What Is Prolapse uterus? Find comprehensive answers at WHAT.EDU.VN. A uterine prolapse happens when the uterus descends from its normal position. We offer clear explanations, symptoms, and treatment options, ensuring you’re informed every step of the way. Explore pelvic organ prolapse, uterine health, and pelvic floor strengthening.
Table of Contents
- What is Uterine Prolapse?
- Identifying the Symptoms of Uterine Prolapse
- What Causes Uterine Prolapse?
- When Should You Consult a Doctor?
- Diagnosing Uterine Prolapse: What to Expect
- Understanding the Stages of Uterine Prolapse
- Effective Treatment Options for Uterine Prolapse
- Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing Uterine Prolapse
- The Role of Pelvic Floor Exercises in Uterine Prolapse
- Vaginal Pessaries: A Supportive Option
- Hormone Replacement Therapy and Uterine Health
- Surgical Interventions for Uterine Prolapse
- Preventing Uterine Prolapse: Proactive Steps
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Uterine Prolapse
- Seeking Support and Additional Resources
- Addressing Specific Concerns: Uterine Prolapse and Sexual Health
- The Impact of Diet and Nutrition on Uterine Prolapse
- Managing Uterine Prolapse During and After Pregnancy
- Understanding the Psychological Effects of Uterine Prolapse
- The Future of Uterine Prolapse Treatment: Innovations and Research
1. What is Uterine Prolapse?
Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus descends from its normal position in the pelvis, potentially dropping into the vaginal canal. This condition arises due to the weakening of pelvic floor muscles and ligaments that support the uterus. Pelvic organ prolapse, including uterine prolapse, is a common issue affecting women, particularly as they age. Factors contributing to this weakening include childbirth, aging, obesity, and chronic straining. Uterine prolapse can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life, leading to discomfort and other complications. For reliable information on uterine and pelvic health, turn to WHAT.EDU.VN for expert insights on pelvic floor health and prolapse conditions.
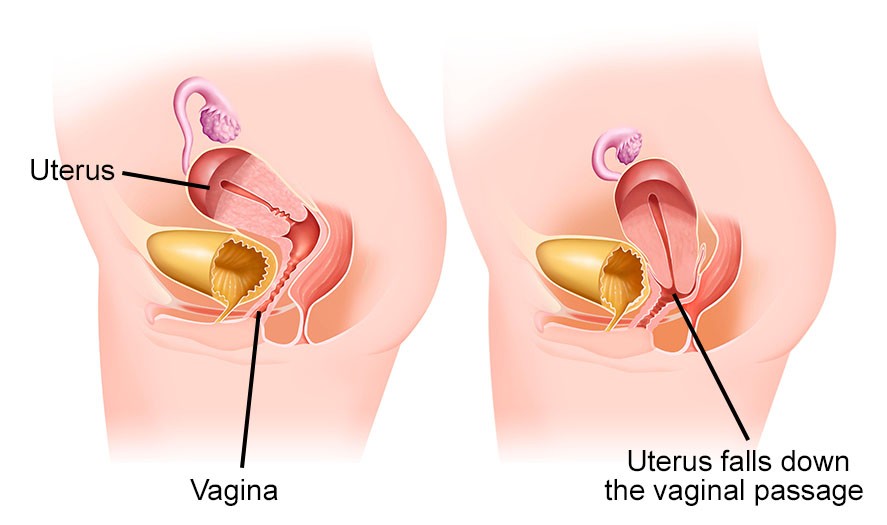 Illustration of a prolapsed uterus, showing the uterus falling down towards the vaginal opening.
Illustration of a prolapsed uterus, showing the uterus falling down towards the vaginal opening.
2. Identifying the Symptoms of Uterine Prolapse
Recognizing the symptoms of uterine prolapse is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms include a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the pelvis, a sensation of something “falling out” of the vagina, and discomfort during intercourse. Women may also experience urinary problems, such as frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder, as well as bowel issues like constipation. Lower back pain is another potential symptom. The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the degree of prolapse. If you experience any of these signs, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. For accurate and easy-to-understand information about recognizing the signs of prolapse, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
3. What Causes Uterine Prolapse?
Uterine prolapse is primarily caused by weakened pelvic floor muscles and supporting tissues. Several factors can contribute to this weakening. Pregnancy and childbirth are major contributors, as the strain of carrying a baby and delivering vaginally can stretch and damage these muscles. Aging and menopause also play a role, as estrogen levels decrease, leading to tissue thinning. Other risk factors include obesity, chronic coughing, constipation, and repetitive heavy lifting. Understanding these causes is essential for prevention and management. To learn more about the risk factors and causes of uterine prolapse, explore the resources available at WHAT.EDU.VN.
4. When Should You Consult a Doctor?
It’s important to consult a doctor if you experience any symptoms of uterine prolapse, such as pelvic pressure, a bulge in the vagina, or urinary problems. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and improve your quality of life. Ignoring the symptoms can lead to more severe complications. A healthcare provider can evaluate your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment options. Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you have concerns. WHAT.EDU.VN offers resources to help you prepare for your doctor’s visit and understand your treatment options.
