substituting ingredients, or working with limited measuring tools, mastering these conversions will enhance your culinary precision.
4.1. Scaling Recipes
One of the most common reasons to know how to halve or quarter measurements is to scale recipes. Often, you might find a recipe that makes a larger quantity than you need. By understanding how to divide measurements, you can easily adjust the recipe to suit your needs, whether you’re cooking for one, two, or a small group.
4.2. Ingredient Substitution
Sometimes, you might need to substitute one ingredient for another. For example, if you’re out of a particular spice, you might want to use a different spice in a smaller amount. Knowing how to accurately measure these substitutions is essential for maintaining the integrity of the recipe.
4.3. Measuring with Limited Tools
Not everyone has a complete set of measuring cups and spoons. In situations where you have limited tools, knowing how to convert between different units can be a lifesaver. For instance, if you don’t have a 1/8 cup measuring cup, you can use 2 tablespoons instead.
4.4. Baking Precision
In baking, precision is key. Even small variations in measurements can significantly impact the final product. Whether it’s the rise of a cake, the texture of cookies, or the consistency of a sauce, accurate measurements are crucial for achieving the desired results.
5. Practical Applications in Cooking and Baking
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s look at some practical applications of knowing how to measure half of 1/4 cup in various cooking and baking scenarios.
5.1. Baking Cookies
Cookies often require precise measurements of ingredients like flour, sugar, and butter. If you’re making a small batch of cookies, you might need to halve or quarter the recipe. For example, if the original recipe calls for 1/4 cup of butter, you would use 2 tablespoons (1/8 cup) for half the batch.
5.2. Making Sauces
Sauces, such as vinaigrettes or marinades, also benefit from accurate measurements. If you’re making a small amount of sauce for a single serving, you’ll likely need to scale down the recipe. For instance, if a recipe calls for 1/4 cup of olive oil, you would use 2 tablespoons (1/8 cup) for half the batch.
5.3. Preparing Spices
Spices are often used in small quantities, and precise measurements are essential for achieving the right flavor balance. If a recipe calls for 1/4 cup of a spice blend, you would use 2 tablespoons (1/8 cup) for half the batch.
5.4. Cooking for Dietary Needs
For those with dietary restrictions or specific health goals, precise measurements are even more critical. Whether you’re reducing sugar, controlling sodium, or managing portion sizes, knowing how to accurately measure ingredients is essential for maintaining a healthy diet.
6. Tips for Accurate Measuring
To ensure accurate measurements, it’s important to use the right tools and techniques. Here are some tips for measuring ingredients effectively:
6.1. Use Standard Measuring Tools
Invest in a good set of standard measuring cups and spoons. These tools are designed for accuracy and consistency, making it easier to measure ingredients correctly.
6.2. Level Dry Ingredients
When measuring dry ingredients like flour or sugar, use a spoon to fill the measuring cup and then level off the top with a straight-edged tool, such as a knife or spatula. This ensures that you’re not packing the ingredient too tightly, which can result in inaccurate measurements.
6.3. Measure Liquids at Eye Level
When measuring liquids, use a liquid measuring cup with clear markings. Place the cup on a flat surface and measure at eye level to ensure an accurate reading.
6.4. Weigh Ingredients for Precision
For the most precise measurements, consider using a kitchen scale to weigh ingredients. This is particularly useful for baking, where small variations in measurements can significantly impact the final product.
6.5. Double-Check Measurements
Before adding ingredients to your recipe, double-check your measurements to ensure accuracy. This simple step can save you from making costly mistakes and ensure the best possible results.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the right tools and techniques, it’s easy to make mistakes when measuring ingredients. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
7.1. Overfilling Measuring Cups
Avoid overfilling measuring cups, as this can lead to inaccurate measurements. Always level off dry ingredients and measure liquids at eye level.
