PEMDAS is an acronym that serves as a vital mnemonic device for remembering the order of operations in mathematics. When faced with an expression containing multiple operations, PEMDAS dictates the sequence in which these operations must be performed to arrive at the correct answer. Let’s delve into what PEMDAS entails and how it’s applied.
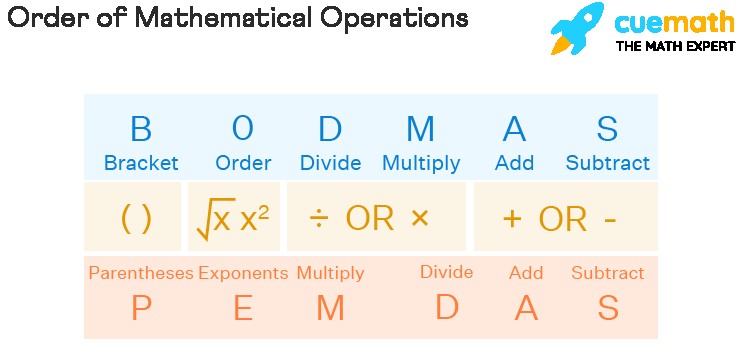
Sometimes, other acronyms like BODMAS, GEMDAS, and even BEDMAS might be used. These represent the same order of operations, simply using different terms depending on region or preference. For instance, BODMAS uses “Brackets” instead of “Parentheses,” and “Order” refers to exponents.
In this guide, we will explore the PEMDAS rule in detail, providing examples and practice questions to solidify your understanding.
| Section | Topic |
|---|---|
| Introduction to PEMDAS | What Is Pemdas and why is it important? |
| PEMDAS Explained | Breaking down each letter of the acronym. |
| The PEMDAS Rule | A step-by-step guide to applying PEMDAS. |
| PEMDAS vs. Other Acronyms | Comparing PEMDAS with similar acronyms like BODMAS. |
| When to Use PEMDAS | Identifying situations requiring PEMDAS. |
| Common Mistakes | Avoiding pitfalls when using PEMDAS. |
| PEMDAS Examples | Illustrated examples of PEMDAS in action. |
| Practice Questions | Test your knowledge with practice problems. |
| FAQs on PEMDAS | Answers to frequently asked questions. |

Introduction to PEMDAS
PEMDAS, or the order of operations, is a fundamental concept in mathematics. It ensures that any mathematical expression has one correct and consistent solution. Imagine a factory where toys are assembled in a specific order: design, build, pack, and quality check. Changing this order would result in faulty products. Similarly, PEMDAS provides a fixed sequence for performing arithmetic operations.
Let’s say Ron and Raven are trying to solve the equation 5 + 2 × 3. Ron calculates 5 + 2 first, getting 7, then multiplies by 3 to get 21. Raven, however, multiplies 2 × 3 first, resulting in 6, then adds 5 to get 11. Who is correct? This is where PEMDAS comes in.
| Ron’s Method | Raven’s Method |
|---|---|
| 5+2×3 = 7×3 = 21 | 5+2×3 = 5+6 = 11 |
PEMDAS provides the definitive answer.
PEMDAS Explained
PEMDAS breaks down as follows:
- P – Parentheses: Expressions inside parentheses or brackets are solved first. This includes all types of brackets: ( ), { }, and [ ].
- E – Exponents: Next, we evaluate exponents or powers.
- M – Multiplication: Multiplication is performed from left to right.
- D – Division: Division is performed from left to right.
- A – Addition: Addition is performed from left to right.
- S – Subtraction: Subtraction is performed from left to right.
The PEMDAS Rule
The PEMDAS rule is a set of guidelines to follow when solving mathematical expressions. It dictates that operations must be performed in the following order: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), and Addition and Subtraction (from left to right).
| Order | Symbol | Operation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [{( )}] | Parentheses |
| 2 | x2 | Exponents |
| 3 | × or ÷ | Multiplication or Division |
| 4 | + or – | Addition or Subtraction |
A common mnemonic to remember PEMDAS is: Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally.
Here’s an example illustrating the PEMDAS rule:
PEMDAS vs. Other Acronyms
PEMDAS is similar to BODMAS (Brackets, Order, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction). The difference lies mainly in terminology, with “Parentheses” and “Brackets” referring to the same concept, and “Order” encompassing exponents.
When to Use PEMDAS
PEMDAS is essential when an expression contains more than one operation. It provides a structured approach, ensuring consistent and accurate results. By following the PEMDAS sequence, mathematical expressions yield a unique and correct answer.
Key Points:
- Always start with operations inside brackets.
- Next, handle exponents.
- Then, work from left to right, performing multiplication or division as they appear.
- Finally, move from left to right, carrying out addition or subtraction as they appear.
Common Mistakes
A common mistake occurs when dealing with nested brackets (brackets within brackets). The rule is to always start with the innermost bracket and work your way outwards. Importantly, remember to apply PEMDAS within each bracket.
Consider this example: 4 + 3 [8 – 2 (6 – 3)] ÷ 2. To solve it correctly, follow these steps:
4 + 3 [8 – 2 (6 – 3)] ÷ 2 =
4 + 3 [8 – 2(3)] ÷ 2 (∵ 6 – 3 = 3) =
4 + 3 [8 – 6] ÷ 2 (∵ 2(3) = 6) =
4 + 3 [2] ÷ 2 (∵ 8 – 6 = 2) =
4 + 6 ÷ 2 (∵ 3 × 2 = 6) =
4 + 3 = 7
PEMDAS Examples
-
Example 1: Simplify 18 ÷ (8 – 2 × 3).
Solution: First, solve the parentheses: (8 – 2 × 3). Within the parentheses, multiply first: 2 × 3 = 6. Then subtract: 8 – 6 = 2. Now, divide: 18 ÷ 2 = 9. Therefore, 18 ÷ (8 – 2 × 3) = 9.
-
Example 2: Simplify (4 × 3 ÷ 6 + 1) × 32
Solution:
Step 1: Multiply 4 by 3: (12 ÷ 6 + 1) × 32
Step 2: Divide 12 by 6: (2 + 1) × 32
Step 3: Remove parentheses after adding 2 and 1: 3 × 32
Step 4: Solve the exponent: 3 × 9
Step 5: Multiply: 3 × 9 = 27. Therefore, (4 × 3 ÷ 6 + 1) × 32 = 27.
Practice Questions
Test your understanding of PEMDAS with these practice problems:
- Solve: 17 + 77 ÷ 11 + 22 − 8 × 5
- Insert operators (+, −, ×, ÷) to make the equation true: 7 _ 2 _ 2 = 12
- Evaluate: 4 × 8 − 2 × 11 + 27 ÷ 3 ÷ 3
- Evaluate: 18 ÷ {29 − 3 − [100 ÷ (52 × 10 − 200)] × 10}
- A rectangular garden is 100 m long and 40 m wide. A square flower bed with a side of 20 m is within the garden. Write an expression for the area of the garden excluding the flower bed.
FAQs on PEMDAS
What Does PEMDAS Mean?
PEMDAS is an acronym representing the order of operations: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction.
How Does PEMDAS Rule Work?
PEMDAS dictates the sequence for solving mathematical expressions. Start with parentheses, then exponents, then multiplication and division (from left to right), and finally addition and subtraction (from left to right).
How to Do PEMDAS With Fractions?
The PEMDAS rule remains the same when dealing with fractions. Apply the order of operations as usual.
What Does the P Stand for in PEMDAS?
P stands for Parentheses.
What is the Use of PEMDAS Calculator?
A PEMDAS calculator simplifies complex arithmetic expressions quickly and accurately by following the order of operations.
Do You Multiply or Divide First in PEMDAS?
Multiplication and division are performed from left to right, whichever operation comes first.
When do we Apply the PEMDAS Rule?
Apply the PEMDAS rule whenever an expression involves multiple operations.
What is the Rule for PEMDAS?
The PEMDAS rule provides the correct sequence for solving mathematical expressions, ensuring consistent and accurate results.