Revenue Cycle Management, or RCM, is a vital financial process that healthcare organizations utilize to manage patient revenue, and WHAT.EDU.VN can help you understand it better. It involves everything from patient registration to final payment. Understanding RCM is crucial for the financial health of healthcare providers. Explore billing processes, payment strategies, and revenue optimization techniques to master the management of healthcare finances.
1. Defining Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is the backbone of the financial operations of any healthcare provider. It’s a comprehensive process that oversees the entire lifecycle of a patient’s financial journey, from the moment they schedule an appointment to the final payment for services rendered. This includes managing billing, insurance claims, and patient payments.
RCM is much more than just sending out bills and collecting payments. It’s a strategic approach to optimizing revenue, reducing costs, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Effective RCM helps healthcare organizations maintain financial stability, invest in better patient care, and navigate the complexities of the healthcare industry.
1.1. Key Objectives of RCM
- Maximize Revenue: Ensure all billable services are accurately coded and billed, leading to optimal reimbursement.
- Reduce Denials: Minimize claim denials by addressing common errors and improving documentation.
- Improve Cash Flow: Accelerate payments and reduce the time it takes to collect revenue.
- Ensure Compliance: Adhere to all relevant regulations and coding standards.
- Enhance Patient Experience: Provide transparent billing practices and excellent customer service.
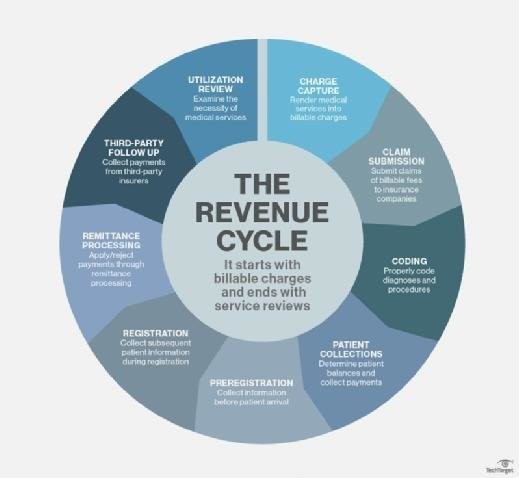
2. The Healthcare Revenue Cycle: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The healthcare revenue cycle is a complex series of interconnected steps that must be managed effectively to ensure financial health. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each stage:
2.1. Pre-Registration and Registration
The cycle begins even before the patient receives care.
- Pre-Registration: Gathering patient information, verifying insurance coverage, and obtaining necessary authorizations.
- Registration: Completing the patient’s record, confirming demographic and insurance details, and ensuring accuracy to minimize billing errors.
2.2. Charge Capture
This stage involves accurately documenting and coding all services provided.
- Documentation: Healthcare providers meticulously record the services provided during the patient’s visit.
- Coding: Assigning appropriate ICD (International Classification of Diseases) and CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes to each service. Accurate coding is essential for proper billing and reimbursement.
2.3. Claim Submission
Once the services are coded, the healthcare provider submits a claim to the insurance payer.
- Electronic Submission: Claims are typically submitted electronically to streamline the process.
- Claim Scrubbing: Before submission, claims are “scrubbed” to identify and correct any errors or omissions that could lead to denials.
2.4. Payment Posting
After the claim is processed, the payer sends payment to the healthcare provider.
- Payment Reconciliation: The provider reconciles the payment with the original claim to ensure accuracy.
- Denial Management: If a claim is denied or partially paid, the provider investigates the reason for the denial and takes corrective action, such as appealing the decision or resubmitting the claim with additional documentation.
2.5. Patient Collections
This stage involves billing patients for any remaining balance after insurance payments.
- Statement Generation: Generating clear and easy-to-understand statements for patients.
- Payment Options: Offering multiple payment options, such as online payments, payment plans, and phone payments, to make it convenient for patients to pay their bills.
- Collection Efforts: Implementing a systematic approach to follow up on overdue payments.
2.6. Appeals
2.6.1 Claim Appeals Process
If a claim is denied by an insurance company, healthcare providers have the right to appeal the decision. Understanding the appeals process is crucial for maximizing revenue and ensuring fair reimbursement. Here’s an overview of the typical claim appeals process:
Step 1: Review the Explanation of Benefits (EOB)
The first step in the appeals process is to carefully review the Explanation of Benefits (EOB) provided by the insurance company. The EOB outlines the reasons for the denial, which can include:
- Lack of Medical Necessity: The insurance company determines that the service was not medically necessary.