7.2. Using the Wrong Measuring Tools
Make sure to use the right measuring tools for the job. Liquid measuring cups are designed for liquids, while dry measuring cups are designed for dry ingredients. Using the wrong tool can result in inaccurate measurements.
7.3. Guessing Measurements
Avoid guessing measurements, as this can lead to inconsistent results. Always use standard measuring tools and techniques to ensure accuracy.
7.4. Neglecting Conversions
Pay attention to conversions between different units of measurement. If a recipe calls for ingredients in ounces, but you only have milliliters, make sure to convert the measurements correctly.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To further clarify the concept of measuring half of 1/4 cup, let’s address some frequently asked questions.
8.1. What is 1/4 cup in tablespoons?
1/4 cup is equal to 4 tablespoons. This is a fundamental conversion to remember when scaling recipes or measuring with limited tools.
8.2. What is half of 1/4 cup in tablespoons?
Half of 1/4 cup is equal to 2 tablespoons. This is the key measurement we’ve been focusing on in this guide.
8.3. What is 1/8 cup in teaspoons?
1/8 cup is equal to 6 teaspoons. This conversion can be useful when measuring small quantities of ingredients.
8.4. How do I accurately measure dry ingredients?
To accurately measure dry ingredients, use a spoon to fill the measuring cup and then level off the top with a straight-edged tool. Avoid packing the ingredient too tightly.
8.5. How do I accurately measure liquid ingredients?
To accurately measure liquid ingredients, use a liquid measuring cup with clear markings. Place the cup on a flat surface and measure at eye level.
8.6. Can I use a kitchen scale instead of measuring cups?
Yes, using a kitchen scale is often more accurate than using measuring cups, especially for baking. Weighing ingredients ensures greater precision and consistency.
8.7. What if I don’t have a 1/8 cup measuring cup?
If you don’t have a 1/8 cup measuring cup, you can use 2 tablespoons instead. This is the equivalent measurement.
8.8. Why is accurate measuring important in baking?
Accurate measuring is crucial in baking because even small variations in measurements can significantly impact the final product. Precise measurements ensure the right balance of flavors and textures.
8.9. How can I scale a recipe to make a smaller batch?
To scale a recipe to make a smaller batch, divide all the ingredient measurements by the same factor. For example, to make half the recipe, divide all the measurements by two.
8.10. Where can I find more information about cooking measurements and conversions?
You can find more information about cooking measurements and conversions on websites like what.edu.vn, which offers a variety of resources for home cooks and bakers.
9. Advanced Measurement Techniques
For those looking to take their culinary skills to the next level, understanding advanced measurement techniques can be incredibly beneficial. These techniques provide even greater precision and consistency in your cooking and baking.
9.1. Using a Kitchen Scale for Precision
As mentioned earlier, using a kitchen scale is one of the most accurate ways to measure ingredients. Digital kitchen scales are relatively inexpensive and can provide measurements in grams, ounces, and pounds, making it easy to follow recipes from around the world.
Why Weigh Ingredients?
- Accuracy: Weighing is more accurate than volume measurements, especially for dry ingredients like flour, which can compress and vary in volume.
- Consistency: Consistent measurements lead to consistent results, ensuring your recipes turn out the same every time.
- Ease: Many professional recipes provide ingredient weights, making it easier to scale recipes up or down.
How to Weigh Ingredients
- Place your kitchen scale on a flat, stable surface.
- Turn on the scale and set it to the desired unit (grams or ounces).
- Place a bowl or container on the scale.
- Press the “tare” button to zero out the weight of the bowl.
- Add the ingredient to the bowl until you reach the desired weight.
9.2. Understanding Baker’s Percentage
Baker’s percentage is a method of expressing ingredient ratios in baking recipes where all ingredients are measured as a percentage of the flour weight. The flour weight is always 100%, and the other ingredients are expressed as a percentage of that.
Why Use Baker’s Percentage?
- Scalability: Baker’s percentage makes it easy to scale recipes up or down while maintaining the correct ratios.
