Perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that you encounter early in your math journey and use throughout your life. Simply put, perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape. Imagine walking around the edge of a park, a garden, or a room; the total distance you walk is the perimeter of that area. Understanding perimeter is crucial not just for math class, but also for practical applications in everyday life.
To understand it better, let’s break down the definition and explore how to calculate the perimeter for different shapes.
Defining Perimeter: Measuring the Boundary
In mathematical terms, the perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary or outline. Think of it as the ‘rim’ or the outer edge. To find the perimeter, you need to measure the length of each side of the shape and then add them all together.
Perimeter is always measured in linear units. This means we use units like centimeters (cm), meters (m), inches (in), feet (ft), and so on. We are measuring a distance, which is one-dimensional.
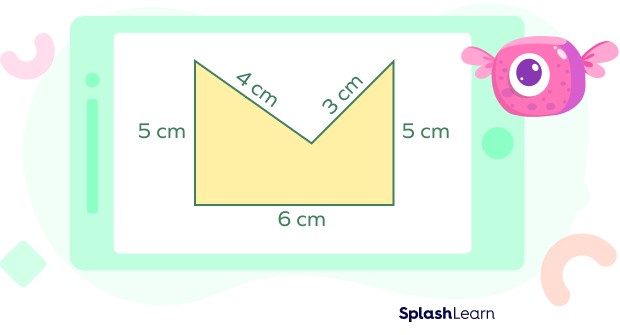
Let’s take a simple example to illustrate this. Consider the shape below:
To find the perimeter of this shape, we sum the lengths of all its sides:
Perimeter = 6 cm + 5 cm + 5 cm + 4 cm + 3 cm = 23 cm
Therefore, the perimeter of this shape is 23 centimeters.
How to Calculate Perimeter: Formulas and Methods
The basic principle for finding the perimeter is always the same: add up the lengths of all the sides. However, for different types of shapes, we can use specific formulas to make the calculation quicker and easier, especially for regular shapes.
Perimeter of Regular Shapes: Utilizing Symmetry
Regular shapes, also known as regular polygons, are shapes where all sides are of equal length and all angles are of equal measure. Examples of regular shapes include squares, equilateral triangles, regular pentagons, and regular hexagons. Because of their symmetry, calculating the perimeter of regular shapes is simplified.
Instead of adding each side individually, we can use a formula:
Perimeter of a Regular Polygon = Number of Sides × Length of One Side
Let’s look at some common regular shapes and their perimeter calculations:
-
Square: A square has 4 equal sides. If one side of a square is ‘s’, then:
Perimeter of Square = 4 × s -
Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides. If one side is ‘a’, then:
Perimeter of Equilateral Triangle = 3 × a -
Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has 5 equal sides. If one side is ‘p’, then:
Perimeter of Regular Pentagon = 5 × p -
Regular Hexagon: A regular hexagon has 6 equal sides. If one side is ‘h’, then:
Perimeter of Regular Hexagon = 6 × h
Here’s a table summarizing formulas for some common regular polygons:
For example, if we have a regular pentagon with each side measuring 7 cm, its perimeter would be:
Perimeter = 5 × 7 cm = 35 cm
Perimeter of Irregular Shapes: Summing All Sides
Irregular shapes, or irregular polygons, are shapes where the sides are not all of equal length, and angles are not all of equal measure. Examples include scalene triangles, rectangles (unless they are squares), and any polygon where sides and angles vary.
For irregular shapes, we cannot use a shortcut formula like we do for regular shapes. The only way to find the perimeter of an irregular shape is to go back to the basic definition:
Perimeter of Irregular Polygon = Sum of the Lengths of All Sides
You simply need to measure the length of each side and add them up. For instance, in the initial example shape we used, it was an irregular shape, and we found its perimeter by adding all five given side lengths.
Real-World Applications of Perimeter: Where Do We Use It?
Perimeter isn’t just an abstract mathematical concept; it has numerous practical applications in our daily lives. Understanding perimeter helps us solve real-world problems related to measurement and space.
Here are some common examples of how perimeter is used in real life:
-
Fencing a Yard or Garden: When you want to put a fence around your backyard or garden, you need to calculate the perimeter to know how much fencing material to buy.
-
Christmas Lights and Decorations: If you’re decorating your house with Christmas lights, you’ll need to find the perimeter of your windows, roofline, or garden to determine the length of lights required.
-
Framing Pictures or Mirrors: To frame a picture or a mirror, you need to know the perimeter to cut the right length of frame material.
-
Building a Border: Whether it’s a border around a flower bed, a rug, or a patio, perimeter helps you calculate the necessary length of border material.
-
Sports Fields and Courts: The dimensions of sports fields like soccer fields, basketball courts, and tennis courts are often defined by their perimeters.
These are just a few examples, and you can find many more applications of perimeter in construction, design, landscaping, and various other fields.
Solved Examples: Step-by-Step Perimeter Calculations
Let’s work through a few examples to solidify your understanding of perimeter calculation.
Example 1: Perimeter of a Triangle
What is the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 8 cm, 6 cm, and 10 cm?
Solution:
To find the perimeter of any triangle, we add the lengths of its three sides.
Perimeter = Side 1 + Side 2 + Side 3
Perimeter = 8 cm + 6 cm + 10 cm = 24 cm
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 24 cm.
Example 2: Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon
Calculate the perimeter of the following irregular pentagon:
Solution:
For an irregular pentagon, we sum the lengths of all five sides.
Perimeter = 2 cm + 3 cm + 3 cm + 5 cm + 4 cm = 17 cm
The perimeter of this irregular pentagon is 17 cm.
Example 3: Perimeter of a Rectangle
What is the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 15 cm and a width of 7 cm?
Solution:
A rectangle has two pairs of equal sides: two lengths and two widths. The formula for the perimeter of a rectangle is:
Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width)
Perimeter = 2 × (15 cm + 7 cm)
Perimeter = 2 × (22 cm) = 44 cm
The perimeter of the rectangle is 44 cm.
Practice Problems: Test Your Perimeter Skills
Ready to test your understanding? Try these practice problems:
- Square Perimeter: Find the perimeter of a square with sides that are each 25 cm long.
- Rectangle Perimeter: Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle that is 40 cm long and 20 cm wide.
- Irregular Shape Perimeter: What is the perimeter of a shape with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, 6 cm, and 6 cm?
- Equilateral Triangle Perimeter: An equilateral triangle has sides of 12 cm each. What is its perimeter?
(Answers: 1. 100 cm, 2. 120 cm, 3. 36 cm, 4. 36 cm)
Frequently Asked Questions About Perimeter
Q: What is the difference between perimeter and area?
A: Perimeter is the distance around a shape, a one-dimensional measurement in linear units. Area is the space inside a shape, a two-dimensional measurement in square units. Think of perimeter as the fence around a yard, and area as the grass within the fence.
Q: Can perimeter be calculated for 3D shapes?
A: Perimeter is specifically a concept for two-dimensional shapes. For three-dimensional shapes, we talk about surface area (the total area of all the faces) and volume (the space occupied by the 3D shape).
Q: Is the circumference the same as the perimeter?
A: Yes, circumference is a special term for the perimeter of a circle or other curved shape. For polygons (shapes with straight sides), we use the term perimeter.
Q: Why is understanding perimeter important?
A: Understanding perimeter is important because it has many practical applications in everyday life, from home improvement projects to understanding measurements in various fields. It’s a fundamental concept in geometry and spatial reasoning.
Conclusion: Perimeter – A Key Geometric Concept
Perimeter is a simple yet essential concept in geometry that describes the distance around a shape. Whether you’re calculating the fence needed for your garden or figuring out the length of trim for a room, understanding perimeter is a valuable skill. By knowing how to calculate perimeter for both regular and irregular shapes, you unlock a powerful tool for problem-solving in mathematics and the real world.