- Coding Errors: Incorrect or incomplete coding of procedures or diagnoses.
- Coverage Issues: The service is not covered under the patient’s insurance plan.
- Prior Authorization Requirements: Failure to obtain prior authorization for the service.
Step 2: Gather Supporting Documentation
Collect all relevant documentation that supports the claim. This may include:
- Medical Records: Detailed notes from the patient’s medical record that justify the necessity and appropriateness of the service.
- Physician’s Orders: Documentation of the physician’s orders for the service or procedure.
- Test Results: Lab results, imaging reports, and other diagnostic test results that support the diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Relevant Policies: Copies of relevant insurance policies and guidelines that support the claim.
Step 3: Prepare the Appeal Letter
Write a clear and concise appeal letter that addresses the reasons for the denial outlined in the EOB. The letter should include:
- Patient Information: Patient’s name, date of birth, and insurance identification number.
- Claim Information: Claim number, date of service, and amount of the claim.
- Reason for Appeal: A detailed explanation of why the denial should be overturned, citing specific medical evidence, coding guidelines, or policy provisions.
- Supporting Documentation: A list of all supporting documents included with the appeal.
Step 4: Submit the Appeal
Submit the appeal to the insurance company within the specified timeframe. Insurance companies typically have deadlines for submitting appeals, so it’s important to adhere to these deadlines to avoid forfeiting the right to appeal.
Step 5: Track the Appeal
Keep track of the appeal and follow up with the insurance company to check on its status. Document all communications with the insurance company, including dates, names, and summaries of conversations.
Step 6: Escalate if Necessary
If the initial appeal is denied, consider escalating the appeal to a higher level within the insurance company or to an external review board. Each insurance company has its own internal appeal process, and there may also be opportunities for external review by a third-party organization.
Tips for Successful Claim Appeals
- Be Thorough: Provide as much supporting documentation as possible to support the claim.
- Be Timely: Submit the appeal within the specified timeframe.
- Be Persistent: Don’t give up if the initial appeal is denied. Escalate the appeal and continue to advocate for the patient.
- Seek Expert Assistance: If you’re struggling with the appeals process, consider seeking assistance from a medical billing specialist or healthcare attorney.
3. The Importance of Data in RCM
Data plays a critical role in effective revenue cycle management. By collecting and analyzing data from every stage of the revenue cycle, healthcare organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize their processes.
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring data is accurate from the start to prevent billing errors.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing trends and patterns to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement.
- Reporting: Creating reports that provide insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as denial rates, collection rates, and days in accounts receivable.
 Data Analysis Revenue
Data Analysis Revenue
4. RCM and Insurer Communications
Effective communication with insurance companies is crucial for successful RCM. This includes verifying patient eligibility, obtaining authorizations, submitting claims, and following up on denials.
- Eligibility Verification: Confirming that patients have active insurance coverage before providing services.
- Authorization: Obtaining necessary authorizations for certain procedures or services.
- Claim Submission: Submitting claims electronically and ensuring they are accurate and complete.
- Denial Management: Investigating and appealing denied claims.
5. Benefits of Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) and RCM Systems
Implementing effective RCM practices and investing in robust RCM systems can bring numerous benefits to healthcare organizations.
5.1. Improved Financial Performance
- Increased Revenue: Optimizing billing and coding practices to maximize reimbursement.
- Reduced Costs: Streamlining processes and reducing administrative expenses.
- Better Cash Flow: Accelerating payments and reducing the time it takes to collect revenue.
5.2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
- Automation: Automating repetitive tasks to free up staff time.
- Streamlined Processes: Improving workflows to reduce errors and delays.
- Better Data Visibility: Providing real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs).
5.3. Increased Compliance
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to all relevant regulations and coding standards.
- Audit Readiness: Preparing for audits by maintaining accurate and complete records.
5.4. Better Patient Experience
- Transparent Billing: Providing clear and easy-to-understand billing practices.
- Convenient Payment Options: Offering multiple payment options to make it easy for patients to pay their bills.
- Improved Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service and addressing patient inquiries promptly and professionally.
6. Revenue Cycle Management and Value-Based Care
As the healthcare industry shifts from fee-for-service to value-based care, RCM is becoming even more critical. Value-based care focuses on improving patient outcomes and reducing costs, and effective RCM can help healthcare organizations succeed in this new environment.
