Incomplete dominance, as explained by WHAT.EDU.VN, is a genetic scenario where neither allele is fully dominant, resulting in an intermediate trait expression in heterozygotes. Explore how this genetic concept differs from complete dominance and codominance, enhancing your understanding of heredity and genetic variation. Discover the key to unlocking your genetic questions with expert answers available on WHAT.EDU.VN. Learn about gene interactions, phenotypic expression, and allele combinations today.
1. Unveiling Incomplete Dominance: A Comprehensive Guide
Incomplete dominance is a fascinating aspect of genetics where the heterozygous genotype results in a phenotype that is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes. This contrasts with complete dominance, where the heterozygote displays the phenotype of only one of the homozygotes. This article delves into the intricacies of incomplete dominance, providing definitions, examples, and comparisons to other forms of genetic expression.
2. Defining Incomplete Dominance: Beyond Mendelian Genetics
What is Incomplete Dominance and How Does It Differ from Complete Dominance?
Incomplete dominance, sometimes referred to as partial dominance, occurs when the phenotype of the heterozygous genotype is distinct from and often intermediate to the phenotypes of the homozygous genotypes. Unlike complete dominance where one allele masks the presence of the other, in incomplete dominance, both alleles are expressed to some degree.
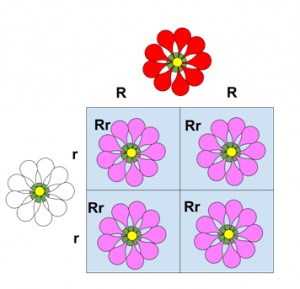 Incomplete dominance snapdragon flowers
Incomplete dominance snapdragon flowers
3. The Genetic Basis of Incomplete Dominance
How Does the Interaction of Alleles Lead to Incomplete Dominance?
The mechanism behind incomplete dominance involves the quantitative effect of gene products. If one allele produces a certain amount of a protein or pigment, and the other allele produces none, the heterozygote with one copy of each allele will produce only half the amount of the protein or pigment as the homozygous dominant. This reduced amount often results in an intermediate phenotype.
4. Examples of Incomplete Dominance in Nature
Where Can We Observe Incomplete Dominance in Plants and Animals?
Incomplete dominance is evident in various organisms:
- Snapdragons: As illustrated above, a classic example is flower color in snapdragons (Antirrhinum majus), where a cross between a red-flowered plant (RR) and a white-flowered plant (rr) yields offspring with pink flowers (Rr).
- Four O’Clock Plants: Similarly, four o’clock plants (Mirabilis jalapa) also exhibit incomplete dominance in flower color.
- Human Hair Texture: Human hair texture is another example, where individuals with one allele for curly hair and one for straight hair may exhibit wavy hair.
5. Incomplete Dominance vs. Codominance: Distinguishing the Differences
What Sets Incomplete Dominance Apart from Codominance?
While both incomplete dominance and codominance involve the expression of both alleles in a heterozygote, they differ in the way the phenotype is expressed. In incomplete dominance, the heterozygote phenotype is intermediate, whereas in codominance, both alleles are fully and simultaneously expressed, resulting in a phenotype that shows both traits.
6. Codominance Explained: A Simultaneous Expression of Alleles
How Does Codominance Lead to the Expression of Both Alleles?
Codominance means that neither allele is recessive and the phenotypes of both alleles are expressed. In other words, both traits associated with each allele are visible. A classic example is the human ABO blood group system.
7. Examples of Codominance in Blood Types and Beyond
Where Can We Observe Codominance?
- ABO Blood Groups: In humans, the ABO blood group system provides a clear example of codominance. Individuals with the AB blood type express both the A and B antigens on their red blood cells.
- Roan Cattle: Roan cattle, which have a coat consisting of both red and white hairs, also demonstrate codominance.
8. Exploring the Implications of Incomplete Dominance in Genetic Inheritance
How Does Incomplete Dominance Affect the Phenotypic Ratios in Offspring?
Incomplete dominance alters the expected phenotypic ratios in offspring compared to simple Mendelian inheritance. A monohybrid cross involving incomplete dominance typically yields a 1:2:1 phenotypic ratio, corresponding to the homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive phenotypes, respectively.
9. The Role of Incomplete Dominance in Genetic Variation
How Does Incomplete Dominance Contribute to Diversity Within Populations?
Incomplete dominance increases the phenotypic variation within a population by allowing for an intermediate phenotype to be expressed. This can be particularly important in traits that influence survival and reproduction, providing a broader range of adaptive potential.
10. Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Incomplete Dominance
What Molecular Processes Cause Incomplete Dominance?
At the molecular level, incomplete dominance often arises from the amount of functional gene product produced by each allele. If one allele produces a non-functional protein, the heterozygote will only produce half the normal amount of functional protein, leading to an intermediate phenotype.
11. Examples in Humans
Are There Specific Traits in Humans That Exhibit Incomplete Dominance?
Yes, several human traits are believed to exhibit incomplete dominance:
- Hair Texture: As mentioned earlier, hair texture in humans can show incomplete dominance, with heterozygotes having wavy hair.
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia: This genetic disorder, which affects cholesterol levels, shows incomplete dominance, with heterozygotes having intermediate cholesterol levels compared to homozygotes.
12. Examples in Animals
Can Incomplete Dominance Be Observed in Animal Traits?
In animals, incomplete dominance is observed in several traits:
- Coat Color in Horses: Certain coat colors in horses, such as palomino (a golden coat with a white mane and tail), result from incomplete dominance.
- Feather Color in Chickens: In chickens, the Andalusian breed displays incomplete dominance in feather color, where a cross between a black-feathered chicken and a white-feathered chicken results in blue-feathered offspring.
13. Examples in Plants
What Are Some Common Examples of Incomplete Dominance in Plants?
Plants provide numerous examples of incomplete dominance:
- Flower Color: Snapdragon and four o’clock plants are the most commonly cited examples, as previously discussed.
- Fruit Size in Eggplants: In eggplants, fruit size can exhibit incomplete dominance, with heterozygotes producing fruits of intermediate size.
14. The Significance of Incomplete Dominance in Plant Breeding
How Do Plant Breeders Utilize Incomplete Dominance?
Plant breeders often utilize incomplete dominance to create hybrid varieties with desirable traits. By crossing two homozygous lines with different traits exhibiting incomplete dominance, they can produce offspring with an intermediate phenotype that combines the best qualities of both parents.
15. The Implications of Incomplete Dominance in Animal Breeding
How Is Incomplete Dominance Relevant in Animal Breeding Programs?
In animal breeding, understanding incomplete dominance can help breeders predict the phenotypes of offspring and select for desired traits. This is particularly useful in traits that are economically important, such as coat color or production traits.
16. Mathematical Representation of Incomplete Dominance
Can We Predict Phenotypic Ratios Using Punnett Squares for Incomplete Dominance?
Yes, Punnett squares can be used to predict the phenotypic ratios in offspring resulting from crosses involving incomplete dominance. For example, crossing two heterozygous individuals (Rr) will result in offspring with the genotypes RR, Rr, and rr in a 1:2:1 ratio, corresponding to the phenotypes red, pink, and white, respectively.
17. Statistical Analysis of Incomplete Dominance Inheritance Patterns
How Do We Confirm Incomplete Dominance Through Statistical Analysis?
Chi-square tests can be used to analyze observed phenotypic ratios in experimental crosses and determine whether they deviate significantly from the expected ratios under incomplete dominance. This helps confirm whether a trait is indeed inherited through incomplete dominance.
18. Incomplete Dominance in Human Genetic Disorders
How Does Incomplete Dominance Play a Role in Certain Genetic Disorders?
In some human genetic disorders, incomplete dominance can influence the severity of the condition in heterozygous carriers. For example, in familial hypercholesterolemia, heterozygotes have intermediate cholesterol levels and are at an increased risk of developing heart disease compared to individuals without the affected allele.
19. The Importance of Accurate Genetic Counseling in Incomplete Dominance Scenarios
Why Is Genetic Counseling Crucial for Families Affected by Incomplete Dominance?
Genetic counseling is essential for families affected by traits inherited through incomplete dominance. Counselors can provide information about the inheritance pattern, the risk of recurrence in future offspring, and the available options for genetic testing and management.
20. The Future of Incomplete Dominance Research
What Future Research Directions Are Being Explored Regarding Incomplete Dominance?
Future research directions include:
- Molecular mechanisms: Further investigating the molecular mechanisms underlying incomplete dominance.
- Epigenetics: Exploring the role of epigenetic modifications in influencing gene expression and phenotypic outcomes in incomplete dominance.
- Complex traits: Studying the contribution of incomplete dominance to complex traits and diseases.
21. Advanced Concepts
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Interactions
As our understanding of genetics deepens, so does our appreciation for the intricate dance between genes. The concept of incomplete dominance, while seemingly straightforward, opens the door to more complex genetic interactions that influence the diversity and variability we see in living organisms.
22. Polygenic Inheritance and Incomplete Dominance: A Combined Effect
How Do Multiple Genes Interact to Influence Traits?
Many traits are influenced not by a single gene but by multiple genes, a phenomenon known as polygenic inheritance. When combined with incomplete dominance, the resulting phenotypes can be even more varied and nuanced.
