What Is Sectionalism? It’s an exaggerated loyalty to regional interests over national unity. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we aim to clarify complex topics like sectionalism, offering insights into historical divisions and their ongoing relevance. This article explores its definition, historical context, and impact, providing you with a comprehensive understanding. Discover the root causes of disunity and how they continue to shape societal challenges today. If you have more questions, ask our experts at WHAT.EDU.VN for free answers.
1. Defining Sectionalism: Loyalty Above All Else
Sectionalism is more than just regional pride; it’s a deep-seated allegiance to the interests of one’s own region, often at the expense of the nation. This devotion can manifest in various ways, from political disagreements to economic policies that favor one area over another. Understanding sectionalism requires examining its causes and consequences, shedding light on its impact on societies. It’s about placing the needs and desires of a specific area above the collective good, leading to fragmentation and conflict.
1.1. What is Regionalism?
Regionalism, while similar, isn’t quite the same as sectionalism. Regionalism is simply the awareness of and loyalty to a region, while sectionalism is acting on that loyalty in a way that is detrimental to the country.
1.2. What is the Difference Between Sectionalism and Nationalism?
Nationalism is pride in one’s country and the belief that its interests should be prioritized, while sectionalism is pride in one’s region and the belief that its interests should be prioritized. Sectionalism is a divisive force that can weaken a nation, while nationalism is a unifying force that can strengthen a nation.
2. The Historical Roots of Sectionalism in the U.S.
The United States has a long history of sectionalism, dating back to the colonial era. The economic, social, and political differences between the North and the South fueled tensions that eventually led to the Civil War. Understanding these historical roots is crucial for grasping the complexities of sectionalism. It wasn’t just about slavery; it involved competing visions for the nation’s future.
2.1. Economic Disparities
The North and the South developed distinct economic systems. The North focused on industry and commerce, while the South relied heavily on agriculture, particularly cotton production. This economic divergence created conflicting interests and priorities.
2.2. Social and Cultural Differences
The North and the South had different social structures and cultural values. The North was more urban and diverse, while the South was more rural and agrarian. These differences contributed to misunderstandings and stereotypes that exacerbated sectional tensions.
2.3. Political Power Struggles
The balance of political power between the North and the South was a constant source of conflict. Issues such as tariffs, internal improvements, and the expansion of slavery into new territories sparked fierce debates and political maneuvering.
3. The Role of Slavery in Fueling Sectionalism
Slavery was the most significant and divisive issue driving sectionalism in the United States. The moral, economic, and political implications of slavery created an irreconcilable divide between the North and the South. The debate over its expansion into new territories intensified the conflict.
3.1. Moral Arguments Against Slavery
Many Northerners viewed slavery as a moral evil and advocated for its abolition. Abolitionist movements gained momentum, putting pressure on the government to take action against slavery. Figures like William Lloyd Garrison and Frederick Douglass championed the cause of emancipation.
3.2. Economic Dependence on Slavery
The Southern economy was heavily dependent on slave labor. Planters argued that slavery was essential for their economic survival and defended it as a positive good. This economic dependence created a strong incentive to resist any efforts to abolish or restrict slavery.
3.3. Political Implications of Slavery
The issue of slavery had significant political implications, particularly regarding representation in Congress and the balance of power between the states. The admission of new states as either free or slave states became a contentious issue, leading to compromises and conflicts.
4. Key Events That Heightened Sectional Tensions
Several key events throughout the 19th century heightened sectional tensions and brought the nation closer to civil war. These events exposed the deep divisions within American society and the failure of compromise to resolve the issue of slavery.
4.1. The Missouri Compromise (1820)
The Missouri Compromise attempted to balance the interests of the North and the South by admitting Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state. It also prohibited slavery in the remaining Louisiana Purchase territory north of the 36°30′ parallel. While it temporarily eased tensions, it ultimately failed to address the underlying issue of slavery.
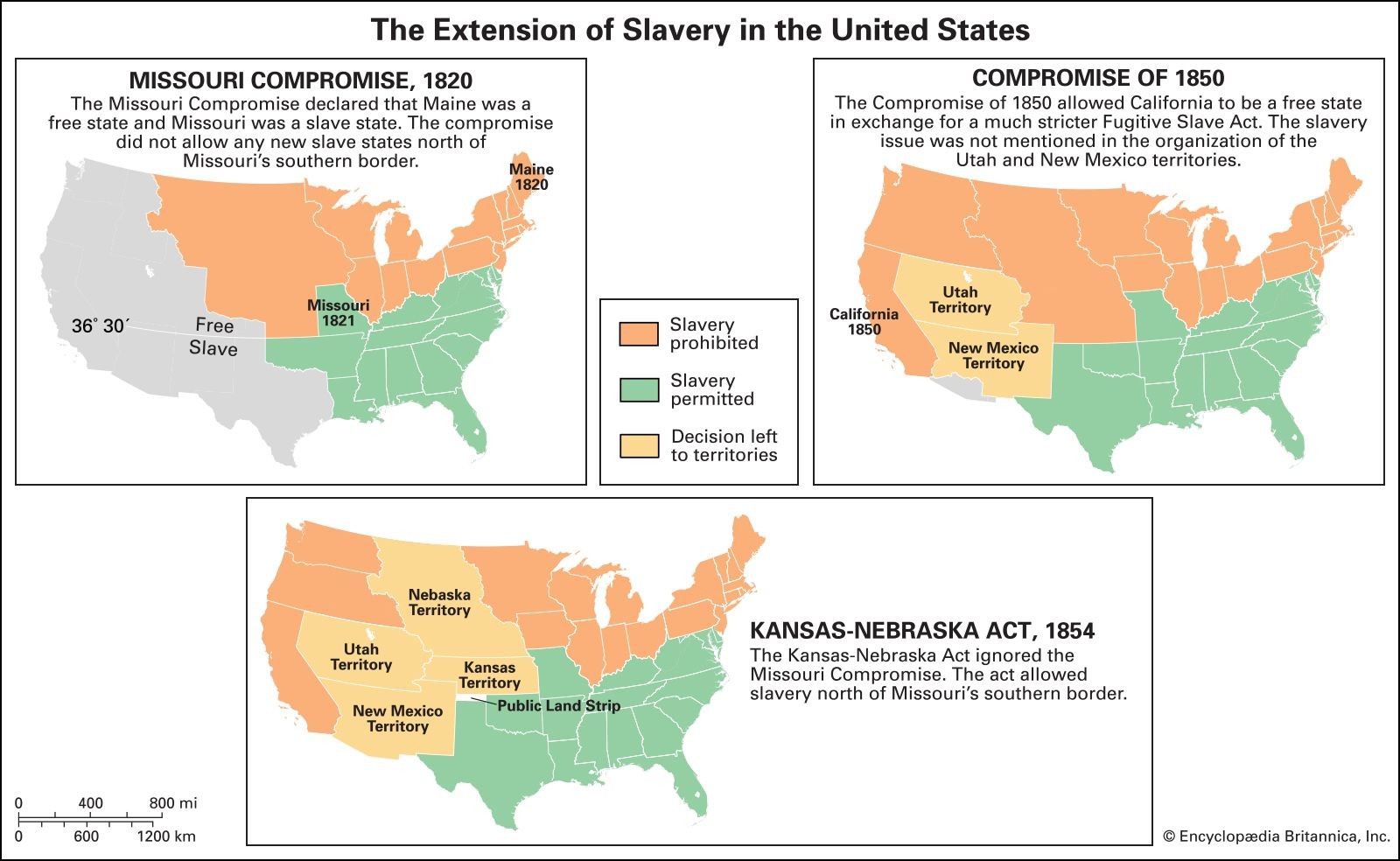 Map of the Missouri CompromiseThe Missouri Compromise, Compromise of 1850, and Kansas-Nebraska Act. This attempt to balance the interests of the North and the South admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state.
Map of the Missouri CompromiseThe Missouri Compromise, Compromise of 1850, and Kansas-Nebraska Act. This attempt to balance the interests of the North and the South admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state.
4.2. The Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was another attempt to resolve the issue of slavery by admitting California as a free state and enacting the Fugitive Slave Act. The Fugitive Slave Act, which required the return of escaped slaves to their owners, further inflamed tensions between the North and the South.
4.3. The Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854)
The Kansas-Nebraska Act allowed the residents of Kansas and Nebraska to decide for themselves whether to allow slavery through popular sovereignty. This led to violence and bloodshed in Kansas, as pro-slavery and anti-slavery forces clashed in what became known as “Bleeding Kansas.”
4.4. The Dred Scott Decision (1857)
The Dred Scott decision by the Supreme Court ruled that enslaved people were not citizens and had no right to sue in federal court. It also declared the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional, further polarizing the North and the South.
4.5. John Brown’s Raid on Harpers Ferry (1859)
John Brown’s raid on Harpers Ferry, an attempt to start a slave rebellion, further heightened tensions and deepened the divide between the North and the South. Brown’s actions were seen as heroic by some Northerners and as an act of terrorism by many Southerners.
5. The Election of 1860 and the Secession of Southern States
The election of 1860 was a pivotal moment in American history. Abraham Lincoln’s victory, despite not being on the ballot in many Southern states, led to the secession of several Southern states and the outbreak of the Civil War.
5.1. Abraham Lincoln’s Victory
Abraham Lincoln’s election as president on an anti-slavery platform was the final straw for many Southerners, who feared that the federal government would eventually abolish slavery.
5.2. Secession of Southern States
Following Lincoln’s election, seven Southern states seceded from the Union: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. These states formed the Confederate States of America and elected Jefferson Davis as their president.
5.3. The Outbreak of the Civil War
The Civil War began in April 1861 with the Confederate attack on Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. The war lasted four years and resulted in the deaths of hundreds of thousands of Americans.
6. The Impact of the Civil War on Sectionalism
The Civil War had a profound impact on sectionalism in the United States. While it ended slavery and preserved the Union, it also left deep scars and unresolved issues that continued to shape American society for decades to come.
6.1. The End of Slavery
The Civil War resulted in the abolition of slavery, a major victory for the anti-slavery movement. However, the end of slavery did not automatically lead to racial equality or the end of racial discrimination.
6.2. Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction Era, which followed the Civil War, was a period of significant social and political change in the South. However, Reconstruction was ultimately unsuccessful in achieving its goals of racial equality and integration, and it was followed by a period of renewed racial discrimination and segregation.
6.3. Lingering Sectional Tensions
Despite the end of the Civil War, sectional tensions persisted in the United States for many years. The South remained economically disadvantaged and resentful of the North, while the North struggled to understand and address the South’s unique challenges.
7. Modern Sectionalism: Is It Still Relevant Today?
While the Civil War ended over 150 years ago, sectionalism is still relevant in the United States today. The country remains divided along various lines, including political ideology, economic inequality, and cultural values.
7.1. Political Polarization
Political polarization has increased in recent years, with Democrats and Republicans becoming more divided on a range of issues. This polarization has made it more difficult to find common ground and address the country’s challenges.
7.2. Economic Inequality
Economic inequality has also increased in recent years, with the gap between the rich and the poor widening. This inequality has created resentment and division, particularly among those who feel left behind by the modern economy.
7.3. Cultural Divisions
Cultural divisions, such as those related to race, religion, and sexual orientation, also contribute to sectionalism in the United States. These divisions can lead to misunderstandings and stereotypes that exacerbate tensions.
8. Examples of Sectionalism in Contemporary Society
Several contemporary issues highlight the ongoing relevance of sectionalism in American society. These examples demonstrate how regional interests and identities continue to shape political debates and social attitudes.
8.1. Immigration Policy
Immigration policy is a contentious issue that often reflects sectional divisions. Some regions, particularly those with large immigrant populations, support more lenient immigration policies, while others favor stricter enforcement.