- Data Analytics: Using data analytics to identify opportunities to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs.
- Care Coordination: Coordinating care across different providers and settings to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Patient Engagement: Engaging patients in their own care to improve adherence and outcomes.
7. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in RCM
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of RCM practices. Some important KPIs include:
- Denial Rate: The percentage of claims that are denied by payers.
- Collection Rate: The percentage of billed charges that are collected.
- Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R): The average number of days it takes to collect payment for services.
- Clean Claim Rate: The percentage of claims that are submitted without errors and are paid on the first submission.
- Cost to Collect: The cost of collecting each dollar of revenue.
8. Common Challenges in Revenue Cycle Management
Despite the best efforts, healthcare organizations often face challenges in managing their revenue cycle. Some common challenges include:
- Coding Errors: Inaccurate or incomplete coding can lead to claim denials and reduced reimbursement.
- Claim Denials: High denial rates can significantly impact revenue and cash flow.
- Changing Regulations: Keeping up with constantly changing regulations and coding standards can be challenging.
- Patient Collections: Collecting payments from patients can be difficult, especially with rising deductibles and copays.
- Technology Issues: Implementing and maintaining RCM systems can be complex and costly.
9. Best Practices for Effective Revenue Cycle Management
To overcome these challenges and optimize their revenue cycle, healthcare organizations should follow these best practices:
- Invest in Training: Provide comprehensive training to all staff involved in the revenue cycle, including coders, billers, and patient access representatives.
- Implement Technology: Invest in robust RCM systems and technology to automate tasks, improve accuracy, and enhance data visibility.
- Monitor KPIs: Regularly monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify areas for improvement.
- Establish Clear Policies: Develop and implement clear policies and procedures for all aspects of the revenue cycle.
- Communicate Effectively: Foster open communication between departments and with payers and patients.
10. The Role of Technology in RCM
Technology plays a vital role in modern revenue cycle management. RCM systems can automate tasks, improve accuracy, and enhance data visibility. Some key features of RCM systems include:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Integration: Seamless integration with EHR systems to streamline data exchange.
- Claim Scrubbing: Automated claim scrubbing to identify and correct errors before submission.
- Denial Management: Tools to track and manage denied claims.
- Reporting and Analytics: Robust reporting and analytics capabilities to monitor KPIs and identify trends.
- Patient Portals: Online portals that allow patients to view their bills, make payments, and communicate with the healthcare provider.
11. Future Trends in Revenue Cycle Management
The field of revenue cycle management is constantly evolving, and healthcare organizations need to stay ahead of the curve to remain competitive. Some future trends in RCM include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to automate tasks, improve accuracy, and enhance decision-making.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automating repetitive tasks such as data entry and claim submission.
- Blockchain: Using blockchain technology to improve security and transparency in the revenue cycle.
- Predictive Analytics: Using predictive analytics to forecast revenue and identify potential issues.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Adopting cloud-based RCM solutions to reduce costs and improve scalability.
12. RCM in Different Healthcare Settings
RCM practices can vary depending on the type of healthcare setting. Here’s a look at RCM in different environments:
12.1. Hospitals
Hospitals often have complex revenue cycles due to the wide range of services they provide. Effective RCM in hospitals requires:
- Coordination: Strong coordination between departments to ensure accurate and timely billing.
- Compliance: Adherence to complex regulations and coding standards.
- Technology: Robust RCM systems to manage large volumes of data and transactions.
12.2. Physician Practices
Physician practices may have simpler revenue cycles than hospitals, but they still need to manage billing, coding, and patient collections effectively. Key considerations for RCM in physician practices include:
- Efficiency: Streamlining processes to minimize administrative overhead.
- Patient Focus: Providing excellent customer service and transparent billing practices.
- Technology: Using RCM systems to automate tasks and improve accuracy.
12.3. Long-Term Care Facilities
Long-term care facilities face unique RCM challenges due to the nature of their services and patient populations. Effective RCM in long-term care facilities requires:
- Coordination: Coordinating with multiple payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance.
- Compliance: Adhering to complex regulations and coding standards.
- Technology: Using RCM systems to manage billing, coding, and patient collections efficiently.
13. Navigating RCM with WHAT.EDU.VN
Understanding and implementing effective Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) can be complex, but WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. We provide a platform where you can ask any questions you have about RCM and receive clear, concise answers from experts.
13.1. How WHAT.EDU.VN Can Help You
- Ask Any Question: Whether you’re curious about the basics of RCM or need help with a specific challenge, our platform is the perfect place to get your questions answered.
- Free Answers: Our service is completely free, so you can get the information you need without worrying about costs.
- Expert Insights: Benefit from the knowledge and experience of industry professionals who can provide valuable insights and guidance.
13.2. Common RCM Questions Addressed on WHAT.EDU.VN
- What are the key steps in the healthcare revenue cycle?
- How can I reduce claim denials and improve reimbursement rates?
- What are the best practices for patient collections?
- How can technology help streamline the revenue cycle?
- What are the latest trends in RCM?
13.3. Real-World RCM Scenarios and Solutions
Here are some common RCM challenges and how WHAT.EDU.VN can help you find solutions:
Scenario 1: High Claim Denial Rates
Problem: Your organization is experiencing high claim denial rates, leading to reduced revenue and increased administrative costs.
Solution: Ask WHAT.EDU.VN experts for advice on identifying the root causes of claim denials and implementing strategies to prevent them, such as improving coding accuracy, verifying patient eligibility, and implementing claim scrubbing processes.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Patient Collections
Problem: Your patient collection process is inefficient, resulting in slow payments and high bad debt.
Solution: Seek guidance from WHAT.EDU.VN on implementing best practices for patient collections, such as offering multiple payment options, sending clear and easy-to-understand statements, and implementing a systematic follow-up process for overdue accounts.
Scenario 3: Lack of Data Visibility
Problem: You lack visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) and are unable to identify areas for improvement in your revenue cycle.
Solution: Consult with WHAT.EDU.VN experts on setting up robust reporting and analytics capabilities to monitor KPIs, such as denial rates, collection rates, and days in accounts receivable, and identify trends and patterns that can inform decision-making.
14. Additional Resources for Learning About RCM
While WHAT.EDU.VN can provide answers to your specific questions, here are some additional resources for learning more about RCM:
- Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA): HFMA offers educational resources, certifications, and networking opportunities for healthcare financial professionals.
- Medical Group Management Association (MGMA): MGMA provides resources and tools for managing physician practices, including RCM best practices.
- American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC): AAPC offers coding certifications and educational resources for medical coders.
- Industry Publications: Stay up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices in RCM by reading industry publications and blogs.
15. FAQs About Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the main goal of revenue cycle management? | The main goal of RCM is to maximize revenue and ensure financial stability for healthcare organizations by efficiently managing all functions associated with revenue generation. |
| What are the key steps in the revenue cycle? | The key steps include pre-registration, registration, charge capture, claim submission, payment posting, and patient collections. |
| How can technology improve RCM? | Technology can automate tasks, improve accuracy, enhance data visibility, and streamline processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs. |
| What are some common challenges in RCM? | Common challenges include coding errors, claim denials, changing regulations, patient collections, and technology issues. |
| What are some best practices for effective RCM? | Best practices include investing in training, implementing technology, monitoring KPIs, establishing clear policies, and communicating effectively. |
| How does RCM relate to value-based care? | RCM supports value-based care by providing data analytics that enable organizations to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. |
| What are some important KPIs to monitor in RCM? | Important KPIs include denial rate, collection rate, days in accounts receivable, clean claim rate, and cost to collect. |
| What role does communication play in RCM? | Effective communication is crucial for verifying patient eligibility, obtaining authorizations, submitting claims, and following up on denials. |
| How can WHAT.EDU.VN help with RCM questions? | WHAT.EDU.VN provides a platform where you can ask any questions you have about RCM and receive clear, concise answers from experts, completely free of charge. |
| What are some future trends in RCM? | Future trends include the use of artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA), blockchain, predictive analytics, and cloud-based solutions. |
16. Conclusion: Mastering RCM for Financial Success
Effective Revenue Cycle Management is crucial for the financial health of healthcare organizations. By understanding the key steps in the revenue cycle, implementing best practices, and leveraging technology, healthcare providers can optimize their revenue, reduce costs, and improve patient satisfaction. Remember, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to support you with any questions you may have along the way.
Do you have questions about Revenue Cycle Management or any other topic? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your questions and get free answers from experts. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of the healthcare industry and achieve financial success. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States or via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit our website at what.edu.vn.