- Skin Color in Humans: Human skin color, for example, is influenced by multiple genes, each contributing to the overall pigmentation. The interaction of these genes, along with environmental factors, results in a continuous spectrum of skin tones.
23. Epigenetic Factors and Incomplete Dominance: How Environment Plays a Role
How Can Environmental Factors Influence the Expression of Genes?
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the DNA sequence itself. Environmental factors such as diet, stress, and exposure to toxins can influence epigenetic modifications, which in turn can affect the expression of genes involved in incomplete dominance.
- Agouti Gene in Mice: The agouti gene in mice provides a compelling example of how environmental factors can influence gene expression and phenotype.
24. The Role of Incomplete Dominance in Evolution
How Does Incomplete Dominance Contribute to Evolutionary Processes?
Incomplete dominance can play a significant role in evolutionary processes by increasing the range of phenotypic variation within a population. This increased variation provides a broader canvas upon which natural selection can act, potentially leading to adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
- Industrial Melanism: Industrial melanism in peppered moths provides a classic example of how natural selection can favor different phenotypes depending on environmental conditions.
25. The Impact on Crop Improvement
How Is Incomplete Dominance Utilized in Modern Agriculture?
Incomplete dominance has practical applications in crop improvement, where breeders can leverage this phenomenon to develop hybrid varieties with superior traits. By carefully selecting parent lines with desirable traits exhibiting incomplete dominance, breeders can create offspring with intermediate phenotypes that combine the best qualities of both parents.
- Hybrid Corn: Hybrid corn is a prime example of how breeders have successfully utilized incomplete dominance to improve crop yields and disease resistance.
26. Ethical Considerations
What Are the Ethical Implications of Manipulating Incomplete Dominance?
As we gain a deeper understanding of the genetic mechanisms underlying incomplete dominance, ethical considerations arise regarding the manipulation of these mechanisms for various purposes. Genetic engineering technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 offer the potential to precisely edit genes involved in incomplete dominance, raising questions about the ethical boundaries of such interventions.
- Designer Babies: The prospect of “designer babies,” where parents can select for certain traits in their offspring, raises concerns about potential social inequalities and the commodification of human life.
27. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Incomplete Dominance
Common Inquiries and Misconceptions Addressed
To further clarify the concept of incomplete dominance, let’s address some frequently asked questions:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between incomplete and complete dominance? | In complete dominance, one allele masks the expression of the other, while in incomplete dominance, the heterozygote exhibits an intermediate phenotype. |
| How does incomplete dominance affect phenotypic ratios? | In a monohybrid cross involving incomplete dominance, the phenotypic ratio is typically 1:2:1, corresponding to the homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive phenotypes. |
| Can incomplete dominance be observed in humans? | Yes, several human traits, such as hair texture and familial hypercholesterolemia, are believed to exhibit incomplete dominance. |
| How is incomplete dominance utilized in plant and animal breeding? | Breeders can leverage incomplete dominance to create hybrid varieties with desirable traits by crossing parent lines with different traits exhibiting incomplete dominance. |
28. Real-World Scenarios
Examples from Various Fields of Study
Understanding incomplete dominance extends beyond the classroom and into various fields of study. Let’s explore some real-world scenarios where this genetic phenomenon plays a role:
- Medicine: Incomplete dominance is relevant in understanding the inheritance patterns and severity of certain genetic disorders, such as familial hypercholesterolemia.
- Agriculture: Plant and animal breeders utilize incomplete dominance to develop hybrid varieties with superior traits, enhancing crop yields and improving livestock production.
- Evolutionary Biology: Incomplete dominance contributes to the range of phenotypic variation within a population, influencing the dynamics of natural selection and adaptation.
29. Summary of Key Points
Reinforcing Understanding Through Concise Review
Incomplete dominance is a fascinating genetic phenomenon where the heterozygote exhibits an intermediate phenotype. It is observed in various organisms, including plants, animals, and humans, and plays a significant role in genetic variation, inheritance patterns, and evolutionary processes. Understanding incomplete dominance is essential for comprehending the complexities of genetics and its implications in diverse fields of study.
30. Further Reading and Resources
Expanding Knowledge Through External Sources
To delve deeper into the topic of incomplete dominance, consider exploring the following resources:
- Textbooks: Consult genetics textbooks for comprehensive coverage of inheritance patterns and genetic interactions.
- Scientific Articles: Search scientific databases for research articles on incomplete dominance in specific organisms or traits.
- Online Resources: Explore reputable online resources such as university websites and educational platforms for additional information and examples.
31. Expert Opinions
Insights from Leading Geneticists
“Incomplete dominance is a prime example of how genetic inheritance can deviate from simple Mendelian patterns,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned geneticist at the University of Genetic Studies. “Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying incomplete dominance is crucial for unraveling the complexities of gene expression and phenotypic variation.”