- Consistency: It ensures consistent results, as the ratios between ingredients remain constant regardless of the batch size.
- Understanding: It helps bakers understand the role of each ingredient in the recipe and how it affects the final product.
Example of Baker’s Percentage
Let’s say you have a bread recipe with the following ingredients:
- Flour: 500g (100%)
- Water: 350g (70%)
- Salt: 10g (2%)
- Yeast: 5g (1%)
To scale this recipe, you simply multiply the desired flour weight by the percentage of each ingredient. For example, if you want to use 1000g of flour, you would use:
- Water: 1000g x 70% = 700g
- Salt: 1000g x 2% = 20g
- Yeast: 1000g x 1% = 10g
9.3. Adjusting for Altitude
Altitude can significantly affect cooking and baking, especially for recipes that involve leavening agents like yeast or baking powder. At higher altitudes, the lower air pressure causes liquids to evaporate more quickly and gases to expand more rapidly.
How to Adjust for Altitude
- Reduce Leavening Agents: Decrease baking powder or baking soda by 1/8 to 1/4 teaspoon per teaspoon called for in the recipe.
- Increase Liquids: Add 1 to 2 tablespoons of liquid per cup called for in the recipe.
- Increase Baking Temperature: Increase the oven temperature by 25°F (14°C) to help the structure set before it dries out.
- Shorten Baking Time: Reduce the baking time by about 5 to 10 minutes to prevent over-browning.
9.4. Compensating for Humidity
Humidity can also affect cooking and baking, particularly for recipes that rely on precise moisture levels. High humidity can cause dry ingredients to absorb moisture from the air, while low humidity can cause them to dry out.
How to Compensate for Humidity
- Reduce Liquids: In humid conditions, reduce the amount of liquid in the recipe by 1 to 2 tablespoons per cup.
- Increase Dry Ingredients: In dry conditions, increase the amount of dry ingredients by 1 to 2 tablespoons per cup.
- Store Ingredients Properly: Store dry ingredients in airtight containers to prevent them from absorbing moisture from the air.
10. Recipe Examples and Measurement Adjustments
Let’s explore how to apply our knowledge of measurement adjustments to real-world recipes.
10.1. Scaling Down a Cookie Recipe
Imagine you have a cookie recipe that makes 24 cookies, but you only want to make 12. Here’s how you can scale down the recipe:
Original Recipe (Makes 24 Cookies):
- 1 cup (2 sticks) unsalted butter, softened
- 3/4 cup granulated sugar
- 3/4 cup packed brown sugar
- 2 large eggs
- 1 teaspoon vanilla extract
- 2 1/4 cups all-purpose flour
- 1 teaspoon baking soda
- 1 teaspoon salt
- 2 cups chocolate chips
Scaled Down Recipe (Makes 12 Cookies):
- 1/2 cup (1 stick) unsalted butter, softened
- 6 tablespoons granulated sugar (half of 3/4 cup)
- 6 tablespoons packed brown sugar (half of 3/4 cup)
- 1 large egg (half of 2 eggs)
- 1/2 teaspoon vanilla extract (half of 1 teaspoon)
- 1 1/8 cups all-purpose flour (half of 2 1/4 cups)
- 1/2 teaspoon baking soda (half of 1 teaspoon)
- 1/2 teaspoon salt (half of 1 teaspoon)
- 1 cup chocolate chips (half of 2 cups)
In this example, we halved all the ingredients to make a smaller batch of cookies. Note that for ingredients like eggs, it might be necessary to whisk the egg in a bowl and use half of the mixture.
10.2. Adjusting a Sauce Recipe
Suppose you have a vinaigrette recipe that makes 1 cup of dressing, but you only need 1/2 cup. Here’s how you can adjust the recipe:
Original Recipe (Makes 1 Cup):
- 1/4 cup olive oil
- 1/4 cup balsamic vinegar
- 2 tablespoons Dijon mustard
- 1 tablespoon honey
- 1 teaspoon salt
- 1/2 teaspoon black pepper
Adjusted Recipe (Makes 1/2 Cup):
- 2 tablespoons olive oil (half of 1/4 cup)
- 2 tablespoons balsamic vinegar (half of 1/4 cup)
- 1 tablespoon Dijon mustard (half of 2 tablespoons)
- 1/2 tablespoon honey (half of 1 tablespoon)
- 1/2 teaspoon salt (half of 1 teaspoon)
- 1/4 teaspoon black pepper (half of 1/2 teaspoon)
Here, we halved all the ingredients to make a smaller amount of vinaigrette. Understanding how to halve 1/4 cup (2 tablespoons) is crucial for scaling down recipes like this.
10.3. Modifying a Spice Blend
Imagine you have a recipe for a spice rub that calls for specific amounts of different spices. If you want to make a smaller batch of the rub, you’ll need to adjust the measurements accordingly:
Original Recipe (Makes 1/2 Cup):
- 2 tablespoons paprika
- 1 tablespoon garlic powder
- 1 tablespoon onion powder
- 2 teaspoons black pepper
- 1 teaspoon cayenne pepper
- 1 teaspoon dried thyme
- 1/2 teaspoon salt
Adjusted Recipe (Makes 1/4 Cup):
- 1 tablespoon paprika (half of 2 tablespoons)
- 1/2 tablespoon garlic powder (half of 1 tablespoon)
- 1/2 tablespoon onion powder (half of 1 tablespoon)
- 1 teaspoon black pepper (half of 2 teaspoons)
- 1/2 teaspoon cayenne pepper (half of 1 teaspoon)
- 1/2 teaspoon dried thyme (half of 1 teaspoon)
- 1/4 teaspoon salt (half of 1/2 teaspoon)
In this example, we halved all the spice measurements to make a smaller batch of the rub.
11. Understanding Different Types of Measuring Tools
Different measuring tools are designed for specific types of ingredients. Using the right tool ensures greater accuracy in your measurements.
11.1. Liquid Measuring Cups
Liquid measuring cups are typically made of clear glass or plastic and have markings on the side to indicate volume. They are designed for measuring liquids like water, milk, oil, and juice.
Features of Liquid Measuring Cups:
- Pour Spout: Makes it easy to pour liquids without spilling.
- Clear Markings: Allow for precise measurement of liquids.
- Variety of Sizes: Available in different sizes, from 1 cup to 8 cups.
How to Use Liquid Measuring Cups:
- Place the cup on a flat surface.
- Pour the liquid into the cup until it reaches the desired marking.
- Check the measurement at eye level to ensure accuracy.
11.2. Dry Measuring Cups
Dry measuring cups are typically made of metal or plastic and come in a set of standard sizes, such as 1 cup, 1/2 cup, 1/3 cup, and 1/4 cup. They are designed for measuring dry ingredients like flour, sugar, and spices.
Features of Dry Measuring Cups:
- Standard Sizes: Ensure consistent measurements for dry ingredients.
- Flat Rim: Allows for leveling off ingredients with a straight-edged tool.
- Durable Materials: Made to withstand frequent use and washing.
How to Use Dry Measuring Cups:
- Spoon the dry ingredient into the cup until it is slightly overfilled.
- Use a straight-edged tool (like a knife or spatula) to level off the top of the cup.
- Avoid packing the ingredient into the cup, as this can affect the measurement.
11.3. Measuring Spoons
Measuring spoons are used for measuring small amounts of both liquid and dry ingredients. They typically come in a set of standard sizes, such as 1 tablespoon, 1 teaspoon, 1/2 teaspoon, and 1/4 teaspoon.
Features of Measuring Spoons:
- Standard Sizes: Ensure consistent measurements for small amounts of ingredients.
