What Is Psi? Pounds per square inch (PSI) is a crucial unit for measuring pressure. Are you looking for a simple and reliable way to understand PSI and its various applications? WHAT.EDU.VN offers free answers to all your questions, providing clear explanations and expert insights. Learn about pressure measurement, tensile strength, and elastic modulus with ease.
1. Defining PSI: Pounds Per Square Inch Explained
Pounds per square inch (PSI) is the amount of pressure exerted by one pound of force applied to an area of one square inch. It’s a standard unit of pressure in the imperial unit system, widely used in various fields and applications. Understanding PSI is essential for anyone dealing with pressure-related measurements and calculations.
1.1. The Fundamentals of PSI
PSI represents the force exerted on a specific area. To visualize this, imagine a one-pound weight resting on a one-square-inch surface. The pressure exerted on that surface is one PSI. This unit is crucial for understanding the strength and limitations of various materials and systems.
1.2. PSI in Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
In pneumatic systems, PSI measures the pressure of gases, such as in air compressors or pneumatic tools. In hydraulic systems, it measures the pressure of liquids, like in hydraulic brakes or heavy machinery. In both cases, PSI helps engineers and technicians ensure systems operate within safe and efficient pressure limits.
1.3. PSI as a Measure of Material Strength
Beyond fluid dynamics, PSI is also used to quantify material strength. Tensile strength, measured in PSI, indicates a material’s ability to withstand pulling forces before breaking. Elastic modulus, also measured in PSI, reflects a material’s stiffness and resistance to deformation under stress.
2. Common Applications of PSI
PSI is integral to a variety of industries and everyday applications, from inflating tires to assessing the structural integrity of materials. Understanding these applications can enhance your appreciation for the importance of PSI in modern technology and safety.
2.1. Tire Pressure: Ensuring Safe and Efficient Rides
One of the most common applications of PSI is in measuring tire pressure. Proper tire inflation, indicated in PSI, ensures optimal vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. Underinflated tires can lead to increased wear, reduced fuel economy, and a higher risk of blowouts.
2.2. Material Testing: Evaluating Tensile and Elastic Strength
In material science, PSI is used to measure tensile strength, indicating how much pulling force a material can withstand before breaking. It’s also used to measure elastic modulus, reflecting a material’s stiffness and resistance to deformation. These measurements are critical in engineering and manufacturing to ensure the safety and reliability of structures and products.
2.3. Industrial Applications: Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
PSI is a fundamental unit in industrial pneumatic and hydraulic systems. In pneumatic systems, it measures the pressure of compressed air used to power tools and machinery. In hydraulic systems, it measures the pressure of liquids used to operate heavy equipment like construction vehicles and industrial presses.
3. Understanding Pressure Measurement: PSI vs. Pascal
While PSI is widely used in the United States, the pascal (Pa) is the standard unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). Converting between PSI and pascals is essential for international collaboration and understanding scientific literature.
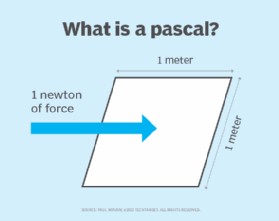
3.1. Pascal (Pa): The SI Unit of Pressure
The pascal (Pa) is defined as the pressure exerted by a force of one newton acting on an area of one square meter. It’s a smaller unit than PSI, making it more suitable for measuring low pressures in scientific and engineering applications.
3.2. Converting Between PSI and Pascal
To convert PSI to pascals, you multiply the PSI value by 6894.76. Conversely, to convert pascals to PSI, you divide the pascal value by 6894.76. This conversion is crucial for ensuring consistency and accuracy in pressure measurements across different systems.
3.3. Other Pressure Metrics: kPa, Atmospheric Pressure, and More
Besides pascals, other pressure metrics include kilopascals (kPa), which are 1,000 pascals, and atmospheric pressure, which is approximately 14.7 PSI at sea level. Understanding these different units and how they relate to PSI is important for various scientific and engineering applications.
4. Delving Deeper: Absolute vs. Gauge PSI
When measuring pressure, it’s important to differentiate between absolute PSI and gauge PSI. Absolute PSI measures pressure relative to a perfect vacuum, while gauge PSI measures pressure relative to atmospheric pressure.