5. Diagnosing Uterine Prolapse: What to Expect
Diagnosing uterine prolapse typically involves a pelvic exam. During the exam, the doctor will assess the position of your uterus and other pelvic organs. You may be asked to strain or cough to see how the prolapse changes with increased pressure. Additional tests, such as an ultrasound or MRI, may be ordered to get a better view of the pelvic organs. These tests can help determine the extent of the prolapse and rule out other conditions. The diagnostic process is usually straightforward and can provide valuable information for treatment planning. For a comprehensive understanding of the diagnostic procedures for uterine prolapse, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
6. Understanding the Stages of Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse is classified into stages based on how far the uterus has descended into the vagina:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage 0 | No prolapse; the uterus is in its normal anatomical position. |
| Stage 1 | The uterus descends slightly into the upper part of the vagina. |
| Stage 2 | The uterus descends further, reaching the lower part of the vagina. |
| Stage 3 | The uterus protrudes from the vaginal opening. |
| Stage 4 | The uterus is completely outside the vagina. |
Understanding the stage of prolapse helps determine the appropriate treatment approach. Mild prolapse (stages 1 and 2) may be managed with conservative treatments, while more severe prolapse (stages 3 and 4) may require surgery. WHAT.EDU.VN provides detailed explanations of each stage of uterine prolapse, helping you understand your diagnosis and treatment options.
7. Effective Treatment Options for Uterine Prolapse
Treatment for uterine prolapse varies depending on the severity of the condition and your overall health. Options include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: These include weight loss, avoiding heavy lifting, and managing constipation.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help support the uterus.
- Pessary: A removable device inserted into the vagina to support the uterus.
- Hormone Therapy: Estrogen can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
- Surgery: This may be necessary for severe prolapse to reposition the uterus.
Your doctor will help you choose the best treatment plan based on your individual needs. For more in-depth information on the various treatment options for uterine prolapse, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
8. Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing Uterine Prolapse
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly help in managing uterine prolapse. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the pelvic floor. Avoiding heavy lifting and straining can prevent further weakening of the supporting muscles. Eating a high-fiber diet and drinking plenty of water can help prevent constipation, which can exacerbate prolapse. Quitting smoking is also beneficial, as chronic coughing can strain the pelvic floor. These lifestyle changes can improve your overall well-being and reduce the symptoms of uterine prolapse. WHAT.EDU.VN offers practical tips and advice on making these lifestyle adjustments.
9. The Role of Pelvic Floor Exercises in Uterine Prolapse
Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, are a cornerstone of conservative treatment for uterine prolapse. These exercises involve contracting and relaxing the muscles of the pelvic floor, which helps strengthen them and provide better support for the uterus. Regular pelvic floor exercises can improve the symptoms of mild to moderate prolapse. A physical therapist can teach you the correct technique and help you develop a consistent exercise routine. For detailed instructions on how to perform pelvic floor exercises effectively, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
10. Vaginal Pessaries: A Supportive Option
A vaginal pessary is a removable device inserted into the vagina to provide support for the uterus and other pelvic organs. Pessaries come in various shapes and sizes and can be fitted by a healthcare provider. They can be a good option for women who want to avoid surgery or who are not good candidates for surgery. Pessaries need to be cleaned regularly to prevent infection. While they can provide relief from symptoms, they do not correct the underlying problem. WHAT.EDU.VN offers comprehensive information on vaginal pessaries, including how they work, their benefits, and potential risks.
11. Hormone Replacement Therapy and Uterine Health
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can play a role in managing uterine prolapse, particularly in postmenopausal women. Estrogen helps maintain the strength and elasticity of the pelvic floor muscles and tissues. As estrogen levels decline during menopause, these tissues can weaken, increasing the risk of prolapse. HRT can help restore estrogen levels and improve the tone of the pelvic floor. However, HRT is not suitable for all women and carries certain risks. Discuss the potential benefits and risks with your doctor. For a balanced and informative overview of hormone replacement therapy and its impact on uterine health, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
12. Surgical Interventions for Uterine Prolapse
Surgery may be recommended for severe cases of uterine prolapse that do not respond to conservative treatments. Surgical options include:
- Uterine Suspension: This involves reattaching the uterus to the pelvic ligaments.
- Vaginal Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus through the vagina.
- Sacrocolpopexy: Attaching the vagina to the sacrum (the bone at the base of the spine) for support.
The choice of surgery depends on the individual’s condition and preferences. Surgery can provide long-term relief from symptoms but also carries risks. Your doctor will discuss the surgical options with you and help you make an informed decision. WHAT.EDU.VN offers detailed information on the different surgical procedures for uterine prolapse, including their benefits and risks.