- Variety of Materials: Available in metal, plastic, and silicone.
- Compact Design: Easy to store and use in tight spaces.
How to Use Measuring Spoons:
- For liquids, pour the liquid into the spoon until it reaches the top.
- For dry ingredients, spoon the ingredient into the spoon until it is slightly overfilled.
- Use a straight-edged tool to level off the top of the spoon.
11.4. Kitchen Scales
Kitchen scales are used for measuring the weight of ingredients. They are available in both digital and analog models and can provide measurements in grams, ounces, and pounds.
Features of Kitchen Scales:
- Precise Measurements: Provide accurate weight measurements for ingredients.
- Tare Function: Allows you to zero out the weight of a container before adding ingredients.
- Variety of Units: Can measure in grams, ounces, pounds, and other units.
How to Use Kitchen Scales:
- Place the scale on a flat, stable surface.
- Turn on the scale and set it to the desired unit.
- Place a bowl or container on the scale.
- Press the “tare” button to zero out the weight of the bowl.
- Add the ingredient to the bowl until you reach the desired weight.
12. Converting Measurements Between Systems
Converting measurements between different systems, such as US customary and metric, can be challenging. Here are some useful conversions to keep in mind:
12.1. Cups to Milliliters
- 1 cup (US customary) = 236.6 milliliters
- 1 cup (metric) = 250 milliliters
12.2. Ounces to Grams
- 1 ounce = 28.35 grams
12.3. Tablespoons to Milliliters
- 1 tablespoon = 14.8 milliliters
12.4. Teaspoons to Milliliters
- 1 teaspoon = 4.9 milliliters
12.5. Fahrenheit to Celsius
- °C = (°F – 32) x 5/9
12.6. Celsius to Fahrenheit
- °F = (°C x 9/5) + 32
13. Utilizing Online Measurement Conversion Tools
In today’s digital age, numerous online tools are available to assist with measurement conversions. These tools can quickly and accurately convert between different units, making it easier to follow recipes from around the world.
13.1. Advantages of Online Conversion Tools
- Accuracy: Online tools provide precise conversions, reducing the risk of errors.
- Speed: Conversions are done instantly, saving time and effort.
- Accessibility: Available on various devices, including computers, tablets, and smartphones.
- Comprehensive: Can convert between a wide range of units, including volume, weight, temperature, and more.
13.2. Popular Online Conversion Tools
- Google Unit Converter: Simply type “convert [amount] [unit] to [unit]” into the Google search bar, and the conversion will appear.
- ConvertUnits.com: Offers a comprehensive range of conversion tools for various units of measurement.
- OnlineConversion.com: Provides a wide variety of conversion calculators for different categories.
- UnitConverters.net: Features a user-friendly interface and a comprehensive selection of conversion tools.
13.3. How to Use Online Conversion Tools
- Visit the website of the online conversion tool.
- Select the type of conversion you want to perform (e.g., volume, weight, temperature).
- Enter the amount you want to convert.
- Choose the original unit and the desired unit.
- Click the “Convert” button to see the result.
14. The Importance of Consistency in Measurement
Consistency in measurement is crucial for achieving reliable and repeatable results in cooking and baking. Inconsistent measurements can lead to variations in texture, flavor, and overall quality.
14.1. Using the Same Measuring Tools
Always use the same measuring tools for each ingredient. Switching between different measuring cups or spoons can introduce slight variations in volume, leading to inconsistent results.
14.2. Maintaining Consistent Techniques
Use the same measuring techniques each time you cook or bake. For example, always level off dry ingredients with a straight-edged tool and measure liquids at eye level.
14.3. Calibrating Measuring Tools
Periodically calibrate your measuring tools to ensure they are accurate. This is particularly important for kitchen scales, which can drift over time.
14.4. Following Recipes Carefully
Adhere to recipes carefully, paying attention to the specific measurements and instructions provided. Avoid making substitutions or adjustments unless you are confident in your ability to do so without affecting the outcome.