32. Call to Action: Explore Your Genetic Potential
Have you ever wondered about your own genetic makeup? Do you have questions about inherited traits or genetic disorders? WHAT.EDU.VN offers a platform to explore your genetic potential and gain valuable insights into your family history. Contact us today to learn more about our genetic counseling services and unlock the secrets of your DNA.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States.
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890.
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
33. Understanding Phenotype Variation
What Factors Influence How Traits are Displayed?
The phenotype, or observable characteristics, of an organism is not solely determined by its genotype. Environmental factors, epigenetic modifications, and complex genetic interactions can all influence how traits are expressed.
- Environmental Effects: Diet, climate, and exposure to toxins can all impact phenotypic expression.
- Epigenetic Modifications: DNA methylation and histone modification can alter gene expression without changing the DNA sequence itself.
- Genetic Interactions: Epistasis, where one gene masks the expression of another, and polygenic inheritance, where multiple genes contribute to a trait, can further complicate phenotypic variation.
34. Quantitative Genetics: Measuring Continuous Traits
How Can We Study Traits That Show a Range of Variation?
Quantitative genetics provides a framework for studying traits that exhibit continuous variation, such as height, weight, and blood pressure. These traits are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors, making them more complex to analyze than simple Mendelian traits.
- Heritability: Heritability is a measure of the proportion of phenotypic variation in a population that is due to genetic factors.
- Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping: QTL mapping is a technique used to identify regions of the genome that are associated with quantitative traits.
35. The Influence of Modifier Genes
What Role Do Modifier Genes Play in Trait Expression?
Modifier genes can influence the expression of other genes, either enhancing or suppressing their effects. These genes can contribute to the subtle variations in phenotype that are observed in individuals with the same genotype.
- Hair Color: In humans, modifier genes can influence the intensity and shade of hair color.
36. Ask Your Questions
Do You Have More Genetic Queries?
Still curious about genetics? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding accurate and reliable answers can be challenging. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question you have and receive expert responses quickly and free of charge.
37. Get Free Answers at WHAT.EDU.VN
Your Go-To Source for Quick and Reliable Answers
Stop wasting time searching endlessly for the information you need. WHAT.EDU.VN offers a convenient and user-friendly platform where you can ask questions on any topic and receive answers from knowledgeable experts. Our service is completely free, so you can get the information you need without breaking the bank.
38. Don’t Hesitate to Ask
Every Question is Welcome
No matter how simple or complex your question may be, we’re here to help. Our community of experts is passionate about sharing their knowledge and providing clear, concise answers. Don’t hesitate to ask anything that’s on your mind.
39. Prompt Response
Quick Turnaround Time
We understand that you need answers quickly. That’s why we strive to provide prompt responses to all questions submitted through our platform. You can count on us to deliver the information you need in a timely manner.
40. Expert Assistance
Knowledgeable Professionals Ready to Help
Our team of experts consists of professionals with years of experience in their respective fields. You can trust that the answers you receive from WHAT.EDU.VN are accurate, reliable, and based on the latest research and evidence.
41. Convenience at Your Fingertips
Accessible Anytime, Anywhere
WHAT.EDU.VN is available 24/7, so you can ask questions and receive answers whenever and wherever it’s convenient for you. Our platform is accessible on any device, so you can get the information you need whether you’re at home, at school, or on the go.
42. Free Consultation
Get Your Questions Answered Free of Charge
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we believe that everyone deserves access to accurate and reliable information. That’s why we offer our question-and-answer service completely free of charge. You can get the answers you need without having to worry about hidden fees or subscriptions.
43. Unlock Your Curiosity
Satisfy Your Thirst for Knowledge
WHAT.EDU.VN is more than just a question-and-answer platform; it’s a community of curious minds eager to explore the world around them. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone who loves to learn, we invite you to join our community and unlock your curiosity.
44. Gain New Perspectives
Expand Your Understanding of the World
By asking questions and receiving answers from diverse perspectives, you can expand your understanding of the world and challenge your own assumptions. WHAT.EDU.VN provides a unique opportunity to engage with different viewpoints and gain new insights into complex topics.
45. Take the Next Step
Unlock Answers for Free Today
Ready to start asking questions and expanding your knowledge? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and discover the power of free expert answers. Our platform is easy to use, and our community of experts is waiting to help you on your journey of discovery.
46. Call to Action: Ask Away!
Still have questions? Want personalized advice? Don’t let confusion hold you back! Visit WHAT.EDU.VN now and ask your questions for free.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States.
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890.
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Take advantage of our expert assistance and get the answers you need to succeed. Unlock your potential with what.edu.vn today!