4.1. Absolute PSI: Measuring Pressure Relative to a Vacuum
Absolute PSI (PSIA) is used when measuring pressure relative to a perfect vacuum. This means it includes the pressure exerted by the atmosphere. It is often used in scientific and engineering applications where precise pressure measurements are required.
4.2. Gauge PSI: Measuring Pressure Relative to Atmosphere
Gauge PSI (PSIG) is used when measuring pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. This is the type of measurement you typically see on tire pressure gauges or pressure cookers. It’s convenient because it measures the pressure above the ambient atmospheric pressure.
4.3. Why the Distinction Matters
The distinction between absolute and gauge PSI is important because it affects how you interpret pressure readings. For example, if a tire pressure gauge reads 30 PSIG, the absolute pressure inside the tire is actually 30 PSI plus atmospheric pressure (approximately 14.7 PSI), totaling 44.7 PSIA.
5. Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) is a crucial concept that incorporates pressure measurements. It refers to specific atmospheric conditions at sea level, typically used for measuring properties of gases.
5.1. Defining Standard Temperature and Pressure
STP is defined as 273.15 K (0 °C) and 1 atmosphere (101.325 kPa or 14.7 PSI). These conditions are used as a reference point for comparing gas properties and conducting scientific experiments.
5.2. The Importance of STP in Chemistry and Physics
In chemistry and physics, STP is used to standardize measurements of gas volume, density, and other properties. It allows scientists to compare results obtained under different conditions and to develop reliable models and theories.
5.3. Other Standards: Normal Temperature and Pressure (NTP)
Besides STP, there’s also Normal Temperature and Pressure (NTP), which is defined as 293.15 K (20 °C) and 1 atmosphere. NTP is often used in industrial and engineering applications as a more convenient reference point.
6. PSI in Different Measurement Systems
PSI is part of the imperial unit system, but it’s useful to know how it relates to other units in different measurement systems, such as technical atmospheres, torr, and bar.
6.1. Converting PSI to Technical Atmospheres
A technical atmosphere is defined as 1 kilogram of force per square centimeter. To convert PSI to technical atmospheres, you divide the PSI value by 14.2233. This conversion is useful in certain engineering and industrial contexts.
6.2. Converting PSI to Torr
Torr is a unit of pressure named after Evangelista Torricelli, the inventor of the barometer. To convert PSI to torr, you multiply the PSI value by 51.71493. Torr is commonly used in vacuum technology and high-precision pressure measurements.
6.3. Converting PSI to Bar
Bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100,000 pascals. To convert PSI to bar, you divide the PSI value by 14.5038. Bar is often used in meteorology and industrial applications for convenience.
7. Organizations Defining PSI Standards
Several national and international organizations define standards for PSI and other pressure metrics. These standards ensure consistency and accuracy in measurements across different industries and countries.
7.1. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
In the United States, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is responsible for developing and maintaining measurement standards. NIST provides guidelines and references for accurate PSI measurements in various applications.
7.2. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses PSI in various environmental monitoring and regulation activities. Accurate PSI measurements are essential for assessing air and water quality and enforcing environmental standards.
7.3. International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
Internationally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) develops standards for pressure measurements, including PSI. ISO standards ensure global consistency and facilitate international trade and collaboration.
8. Common Misconceptions About PSI
It’s important to address some common misconceptions about PSI to ensure accurate understanding and application of this unit of measurement.
8.1. PSI is Only Used for Tire Pressure
While PSI is commonly associated with tire pressure, it’s used in many other applications, including measuring material strength, hydraulic pressure, and pneumatic system performance.
8.2. Higher PSI Always Means Better Performance
Higher PSI doesn’t always mean better performance. In some cases, exceeding the recommended PSI can lead to safety hazards or equipment damage. It’s important to adhere to manufacturer recommendations and industry standards.
8.3. PSI is Interchangeable with Other Pressure Units
PSI is not directly interchangeable with other pressure units like pascals or bar. Accurate conversions are necessary to ensure correct measurements and avoid errors.