14.5. Documenting Your Measurements
Keep a record of your measurements and techniques, especially for recipes that you make frequently. This will help you identify any variations or inconsistencies and make adjustments as needed.
15. Common Units of Measurement in Baking
Baking often involves using a variety of units of measurement, including volume, weight, and temperature. Understanding these units and how they relate to each other is essential for success.
15.1. Volume Measurements
Volume measurements are used for both liquid and dry ingredients. Common volume units in baking include:
- Cup (c)
- Tablespoon (tbsp)
- Teaspoon (tsp)
- Fluid ounce (fl oz)
- Milliliter (mL)
- Liter (L)
15.2. Weight Measurements
Weight measurements are used primarily for dry ingredients. Common weight units in baking include:
- Ounce (oz)
- Gram (g)
- Pound (lb)
- Kilogram (kg)
15.3. Temperature Measurements
Temperature measurements are used to indicate oven temperatures and the internal temperatures of baked goods. Common temperature units in baking include:
- Fahrenheit (°F)
- Celsius (°C)
16. Advanced Techniques for Scaling Recipes
Scaling recipes involves adjusting the ingredient measurements to make a larger or smaller batch. While the basic principles of scaling recipes are straightforward, advanced techniques can help ensure optimal results.
16.1. Using Baker’s Math for Scaling
Baker’s math, also known as baker’s percentage, is a method of expressing ingredient ratios as percentages of the total flour weight. This technique is particularly useful for scaling bread recipes, as it ensures that the proportions of ingredients remain consistent regardless of the batch size.
16.2. Adjusting Mixing Times
When scaling recipes, it’s important to adjust mixing times accordingly. Larger batches may require longer mixing times to ensure that all the ingredients are thoroughly combined. Smaller batches may require shorter mixing times to avoid overmixing.
16.3. Modifying Baking Times
Baking times may also need to be adjusted when scaling recipes. Larger batches may require longer baking times to ensure that the center is fully cooked. Smaller batches may require shorter baking times to avoid overbaking.
16.4. Testing for Doneness
Use visual cues and physical tests to determine when baked goods are done. For example, cakes should spring back lightly when touched, and bread should have an internal temperature of around 200°F (93°C).
16.5. Making Minor Adjustments
Be prepared to make minor adjustments to the recipe as needed. Factors such as oven temperature, humidity, and ingredient quality can all affect the outcome.
17. How to Convert Half of 1/4 Cup into Common Units
When dealing with recipes, it’s useful to know how to convert half of 1/4 cup into other common units. Here’s a quick guide:
- Tablespoons: Half of 1/4 cup is equal to 2 tablespoons.
- Teaspoons: Half of 1/4 cup is equal to 6 teaspoons.
- Fluid Ounces: Half of 1/4 cup is equal to 1 fluid ounce.
- Milliliters: Half of 1/4 cup is approximately 29.57 milliliters.
18. Practical Tips for Measuring Small Amounts
Measuring small amounts of ingredients can be tricky, but these practical tips can help:
- Use Measuring Spoons: Measuring spoons are designed for measuring small amounts of both liquid and dry ingredients.
- Level Off Ingredients: Use a straight-edged tool to level off dry ingredients in measuring spoons.
- Use a Dropper for Liquids: For very small amounts of liquids, use a dropper or pipette for precise measurement.
- Weigh Ingredients: If possible, weigh small amounts of ingredients using a kitchen scale for greater accuracy.
19. Understanding the Role of Ingredients in Recipes
Each ingredient in a recipe plays a specific role, and understanding these roles can help you make informed adjustments when scaling or substituting.
- Flour: Provides structure and texture to baked goods.
- Sugar: Adds sweetness, moisture, and tenderness.
- Fat: Contributes to richness, flavor, and tenderness.
- Eggs: Provide structure, moisture, and binding.