13. Preventing Uterine Prolapse: Proactive Steps
Preventing uterine prolapse involves taking proactive steps to maintain the strength and health of the pelvic floor. Regular pelvic floor exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and managing constipation are all important preventive measures. Women who have had children should start pelvic floor exercises soon after delivery. Quitting smoking and managing chronic coughs can also help prevent prolapse. Taking these steps can reduce your risk of developing uterine prolapse and improve your overall quality of life. For practical tips and advice on preventing uterine prolapse, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Uterine Prolapse
Here are some frequently asked questions about uterine prolapse:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can uterine prolapse be cured? | While uterine prolapse cannot always be completely cured, symptoms can be effectively managed with various treatments, including lifestyle changes, pelvic floor exercises, pessaries, and surgery. |
| Is uterine prolapse dangerous? | Uterine prolapse is not life-threatening but can significantly impact quality of life due to discomfort and other symptoms. |
| Can I get pregnant if I have uterine prolapse? | Yes, it is possible to get pregnant with uterine prolapse, but it may increase the risk of complications during pregnancy. Consult with your doctor for guidance. |
| Will uterine prolapse get worse over time? | Without treatment, uterine prolapse can worsen over time. Early intervention and management can help slow or prevent progression. |
| Are there any home remedies for uterine prolapse? | While there are no proven home remedies to cure uterine prolapse, lifestyle changes and pelvic floor exercises can help manage symptoms. |
| How long does it take to recover from uterine prolapse surgery? | Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery. Generally, it takes several weeks to a few months to fully recover. |
| Can uterine prolapse affect my sex life? | Yes, uterine prolapse can cause discomfort during sex. Treatment can help improve sexual function and comfort. |
| What is the best exercise for uterine prolapse? | Pelvic floor exercises (Kegels) are the best exercises for strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and supporting the uterus. |
| Is uterine prolapse hereditary? | While there is no direct genetic link, having a family history of pelvic floor weakness may increase your risk. |
| Can I still exercise if I have uterine prolapse? | Yes, but avoid high-impact exercises and heavy lifting. Focus on low-impact activities and pelvic floor strengthening exercises. |
For more detailed answers to these and other questions about uterine prolapse, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
15. Seeking Support and Additional Resources
Dealing with uterine prolapse can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s important to seek support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends. Support groups can also provide a valuable source of information and emotional support. There are many online resources available, including websites and forums dedicated to pelvic health. Don’t hesitate to reach out and get the help you need. WHAT.EDU.VN provides links to various support organizations and resources for women with uterine prolapse.
16. Addressing Specific Concerns: Uterine Prolapse and Sexual Health
Uterine prolapse can significantly impact sexual health, leading to discomfort, pain, and decreased sensation during intercourse. Many women with prolapse experience anxiety and self-consciousness about their condition, which can further affect their sex lives. However, with proper management and treatment, it is possible to improve sexual function and comfort. Options include using vaginal lubricants, trying different sexual positions, and undergoing treatment for the prolapse itself. Open communication with your partner and healthcare provider is essential. For more information on addressing sexual health concerns related to uterine prolapse, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
17. The Impact of Diet and Nutrition on Uterine Prolapse
While diet and nutrition cannot directly cure uterine prolapse, they can play a supportive role in managing symptoms and promoting overall pelvic health. A high-fiber diet can help prevent constipation, which can strain the pelvic floor. Adequate hydration is also important for maintaining bowel regularity. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support tissue health and muscle function. Some women find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms, so it’s helpful to keep a food diary to identify potential triggers. WHAT.EDU.VN offers dietary recommendations for women with uterine prolapse.
18. Managing Uterine Prolapse During and After Pregnancy
Pregnancy and childbirth are major risk factors for uterine prolapse. During pregnancy, the weight of the growing uterus can put significant pressure on the pelvic floor. Vaginal delivery can further stretch and damage these muscles. Women who develop prolapse during pregnancy should work with their healthcare provider to manage their symptoms. After delivery, it’s important to start pelvic floor exercises as soon as possible to help restore muscle tone. In some cases, prolapse may worsen after pregnancy and require further treatment. WHAT.EDU.VN provides guidance on managing uterine prolapse during and after pregnancy.
19. Understanding the Psychological Effects of Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse can have a significant impact on a woman’s psychological well-being. Symptoms such as pelvic pressure, urinary problems, and sexual dysfunction can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Many women experience a loss of self-esteem and body image issues. It’s important to acknowledge these psychological effects and seek support if needed. Counseling, therapy, and support groups can provide a safe space to discuss your feelings and develop coping strategies. WHAT.EDU.VN offers resources to help you address the psychological effects of uterine prolapse.
20. The Future of Uterine Prolapse Treatment: Innovations and Research
The field of uterine prolapse treatment is constantly evolving, with ongoing research focused on developing new and improved therapies. Innovations include minimally invasive surgical techniques, new types of pessaries, and regenerative medicine approaches to strengthen pelvic floor tissues. Researchers are also exploring the role of genetics and other risk factors in the development of prolapse. These advancements hold promise for improving the long-term outcomes and quality of life for women with uterine prolapse. Stay informed about the latest developments in uterine prolapse treatment by visiting WHAT.EDU.VN.
Are you looking for quick and free answers? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding reliable information. That’s why we offer a platform where you can ask any question and receive prompt, accurate responses from knowledgeable individuals. Don’t let unanswered questions hold you back—visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the convenience of free consultation services.
Contact us at:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn