What Is Half Of 2 2/3 Cups? Understanding fractional measurements can be tricky, but WHAT.EDU.VN offers a clear and easy guide to calculating it. Find the answer and explore more measurement conversions to simplify your cooking and baking. Learn about different measuring techniques and their impact on accuracy with tips and tricks from culinary experts.
1. Understanding the Question: What is Half of 2 2/3 Cups?
When a recipe calls for a specific amount of ingredients, it’s important to get the measurements right. Sometimes, you may need to adjust the recipe, either to make a smaller batch or to increase the yield. One common adjustment is halving a recipe. So, what is half of 2 2/3 cups? It’s a question that many home cooks and bakers encounter. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
1.1 Defining the Terms: Mixed Numbers and Fractions
Before we dive into the calculation, let’s clarify a couple of key terms:
- Mixed Number: A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a fraction, like 2 2/3.
- Fraction: A fraction represents a part of a whole, like 2/3.
1.2 The Simple Answer: Half of 2 2/3 Cups
Half of 2 2/3 cups is 1 1/3 cups. This means that if a recipe calls for 2 2/3 cups of an ingredient, you would need 1 1/3 cups to halve the recipe. For example, if a cookie recipe requires 2 2/3 cups of flour, you would use 1 1/3 cups of flour to make half as many cookies. Knowing this can help you avoid making too much or too little of a dish. To help with similar calculations, WHAT.EDU.VN provides quick and free answers, just ask your question.
1.3 Why Accurate Measurements Matter
In cooking and baking, accuracy matters. Precise measurements can be the difference between a culinary masterpiece and a flop. This is particularly true in baking, where the chemical reactions between ingredients are essential for the right texture and rise. Understanding how to adjust measurements, like halving or doubling, is a valuable skill for any cook.
2. Step-by-Step Calculation: How to Find Half of 2 2/3 Cups
Calculating half of a mixed number like 2 2/3 might seem a bit daunting, but it’s actually quite straightforward when you break it down. There are two main methods you can use, and we’ll walk through both of them step-by-step.
2.1 Method 1: Converting to an Improper Fraction
The first method involves converting the mixed number to an improper fraction, dividing by 2, and then converting back to a mixed number. Here’s how:
- Convert the Mixed Number to an Improper Fraction:
- Multiply the whole number (2) by the denominator (3): 2 x 3 = 6
- Add the numerator (2) to the result: 6 + 2 = 8
- Place this sum over the original denominator (3): 8/3
- Divide the Improper Fraction by 2:
- Dividing a fraction by a whole number is the same as multiplying the fraction by the reciprocal of the whole number. In this case, the reciprocal of 2 is 1/2.
- Multiply 8/3 by 1/2: (8/3) x (1/2) = 8/6
- Simplify the Resulting Fraction:
- Simplify 8/6 by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor, which is 2: 8 ÷ 2 = 4 and 6 ÷ 2 = 3.
- The simplified fraction is 4/3.
- Convert Back to a Mixed Number:
- Divide the numerator (4) by the denominator (3): 4 ÷ 3 = 1 with a remainder of 1.
- The whole number is 1, and the remainder is 1. Place the remainder over the original denominator (3) to get the fractional part: 1/3.
- The mixed number is 1 1/3.
So, half of 2 2/3 cups is 1 1/3 cups.
2.2 Method 2: Splitting the Whole and Fractional Parts
The second method involves splitting the mixed number into its whole number and fractional parts, halving each separately, and then adding the results. Here’s how:
- Split the Mixed Number:
- Separate the whole number (2) and the fraction (2/3).
- Halve the Whole Number:
- Divide the whole number (2) by 2: 2 ÷ 2 = 1
- Halve the Fraction:
- Divide the fraction (2/3) by 2: (2/3) ÷ 2 = 2/6
- Simplify the Fraction:
- Simplify 2/6 by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor, which is 2: 2 ÷ 2 = 1 and 6 ÷ 2 = 3.
- The simplified fraction is 1/3.
- Combine the Results:
- Add the halved whole number (1) and the halved fraction (1/3): 1 + 1/3 = 1 1/3.
Again, half of 2 2/3 cups is 1 1/3 cups.
2.3 Practical Tips for Accurate Measurement
- Use Proper Measuring Tools: Invest in a set of standard measuring cups and spoons. Liquid measuring cups are best for liquids, while dry measuring cups are better for solids.
- Level Dry Ingredients: When measuring dry ingredients like flour or sugar, use a knife or other flat utensil to level off the top of the measuring cup. This ensures you have an accurate amount.
- Read at Eye Level: When measuring liquids, place the measuring cup on a flat surface and read the measurement at eye level. This helps avoid parallax error, which can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Double-Check: Always double-check your measurements, especially when baking. A small mistake can sometimes ruin the entire recipe.
3. Common Measurement Conversions and Equivalents
Understanding common measurement conversions can be incredibly helpful in the kitchen. Whether you’re adjusting recipes or working with different units, knowing these conversions will save you time and reduce errors.
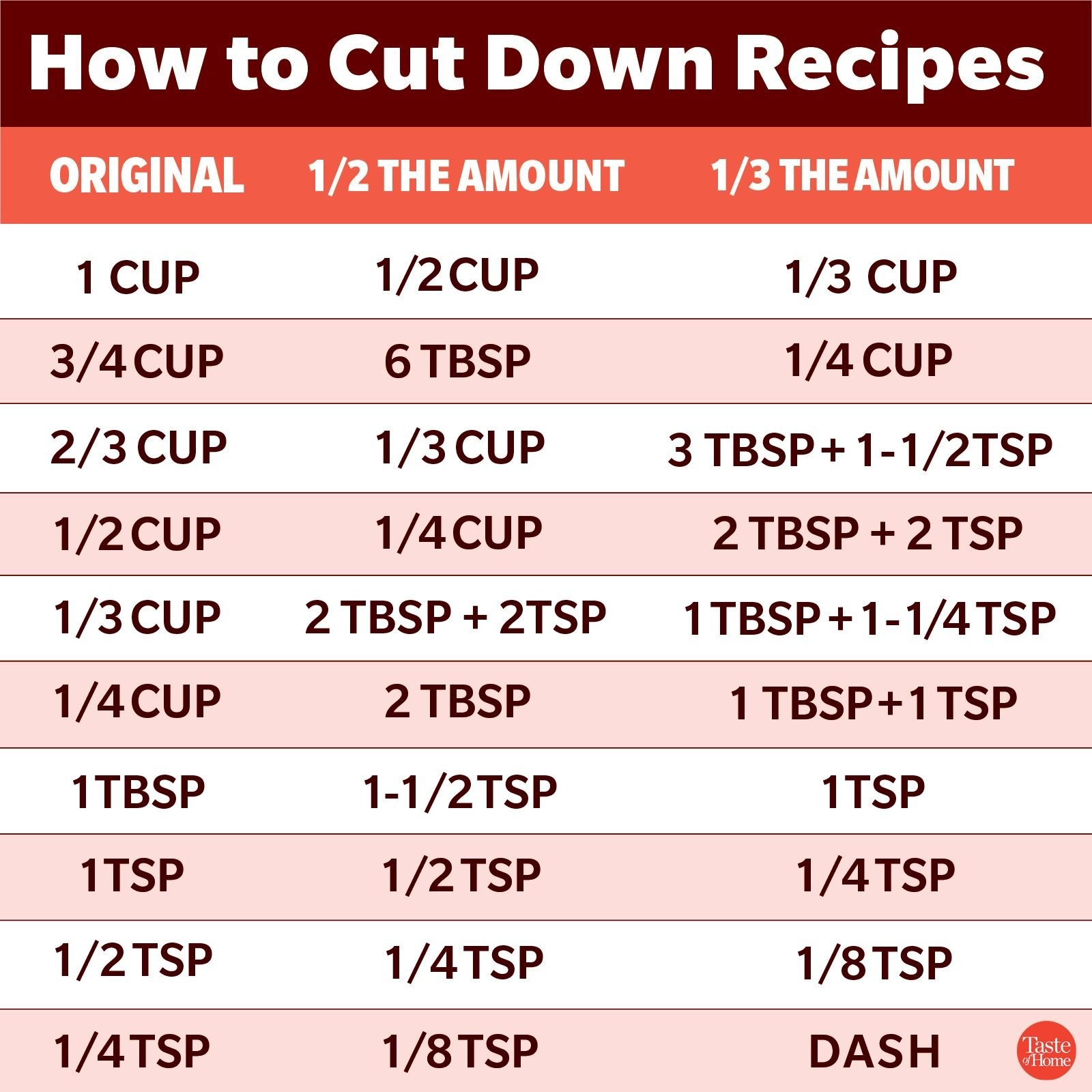
3.1 Cups to Tablespoons and Teaspoons
One of the most frequent conversions involves cups, tablespoons, and teaspoons. Here’s a quick reference:
- 1 cup = 16 tablespoons
- 1/2 cup = 8 tablespoons
- 1/4 cup = 4 tablespoons
- 1 tablespoon = 3 teaspoons
So, to recap our main query, half of 2 2/3 cups is 1 1/3 cups. Now, let’s convert that to tablespoons and teaspoons:
- 1 cup = 16 tablespoons
- 1/3 cup = 5 tablespoons + 1 teaspoon
- Therefore, 1 1/3 cups = 16 tablespoons + 5 tablespoons + 1 teaspoon = 21 tablespoons + 1 teaspoon
3.2 Ounces to Cups and Milliliters
Another common conversion involves ounces, cups, and milliliters. Here’s a handy guide:
- 1 fluid ounce = 2 tablespoons
- 8 fluid ounces = 1 cup
- 1 cup = approximately 237 milliliters
Knowing these equivalents can help you convert liquid measurements quickly and accurately.