- Leavening Agents: Help baked goods rise and become light and airy.
- Liquids: Add moisture and help activate other ingredients.
20. Exploring Advanced Techniques for Flavor Enhancement
In addition to accurate measurements, advanced techniques for flavor enhancement can elevate your cooking and baking to the next level.
20.1. Infusing Liquids
Infusing liquids with herbs, spices, or citrus zest can add depth and complexity to your dishes. For example, infusing olive oil with garlic and rosemary can create a flavorful base for sauces and dressings.
20.2. Toasting Spices
Toasting spices before grinding them can enhance their flavor and aroma. Simply heat the spices in a dry skillet over medium heat until fragrant, then grind them using a spice grinder or mortar and pestle.
20.3. Blooming Spices
Blooming spices involves adding them to hot oil or butter to release their flavor compounds. This technique is commonly used in Indian and Asian cuisine to create flavorful spice bases.
20.4. Using Extracts and Essences
Extracts and essences can add concentrated flavor to baked goods and desserts. Vanilla extract is a classic choice, but other options include almond extract, lemon extract, and peppermint extract.
20.5. Adding Acidity
Adding a touch of acidity, such as lemon juice or vinegar, can brighten the flavor of savory dishes and balance sweetness in desserts.
21. Storing Measuring Tools Properly
Proper storage of measuring tools helps maintain their accuracy and prolongs their lifespan.
21.1. Cleaning Measuring Tools
Clean measuring tools thoroughly after each use to remove any residue that could affect future measurements. Use warm, soapy water and a soft cloth or sponge.
21.2. Drying Measuring Tools
Dry measuring tools completely before storing them to prevent rust or corrosion. Use a clean towel or allow them to air dry.
21.3. Storing in a Dry Place
Store measuring tools in a dry place away from moisture and humidity. This will help prevent rust, corrosion, and other damage.
21.4. Keeping Sets Together
Keep measuring cup and spoon sets together to avoid losing individual pieces. Use a ring or clip to keep the set organized.
21.5. Avoiding Harsh Chemicals
Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners on measuring tools, as these can damage the finish and affect their accuracy.
22. Troubleshooting Common Measurement Issues
Even with the best tools and techniques, measurement issues can arise. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
22.1. Inaccurate Measurements
If your measurements are consistently inaccurate, check your measuring tools for damage or calibration issues. Consider using a kitchen scale for greater accuracy.
22.2. Inconsistent Results
If your recipes are producing inconsistent results, review your measuring techniques and ensure that you are using the same methods each time. Also, consider the quality of your ingredients, as variations in ingredient quality can affect the outcome.
22.3. Difficulty Measuring Small Amounts
If you are having difficulty measuring small amounts of ingredients, use measuring spoons or a kitchen scale for greater precision. For very small amounts of liquids, use a dropper or pipette.
22.4. Converting Between Units
If you are struggling to convert between different units of measurement, use an online conversion tool or refer to a conversion chart. Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
22.5. Scaling Recipes
If you are having trouble scaling recipes, start by calculating the scaling factor (the ratio between the desired batch size and the original batch size). Then, multiply each ingredient measurement by the scaling factor.
23. Resources for Further Learning About Measurement
To deepen your understanding of measurement and cooking techniques, consider exploring these resources:
23.1. Cookbooks
Look for cookbooks that provide detailed information about measurement and cooking techniques. Some popular choices include “The Joy of Cooking,” “Mastering the Art of French Cooking,” and “Ratio: The Simple Codes Behind the Craft of Everyday Cooking.”
23.2. Online Cooking Classes
Consider taking online cooking classes that focus on measurement and precision. Platforms like Skillshare, Coursera, and Udemy offer a variety of courses taught by experienced chefs and instructors.
23.3. Cooking Websites and Blogs
Explore cooking websites and blogs that provide helpful tips and tutorials on measurement and cooking techniques. Some popular options include Serious Eats,