8.2. Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations also spark sectional debates, with some regions prioritizing economic development over environmental protection and others advocating for stronger environmental safeguards.
8.3. Healthcare Reform
Healthcare reform is another issue that often divides the country along sectional lines. Some regions support government-funded healthcare programs, while others prefer a market-based approach.
9. Overcoming Sectionalism: Fostering National Unity
Overcoming sectionalism requires a concerted effort to foster national unity and address the underlying issues that divide the country. This includes promoting dialogue, understanding, and cooperation across different regions and groups.
9.1. Promoting Dialogue and Understanding
Encouraging dialogue and understanding between different regions and groups is essential for overcoming sectionalism. This can be achieved through education, cultural exchange programs, and community initiatives.
9.2. Addressing Economic Inequality
Addressing economic inequality is crucial for reducing resentment and division. This can be achieved through policies that promote economic opportunity, such as education reform, job training programs, and a higher minimum wage.
9.3. Fostering a Sense of Shared Identity
Fostering a sense of shared national identity is also important for overcoming sectionalism. This can be achieved through promoting civic engagement, celebrating national holidays, and highlighting the country’s shared history and values.
10. FAQs About Sectionalism
Here are some frequently asked questions about sectionalism to further clarify the concept.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the main causes of sectionalism? | Economic disparities, social and cultural differences, and political power struggles. |
| How did slavery contribute to sectionalism? | It created moral, economic, and political divisions between the North and the South. |
| Is sectionalism still relevant today? | Yes, it manifests in political polarization, economic inequality, and cultural divisions. |
| How can we overcome sectionalism? | By promoting dialogue, addressing economic inequality, and fostering a sense of shared national identity. |
| What was the Missouri Compromise? | An attempt to balance the interests of the North and the South by admitting Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state. |
| What was the Kansas-Nebraska Act? | It allowed residents of Kansas and Nebraska to decide for themselves whether to allow slavery, leading to violence in Kansas. |
| What was the Dred Scott decision? | A Supreme Court ruling that enslaved people were not citizens and had no right to sue in federal court. |
| What was John Brown’s Raid on Harpers Ferry? | An attempt to start a slave rebellion, further heightening tensions between the North and the South. |
| What happened after Lincoln’s Election? | Following Lincoln’s election, seven Southern states seceded from the Union: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. |
| How did the Civil War impact sectionalism? | The Civil War resulted in the abolition of slavery, a major victory for the anti-slavery movement, though racial equality was still an issue for many years afterwards. |
11. How WHAT.EDU.VN Can Help You Understand Sectionalism
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing clear, concise, and accurate information on a wide range of topics, including sectionalism. Our platform offers a wealth of resources to help you deepen your understanding of this complex issue.
11.1. Free Answers to Your Questions
Do you have questions about sectionalism or other historical events? Our experts are here to provide you with free answers. Simply submit your question on our website, and we will do our best to provide you with a comprehensive and informative response.
11.2. Expertly Curated Content
Our content is carefully curated by experts in their respective fields. We strive to provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date information available. Our articles are written in a clear and accessible style, making complex topics easy to understand.
11.3. A Community of Learners
WHAT.EDU.VN is more than just a website; it’s a community of learners. We encourage you to engage with our content, ask questions, and share your own insights. Together, we can build a better understanding of the world around us.
12. Conclusion: Sectionalism’s Enduring Legacy
Sectionalism is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has shaped American history and continues to influence contemporary society. By understanding its roots, key events, and ongoing manifestations, we can work towards fostering national unity and addressing the underlying issues that divide us. Remember, knowledge is the first step towards progress.
Do you have more questions about sectionalism or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask our experts at WHAT.EDU.VN for free answers. We are here to help you learn and grow.
Ready to Learn More?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your questions for free. Our team of experts is ready to provide you with the answers you need. Join our community of learners and start exploring the world around you.
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Let what.edu.vn be your guide to understanding the complexities of sectionalism and other important topics. Ask your questions today and get the answers you need, absolutely free.