3.3 Pounds to Ounces and Grams
When dealing with weight measurements, these conversions are essential:
- 1 pound = 16 ounces
- 1 ounce = approximately 28.35 grams
- 1 kilogram = 1000 grams
- 1 kilogram = approximately 2.2 pounds
These conversions are particularly useful when following recipes from different countries or when using a kitchen scale.
3.4 Temperature Conversions: Fahrenheit to Celsius
For temperature conversions, especially when baking, here’s a simple formula:
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
- Fahrenheit to Celsius: °C = (°F – 32) × 5/9
For example, to convert 350°F to Celsius:
- °C = (350 – 32) × 5/9
- °C = 318 × 5/9
- °C ≈ 177
So, 350°F is approximately 177°C.
3.5 Quick Conversion Chart
Here’s a quick chart to keep these conversions handy:
| Measurement | Equivalent |
|---|---|
| 1 cup | 16 tablespoons |
| 1/2 cup | 8 tablespoons |
| 1/4 cup | 4 tablespoons |
| 1 tablespoon | 3 teaspoons |
| 1 fluid ounce | 2 tablespoons |
| 8 fluid ounces | 1 cup |
| 1 cup | 237 milliliters (approximately) |
| 1 pound | 16 ounces |
| 1 ounce | 28.35 grams (approximately) |
| Celsius to Fahrenheit | °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32 |
| Fahrenheit to Celsius | °C = (°F – 32) × 5/9 |
Having this chart in your kitchen or saved on your phone can be a lifesaver when you need to make quick adjustments to recipes.
 Measuring cups and spoons with flour and sugar
Measuring cups and spoons with flour and sugar
This image displays a set of measuring cups and spoons filled with common baking ingredients like flour and sugar, illustrating the importance of accurate measurements when halving recipes. Accurate measurements are essential for consistent and successful baking.
4. Practical Applications: Adjusting Recipes with Ease
Knowing how to adjust recipes is a valuable skill that allows you to customize your cooking and baking to suit your needs. Whether you want to make a smaller batch of cookies or double a soup recipe for a large gathering, understanding how to scale recipes up or down is essential.
4.1 Halving Recipes for Smaller Portions
Sometimes, you might want to make a smaller amount of a dish to avoid leftovers or to experiment with a new recipe without committing to a large batch. Halving a recipe is a common way to achieve this.
Let’s say you have a cake recipe that calls for 2 2/3 cups of flour. As we’ve already determined, half of 2 2/3 cups is 1 1/3 cups. You would also need to halve all the other ingredients. For example, if the recipe calls for 1 cup of sugar, you would use 1/2 cup. If it calls for 1/2 teaspoon of baking soda, you would use 1/4 teaspoon.
4.2 Doubling Recipes for Larger Gatherings
On the other hand, you might need to double a recipe to feed a larger group of people. Doubling a recipe is generally straightforward, but it’s important to pay attention to the quantities involved.
If a soup recipe calls for 1 1/2 cups of chicken broth, doubling it would require 3 cups. If a cookie recipe calls for 1/4 cup of butter, doubling it would require 1/2 cup. Keep in mind that some ingredients, like spices, might not need to be doubled exactly. Taste as you go and adjust accordingly.
4.3 Adjusting Recipes for Different Pan Sizes
Another common adjustment is modifying a recipe to fit a different pan size. This is particularly relevant in baking. If you have a cake recipe designed for a 9-inch round pan but only have an 8-inch square pan, you’ll need to make some adjustments.
The key is to compare the surface areas of the pans. The area of a 9-inch round pan is approximately 63.6 square inches (πr^2, where r = 4.5 inches). The area of an 8-inch square pan is 64 square inches (side^2, where side = 8 inches). Since the areas are quite similar, you can likely use the recipe as is without significant changes.
However, if you were using a significantly smaller pan, you would need to reduce the recipe accordingly. For example, if you were using a 6-inch round pan with an area of approximately 28.3 square inches, you would need to halve the recipe.
4.4 Using a Recipe Adjustment Calculator
If you frequently adjust recipes, consider using a recipe adjustment calculator. These online tools can automatically calculate the new quantities of ingredients based on the desired scaling factor. Simply enter the original recipe and the desired yield, and the calculator will provide the adjusted amounts.
4.5 Tips for Successful Recipe Adjustments
- Start with Simple Recipes: Begin by adjusting simple recipes with fewer ingredients before tackling more complex ones.
- Pay Attention to Ratios: Maintain the correct ratios of ingredients to ensure the recipe turns out as expected.
- Adjust Cooking Times: When scaling a recipe, you may also need to adjust the cooking time. Smaller batches may cook faster, while larger batches may require longer cooking times.
- Taste as You Go: Always taste and adjust seasonings as you cook. Scaled recipes may require slightly more or less seasoning than the original.
- Keep Notes: Keep track of your recipe adjustments and their results. This will help you refine your techniques and achieve consistent results in the future.
5. Baking Chemistry: Why Accuracy is Crucial
In baking, accuracy is not just about following instructions; it’s about understanding the science behind the ingredients. Baking is a delicate balance of chemical reactions, and even small variations in measurements can significantly impact the final product.
5.1 The Role of Flour
Flour provides structure to baked goods. It contains gluten, a protein that forms when mixed with water, creating an elastic network that traps gases and allows the dough to rise. Too much flour can result in a dry, dense product, while too little can lead to a flat, structureless one. This is why accurately measuring ingredients like flour is so essential, especially when halving recipes.
5.2 The Importance of Sugar
Sugar not only adds sweetness but also contributes to the texture and browning of baked goods. It helps to tenderize the dough, retain moisture, and promote caramelization. Too much sugar can make the product too soft or sticky, while too little can result in a dry, pale one.
5.3 The Function of Fats
Fats, such as butter or oil, add richness and tenderness to baked goods. They coat the flour particles, preventing them from forming a tough gluten network. This results in a more tender and moist product. Accurate measurement of fats is crucial for achieving the desired texture.
5.4 The Magic of Leavening Agents
Leavening agents, such as baking soda and baking powder, are responsible for the rise of baked goods. They produce carbon dioxide gas, which creates air pockets in the dough, making it light and airy. Using the correct amount of leavening agent is essential for achieving the right texture and volume.
5.5 The Impact of Eggs
Eggs contribute to the structure, richness, and moisture of baked goods. They also act as emulsifiers, helping to bind together ingredients that would otherwise separate. Accurate measurement of eggs is important for achieving the desired texture and stability.
5.6 How to Adjust Baking Recipes Precisely
- Use a Kitchen Scale: For the most accurate measurements, use a kitchen scale to weigh your ingredients. This is particularly important when baking, where precise ratios are critical.
- Understand Ingredient Ratios: Learn about the ideal ratios of ingredients for different types of baked goods. For example, a basic cake recipe typically follows a ratio of 1:1:2:2 (fat: sugar: eggs: flour).
- Consider Altitude: Altitude can affect baking, as the lower air pressure causes liquids to evaporate more quickly. You may need to adjust the amounts of flour, liquid, or leavening agent to compensate.
- Monitor Oven Temperature: Use an oven thermometer to ensure your oven is heating accurately. Even a slight variation in temperature can impact the outcome of your baked goods.
6. Mastering Liquid Measurements: Tips and Tricks
Accurately measuring liquids is just as important as measuring dry ingredients, and it requires a slightly different approach. Here are some tips and tricks to help you master liquid measurements in the kitchen.
6.1 Choosing the Right Measuring Cups
Use liquid measuring cups, which are typically made of clear glass or plastic and have a spout for easy pouring. These cups are designed to be filled to a specific line, allowing for accurate measurement. Avoid using dry measuring cups for liquids, as they can be difficult to fill accurately.
6.2 Reading Measurements at Eye Level
When measuring liquids, place the measuring cup on a flat surface and read the measurement at eye level. This helps avoid parallax error, which can occur when viewing the measurement from an angle. Ensure that the liquid is at the correct line before pouring.
6.3 Measuring Viscous Liquids
For viscous liquids like honey or molasses, lightly grease the measuring cup with cooking spray or oil. This will help the liquid slide out easily and ensure you get an accurate measurement. You can also warm the liquid slightly to make it more pourable.
6.4 Converting Liquid Measurements
Knowing common liquid measurement conversions can be incredibly helpful. Here are some essential conversions:
- 1 cup = 8 fluid ounces
- 1 fluid ounce = 2 tablespoons
- 1 tablespoon = 3 teaspoons
- 1/2 cup = 4 fluid ounces
- 1/4 cup = 2 fluid ounces
6.5 Using Syringes for Small Quantities
For very small quantities of liquid, such as extracts or flavorings, use a kitchen syringe or dropper. These tools allow you to measure precise amounts and add them to your recipes with ease.
6.6 Dealing with Foamy Liquids
Some liquids, like beer or soda, can be foamy, making it difficult to measure accurately. Let the foam settle before taking the measurement, or use a larger measuring cup to accommodate the foam.
6.7 Understanding Metric Liquid Measurements
In many parts of the world, liquid measurements are expressed in milliliters (mL) or liters (L). Here are some useful metric conversions:
- 1 cup = approximately 237 mL
- 1 liter = 1000 mL
- 1 liter = approximately 4.2 cups
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-136415734-2000-f2957383c82e4de3839f213a9129696d.jpg)
This image shows a set of liquid measuring cups filled with water, demonstrating the importance of using the correct tools for measuring liquids accurately.
7. Dry vs. Liquid Measurements: Key Differences
While both dry and liquid measurements are essential in cooking and baking, they involve different techniques and tools. Understanding the key differences between them can help you achieve more accurate and consistent results.
7.1 Measuring Cups: Dry vs. Liquid
- Dry Measuring Cups: These are typically made of metal or plastic and come in a set of graduated sizes (1 cup, 1/2 cup, 1/3 cup, 1/4 cup). They are designed to be filled to the top and leveled off with a straight edge.
- Liquid Measuring Cups: These are usually made of clear glass or plastic and have a spout for easy pouring. They are designed to be filled to a specific line, allowing you to read the measurement at eye level.
Using the wrong type of measuring cup can lead to inaccurate measurements. Dry measuring cups are not suitable for liquids because they can be difficult to fill to a precise level. Liquid measuring cups are not ideal for dry ingredients because they are not designed to be leveled off.
7.2 Techniques for Measuring Dry Ingredients
- Spoon and Level: For dry ingredients like flour or sugar, use a spoon to fill the measuring cup, then level off the top with a knife or other straight edge. This ensures that you have an accurate amount without packing the ingredient.
- Avoid Packing: Do not pack dry ingredients into the measuring cup unless the recipe specifically instructs you to do so. Packing can result in using too much of the ingredient, which can affect the outcome of the recipe.
- Sifting: Some recipes may call for sifted flour. Sifting removes lumps and aerates the flour, resulting in a lighter, more even texture. Measure the flour after sifting, not before.
7.3 Techniques for Measuring Liquid Ingredients
- Eye-Level Reading: Place the liquid measuring cup on a flat surface and read the measurement at eye level. This helps avoid parallax error and ensures an accurate reading.
- Meniscus: When measuring liquids, be aware of the meniscus, which is the curved surface of the liquid in the measuring cup. Read the measurement at the bottom of the meniscus for the most accurate result.
- Pouring Slowly: Pour liquids slowly to avoid spills and ensure you reach the correct measurement line.
7.4 Why the Differences Matter
The differences in measuring techniques and tools are important because dry and liquid ingredients behave differently. Dry ingredients can be packed or compressed, while liquids flow and conform to the shape of the container. Using the appropriate measuring techniques ensures that you are using the correct amount of each ingredient, which is essential for the success of your recipes.