9. Frequently Asked Questions About PSI
To further clarify the concept of PSI, here are some frequently asked questions along with their answers.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What exactly does PSI mean? | PSI stands for pounds per square inch and measures the amount of force exerted on an area of one square inch. |
| How do I convert PSI to pascals? | To convert PSI to pascals, multiply the PSI value by 6894.76. |
| What is the difference between gauge and absolute PSI? | Gauge PSI measures pressure relative to atmospheric pressure, while absolute PSI measures pressure relative to a perfect vacuum. |
| Why is tire pressure measured in PSI? | Tire pressure is measured in PSI to ensure optimal vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. |
| Where else is PSI used besides tire pressure? | PSI is used in material testing, hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, and various industrial applications. |
| What is standard temperature and pressure (STP)? | STP is defined as 273.15 K (0 °C) and 1 atmosphere (14.7 PSI) and is used as a reference point for measuring gas properties. |
| How do I check my tire pressure? | Use a tire pressure gauge to measure the PSI in your tires and compare it to the recommended pressure listed in your vehicle’s owner’s manual or on the tire sidewall. |
| What happens if my tire pressure is too high? | Overinflating your tires can lead to a rough ride, increased wear on the center of the tire, and a higher risk of blowouts. |
| What happens if my tire pressure is too low? | Underinflating your tires can lead to decreased fuel economy, increased wear on the edges of the tire, and a higher risk of tire failure. |
| Who sets the standards for PSI measurements? | Organizations like NIST, EPA, and ISO set the standards for PSI measurements to ensure consistency and accuracy across different industries and countries. |

10. Why Accurate PSI Measurement Matters
Accurate PSI measurement is crucial for safety, efficiency, and reliability in various applications. From ensuring proper tire inflation to assessing the structural integrity of materials, PSI plays a vital role in modern technology and industry.
10.1. Ensuring Safety in Automotive Applications
In automotive applications, accurate PSI measurement is essential for ensuring safe tire inflation. Properly inflated tires provide optimal handling, braking, and stability, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall vehicle safety.
10.2. Enhancing Efficiency in Industrial Processes
In industrial processes, accurate PSI measurement is crucial for optimizing the performance of pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Proper pressure control enhances efficiency, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes the risk of equipment failure.
10.3. Guaranteeing Reliability in Material Testing
In material testing, accurate PSI measurement is necessary for assessing the tensile strength and elastic modulus of materials. These measurements ensure that structures and products are designed to withstand the stresses and strains they will encounter in real-world conditions, guaranteeing reliability and durability.
11. Additional Resources for Learning About PSI
For those who want to delve deeper into the world of PSI, numerous resources are available, including online calculators, educational websites, and industry publications.
11.1. Online PSI Calculators and Converters
Online PSI calculators and converters can help you quickly and accurately convert between PSI and other pressure units. These tools are useful for students, engineers, and anyone working with pressure measurements.
11.2. Educational Websites and Articles
Many educational websites and articles provide detailed explanations of PSI and its applications. These resources are valuable for learning about the fundamentals of pressure measurement and staying up-to-date with the latest industry trends.
11.3. Industry Publications and Standards Documents
Industry publications and standards documents offer in-depth information on PSI measurement techniques, best practices, and regulatory requirements. These resources are essential for professionals working in engineering, manufacturing, and related fields.
12. The Future of PSI Measurement
As technology advances, the future of PSI measurement is likely to involve more sophisticated sensors, data analytics, and automation. These innovations will enable more precise and efficient pressure monitoring and control in various applications.
12.1. Advances in Pressure Sensor Technology
Advances in pressure sensor technology are leading to more accurate, reliable, and compact sensors. These sensors can be integrated into a wide range of devices and systems, enabling real-time pressure monitoring and control.
12.2. Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
Data analytics is being used to analyze PSI data and predict potential equipment failures. This allows for proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving overall system reliability.
12.3. Automation and Remote Monitoring
Automation and remote monitoring technologies are enabling operators to monitor and control pressure systems from anywhere in the world. This enhances efficiency, reduces labor costs, and improves safety in various industrial and commercial applications.
Do you have more questions about PSI or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask on WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can get free answers to all your queries. Our community of experts is ready to help you understand complex concepts and find the information you need.
Facing challenges in finding quick and free answers? Unsure where to ask or how to get reliable information? Worried about consultation costs?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the ease of asking any question and getting prompt, accurate responses from knowledgeable individuals. Join our community and unlock a world of free knowledge and expert advice.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn