The Messages app on your iPhone is a versatile tool, capable of sending different types of messages depending on the recipient and your network connection. You might have heard of iMessage and SMS/MMS, but there’s a newer standard in town: RCS. So, What Is Rcs Texting, and how does it differ from the messages you’re already familiar with? This guide will delve into Rich Communication Services (RCS), explaining its features, benefits, and how it fits into the messaging landscape on your iPhone and beyond.
Understanding RCS Text Messaging
RCS, or Rich Communication Services, is designed to be the successor to SMS and MMS. It’s a modern messaging protocol aimed at enhancing the text messaging experience, bringing features closer to those found in popular messaging apps. When you send messages that aren’t iMessage, your iPhone might use RCS if both your device and your carrier support it. These RCS messages are displayed in green bubbles, similar to SMS/MMS.
Key Features of RCS Texting:
- High-Quality Media Sharing: Unlike SMS/MMS which often compress photos and videos, RCS allows for sending high-resolution images and videos. This means clearer and more vibrant media sharing directly within your text messages.
- Enhanced Group Chats: RCS supports more feature-rich group messaging, making group conversations more interactive and seamless.
- Read Receipts and Typing Indicators: Just like iMessage and many other messaging apps, RCS offers delivery and read receipts, letting you know if your message has been delivered and seen. Typing indicators also show you when someone is responding.
- Link Previews and More: RCS can support link previews, providing a visual snippet of web links shared in messages. It’s designed to be a more versatile and feature-rich communication method compared to traditional SMS.
How RCS Works on iPhone:
Apple has adopted RCS, starting with iOS 18. For RCS to work on your iPhone, a few things need to be in place:
- iOS 18 or Later: RCS support is integrated into iOS 18 and subsequent versions. Ensure your iPhone is updated to the latest software.
- Carrier Support: RCS is a carrier-provided service. Your mobile carrier needs to support RCS messaging on iPhones. You should check with your carrier to confirm if they offer RCS support for your plan and device.
- Text Messaging Plan: You’ll need a text messaging plan from your carrier that includes RCS.
When your iPhone connects to your cellular network, it communicates with your carrier to establish an RCS connection. This process involves exchanging identifiers to authenticate your device. These identifiers can include your IMEI, IMSI, IP address, and phone number, which are shared with your carrier and their partners to enable RCS services. It’s worth noting that your IP address might also be shared with other RCS users.
You can manage RCS settings on your iPhone by navigating to Settings > Apps > Messages > RCS Messaging, where you can turn RCS on or off. Activating RCS may take a few hours to become fully functional after setup.
RCS vs. iMessage and SMS/MMS: Key Differences
To fully understand what is RCS texting, it’s crucial to compare it with iMessage and SMS/MMS, the other messaging protocols on iPhones.
iMessage
iMessage is Apple’s proprietary messaging service, exclusive to Apple devices (iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple Watch). iMessages are distinguished by their blue bubbles and offer a range of features:
- Apple Ecosystem: iMessage works only between Apple devices.
- End-to-End Encryption: iMessage conversations are end-to-end encrypted, providing a higher level of privacy and security.
- Rich Features: iMessage supports a wide array of features like high-resolution media, message effects, Tapbacks, and more.
- Data or Wi-Fi: iMessage uses Wi-Fi or cellular data to send messages.
SMS/MMS
SMS (Short Message Service) and MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) are the most basic forms of text messaging, supported by virtually all mobile phones. SMS/MMS messages appear in green bubbles on iPhones and have the following characteristics:
- Universal Compatibility: SMS/MMS works across all mobile devices, including non-smartphones.
- Basic Features: SMS is limited to text, while MMS allows for sending photos and videos, albeit often compressed and of lower quality.
- Carrier-Provided: SMS/MMS are carrier-provided services and rely on cellular networks.
- No End-to-End Encryption: SMS/MMS messages are not end-to-end encrypted.
Here’s a quick comparison table:
| Feature | RCS | iMessage | SMS/MMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble Color | Green | Blue | Green |
| Encryption | No End-to-End | End-to-End | No End-to-End |
| Media Quality | High Resolution | High Resolution | Lower Resolution |
| Features | Rich Features (Read Receipts, Typing Indicators, etc.) | Extensive Rich Features | Basic Text & Media |
| Device Compatibility | iPhones & Non-Apple Devices | Apple Devices Only | All Mobile Devices |
| Network | Cellular Data/Wi-Fi | Cellular Data/Wi-Fi | Cellular Network |
| Carrier Dependent | Yes | No | Yes |
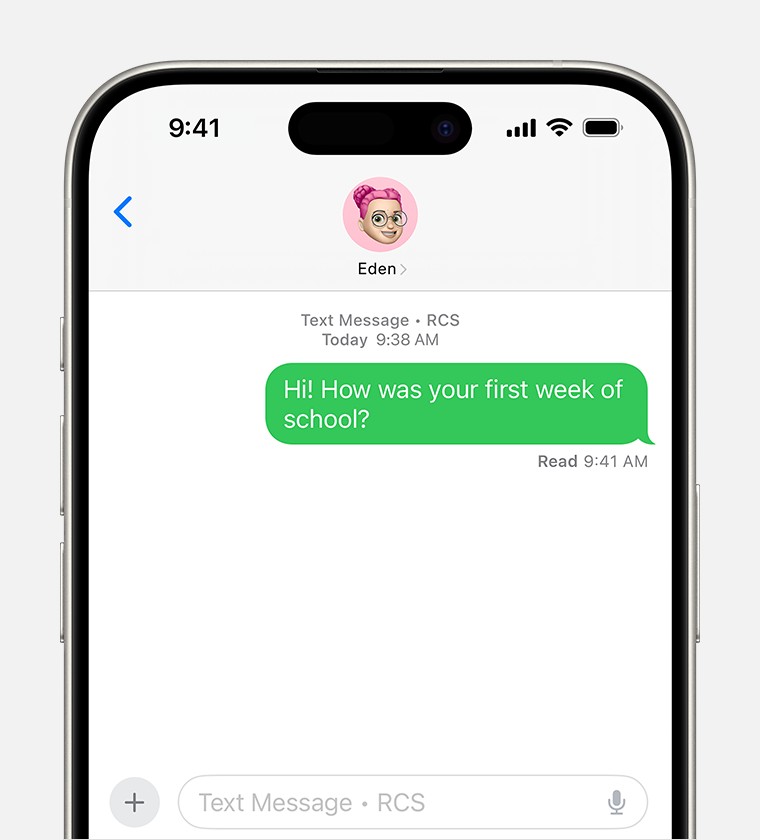
Conclusion: RCS as the Next Step in Texting
What is RCS texting? It’s the evolution of traditional SMS/MMS, bringing enhanced features and improved media sharing capabilities to standard text messaging. While iMessage offers a robust, feature-rich, and encrypted messaging experience within the Apple ecosystem, RCS aims to bridge the gap with non-Apple devices, providing a more modern and versatile messaging solution for everyone. As RCS adoption grows, it promises to enhance the texting experience for iPhone users when communicating with those outside the Apple ecosystem, offering a significant upgrade over the limitations of SMS/MMS. For users wondering about better communication beyond blue bubbles, RCS is a noteworthy advancement to watch and utilize.