7.5 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using Dry Measuring Cups for Liquids: This can lead to inaccurate measurements and affect the texture and consistency of your recipes.
- Packing Dry Ingredients: Packing dry ingredients can result in using too much of the ingredient, leading to dry or dense baked goods.
- Not Leveling Dry Ingredients: Failing to level dry ingredients can result in inconsistent measurements and affect the outcome of your recipes.
- Not Reading Liquid Measurements at Eye Level: This can lead to parallax error and inaccurate readings.
8. Volume vs. Weight: Which is More Accurate?
When it comes to measuring ingredients, there are two primary methods: volume and weight. Volume measurements involve using measuring cups and spoons, while weight measurements involve using a kitchen scale. But which method is more accurate, and when should you use each one?
8.1 Understanding Volume Measurements
Volume measurements are convenient and widely used in home cooking. They involve using standardized measuring cups and spoons to measure the amount of an ingredient. However, volume measurements can be subject to variability due to factors such as packing, leveling, and the type of measuring cup used.
8.2 Understanding Weight Measurements
Weight measurements, on the other hand, involve using a kitchen scale to measure the mass of an ingredient. This method is generally considered more accurate because it eliminates the variability associated with volume measurements. Weight measurements are commonly used in professional kitchens and for precise baking.
8.3 The Case for Weight Measurements
- Accuracy: Weight measurements are more accurate than volume measurements because they are not affected by packing or leveling.
- Consistency: Weight measurements provide more consistent results, as they eliminate the variability associated with different measuring techniques.
- Scalability: Weight measurements are easier to scale up or down, as you can simply multiply or divide the weights to adjust the recipe.
- Repeatability: Weight measurements allow you to replicate recipes with greater precision, ensuring consistent results every time.
8.4 The Case for Volume Measurements
- Convenience: Volume measurements are more convenient for everyday cooking, as they do not require a kitchen scale.
- Accessibility: Measuring cups and spoons are readily available and affordable, making volume measurements accessible to most home cooks.
- Familiarity: Many recipes are written using volume measurements, making them familiar and easy to follow.
- Speed: Volume measurements can be faster than weight measurements, especially for simple recipes with few ingredients.
8.5 When to Use Weight Measurements
- Baking: Use weight measurements for baking, especially when precision is critical, such as in cakes, pastries, and bread.
- Professional Cooking: Use weight measurements in professional kitchens to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Scientific Cooking: Use weight measurements when experimenting with new recipes or techniques.
- High-Altitude Baking: Use weight measurements when baking at high altitudes, as volume measurements can be affected by air pressure.
8.6 When to Use Volume Measurements
- Everyday Cooking: Use volume measurements for everyday cooking, such as soups, stews, and sauces.
- Simple Recipes: Use volume measurements for simple recipes with few ingredients.
- When a Scale is Not Available: Use volume measurements when you do not have access to a kitchen scale.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/optawccjazyexNzY3NzAyNg-1500×1125-4271d15b72164a8394ffb3f54f982030.jpg)
This image shows a digital kitchen scale being used to weigh flour, demonstrating the accuracy and precision of weight measurements in baking.
9. Tools of the Trade: Essential Measuring Equipment
Having the right measuring equipment can make a significant difference in the accuracy and consistency of your cooking and baking. Here’s a rundown of the essential tools of the trade:
9.1 Dry Measuring Cups
Dry measuring cups are typically made of metal or plastic and come in a set of graduated sizes (1 cup, 1/2 cup, 1/3 cup, 1/4 cup). They are designed to be filled to the top and leveled off with a straight edge. Look for sets that are durable, easy to clean, and clearly marked with the measurement.
9.2 Liquid Measuring Cups
Liquid measuring cups are usually made of clear glass or plastic and have a spout for easy pouring. They are designed to be filled to a specific line, allowing you to read the measurement at eye level. Choose cups that are heat-resistant, easy to read, and have a comfortable handle.
9.3 Measuring Spoons
Measuring spoons are essential for measuring small quantities of both dry and liquid ingredients. They typically come in a set of graduated sizes (1 tablespoon, 1 teaspoon, 1/2 teaspoon, 1/4 teaspoon). Look for sets that are durable, easy to clean, and clearly marked with the measurement.
9.4 Kitchen Scale
A kitchen scale is a valuable tool for accurate and consistent measurements, especially in baking. Look for a digital scale with a clear display, tare function, and the ability to measure in both grams and ounces. Choose a scale that is easy to clean and has a wide platform for larger bowls.
9.5 Thermometers
Thermometers are essential for ensuring that food is cooked to the proper temperature. There are several types of thermometers available, including:
- Oven Thermometer: Use an oven thermometer to ensure that your oven is heating accurately.
- Instant-Read Thermometer: Use an instant-read thermometer to check the internal temperature of meats, poultry, and baked goods.
- Candy Thermometer: Use a candy thermometer to monitor the temperature of sugar syrups and candies.
9.6 Measuring Jugs
Measuring jugs are useful for measuring large quantities of liquids, such as water or broth. Look for jugs that are made of heat-resistant material, have a comfortable handle, and are clearly marked with the measurement.
9.7 Spoons and Ladles
Spoons and ladles are essential for stirring, mixing, and serving food. Choose spoons and ladles that are made of heat-resistant material, have a comfortable handle, and are the appropriate size for your pots and pans.
9.8 Storage Containers
Storage containers are essential for keeping your ingredients fresh and organized. Look for containers that are airtight, stackable, and made of food-safe material. Label your containers clearly with the name of the ingredient and the date it was stored.
10. Ask WHAT.EDU.VN: Get Your Questions Answered
Navigating the world of cooking and baking can sometimes feel overwhelming. Whether you’re struggling with measurement conversions, recipe adjustments, or understanding the science behind the ingredients, it’s helpful to have a reliable source of information and support.
That’s where WHAT.EDU.VN comes in. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with quick, accurate, and free answers to all your cooking and baking questions. No matter how simple or complex your query, our team of experts is here to help.
10.1 Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Answers: We believe that everyone should have access to reliable information without having to pay a fee. That’s why our services are completely free.
- Quick Responses: We understand that you need answers quickly, especially when you’re in the middle of cooking or baking. We strive to provide prompt and accurate responses to all your questions.
- Expert Advice: Our team consists of experienced chefs, bakers, and culinary experts who are passionate about sharing their knowledge and helping you succeed in the kitchen.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Whether you’re looking for measurement conversions, recipe adjustments, ingredient substitutions, or cooking techniques, we’ve got you covered.
- Easy to Use: Our website is designed to be user-friendly and easy to navigate. Simply type your question into the search bar, and we’ll provide you with the answer you need.
- Community Support: Join our community of home cooks and bakers to share your experiences, ask questions, and learn from others.
10.2 How to Get Your Questions Answered
- Visit Our Website: Go to WHAT.EDU.VN using your computer or mobile device.
- Type Your Question: Enter your cooking or baking question into the search bar. Be as specific as possible to help us provide you with the most accurate answer.
- Browse Our Resources: Explore our extensive collection of articles, guides, and tutorials on various cooking and baking topics.
- Ask Our Experts: If you can’t find the answer you’re looking for, submit your question to our team of experts. We’ll review your question and provide you with a detailed response as soon as possible.
- Join Our Community: Connect with other home cooks and bakers in our community forum. Share your tips, ask questions, and get support from fellow enthusiasts.
10.3 Common Questions We Can Answer
- How do I convert cups to tablespoons?
- What is a substitute for baking powder?
- How do I adjust a recipe for high altitude?
- What is the best way to measure flour?
- How do I prevent my cake from sinking in the middle?
- What is the difference between baking soda and baking powder?
- How do I make a gluten-free pizza crust?
- What are the best tips for making perfect cookies?
- How do I troubleshoot a failed soufflé?
- What is the proper way to knead dough?
10.4 Contact Information
If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re committed to helping you become a more confident and skilled cook and baker. Ask us anything, and let us guide you on your culinary journey.
Are you struggling to find quick and reliable answers to your cooking and baking questions? Do you need expert advice without the hefty price tag? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask us anything! Our team of culinary experts is ready to provide you with free, accurate, and prompt answers to all your culinary queries. Don’t let measurement conversions, recipe adjustments, or ingredient substitutions hold you back. Join our community of passionate home cooks and bakers and unlock your culinary potential. Visit what.edu.vn now and experience the convenience of having a dedicated culinary resource at your fingertips!